Summary on the theme of masterʼs works
- Goals and objectives of the masterʼs work
- 1. Actuality
- 2. Scientific novelty
- 3. A summary of the masterʼs work
- 3.1. Brief description of the mine
- 3.2. Generalitiesu
- Conclusion
- List of references
Content
Goals and objectives of the masterʼs work
Purpose – to perform engineering analysis of the fire protection of the surface complex of mine named after
M. I. Kalinin GP DUEK
and on this basis to develop scientifically-based measures for its improvement.
To successfully complete this work, it is necessary: to assess the existing fire protection features of the surface complex, which are used at the minenamed after M. I. Kalinin; assess the feasibility of their use; analyze the possibility of using modern mine, currently existing, fire protection.
1. Actuality
Analysis of accidents in coal mines shows that the state of fire protection on the vast majority of mines Ukraine inadequately their fire hazard. Fires occur in the surface complex indoor workshops, garages, warehouses, materials and equipment, buildings AUP. The main causes of fire are careless handling of fire and improper use of equipment [1].
Tower copra are among the most flammable objects surface complex coal mines. At these sites occurs from 3 to 5 fires per year that result in substantial property damage. Fires caused by tower copra threaten the flame and combustion products throughout the mine as copra tower located above the skip and the air shafts [2].
In case of delayed application of fire extinguishing means fires can cover most of the tower copra and threaten access to adjacent rooms and buildings.
2. Scientific novelty
Currently in Ukrainian mines as the primary extinguishing agent used water. Water is an effective tool in fighting fires, it is also the cheapest, and also affordable way. Inter alia, the water has a number of advantages: high specific heat, chemical inertness, cooling properties. However, along with this water has a number of drawbacks. This high surface tension, and the limited working temperature range, the inability to extinguish oil, some chemicals and electrical equipment, etc. In this regard, for the fire protection of the surface complex named after M. I. Kalinin, proposed use, as water and powder automatic fire extinguishing systems.
3. A summary of the masterʼs work
3.1. Brief description of the mine
Field of mine named after M. I. Kalinin is located in the south-eastern part of the southern wing Kalmius-Toretskoy Basin Donetsk-Makeevka carboniferous area and is located in the northeastern part of the city of Donetsk. In the administrative division of the projected mining claim mine is located in the Kalinin, Voroshilov Kiev and regions of Donetsk region and Chervonogvardeysky Makeyevka Donetsk region. Dimensions mine field along strike – 8.0 km down-dip – 4.5 km.
Mine developed layers h10, h8, h7 – Smolyaninovsky Formation strata and k5, k²5, k²2 – Kamenka suite. Currently, a layer of h10, capacity of 1.2–1.3 m. Coalbed particularly dangerous to sudden outbursts of coal and gas, dangerous exposure to coal dust and methane emissions suflyarnym, not prone to spontaneous combustion. Mine field opened by five vertical shafts, of which three cage and skip one passed by the central industrial area of the mine, and one vent is located on the flank.
Mine ventilation is carried out by a combined scheme with two main fan suction method. Each main ventilation system consists of the same type of centrifugal fans, one of them working, and the second – a reserve, with the same parameters of technical characteristics. We skip shaft mounted fan main ventilation ВЦ-5. On the eastern ventilation shaft mounted fan main ventilation ВЦД-47У. Preliminary production ventilated with fans of local ventilation [3].
3.2. Generalities
Technical fire protection
Fire – this formidable enemy, which carries not only enormous damage, but can be a serious threat to human life. To come out victorious in this fight, you need to comply with fire safety and timely able to use fire protection.
There are primary and technical means fire [4].
The primary means of fire include: scrap, boat hook, an ax, a shovel, buckets, fire extinguishers, tanks for sand and water, fire hydrants. All fire-fighting equipment is on special fire boards and is only used in case of fire.
Fire extinguishers are momentary action are therefore used in the initial stages of a fire. Depending on the class of fire extinguishers are: water, air, foam, carbon dioxide and powder. For operational use in case of fire extinguishers installed in prominent and easily accessible places. Example water and powder fire extinguishers used on mine named after M. I. Kalinin is shown in figure 1.

Figure 1 – Water (OVSH–9z) and powder (OP–8) fire extinguishers
Technical fire protection – a system of automatic fire detection and extinguishing, smoke, warning, fire water, and other technical means for the protection of people and property from fire:
– Automatic sprinkler installation – installation automatically asking for detecting and extinguishing the fire, regardless of the external power supply and control systems, and at the same time performing the functions of fire alarm and fire extinguishing fires autonomous (receive-control and management, control units, sprinklers, modules fire, extinguishing aerosol generators, signaling flow of fluid pressure alarms, battery fire, etc.). Example unattended installation fire fighting the figure 2;
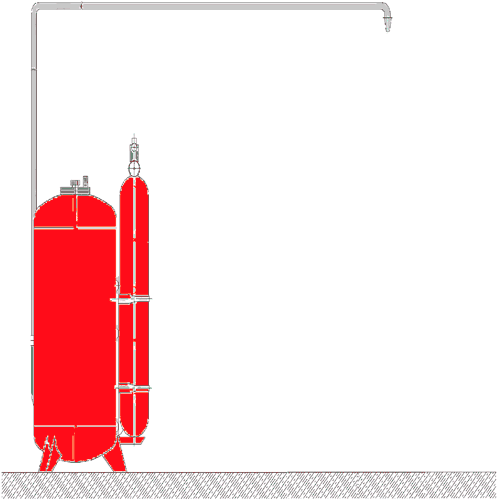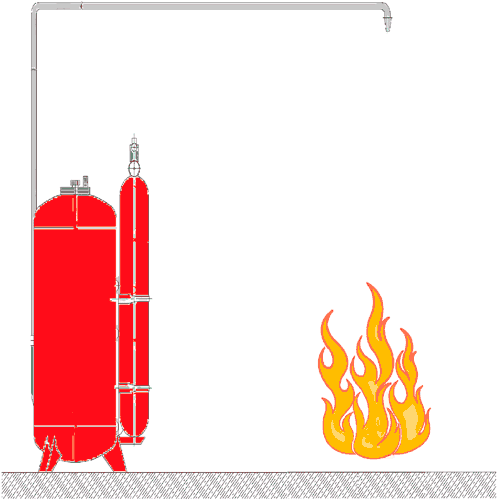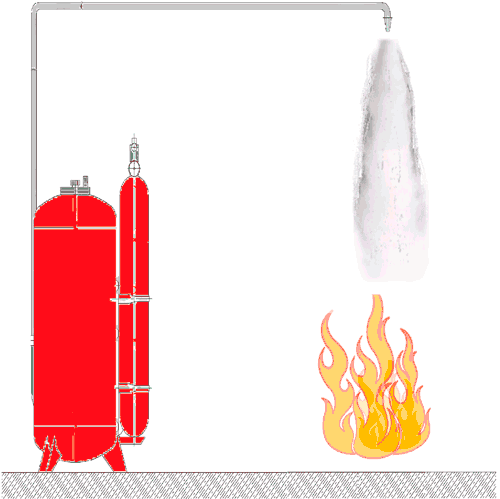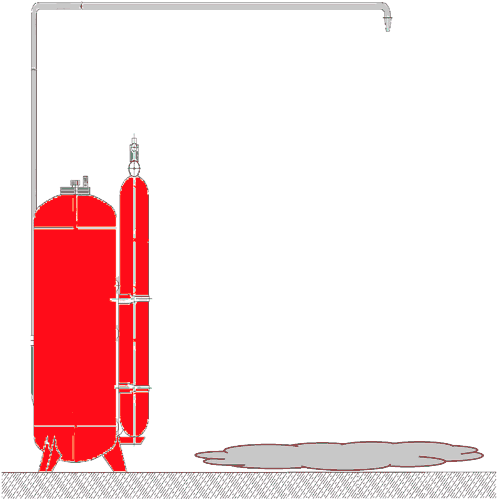
Figure 2 – Automatic installation of fire fighting (Animation: 21 frames, 121 KB, 5 cycles of repeating)
– Fire alarm system – a set of cooperating hardware designed to detect fire factors, collection, processing, recording, generating and transmitting signals in a given form of fire and other information, as well as, if necessary, issuing signals to the control unit by means of fire engineering protection, technological, and other electrical equipment (receive-control and fire control, staging modules, remote panels, fire alarm systems, etc.);
– System of fire warning and evacuation – a complex of technical means and organizational measures designed to organize evacuation in case of fire and evacuation process control directly (verbal, auditory, visual and combined sirens, amplifying, recording and switching equipment, lighting evacuation direction signs, etc.);
– Transmission system of notifications about emergencies – a set of co-operating hardware designed for the transmission and reception of communication channels at the point where you installed the monitoring station, fire alarm systems, service, control and diagnostic notifications, and (in the presence of the reverse channel) for transmitting and receiving control commands;
– The extinguishing substance – a substance having the physico-chemical properties, allowing to create conditions for the termination of combustion (water, foam, powders, gases and their mixtures, sprays etc.);
– Fighting water supply – a set of technical means and facilities for the supply of water to extinguish a fire (outside fighting water supply, internal fighting water supply);
– Fire protection – fire hazard reduction materials and designs through a special treatment or coating (layer);
– Fire-technical equipment, fire equipment, fire rescue unit, manual fire tools, personal protective equipment firefighters self-rescuers;
– Fire extinguishers;
– Smoke protection of the building – a system of space-planning, design solutions of buildings and engineering devices designed to prevent smoke protected escape routes and limit the spread of combustion products in a fire (smoke hatches and drive systems, valves smoke, ventilators for smoke protection, smoke-tight door, tambour gateway nezadymlyaemye stairwells, etc.);
– Fire barrier – designed to prevent the spread of fire and combustion products from the fire compartment or premises to other premises (fire walls, fire barriers, fire overlap, fire zones);
– Fire dampers – a device that automatically shuts in the fire opening, channel or conduit in fire barriers and preventing the spread of fire and smoke within the rated time;
– Fire fighting equipment, etc.
Extinguishing agents
For fire suppression should stop access oxidant (oxygen from the air) or combustible materials in the combustion zone to reduce their intake values at which combustion can not occur; cool the combustion zone below the auto-ignition temperature or lower the temperature of the burning material below the ignition temperature; dilute combustibles combustible substances.
Basic extinguishing agents – water liquid and vapor state, chemical and mechanical air-foam, aqueous solutions of salts, inert gases, halogenated extinguishing agents, dry extinguishing powder.
The most common means of extinguishing fires is water.
Water is used in the form of compact or atomized jets mist in the state (droplet size of 10 microns), and with a wetting agent. In a compact and sprayed jets of fire monitors and manual fire trunks water used to extinguish the most solid combustible substances and materials (round and sawn materials and wood products), heavy oil, to create a water curtain and cooling facilities near the fire. Water mist effectively extinguished solids and materials, combustible and flammable liquids even. This reduces water consumption, minimal wetted and spoil materials, reduced temperature in a burning room and deposited smoke.
For extinguishing substances, poorly wettable with water (e.g., cotton, peat), in water to reduce its surface tension is introduced special wetting.
Water vapor is used to extinguish fires in rooms up to 500 м³ and small fires in open areas and installations. Steam moisturizes and reduces burning objects zhaet oxygen concentration.
Foam is a mass of bubbles of gas enclosed in the thin membrane liquid. Spreading on the surface of the burning liquid, it isolates the foam from the flame, whereby the vapor flow ceases in the combustion zone. Due to the fact that the foam contains water, there is some surface cooling fluid.
Used two types of foam: chemical and mechanical air. Chemical foam obtained by reacting an alkali and acid solution in the presence of specific substances – foaming agents, forming carbon dioxide. Gas bubbles enveloped water with a foaming agent as a result creates a stable foam, which can stay long on the surface of the liquid. Air-mechanical foam is a mixture of air, water and foaming agent. The foam is used to extinguish flammable liquids.
Inert gases, mainly carbon dioxide and nitrogen, reduce the concentration of oxygen in the hearth burning and retard burning intensity. They should be used in those cases where the use of water may cause an explosion, combustion spread, damage equipment and devices and unique values (in museums, etc.). They are poorly quenched materials capable smolder (wood, paper), and does not extinguish the fibrous materials (cotton, cloth, etc.). Carbon dioxide – an indispensable tool for quickly put out small fires, as well as due to their non-conductive extinguishing tanned motors and other electrical installations.
Powder formulations used to extinguish flammable liquids, liquefied gases, etc. Extinguishing their action is based on the isolation of the burning material from oxygen or air insulation vapors or gases from the combustion zone. Negative property of such powders is that they do not cool the burning substance and they can be reignited by the heated structures. Application of the powder formulations is limited due to their relatively small fire-extinguishing efficiency, moreover, they become compressed during storage [5].
Conclusion
In the course of the masterʼs work, analyzed the state of fire protection of the surface complex mine
named after M. I. Kalinin GP DUEK
On this basis it had issued recommendations and developed measures for its improvement.
List of references
- Анализ аварий и горноспасательных работ на предприятиях, обслуживаемых ГВГСС в угольной промышленности Украины за 2010 год. – Донецк, 2011. – 76 с.
- Дикенштейн И. Ф., Яковлева Н. С., Король А. А., Диденко А. А.
НИИ горноспасательного дела и пожарной безопасности
Респиратор
Автоматическая противопожарная защита башенных копров. - Шахта им. М. И. Калинина. Электронный ресурс. – Режим доступа: http://goo.gl/mtjirc .
- НАПБ 01.009-2004 Правила пожарной безопасности для предприятий угольной промышленности Украины.
- Огнетушащие вещества и средства для тушения пожаров. Электронный ресурс. – Режим доступа: http://goo.gl/6H7z7g.
- Булгаков Ю. Ф.
Тушение пожаров в угольных шахтах
. – Донецк: НИИГД, 2001. – 280 с. - Инструкция по разработке проекта противопожарной защиты угольной шахты. Донецк: Минуглепром СССР, – 1978. – 49 с.
- ТКП 45-2.02-242-2011 (02250) Ограничение распространения пожара. Противопожарная защита населенных пунктов и территорий предприятий. Строительные нормы проектирования.
