Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. The relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study
- 3. Review of research and development
- 3.1 Review of national sources
- 4. The experimental part
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET, PET) is a thermoplastic, the most common representative of the class of polyesters, known as
different brand names. The polycondensation product of ethylene glycol with terephthalic acid (or its dimethyl ester) is a hard, colorless,
transparent material in the amorphous state and a white opaque in the crystalline state. Goes in a transparent state when heated to the
transition temperature and remains there during sharp cooling and rapid passage through the so — called zone of crystallization
.
One important parameter of PET is the intrinsic viscosity determined by the length of the polymer molecule. With increasing intrinsic
viscosity the rate of crystallization decreases. Durable, wear — resistant, good insulator does not decompose in nature for a long period
of time (the process of decomposition takes about 100 years) [1].
1. The relevance of the topic
World production of plastics has increased by 5–6 % annually. Moreover, the rapidly developing today is the market to most of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) [2].
As the demand for PET grows, naturally increasing the amount of waste. Today, PET waste represent over 30 % of all waste plastics, 80 % of which is now recycled.
The consumption of polymers is constantly growing. Plastic, pressed paper, metal, cardboard, glass. But at the same time volumes of plastic products (primarily packaging), that go to the landfill after use, increase. As you know, the timing of the decomposition of traditional plastics are tens and hundreds of years, but space for landfills is limited. Consequently, the problem of disposal of plastic waste is becoming more topical.
Another serious problem of plastic waste is related to the presence of various additives: stabilizers, dyes, plasticizers, special additives containing heavy metals such as cadmium, lead, mercury. Incineration of such waste does not exclude the ingress of heavy metals in the environment (water, air, etc.). One of the ways to solve the plastic waste — recycling of used plastic products and industrial wastes — recycling, the end product of which is the secondary polymer in the form of Fleck — chopped and peeled flakes, or regranulate. An additional cause of stimulating the recycling and especially relevant today, due to the decreasing dependence of the plastics industry from oil as a source of raw materials [3].
2. The purpose and objectives of the study
The purpose of research in master's degree work is the processing of polyethylene terephthalate with obtaining chemical products, such as, terephthalic acid, benzoic acid, ethylene glycol.
To achieve this purpose it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
- To carry out low — temperature pyrolysis of waste PET and to determine the composition of the products of pyrolysis;
- To carry out high — temperature pyrolysis of waste PET and to determine the composition of the products of pyrolysis;
- To identify ways of chemical recycling of PET in the initial chemical products (benzoic acid, terephthalic acid, ethylene glycol).
3. Review of research and development
A large part of existing in the world of plants, processing PET bottles use technology that allows to obtain secondary plastic so — called Flex. This processing technology is inferior to the more modern method of pyrolysis processing of plastic bottles; however, because it is quite widespread, it makes sense to talk about it.
In this case, plastic bottles (PET) are loaded via conveyor belt into a hopper of the crushing plant. This device is old and dirty bottles are crushed to flex-flakes having dimensions of approximately 12–20 mm. After which these flakes go into the hopper for cleaning the conveyor belt where they are cleaned of extraneous contamination.
After the process of washing the flex flakes are fed into the centrifuge for water and then they go to a dryer where any remaining moisture is removed. Prepared clean and dry flakes are packed in big bags. After that how flex can be recycle in higher quality products using a granulator (PET granulate) or to realize the resulting processing products.
The buyers of PET flex are companies and factories producing plastics and industrial objects that have an extreme need of the secondary raw materials of PET. Thus, the market for products using this method of processing is quite wide, although it is significantly inferior to the market of products resulting from processing of plastic bottles by pyrolysis [4].
The pyrolysis of plastic in this case, if we are talking about disposal of solid waste, is the incineration of plastic waste containing hydrocarbons in an oxygen-free environment at a temperature of about 600 C. During this process, solid substances are transformed into hot gas which can be used to generate heat energy and liquid fuel oil.
From the liquid obtained by pyrolysis of plastics nowadays people learned how to make synthetic fuel, which after additional purification can be used in internal combustion engines. However, the purification technology in this case is so complicated that about any profitability of this method can’t yet be considered.
In this idea, actually, there is just nothing new. In Germany before the Second world`s war, the method of pyrolysis was widely used for obtaining fuel: Nazi tanks arrived in the USSR on liquid fuel, which was manufactured from coal technology Fisher — Tropsch. Of course, since then the requirements for fuel quality has changed dramatically.
During the pyrolysis process approximately 99,9 % of harmful substances that have been added to polymers during production are destroyed. Remaining after pyrolysis ash is briquetted and can be used as furnace fuel. Therefore, pyrolysis waste plastic are totally safe.
However, this method is not devoid of drawbacks, the most important among which is the fact that the pyrolysis process produces a lot of harmful chemical compounds. So they did not get into the atmosphere it is necessary to use fairly complex systems of filtration and purification.
This is a fairly expensive equipment, which is not the best way affects the profitability of this method of recycling plastics. In addition, since the amount of consumption of plastics is growing every day, the market is experiencing a shortage of polymeric raw materials [5].
3.1 Review of national sources
In 2007, Ukraine had registered a patent Method for processing of polymer waster
.
This patent is based on processing of polymer waste, which includes pulverizing the waste, with subsequent low — temperature pyrolysis, that is characterized by the fact that the process of low — temperature pyrolysis is carried out in two stages, using exposure to induction heating at a temperature of 130–430 C and a pressure of 0.01–0.07 MPa, and the resulting liquid substance is sent to distillation condensers in refrigerators with the possibility of obtaining two fractions — gasoline and diesel fuel and grease [6].
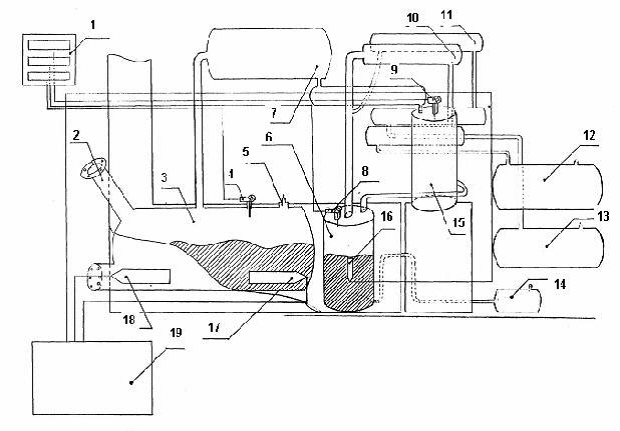
Figure 1 — Recycling of polymer waste
1 — thermometer; 2 — hatch feed; 3 — the capacity of heating the raw material; 4 — thermocouple; 5 — safety valve; 6 — heating capacity; 7 — heat exchanger; 8, 9 — thermocouple; 10 — fridge gasoline fraction; 11 — fridge the diesel fraction; 12 — tank for storing gasoline fraction; 13 — container for the storage of diesel fraction; 14 — capacity for storage of grease; 15 — water refrigerator; 16, 17, 18 — induction heaters; 19 — generator.
4. The experimental part
At this stage in a master`s work preliminary experiments on low — temperature pyrolysis high — temperature pyrolysis and by alkaline hydrolysis are conducted.
Thermal decomposition (or pyrolysis) is a thermal decomposition of organic materials in the presence of oxygen or without it. Pyrolysis of polymer wastes allows obtaining high calorific fuels, raw materials and semi — finished products, used in various technological processes, as well as the monomers used for polymer synthesis. Gaseous and liquid products of thermal decomposition of plastics can be used as fuel. Application Range of the solid (waxy) pyrolysis products of waste plastics is wide enough (the components of various protective compounds, lubricants, emulsion, impregnating materials, etc.) [7].
To study low — temperature pyrolysis the installation, consisting of following items, has been made: hot plates, sand baths, round bottom flasks, the direct water of the refrigerator water seal. Thermal degradation of polyethylene terephthalate was carried out at a temperature 400 С the removal of decomposition products.
As a result of the experiment a product similar to asphalt was obtained, on the tube of the flue white and yellow crystals appeared, presumably crystals of benzoic and terephthalic acids.
Examination of the resulting crystals showed that they do not dissolve in water, but the boiling point of water, divided into 2 factions, one of which remained in the solid shape and the other part was in the molten state, in the form of drops deposited on the bottom of the flask. Yellow crystals soluble in benzene, presumably that is the benzoic acid.
Low — temperature pyrolysis process is slow. In order to intensify the decomposition of PET, for further research, decision to use high — temperature pyrolysis was made.
Study conducted by well — known methods according to GOST 6382–2001. Into the crucible with a lid the crushed PET was put, transferred into muffle furnace, the furnace door was closed and the temperature (table 1) was kept for 7 minutes.
Then removed from the muffle furnace and cooled crucible on an asbestos plate for 5 minutes. After that, the crucible with the lid placed in the desiccator and cooled to room temperature. After cooling, the crucible with the non — volatile residue is weighed and makes the calculation.
The results of the experiment are shown in table 1. It is seen that the yield of volatiles increases with increasing temperature.
| Temperature, C | Exit of volatiles, % |
| 600 | 80.15 |
| 680 | 89.66 |
| 720 | 90.65 |
| 800 | 93.6 |
| 840 | 94.81 |
| 1000 | 96.25 |
The interest represents of chemical processing, which does not require high temperatures and, at the same time, allows obtaining valuable chemical products.
Chemical processing is the transformation of the polymer chains of PET. Usually convolutions by splitting the circuit are either
complete depolymerization into monomers or partial depolymerization into oligomers. PET is a polycondensation`s product of ethylene
glycol terephthalic acid (or its dimethyl ester). PET can be broken down into some reagents, such as water, alcohols, acids, glycols
and amines. In addition, because PET is formed by reversible reaction of polycondensation, it can be converted back to monomers or
oligomers using the reaction in the opposite direction by adding the condensation product. The products of such processing can be
cleaned and reused in the form of raw materials for the production of high quality chemical products. Among all methods of processing,
chemical processing is most appropriate, based on the principle of ecological sustainability
which is defined as the process that meets
the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. This is due to the fact
that as a result of chemical processing turns raw materials (monomers) from which the initially produced polymer. Thus, under ideal conditions
there is no need for additional resources for PET production [8].
Alkaline hydrolysis of PET conducts as follows. In a round bottom flask mounted in a heating mantle the crushed PET was placed in the amount of 75 grams. When PET is heating in the presence of NaOH in an amount of 10 grams dissolved in 100 ml of water, the formation of sodium salts of benzoic and terephthalic acids. Heating occurres at about 100 C, to full boiling of the liquid in the reaction flask. In the flask appeared were light yellow crystals, almost white color on the surface of pieces of plastic.
The resulting reaction residue is dissolved in water.
When added to a solution of sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, a white precipitate falls, presumably benzoic or terephthalic acid. Made the filtration of the solution on a folded paper filter, and the result dropped the white crystals, which were dried at room temperature. The rest burns without soot, yellow flame, benzene is not soluble, we can assume that we had the terephthalic acid.
Conclusion
Thus, when conducting low temperature pyrolysis and alkaline hydrolysis following products were obtained: benzoic acid and terephthalic acid. Further investigation of the decomposition of PET should be conducted. It is also necessary to conduct a more detailed study of the resulting products of decomposition of the PET.
References
- Гуль В. Е. Структура и механические свойства полимеров. — М.: Высшая школа. — 1966.
- Research in the field of synthesis and processing of polyethylene and nanocomposites on its basis. [Electronic resource]. — Access mode: https://domashke.net/referati/referaty-po-himii/statya-issledovaniya-v-oblasti-sinteza-i-pererabotki-polietilentereftalata-i-nanokompozitov-na-ego-osnove.
- Митрофанов Р. Ю., Чистякова Ю. С., Севодин В.П. Переработка отходов полиэтилентерефталата // Твердые бытовые отходы. — 2006. — № 6.
- Recycling trash. Investing in the future. [Electronic resource]. — Access mode: http://ztbo.ru/zavodi-tbo/zavod-po-pererabotke-pet-plastikovix-butilok.
- The pyrolysis of plastic and plastic. [Electronic resource]. — Access mode: http://ztbo.ru/o-tbo/stati/piroliz/piroliz-plastika-i-plastmassi.
- The base patents of Ukraine. [Electronic resource]. — Access mode: http://uapatents.com/2-21712-sposib-pererobki-polimernikh-vidkhodiv.html.
- Recycling of waste plastics on the PROMETHEUS complex by pyrolysis. [Electronic resource]. — Access mode: http://www.potram.ru/index.php?page=25.
- NatureTime. Recycling of PET. [Electronic resource]. — Access mode: http://nature-time.EN/2014/01/pererabotka-pet.
