Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. The essence of competition in modern conditions
- 2. The competitiveness of the enterprise as an economic category
- 3. The approaches to determine the level of competitiveness of the enterprise
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The relevance
In a market economy a major factor in the success of the enterprise is competitive, which depends on the quality of management and many other internal and external factors. Increased competition between enterprises and trade organizations makes us look for new means of influence on the decisions of buyers.
Insufficiency the necessary theoretical and practical skills ensure the competitiveness of products and enterprises as a whole, often leads to serious miscalculations in setting prices, in some cases, lead to substantial losses and bankruptcy of enterprises [1].
The aims and objectives of the study
The aim of this study is to further develop the theoretical foundations and the development of guidelines for improving the competitiveness of the enterprise management.
To achieve this aim it is necessary to solve the following problems:
- to reveal nature and significance of the company’s competitiveness;
- to identify indicators and the factors that affect competitiveness;
- to form a mechanism of management of competitiveness;
- to analyze the existing methods for determining the level of competitiveness;
- to develop guidelines to improve competitiveness.
The object and subject of study
The object of the research is the management of competitiveness of the enterprise in modern conditions.
The subject of the study are theoretical aspects and methodical bases of management of competitiveness of the enterprise in modern conditions.
Analysis of recent research and publications
The theoretical contribution to the study of problems of management of competitiveness of the enterprise made by such foreign and domestic scientists: M. Porter, G. Yasheva, F. Hayek, F. Edzhuort, A. Kurno, Dzh. Robinson, E. Chemberlin, A. Zakharov, N. Zaytsev , R. Fathutdinov, I. Zulkaev, L. Ilyasova. The work of these scientists identified the essence of competitiveness, reduced s classification developed indicators and factors that affect the company’s competitiveness. But despite the comprehensive review of the topic, there is still no clear definition of methodological approaches to the assessment of the competitiveness of enterprises. Currently, the economic literature there are numerical methods for determining the amount of the competitiveness, but each has its drawbacks, so there is a problem of application of these methods in practice.
Testing results
The main results of the study were presented at the IV International scientific-practical conference Strategy of development of economic systems at the micro and macro levels
(2013, Dnepropetrovsk); conference Days of the theory and practice of investment
(2014, Donetsk, Donetsk National Technical University); I International scientific-practical conference Innovative prospects of Donbass
(2015, Donetsk, Donetsk National Technical University); I International scientific-practical conference of young scientists and students Actual problems of economic and social development of Donbass
(2015 Donetsk, Donetsk National Technical University).
1. The essence of competition in modern conditions
Competition is an important attribute of a market economy. The market itself, its mechanism of action can not normally exist without advanced forms of competition. According to the eminent British economist F. Hayek, society that rely on competition, more successful than others reach their goals
. Competition
as a category has many definitions. Competing in a simpler form it is treated as a competition between people companies, organizations, territories that are interested in achieving the same goal. The subject of the competition appears a product or service through which contestants try to win consumers. The object of the competition is the consumer and the buyer, for receipt of which the parties compete.
Competition is the most effective method of mutual coordination of individual actions of market entities without central interference in their activities. F. Hayek argues that one of the main arguments in favor of competition that it eliminates the need for conscious social control and gives a person the opportunity to decide the earning potential of an enterprise dressings related inconvenience and risk
[13].
Competition comes from the Latin ñîncurrentia
, which means that clas
, competition
[14]. According to the American interpreter Merriam Webster’s Dictionary Sollegiate competition means a struggle between two or more parties acting independently to protect their business by providing the most favorable conditions for the consumer. It is this interpretation as a first approach to the determination of the competition was formed in economic theory. Adam Smith believed fair competition, without collusion, competition, which is held between the sellers (or buyers) for the most favorable terms of sale of goods. A. Smith first showed that competition by equalizing the rate of profit leads to the optimal allocation of labor and capital. It must balance personal interests and economic efficiency. In this sense, A. Smith identified competition with invisible hand
of market.
Contrary to the existing stereotypes in his time, according to which any activity on the market is contrary to the interests of society, À. Smith as an example of price competition convincingly proved a number of significant provisions, which became later the doctrine of postulates the maximum to meet the needs
. A. Smith saw the so-called version of pure competition, which has no restrictions on time and do not include the mandatory presence of monopolistic positions in the economy
. Over time, his followers expanded the scope of the assumptions, the theory closer to real life. It should be noted that according to the Marxist interpretation of the competition is the antagonistic struggle between private producers for more favorable conditions for the production and distribution of goods
[15].
Another approach to the determination of competition is structure. F. Edgeworth, A.& nbsp;Cournot, J. Robinson, E. Chamberlin and other scientists were the founders of the theory of the main types of market they have identified four types: perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly and monopoly. This group of scientists examined the structural competition. The emphasis shifted from the struggle itself companies with each other on the analysis of the market structure and the conditions prevailing in it. In the course of Economic’s
competition implies the market a large number of independent buyers and sellers, and the possibility of the buyers and sellers to enter the market and leave the his [16].
Competition is classified in many ways (picture 1).
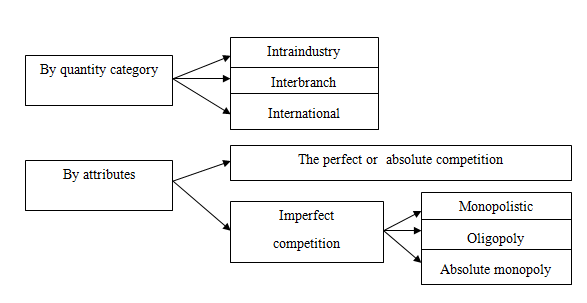
Picture 1 – The classification of the competition
2. The competitiveness of the enterprise as an economic category
The competitiveness of Ukrainian enterprises in the global market, which is rapidly developing at the moment, is a key challenge of entering enterprises in the global economic community. Ukraine’s desire to join the leading regional formation is still only a desire, since the products on the world market the majority of Ukrainian producers can be realized only within the framework of dumping or illegal transactions. In the competitive world market it recognized less than 1% of Ukrainian goods and services. At the same time, Ukraine's economy is 70% dependent on exports [2]. This confirms the fact that Ukraine’s exports on average twice the import (picture 2).
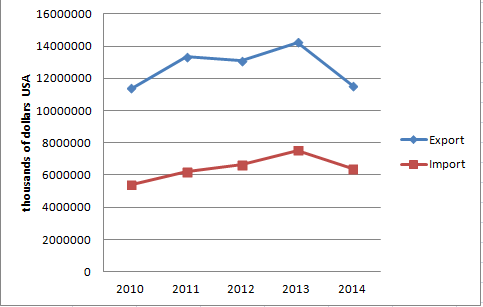
Picture 2 – Dynamics of volumes of export and import in Ukraine from 2010 to 2014
Understanding the competitiveness of the enterprise is treated by specialists in many ways. The study was the analysis of the definitions of categories of the company’s competitiveness
, their classification, identified the advantages and disadvantages. Currently, there are 3 groups of definitions. As an example, consider the definition of who provided Zakharov A., [3], Fatkhutdinov R. [4], Zaitsev N., [5] (picture 3).
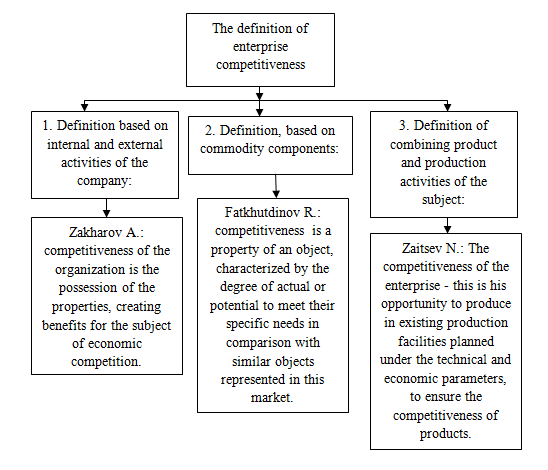
Picture 3 – Classification of approaches to the definition of competitiveness of the enterprise
M. Porter believes that the company ahead of their rivals if they have a strong competitive advantage. It defines the competitiveness of the enterprise as a result of interplay of factors generated by the objective development of the productive forces and reflect the results of the policy of large monopolies in the fight for quality, markets and profit [1].
All authors agree only in that a comparative competitiveness, and hence the relative estimation of properties of the product.
Competitiveness has many meanings and ways to study, as well as many levels (scales) or degrees (picture 4).
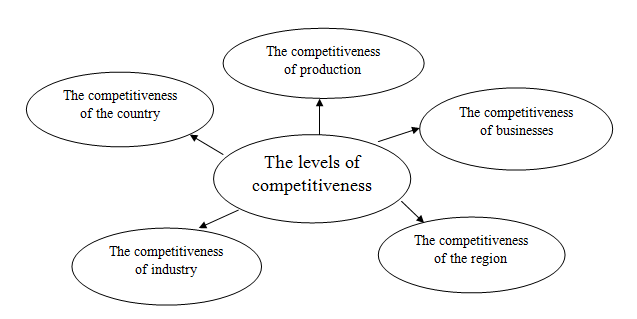
Picture 4 – The levels of competitiveness
The economy is still no clear definition of a single criterion of competitiveness, because such a complex concept can not be described in one figure. The refore, the competitiveness can be measured by several indicators, namely: economic, financial, investment and innovation, technical and technological, social, environmental [6]. Their structure is shown in picture 5.

Ðicture 5 – The structure of the indicators of competitiveness of the enterprise
(animation: 7 shots, 6 cycles of repetition, 14 kilobytes)
Currently, there are many classifications of factors influence competitiveness. In the works of M. Porter [1] they are presented in this form:
External factors:
- the level of competitiveness of the country;
- the competitiveness of the industry;
- the level of competitiveness of the region;
- the competitiveness of the organization, produced goods;
- the strength of competition in the output of the system, among its competitors;
Internal factors:
- patentability of goods (with an increase of patentability goods increased competitiveness);
- rational organizational structures and production systems (structure must conform to the principles of rationalization of structures and processes, then it will increase the competitiveness of the goods);
- system staff competitiveness (improving the competitiveness of personnel increases the competitiveness of the goods) [1].
3. The approaches to determine the level of competitiveness of the enterprise
Despite the fairly deep level of development problems of competitiveness, a common approach to quantify it still lacks. Problems of analysis and evaluation of the competitiveness of complex and multifaceted. His contribution to the solution of these problems made by such foreign and domestic scholars like M. Porter [1], Barinov V. [10], Zakharov A. [3], Marakulina M. [11], Emelyanov S. [12] and other, which developing the theoretical and methodological aspects of the evaluation of the competitiveness of enterprises. However, until now no clear sistematitsiya the results of research. The most famous to date models and methods of evaluation of the product and the company can be divided into two groups: analytical and graphical methods (picture 6). This distribution methods for assessing the competitiveness of the product and methods of assessing the competitiveness of businesses rather arbitrary, since they are largely the same, changing only the object of study.
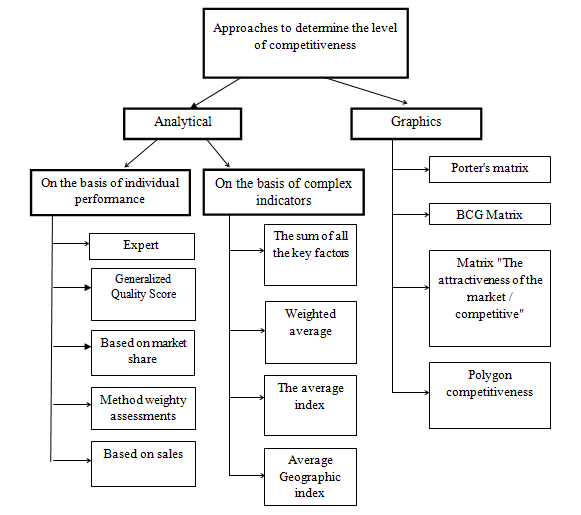
Picture 6 – Classification of approaches determine the level of competitiveness
Thus, in theory and practice, there are a large number of both analytical and graphical methods for assessing competitiveness. Each method has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. For example, the advantage of analytical methods is their objective, but the disadvantage can be a large amount of output. The advantage of graphical methods is their ease of use in practice, but there are disadvantages, in particular, that the results of the assessment do not have the exact answer to the question of whether the company competitive. In general, it is impossible to determine which of the methods is the best, because each of them has its application in particular situations.
Conclusion
In this work it was studied in detail the concept of competitiveness of the company and find out what is the relative characteristic that expresses the differences of development of the company from the development of competitive firms in the degree of satisfaction of the needs of people with their products and production efficiency. The competitiveness of the enterprise characterizes the opportunities and dynamics of its adaptation to the conditions of market competition. We explore the various types of competitive methods of its calculation, indicators and factors affecting it.
References
- M. Porter International competition: Trans. from English. / Ed. VD Shchetinina. – M .: International Relations, 1993.
- State Committee of Statistics of Ukraine [electronic resource]. – Access: http://www.ukrstat.gov.ua/.
- Zakharov A. The competitiveness of businesses: the nature, methods, evaluation and growth mechanisms // Business and banks. – 2004. – ¹ 1.
- Fatkhutdinov R. Management of competitiveness of the organization: Proc. benefits. – M.: CEMA, 2004.
- Zaitsev N. Economy organization. – M.: Infra-M, 2000.
- Mironov M. Your competitiveness. – M.: Alpha Press, 2004.
- Philosophical Encyclopedic Dictionary. – M.: INFRA – M, 1997.
- Thompson Arthur, A. Strickland, Strategic Management: Concepts and situation analysis, the 12-th edition. from English. – M.: Publishing House
Williams
, 2003. - Zulkarnaev I., Ilyasov L. The method of calculation of the integrated competitiveness of the industrial, commercial and financial enterprises // Marketing in Russia and abroad. – 2001. – ¹ 4.
- Barinov V. Roswitha organization in a competitive environment // Management in Russia and abroad. – 2000. – ¹ 6.
- Marakulin M. Office of compromise as a factor in the competitiveness of the company // Management in Russia and abroad. – 2003. – ¹ 4.
- Emelyanov S. US international competitiveness of national Buisness. – M.: Economics, 2001.
- Kuzmin A. Management of competitiveness of the enterprise (organ³zatsii): Ouch. Benefit / Natsionalnyy Univ
Lvovskaya politechnika
. – L.: Publishing National University thatLvovskaya politechnika
, 2004. - Shershneva Z. Strategic Management: Textbook / Kyiv National Economic University Press. – K.: KNEU, 2004.
- Shutov M. Economics and management of health: a regional perspective: Ouch. pos. for students. – H.: Basis, 2000.
- Balabanov L. Marketing management of competitiveness of enterprises: A Strategic Approach / Donetsk State. Univ of economy and trade. M.Tugan-Baranovsky. – Donetsk: DonGUET, 2006.
