Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the research topic
- 2. Purpose and object of research
- 3. Review of research and development
- 4. Process approach as a tool to optimize the activities of the enterprise
- Conclusions
- References
Introduction
In conditions of insufficient competitiveness of domestic enterprises on the world market, the use of a process approach in the management of an organization is an important and promising way out of this situation.
The goal of any business activity – Receiving a profit. In a market economy, an enterprise must constantly increase its potential – estimated future profit levels. The level of enterprise competitiveness is an integral indicator of its potential. Capacity building involves the improvement of the enterprise’s activities: improving quality, reducing production costs, fulfilling orders on schedule, and so on.
The process approach is the most important sign of perfect management. This approach, used as a baseline in the international standards of the ISO 9000:2000 series, is in fact not new. At the end of the 60s, a methodology for structural analysis and projection of complex SADT systems was developed.
The main idea of the process approach is that the successful management of the enterprise can be implemented through the description and selection of the processes of structural and functional units of enterprises. Enterprises using a process approach are able to create and maintain conditions that affect the quality assurance of production processes, ensuring customer satisfaction. It is the process approach that allows managers to identify and shape the management of key processes in the development of all activities of the enterprise, integrating the often fragmented actions of structural-functional departments and directing their efforts towards a single result.
Relevance of the research topic
The relevance of the topic is determined by the fact that ensuring the competitiveness of any enterprise in a market economy is impossible without continuous improvement of its activities aimed at improving the quality of products. Quality assurance is a complex problem that should be addressed throughout the enterprise.
Domestic enterprises operating in international markets must comply with the requirements of the Quality Management System (QMS), a distinctive feature of this system, built in accordance with the requirements of the ISO 9000 series, is enterprise management based on the process approach.
Purpose and object of research
The purpose of the work is to describe and improve the process model of management of the activity of the certification department of the State Enterprise Donetskstandartmetrology
.
The main objectives of the study:
- Investigate the activities of the department in terms of the process approach.
- Make a list of the main business processes and on the basis of the data obtained to draw conclusions about the rational use of resources, the number and load of personnel, etc.
- Identify the missing and duplicate business processes and make appropriate adjustments.
- Calculate the losses and make suggestions for improving the process model of management of the department.
- Based on the results, build a new model of business processes.
Research object: activity of certification department of the State Enterprise Donetskstandartmetrology
.
Research subject: the main business processes of the certification department of the State Enterprise Donetskstandartmetrology
.
3. Review of research and development
The theoretical basis for the implementation of the process approach in an industrial enterprise, the evaluation of process criteria, as well as the analysis of leading foreign quality systems, process modernization concepts were laid by foreign quality experts, including B. Andersen, E. Deming, J. Juran and others.
The content of the process approach to management and the essence of business processes are widely discussed in the works of O. V Bucha, I. N. Gerchikova, S. T. Gura, N. M. Zhigunova, V. A. Lipuntsova, M. Robson, R. A. Fatkhutdinova, S. V. Shaposhnikova and others.
Approaches to assessing the effectiveness of business processes are presented in the works of such authors as V. V. Kolocheva, G. Kokins, V. A., V. V. Repin, L. E. Fedyukin.
Problems of increasing the effectiveness of enterprise business processes are discussed in the works of M. G. Beach, R. Camp, E. A. Mikhailova, Hammer, J. Champi, E. V. Runs and others.
4. Process approach as a tool to optimize the activities of the enterprise
The process approach has been used as a tool for strategic management since the 1980s and 1990s. The parallel formation of the project approach along with the process approach led to the development of competition between them. Among theorists and practitioners of management, the process and project approaches continue to be viewed as opposed; Thus, when choosing a strategic management toolbox, a company should prefer one of two alternatives.
The juxtaposition of the process and project approaches in management is dictated by the choice of a development strategy, which relies, respectively, on internal resources or external sources. This approach is demonstrated by T. Kuran, J. Holland, J. Schumpeter: ... this choice has its roots in the theory of organizational development and (later) in the theory of organizational learning. Many twentieth-century theorists have been challenging organizations to choose between finding new opportunities and using existing resources
[2]. At the same time, the development of the theory of organization declared by J. Marsh in the early 1990s reveals a new layer of problems: Marsh encourages organizations to seek a balance between exploration strategy and exploitation strategy
[7]. Thus, the project is a tool of the search strategy, and the main role in the use strategy is assigned to business processes.
The essence of the process approach to management is to manage economic resources as processes. This approach considers business processes as an object of management – as opposed to managing the functionality and organizational structure.
The main characteristics of process-oriented management are its following elements:
process owner – this person is responsible for its results;
process settings – performance indicators;
consumer process results;
process input – objects converted to create output streams;
the exit of the process, i.e. the purpose of its existence (product, service);
management – impact on the process through internal standards, standards and regulations.
The process approach is based on the following principles:
planning for continuous improvement of the quality of the final product;
focus on customer satisfaction;
creation of an effective personnel motivation system;
corporate responsibility for the results of the economic activities of all participants in management units.
The orientation of the management system on the principles of the process approach can be implemented in two ways:
evolutionary, which means making changes to the existing management system;
through business process reengineering, which implies a fundamental rethinking and a radical restructuring of business processes to achieve fundamental improvements in modern efficiency indicators: cost, quality, service and efficiency
[5]. Reengineering is based on evolutionary transformations of the organizational structure associated with the rethinking of the conceptual framework of business management.
A key category of the process approach to managing an organization is the business process. A review of scientific and practical studies of the process approach allows us to conclude that there is no single approach to determining the category business process
.
The existence of various interpretations is due to the presence of various tasks for which the process approach is intended. Despite the fact that there are many definitions of the concept business process
, most often the corporate practice uses the categorical apparatus of the ISO 9001 standard. According to it, the business process is – this is a set of interrelated and interacting activities that use inputs
to get the desired result. The version of the ISO 9001 standard is based on the Shewhart-Deming continuous improvement cycle (PDCA: plan, do, check, act), which makes the structure of the standard consistent. E. Deming also formulated a series of pragmatic axioms
: ... any activity can be considered as a technological process and therefore can be improved
[4]. Thus, when managing the quality of an organization’s activity and the quality of the result of this activity, a process approach is needed.
Further research raises the problem of classifying business processes. Many scientists adhere to the characteristics of the process approach, which provides for the division of business processes into three groups. So, they identify the main business processes, whose task is to focus on the provision of such services and the production of such products that provide the greatest value to the client and provide a stable income for the enterprise. Auxiliary business processes provide all kinds of necessary resources for the execution of core business processes. The third view is – business processes of development and management [3]. So, any business process has its own purpose. The general model of the enterprise process activity is shown in fig. 1.
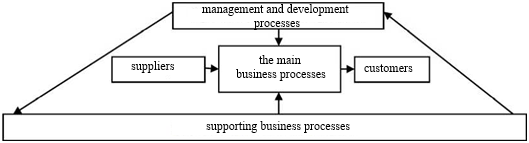
Figure 1 – General management model within the process approach
In accordance with the international standard ISO 9001, containing the requirements for the quality management system of organizations, the business process can be represented by a diagram (fig. 2).

Figure 2 – Business process diagram in accordance with ISO 9001
(animation: 6 frames, 5 cycles of repetition, 78 kilobytes)
According to the ISO 9001:2015 standard, the presentation of interrelated processes and their management as a system can help an organization achieve its planned performance. This approach allows you to manage the interactions and relationships of processes, improves the structure and activities of the organization as a whole.
The purpose of applying the process approach used as a tool for strategic management is to maximize the satisfaction of interested parties. The latest, in accordance with the quality standard ISO 9001:2008, are consumers, owners, employees of the enterprise, suppliers, partners and society as a whole; Thus, the mechanism for assessing the effectiveness of business processes should be based on a system of indicators that can take into account the effects of the company’s activities for all stakeholders.
In the economic literature provides a lot of classifications of indicators of business processes. Consider the most common classification criteria:
unit of measure, which allows you to group indicators in four main areas: cost indicators, using value values;
quality indicators, manifested in physical units; time indicators (timeliness and duration);
relative performance indicators expressed as a percentage;
characteristic of the process, according to which there are distinguished performance indicators (the ratio between the result and costs), performance (level of achievement of goals) and flexibility – the ability of the business process to adapt to changes in the external environment;
purpose of use: competence indicators, performance indicators, diagnostic indicators;
the scale of the process that divides indicators into local and global.
Despite the diversity of classification criteria, the use of only one classification is not possible, since the assessment of the business process requires the use of a system of indicators. Under the system it is advisable to understand the totality of indicators, allowing to obtain a comprehensive assessment of the business process. This system should provide:
focus on the implementation of strategic orientations;
permanent focus on improving production and financial performance;
cost optimization;
employee motivation to achieve strategic, tactical and operational goals;
maximum transparency of performance indicators for stakeholders.
Conclusions
The introduction of the process approach in the enterprise due to a number of features. The most significant features are: a large number of processes, the complexity of their implementation and performance evaluation, a large number of staff, voluminous regulatory and technical documents, a wide range of purchased raw materials and materials, the specificity of the main equipment. These features are taken into account at all stages of the implementation of the process approach and in all documents of the enterprise QMS.
List the key results of the implementation of the process approach to strategic management [1]:
- Creation of a company’s business process management system;
- Distribution of powers and responsibilities between the owners (managers) of business processes;
- Creating a system of business process indicators;
- Formation of a system of business process regulations;
- Create a system of continuous improvements in business processes;
- Reduce the duration of processes and reduce the cost of their implementation;
- Improving the quality of business processes;
- Increase manageability and transparency of the company;
- Optimizing the organizational structure based on processes, not functions;
- Increase in employee productivity;
- Business process risk reduction;
- Automate optimized processes;
- Ability to replicate business processes;
- Reduction of time for training new employees;
- Achieving an economic effect that ensures the company’s full payback on the implementation of a process management approach.
References
- Абрамов В. С., Абрамов С. В. Стратегический менеджмент: ч. 1. Сущность и содержание: учебник и практикум для бакалавриата и магистратуры. М.: Юрайт, 2017. – с. 270 [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://www.biblio-online.ru//... – Загл. с экрана.
- Баранская А. Н. Две стороны одной медали // Креативная экономика. 2010. № 12. c. 130–135. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/... – Загл. с экрана.
- Вайцеховская С. С., Кухарь Н. Ю., Овсянникова А. В. Инновации в системе управления бизнес-процессами // Инновации в науке: пути развития: сборник материалов междунар. науч.-пракг. конф. Чебоксары: АУ ЧР ДПО
УМЦ
, 2012. с. 538–542. - Деминг Э. Выход из кризиса: Новая парадигма управления людьми, системами, процессами. М.: Альпина Паблишер, 2016. – c. 417
- Хаммер М., Чампи Дж. Реинжиниринг корпорации. Манифест революции в бизнесе. М.: Манн, Иванов и Фербер, 2011. – с. 288 [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://pqm-online.com/... – Загл. с экрана.
- Charan Я., Colvin G. Why CEO’s Fail // FORTUNE Magazine. 21.06.1999. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://thebeacongroup.ca/... – Загл. с экрана.
- March J. Exploration and exploitation in organizational learning // Organizational Science. 1991. № 1 (2). – P. 71–86.
- ISO 9001:2015
Системы менеджмента качества. Требования
. - Ефимов В. В. Процессы и процессно-ориентированный подход [Текст]: учеб. пособие для вузов./ Ефимов В. В. – Ульяновск: УлГТУ, 2009. – с. 435 [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://window.edu.ru/... – Загл. с экрана.
