Abstract
Сontent
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Review of research and development
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The study of the processes occurring when blowing ladle with inert gas is a very relevant topic in today's industry.
Thanks to research in this area we can find: the optimal arrangement of the vent; the required flow rate of the injected gas; determine the probable lining wear, depending on the location of the vent hole and blowing intensity. These studies will allow to optimize gas consumption, extend the life of steel ladle linings.
1. Theme urgency
We conducted a study of the existing mathematical model, which is made in the application package Ansys. This model allows you to fully evaluate the hydrodynamic and thermal state of the melt.
The main objectives of the study by obtaining vector movement pattern speed of the melt in the two-dimensional model that allows to quantify the nature of the movement of fluids. In this model, the method of finite elements.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
Development of technology systems ladle steel refining in a ladle necessitates optimization of mixing conditions of the metal in the ladle, which is usually done by injecting into the melt a certain quantity of inert gas (argon). Especially, the issue of rational mixing of metal in the ladle by blowing argon, is relevant for the ladle furnace installations. This is due to the fact that in the ladles used in the UE, is provided, usually one - two (sometimes three) blowing unit, the location of which is regulated certain technological considerations. Firstly, the blowing units should be placed so that the argon blown into the metal does not enter the area of ??the electrodes used to heat the metal and slag. Secondly, one of the nodes must be placed purge in the feeding zone ferroalloys, providing a high degree of absorption. Thirdly, the purge unit can not be located in the zone falling metal stream during filling of the ladle. Fourthly, the purge unit can not be placed near the wall of the bucket, since in that case will be increased refractory wear in the upstream propagation. Fifthly, according to the processing sequence of operations performed on the machine bucket metal argon purge rate can vary over a considerable range. Because the main objective of this study is to establish the optimal conditions of the melt mixing in processing it to the UE, which would allow to solve the following problems:
- definition of rational number of blowing units and their position in the bottom of the ladle.
- prevention of dead zones in the liquid metal bath in the ladle.
- determine the conditions, the corresponding sound mixing intensity in accordance with the metal processing technology in the ladle.
- Optimization of conditions for the interaction (mixing) of the metal and slag in the purge process.
3.Review of research and development
The process of mixing liquids in a confined space is a complex physical phenomenon. In order to analyze this phenomenon with respect to a particular technological problem it seems appropriate to the use of certain criteria which make it possible to perform a comparative assessment at the macro and micro levels. As part of the evaluation of the effectiveness of mixing a certain amount of liquid most commonly used integrated indicator "intensity mixing" (mixing time). The agitation of the metal in the ladle is very important technological parameters in the processing of steel in the SAR. Firstly, the intensity of mixing of the metal determines the length of certain processing steps, including metal homogenize the chemical composition and temperature of the slag or metal refining process. Second, gas metal mixing process is quite difficult, and the liquid bath are formed as the intensive circulation zone and "stagnation region", a manifestation of which may adversely affect the final performance in the whole processing. Thirdly, the use of argon as a substance that provides a mixing process allows for additional processing costs and consequently reducing the amount of argon that is used decreases. With all these features, it was decided that the study will be conducted in a "cold" water model. The main objectives of physical modeling with respect to this work can be formulated as follows:
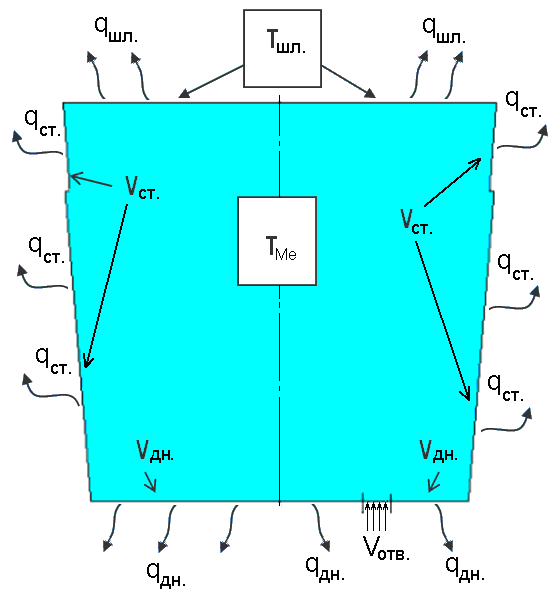
Figure 1 – Driving the inner cavity of the bucket with the initial and boundary conditions
Conclusion
After analyzing the data, we can draw a conclusion about the nature of the movement of the metal flow. Most large melt flow rate are observed in the rising flow area in vicinity of the blowing apertures, further metal flow developing involves large movement in the metal layers and zones are formed circulation. The process of stabilizing. Most thorough mixing the melt was observed under a stream of blowing openings through two blowing apertures offset rn / RL = 0.95 ... 0.6, that is closer to the walls of the ladle. In this case, the observed motion of the metal flows along the lining of the bucket, which is a favorable factor, as the hottest upper layers of metal fell into the axial zone of the liquid bath. With this arrangement, the scavenging holes observed a small proportion of low-speed flow, which were located in the bottom part and in the zone of the slag zone. Due to all these factors, there was less wear lining slag belt and minimizing the involvement of slag into the interior of the melt. The same study showed that a change in the intensity of the purge virtually no impact on the nature of the melt mixing. And the most intense attack metal flows are working lining of the ladle slag slightly below the waist. However, despite this, the present location of the vent is the best.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: May 2017. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- А.Н. Смирнов, Е.В. Ошовская, И.Н. Салмаш, В.М. Сафонов, К.Е. Писмарев Некоторые вопросы оценки интенсивности перемешивания при продувке металла в ковше инертным газом // «Металл и литье» - № 3 – 4, - 2007. – с. 44 - 49
- D.Mazumdar, H.B.Kim, R.I.L.Guthrie. Критерии моделирования потока при обработке металла в сталеразливочном ковше с газовой продувкой: экспериментальное исследование // - Ironmaking and Steelmaking. 2000 - Vol.27. No4. - P.302-308
- M.Iguchi, K.Takanashi, H.Kawabata. Модельное изучение свойств жидкостного потока в резервуарах с донной продувкой при возникновении обратного эмульгирования // - ISIJ International. - Vol.38 (1998). No.10 - pp.1080-1085
- M.Iguchi, K.Takanashi, O.Ilegbusi Влияние физических свойств верхнего масляного слоя на характеристики газожидкостного потока в резервуарах с донной подачей газа //- ISIJ International. Vol.38 (1998). - No.9. - pp.1032-1034
