Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. RESEARCH METHODS
- 2. ROLLING ACCORDING TO THE LONGITUDINAL
- 3. Research results
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The increase in absolute compression during rolling in horizontal rolls of plate mills contributes to their productivity. Equipping the new thick-sheet mills with powerful stands with horizontal rolls allows the rolling process to be carried out with large absolute compressions, which leads to additional broadening of the ends [1], i.e. to additional fan-shaped broadening.
In the literature [2, 3] there is an opinion about the similarity of fan-shaped broadening with the usual broadening, and a significant factor affecting the broadening is the compression during rolling. In the production of thick sheets, usually the total extract from the slab to the sheet is well defined, and the number of passes tend to reduce to ensure high productivity of mills.
Determination of the quantitative dependence of the fan-shaped broadening of the fractional deformation will allow you to control the shape of the rolls on the plate mills, having in its composition a cage with vertical rolls, choosing a rational amount of compression side (end) faces when rolling sheets on a longitudinal or transverse scheme without intermediate edging in horizontal rolls.
Currently, little attention is paid to the study of the diversity of sheets when rolling on thick-sheet mills without splitting the width.
RESEARCH METHODS
According to the law of similarity deformable bodies must be geometrically and physically similar.
The geometric similarity is observed when the relations of the corresponding linear dimensions (length l, width b, height h) of the model (index "M") and nature (index "H") are equal, i.e.:
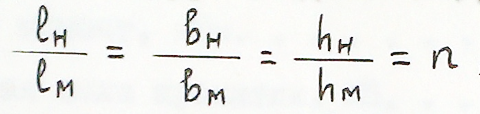
Where (n) is the scale of modeling.
The choice of the scale of simulation (n) is due to the capabilities of the laboratory mill and the requirements for the accuracy of the experiment, therefore n =1:10 was chosen.
In our work, pure technical lead was used as a material for experiments at room temperature. The choice of lead for modeling hot rolling of steel is explained by the fact that lead is known to recrystallize at room temperature and the processes of its hardening and softening occur, similar to the processes of hardening and softening of steel during hot deformation. And the strength and plastic characteristics () of lead in the cold state approximately correspond to the strength and plastic characteristics of steel for hot rolling.
The samples, cast lead slabs, were subjected to preliminary deformation in horizontal rolls with a relative compression of 10%, after which they were milled.
Brief technical characteristics of the laboratory mill 340:
Rolling of lead samples was carried out at the laboratory mill 340, consisting of a four-roll horizontal stand and a stand with vertical rolls.
Technical characteristics of the mill:
Diameter of working rolls, mm..................110,
Diameter of support rolls, mm..................250,
Diameter of vertical rolls, mm..........100,
The type and power of motor, kW ДП72......67,
Torque, kNm.........................3.7 V,
Permissible rolling force, MN..............4.5.
ROLLING ACCORDING TO THE LONGITUDINAL
To control the shape of the rolled sheet on the reversing plate mill, not having in its composition of stands e of the vertical rolls is accomplished by selection of appropriate sizes of slabs and sheets, as well as broach before the breakdown of the width. However, it is not always possible to find a rational dimensions of the plates and slabs, which would have provided sheets of rectangular shape. Therefore, the problem of controlling the shape of the rolls on the reversible plate mills is relevant there is very little information about the impact of fractional deformation on the heterogeneity of the sheets, rolled but longitudinal IDN on the transverse schemes. According to, the number of passes at each stage of rolling thick sheets has a significant impact on the diversity of sheets. However, the conclusions made in this work are somewhat contrary to the results of our research, which requires additional experiments.
Sheets rolled along a longitudinal scheme in three stages have either extended or narrowed ends depending on the ratio of the extracts at the rolling stages (μ 1 , μ 2 ,μ 3 ). Therefore, for sheets with narrowed ends, you need to find activities that contribute to the expansion of their ends, and for sheets with extended ends – on the contrary.
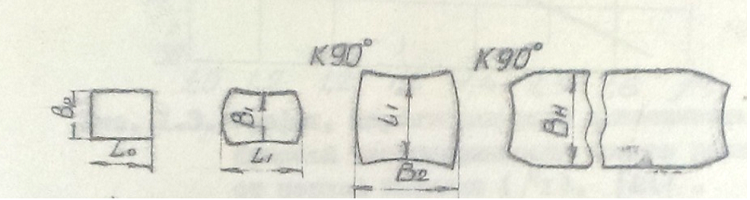
Figure 1 - The forming of the sheet during rolling by the longitudinal scheme
Research results
To study the effect of fractional deformation on the shape of the peals, samples were made-models of slabs of four sizes, 3 samples for each size. Rolling of samples was carried out in cylindrical rolls with the same total extraction, but for a different number of passes. (Table 1)

The results of the experiment built curves raznoshennoy (δ k ) and lengths of the ends of the rolls (Lк) from the hood and medium compression Fig. 2 and 3.

Figure 2-influence of strain fraction on sheet width(the numbers on the curve - group number of samples)

Figure 3-the Dependence of the length of the ends of the peals on the fractional deformation
The curves of the dependence of the average diversity of sheets are well described by the equation of parabolic type.
The effect of the average compression per pass on the diversity of sheets can be represented as:
- for laboratory conditions:




