Improving the system of financial planning as a tool to ensure the financial security of the enterprise
content
- Introduction
- 1. The relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study
- 3. The content of the work
- Conclusion
- The list of sources
Introduction
At the present stage of production development one of the leading places is occupied by the problems of financial security of enterprises. The process of consolidation of financial capital through the use of reproductive tools that are needed for the growth of incomes of the enterprises and the country as a whole necessitates the study of factors that enhance the financial security of enterprises. In modern conditions of functioning of enterprises, which are characterized by uncertainty and high dynamics of the external environment, there is an objective necessity of application of effective financial management. One of the fundamental functional components that ensure the performance of financial management is financial planning. Using it in the enterprise is difficult to achieve a stable financial state for the future to generate sufficient financial resources for the development at minimum cost, and hence, to succeed in the market.
The relevance of the topic
Domestic and foreign practical experience suggests that the problem of improving financial planning at the micro level continues to be relevant. Planning stabilizes activity of the enterprise in the conditions of unpredictability of market relations. Financial planning applies to all operational processes, permeates, penetrates, and binds to a single link marketing, personnel and production planning. Through financial planning are specified scheduled forecasts are defined interrelated tasks and the sequence of their implementation in achieving your goals. The importance and relevance of all the identified issues resulted in a considerable interest of scientists to study the financial planning of the company. It should be noted versatility of the lighting issues of financial planning in the scientific literature, and as a consequence, the lack of a common terminological base of knowledge.
The purpose and objectives of the study
The aim of the thesis is the formation of a holistic view of financial planning as a tool for raising the level of financial security of enterprise and development of recommendations for its use.
To achieve this goal in the process, it is necessary to solve following tasks:
to investigate the economic essence of financial planning;
to study the types and methods of financial planning;
to study the nature of the financial security;
to analyze the financial condition of the company;
to propose ways of improving financial planning through financial security.
The content of the work
3.1 Theoretical foundations of financial planning and financial security of the enterprise
The basis of the mechanism of financial management of the enterprise is financial planning – the process of developing a system of financial plans and planning (normative) indicators for the development of enterprises with necessary financial resources and improve the efficiency of its financial activities in the upcoming period [1,p. 353].
Financial planning for the enterprise (or in-house financial planning) comprises three main systems:
the prediction of financial activities (strategic financial planning);
the current planning of financial activities;
operational planning of financial activity. All of the financial planning system interrelate and are implemented in sequence, at the same time, each of these systems are inherent to the period, and their forms of implementation of its results.
The most complicated among the systems of financial planning is the system for forecasting financial activity, which is aimed primarily at the development of financial strategy of enterprise.
The current system of financial planning based on the developed financial strategy and is developing specific types of current financial plans that allow you to determine the coming period, all sources of financing of enterprise development, to form the structure of its revenues and costs, to ensure the continued solvency of the company, determining the structure of its assets and capital at the end of the planning period.
The system of operational planning of financial activities is the development of a set short-term targets for financial support of the main directions of economic activity of the enterprise. The main form of such planned financial targets is the budget, which is a financial operational plan the short-term period, developed normally until one year (generally during the forthcoming quarter or month), reflecting the expenses and receipts of financial resources in the implementation of specific economic activities. Budget details indicators of current financial plans and is the main planning document brought to "responsibility centers" of all types. In [13, p. 322] a financial plan is defined as a generalized planning document that reflects the receipt and expenditure of funds on current (within one year) and long term (over one year) period, which includes the development of operational and recurrent budgets, and forecasts of financial resources for two or three years.
Financial planning and budgeting in works [2;4;6] are considered as the basis to enhance the results of financial operations as they provide the use opportunities in a changing market, allowing you to simulate different situations in a timely manner to adjust the operation of the enterprise and to choose the most promising ways of its development. In the works of Kirkach S. M., Naumenkova S. V., Titanic HP [5;9; 12] performed a detailed analysis of approaches to definition of essence of financial planning. Moreover, in the work of Kirkach S. M. [5] the emphasis is on the selection of keywords when analyzing the definitions of financial planning – process, tool, type of activity.
Financial planning is a management function, and in accordance with this serves as a basis for making financial and economic management decisions. On the other hand financial planning, as a functional component of financial management performs a number of functions reflecting the purpose and the principal activities of the company undertaken in the financial planning process. Under the functions of planning refers to marginalize the work generated by the division of labor in the planning process, that is, any work, any action to be taken in the process of developing the plan and aimed to change the state of the enterprise [11]. Planning is inextricably linked to the forecasting, which allows to reduce the uncertainty of the future, assessing the possible financial impact of decisions and external factors, and thus to improve the accuracy and reliability of planning decisions. Forecasting and accompanies the implementation of the plan, enabling timely tracking of internal and external threats that arise in the course of its execution, and adjust the plan.
Difference of financial forecasting from financial planning consists that at forecasting assess the possible future financial impact of decisions and external factors, when planning recorded financial performance that the company seeks to obtain in the future. Company's financial security – means the protection of the financial interests of the enterprise at all levels of their financial relationship from the influence of internal and external threats, which ensures its preservation and development in the current and strategic prospects.
Inadequate attention to the problems of security activities may, even at a high yield business, lead to the fact that the business entity will become highly vulnerable to various kind of risks, but in the future can lead to its bankruptcy. Therefore, actualizes its importance, the problem of developing a system of financial security of business entities identify risks and threats that lead to imbalance and loss of financial security, choice and justification of measures to counteract this trend. Threat is any circumstance or event that might lead not only to violation of the established business processes, loss or reduction in income, but and violate the security policy of the enterprise [7].
Such threats include: inefficient financial policy of the enterprise, the lack of financial resources, insufficient control over management and optimization of assets and liabilities of the company, the high level of competition in the market, the unstable situation of the economy, due to which one can observe the exacerbation of all these factors. The main external risks and threats affecting the loss of financial security, the following:
purchase shares, debts of the enterprise unwanted partners;
significant financial obligations of the company (as a large amount of debt and large debts to the company);
the underdevelopment of capital markets and their infrastructure;
underdeveloped legal system protecting investors ' rights and enforcement of legislation;
crisis monetary and financial systems;
the instability of the economy;
the imperfection of the mechanisms of formation of economic policy.
Internal risks and threats affecting the financial safety include the intentional or accidental mistakes by management in the field of financial management related to:
the choice of strategy of the enterprise;
control and optimization of assets and liabilities of the company (development, implementation, and control receivables and payables, the choice of investment projects and their sources of financing, optimization of depreciation and tax policy).
A key factor in the successful development of the company – a competent and professional management of the enterprise, and a major risk factor, as noted by B. Leontiev and G. Kleiner, "the factor, NNN" – the incompetence, dishonesty, negligence. [8] On the relationship between planning, including financial, and financial security indicate and the authors [3]. For example, they note that achieving a high level of financial and economic security of the enterprise is possible only under condition of stable, sought-after activities, as in this case, the company is able to meet current challenges in the production and sales of products reimburse incurred costs, to pay salaries, pay taxes and generate resources to meet strategic objectives. One of our core strategic objectives is return on investment in projects aimed at the development of current activities. In this regard, strategic, investment and operating Finance activities are closely interrelated and require for their effective implementation of the application of the planned (forecast) methods. The first object of forecasting economic indicators is sales. In order to make the forecast sales plan and forecast plan cost you must analyze factors such as: past sales volume, market conjuncture and its possible change, the overall economic situation, the yield of products, pricing policies, production capacities, long-term trends in sales of different types of products, the dynamics of the cost structure depending on the volume of sales.
The results of predict are used in all areas of corporate planning, including overall strategic planning, financial planning, production planning and inventory control, marketing planning and management of trade flows and trade transactions. The second object of the prediction is the amount of assets and sources of their formation (liabilities) needed to obtain the forecast of revenue from sales. In other words, on the basis of the planned volume of activity, the planned volume of assets (equipment, space, payroll, inventory, cash) and capital structure (own and borrowed funding). Forecasting of the balance sheet is carried out in a simplified form in the aggregated balance sheet: assets (fixed and working capital) and liabilities (equity and debt).
For the functioning of the system of financial-economic security the availability of information on the value of future income and expenditure of the enterprise is critical. To ensure the financial security of the enterprise's financial planning must take into account the financial risks associated with financial decision-making, as well as the possibility of the elimination or reduction of risks. Therefore, the uncertainty of the market environment, especially important is the sixth stage in the system development of the financial plan. At this stage, the assessment quantified the risk, when any of the key directions of economic development of the enterprise. However, the definition of risk in quantitative form to take into account all internal and external factors which in any way may influence the effect of the decision is almost impossible. Any enterprise, in its essence, is a closed system: it has multiple ties with other companies in the industry and other market actors. Therefore, to predict all possible variants of development of the enterprise is impossible. Management decisions in this case, it occurs in conditions of uncertainty of consequences, and the level of risk in this case increases.
3.2 analysis of the financial condition of an enterprise using the method of hierarchy analysis
In the second part of the thesis, we will analyze the financial condition of the enterprise using the method of hierarchy analysis (AHP). Analytic hierarchy process (AHP) developed by T. Saaty, involves the decomposition of problems into more simple component parts and processing the judgments of decision makers through pairwise comparisons of these judgments. The result is determined by the relative importance of the investigated alternatives for all criteria in the hierarchy. The relative importance is expressed numerically as vectors of priorities. Thus obtained values of the vectors are estimates of the scale relations and correspond to the so-called strict assessments. In the first stage of MAI outlines the problem and formulates the objective to be achieved. The goal is to select the figure to a greater extent than other describing the financial condition of the company. The second stage consists in building the hierarchy. The top of the construction of a hierarchical structure (Fig. 1) is the goal (level 0): Assessment of the financial condition of the company (K). The next (first) level there are criteria specifying the purpose. It could be financial stability (K1) and business activity of the company (K2).
On the second level there are 4 criteria that specify the criteria of the first level:
the liquidity of the company (K11);
the solvency of the company (K12);
the profitability of the company (K21);
turnover (K22).
On the third (bottom) level are the 12 elements (indicators) for assessing the financial condition of the enterprise:
absolute liquidity ratio (К111);
the quick ratio (K112);
the coverage ratio (К113);
the coefficient of ownership (К121);
the solvency ratio (К122);
leverage ratio (К123);
the profitability of property (К211);
return on equity (К212);
the sales margin (К213);
total capital turnover (К221);
the turnover of equity (К222);
the turnover of capital raised (К223).
In accordance with the MAI the lower level items of the hierarchy have to be compared pairwise on the elements of the higher level etc. up to the top of the hierarchy.
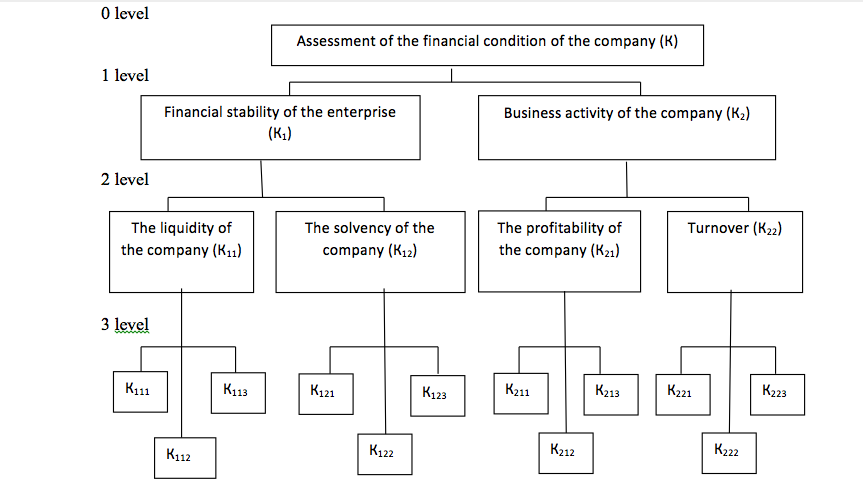
Figure 1 - Hierarchical structure to assess the financial condition of the company
The third step refers to the comparison of hierarchy elements. Formed assessment of the relative importance of factors at each level of the hierarchy using a matrix of pairwise comparisons of subjective judgment reflecting the evaluation of the importance factors. Paired comparisons are made in terms of dominance of one element over another, given a 9-point scale.
The next step is to calculate the vector of priorities on this matrix, i.e., compute the main eigenvector, which after normalization becomes the vector of priorities. In the absence of W, it is possible to obtain a rough estimate of this vector the following four ways, listed below in order of increasing precision of estimates.
Sum the elements in each row and normalize them by dividing each amount by the sum of all elements. The sum of the results will be equal to one. The first element of the result vector will be a priority of the first object, the second – the second object, etc.
Sum the elements of each column, find the inverse of these amounts. To normalize them so they sum to one. To do this, divide each value by the inverse of the sum of all feedback values.
Divide the elements of each column in the sum of the elements in that column (i.e., normalize the column). Then add up the elements of the resulting row and divide this amount by the number of line items (the average of the normalized columns).
Find the geometric mean for each row (multiply all n elements of the row and from the works to remove the root of the n – th degree). To normalize the resulting numbers (divide by sum).
For consistency estimates in the General case, we multiply the matrix of comparisons on the resulting vector of priorities, get a new vector. Dividing the first component of this vector by the first component of the vector priorities, the second component of the new vector to the second component of the vector of priorities, etc., we define another vector. Dividing the sum of the component of this vector to number of components, we find an approximation to the number (called the maximum or principal's own value). We find, therefore, the consistency ratio.
On the basis of the results obtained in the third part of the thesis we will assess businesses and develop recommendations to improve the financial security of the enterprise.
Conclusion
Currently in the Russian economy operate side by side with insolvent companies and quite prosperous, financially well-off entities that have been able to progressively perceive the change to a mixed economy, a wide range of forms of ownership, the inevitability of advanced build quality and range of products for wide consumer demand. Each company has a certain capital, through which it receives the bulk of the profits. Errors relating to investment, inevitably lead to the loss of financial stability and even bankruptcy. Thus, the system of planning and management of internal resources is a key factor in the success of the enterprise in the conditions of market economy.
The list of sources
Бланк И.А. Словарь-справочник Финансового менеджера / Бланк И.А. – К.: Ника-Центр, 1998. – 480 с.
Бурцев, В.В. Через бюджетирование к эффективному менеджменту [текст] / В.В. Бурцев // Финансовый менеджмент. – 2005. – № 1.
Васильев В.Л. Прогнозирование финансовых результатов предприятия как элемент системы экономической безопасности / В.Л. Васильев, Ф.Н.
Рузанов, Н.А. Шмонов. [Електронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.konspekt.biz/index.php?text=53066
Великая, Е.Г. Стратегическое управление затратами на основе бюджетирования [текст] / Е.Г. Великая // Финансы и кредит. – 2012. – № 9. – С. 10 – 27.
Киркач С.М. Конкретизація сутності фінансового планування з позиції функціонування підприєства (банку) [Електроний ресурс] / Киркач С.М. // Проблеми і перспективи розвитку банківської системи України: зб. наук. пр.; гол.ред. А.О. Єпіфанов. – Суми: ДВНЗ "Українська академія банківської справи", 2012. – №34.– Режим доступу: http://archive. nbuv.gov.ua /portal/soc_gum/pprbsu/2012_34/34_01_15.pdf
Кокин. А.С. Значение финансового планирования для обеспечения стабильной деятельности организации // А.С. Кокин, Г.Н. Яковлева // Вестник Нижегородского университета им. Н.И. Лобачевского, 2011, № 5 (1), с. 218–222.
Кузенко Т. Б. Фінансова безпека підприємства: Нав- чальний посібник / Кузенко Т. Б., Мартюшева Л. С., Грачов О. В., Литовченко О. Ю.– Харків: ХНЕУ, 2010.– 298 с.
Лапуста М.Г., Шаршукова Л.Г. Риски в предпринимательской деятельности. М.: ИНФРА-М, 1998. С. 96.
Науменкова С.В. Фінансове планування як складова системи ефективного управління фінансами акціонерного товариства / С.В.Науменкова, О.І. Глазун // Вісник української академії банківської справи. – 2004. – № 1 (16). – С.71 – 85.
Отливанская Г. А. Финансовое планирование в современной экономической науке / Г. А. Отливанская, Р. А. Бабашов. [Електронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.economy.nayka.com.ua/?op=1&z=2507
Планирование финансов [Електроний ресурс]. – Режим доступу: http://www.debtexpert.ru/debts-941-2.html
Татьянич Л.С. Роль фінансового планування на підприємстві в умовах ринкового господарювання / Татьянич Л.С. // Вісник бердянського університету менеджменту і бізнесу. – 2010. – №1 (9). – С. 78 – 83.
Финансы, денежное обращение и кредит: Учебник / М.В. Романовский и др.; Под ред. М.В. Романовского, О.В. Врублевской. – М.: Юрайт- Издат, 2006. – 543 с
