Abstract
Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. The content of foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise
- 2. Internal and external environmental factors affecting the foreign economic activity of industrial enterprises
- 3. Methods of assessing the effectiveness of foreign economic activity of industrial enterprises
- 4. Methods of improving the efficiency of foreign economic activity of metallurgical enterprises
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Metallurgical industry is a key in any developed country of the world, as for the vast number of areas of the real economy metal is necessary as a raw product. It is the products of metallurgy that is one of the main types of goods in international exchange due to globalization. Globalization of the world economy is the integration of national economies into the world economy, which cultivates the development of foreign economic activity (FEA) on this basis. Participation in foreign trade opens up domestic markets for foreign competitors, but on the other hand – increases the prospects of domestic enterprises in the world markets. The liberalization of foreign economic activity aggravates the conditions of competition for enterprises and forces them to improve their activities in the new conditions both in the domestic and foreign markets. These circumstances require new scientific proposals to improve the competitiveness of national industrial enterprises and methods of foreign economic activity. This direction still remains. Moreover, the conditions of foreign economic activity of enterprises are constantly changing. The study, analysis and generalization of the theoretical foundations of the macro–environment of the enterprise and its impact on foreign economic activity (FEA) of economic entities, is an important scientific and practical problem for industrial enterprises and confirms the relevance of the chosen topic of study. The subject of the study is the organizational and methodological basis of the macro environment of economic entities involved in foreign economic activity.
The object of the study are industrial enterprises engaged in foreign trade. The purpose of this work is to substantiate the theoretical foundations of the development of foreign economic activity of the metallurgical industry. To achieve this goal, the following tasks are set:
- to study the essence of foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise;
- analyze the mechanism of influence of the external and internal environment of the enterprise on its activities;
- to clarify the method of formation of the mechanism of monitoring and analysis of macro–environment factors in the foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise;
- identify measures of state support for enterprises conducting foreign trade in difficult macroeconomic conditions..
Industrial enterprise as a subject of foreign trade, under the influence of the macro environment, is studied in the works of I. O. Degtyareva, E. A. Ivanova, E. A. Barchinoi, Sarkisova, L. E. Ostrovskogo etc. Theoretical aspect of the studied V. A. Slepov, S. K. Kazantseva, division of the external environment on factors Chechevitsyna A. N. , Faminsky I. P. , Ignatov V. G., Alebastrova L. N. , the practical aspect was analyzed Chuev I. N.
1. The content of foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise
Foreign economic activity (FEA) is related to the market field of activity, is based on the criteria of Commerce, is closely related to the industry and is distinguished by legal independence and economic, as well as legal independence from sectoral departmental care [1]. Not only enterprises, but also States are participants of foreign economic activity. The role of the state in foreign economic activity is to develop legal, trade and political mechanisms that foster the development of foreign economic relations and increase their efficiency. Pragmatic state foreign economic policy leads to an increase in the growth rate of national income, the efficiency of capital investment in foreign economic activity, the development of scientific and technological progress, the revival of the investment climate. Direct participation in foreign economic activity of the enterprise is realized through the conclusion of contracts with foreign partners and, accordingly, executing them. The development of foreign trade enterprises contributes to the efficiency of the real economy of the country. An enterprise is an economic entity that produces works, provides services and sells goods using its economic resources. The sphere of economic activity of the enterprise, which is associated with international commercial, industrial integration and cooperation, export and import of goods and services, with access to the foreign market, is called foreign economic activity. FEA is, as a rule, an integral part of the overall work of Russian enterprises. Development of foreign economic activity gives new opportunities to the enterprise. Such as the use of not one but several markets for the sale of goods of own production or the acquisition of the necessary equipment and technologies.
FEA of an industrial enterprise is a production and economic activity that is associated with the movement of goods, technologies, capital across the state border. Countries are included in international trade, specializing in certain services and goods for the following reasons:
- There is no country on Earth that is able to produce absolutely everything that its consumers need.
- Lack or lack of necessary resources in their own country.
In the international division of labour, countries specialize in a number of factors. This is facilitated by differences not only in climatic conditions, but also in the provision of natural, productive resources: labor, management, investment, and it is also important to combine these conditions that the country has. All these differences lead to the fact that the production of such goods is cheaper in some countries and more expensive in others. The demand for certain goods depends, among other things, on the traditions and habits of the population, which also makes adjustments to the prices of the same goods in different countries. FEA of the enterprise is carried out on a currency basis, in contrast to internal economic activity, and is regulated by special measures of the state. The foreign economic activity of the enterprise is greatly influenced by the stability of the national economy and the level of its development, the legal norms of its own country and the countries in which foreign trade is carried out, the differences in world prices. The company itself determines the type of its activity, sets tasks and seeks solutions for their implementation. Economic opportunities and needs of the company are a condition for choosing the legal form of its foreign economic activity.
The company carries out any kind of foreign economic activity, if they are not prohibited by law and meet the objectives set out in the Charter. One of the main components of foreign economic activity of the enterprise is foreign trade activity – it is business activity in the field of international trade and exchange of works, goods, results of intellectual activity and information. An enterprise that participates in foreign trade activities is an independent legal entity. It has the right to possess separate property, to acquire property and personal non–property rights. At the same time, it is the duty to be a plaintiff in the courts; the objectives of the enterprise should be clearly specified in its statutory documents. In addition to Russian legal entities, participants in foreign trade activities can be Russian individuals who are individual entrepreneurs, as well as foreign legal entities and individuals. Although the participants of foreign trade and foreign trade activities are independent entities, but the most important aspects of this sphere are regulated by the state. An enterprise participating in foreign trade activities enters into an international commercial transaction. This means a contract between two or more parties located in different countries. There are absolute and relative advantages of foreign trade. The ability of a country to produce any product cheaper than in other regions of the world, determine the so–called absolute advantages of this country over others. Each country has an economic priority over the others. This advantageous position gives such countries the prerogative to specialize in the production of certain types of products, and all necessary to buy abroad – in those countries where it is cheaper to make. In addition to absolute advantages, international trade is cultivated by relative advantages. This is the cost ratio that occurs in the production of the same product in different countries. That is, the cost of production of any product in one country is lower than in the production of the same product in another country. Thus, the exchange of goods allows all countries to benefit from the correct formation of the structure of imports and exports. This, as well as the following factors, is the reason for the expansion of foreign trade exchange [2]:
- acquisition of the necessary raw materials, components, new technologies in the foreign trade market;
- attraction of engineering, production and other services for the needs of the economy, taking into account their originality, better quality and lower prices compared to the domestic market;
- attraction of foreign investments for expansion or modernization of production, improvement of export potential and increase of competitiveness in foreign markets;
- participation in the international division of labor, specialization and cooperation of production in order to increase the opportunities of the domestic economy;
- interdependence of barter trade in terms of quality, price and opportunities for expansion of production;
- instability of the political and economic situation in the state associated with the deterioration of the investment climate, the deterioration of economic growth);
- increased competition from foreign companies operating in the domestic market;
- the possibility of hedging the risk of loss of income due to increased competition in the domestic market and the prospect of conquering foreign markets;
- search for economic resources that are not available in their own country;
- search for the most favorable infrastructure and climatic conditions for the implementation of its activities;
- possibility to increase profits from more efficient use of production facilities;
- possibility to use know–how in the framework of activities with foreign partners;
- increase in demand due to potential foreign customers;
- the possibility of using cheaper external resources, diversification of sources of supply.
- political factors in foreign trade. In foreign trade, economic benefits are often inferior to political factors;
- the opportunity to export their capital abroad, followed a more favorable it investment;
- the possibility of importing foreign capital into the country, which contributes to the organization of the necessary and competitive production.
All of the above is a catalyst for foreign trade. But, in addition, foreign trade is one of the drivers of improving the living standards of the population. Foreign trade activity of the enterprise distinguishes as the main, mainly, transactions on barter goods in material form (commercial export and import). A foreign trade contract is a legal form of a foreign trade transaction. A vast area of foreign economic relations are counter–transactions (Approx. And.) The more extensive and diverse the list of forms and types of foreign trade enterprises, the more effective and useful are the external relations of States as such. This will solve the following problems:
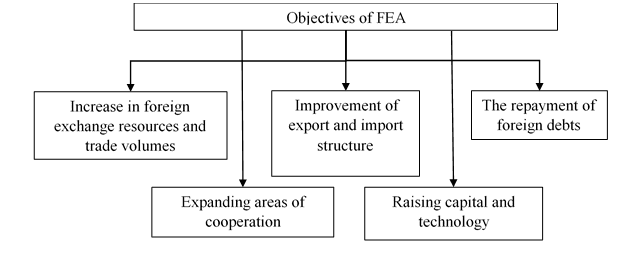
Fig. 1.1 — Tasks to be solved in the conduct of foreign trade
However, a review of the economic literature revealed that today there is no clear definition of the category of foreign economic activity. A comparative analysis of approaches to the definition of the category "FEA" at different levels is presented in the table (Annex. Bel.) The concept of FEA presented by Kirillov is the most interesting. Not only as a result of joint activities and partnerships between the two countries, foreign economic relations are created. At the same time, the summation of relations between such concepts as foreign trade, foreign economic relations and foreign economic relations is carried out. At the same time, foreign economic activity will be considered as a demonstration of established foreign economic relations, on the basis of the formation of many foreign economic relations [3].
To more fully characterize today's FEA as the very essence, it is possible to introduce separate components of the concept (or objects, if the whole concept is considered as a subject) into this definition. And then, using the features and criteria that distinguish the features of the functioning of each of the constituent entities, to give an integrated formulation. As a result, it is possible to give the following concept "FEA" (mainly from the position of the enterprise) – is part of its functions, indicating through a set of production and economic, organizational, economic and operational and commercial actions, according to the foreign economic relations of the state, combined with the activities of the business entity in foreign economic transactions, the purpose, nature and means of which are synthesized, according to the production technology, in accordance with the goals and objectives for its functioning and development [3]. In General, foreign trade of any enterprise is rational to consider as an expression of established foreign economic relations, due to the formation and development of foreign economic relations. In the current circumstances, the management of foreign trade is one of the types of economic activities of the state (enterprises, institutions), strongly associated with the export and import of goods, works and services, foreign loans and investments, the implementation of common projects with the business community of other States, including the field of socio–cultural programs. In the course of foreign economic activity, enterprises apply foreign trade prices. Prices are grouped on the basis of the applications: the rates of the unified country, or waist of the regional (regional, local). There are some features of the use of prices used in foreign trade.
Foreign trade prices are based on the prices of the world's leading trade markets. For exported goods in the country entered the special prices for export. Sometimes, when setting for export, for some scarce goods, customs duty is added to the prices. In some cases, imported consumer goods are subject to free retail prices, based on the ratio of supply and demand. In everyday foreign trade practiced many types of prices, depending on the variety of features of transactions of sale. Prices, when signing contracts, are negotiated by contractors and formed under the influence of the world, however, may differ from them. The reference price is set at the proposal of the seller (offer) and may change during negotiations or during the performance of the contract. Export prices mainly increase relative to domestic prices at the expense of additional costs (see Fig. 1.2):
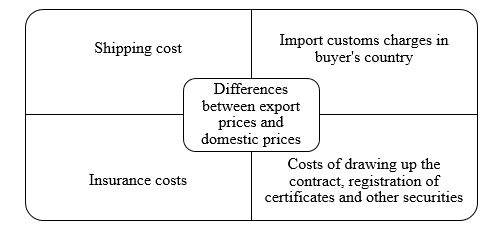
Fig. 1.2 — Costs included in the export price
In foreign trade there are two kinds of prices: the estimated installed individually exporters of certain manufactured goods; the published prices – prices that are distributed in the company and additional sources. When performing foreign economic operations related to the sale of goods, the participants of foreign economic activity sometimes face a number of uncertainties due to the different interpretation of the contractors of mutual rights and obligations, namely: the delivery of products from the place of departure to the destination. This may relate to differences in rules and customs around the world. To find a consensus in such circumstances is possible only by the use of counterparties of a single package of international rules for unambiguous interpretation of terms used in foreign trade. To this end, in 1936, the first edition of the international rules for the clarification of trade terms (edition Incoterms–1936) of The international chamber of Commerce was published. These rules are periodically amended and supplemented and published By the international chamber of Commerce (1953, 1967, 1976, 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010 years).
The use of these rules in foreign economic contracts (contracts), when agreeing on the terms of delivery of goods, makes it possible to avoid differences in the interpretation of contractors of their obligations in the delivery of goods from the seller to the buyer. The rules clearly define the obligations of the seller to deliver the goods to the specified place and set the time of transfer of the risk of accidental loss or damage to the goods. Incoterms rules apply only to the relationship between the seller and the buyer in the framework of contracts of sale (Approx. C) [4]. To carry out an export transaction, the manufacturer of the goods needs to perform a certain sequence of actions (see Fig.1.3) [5]:
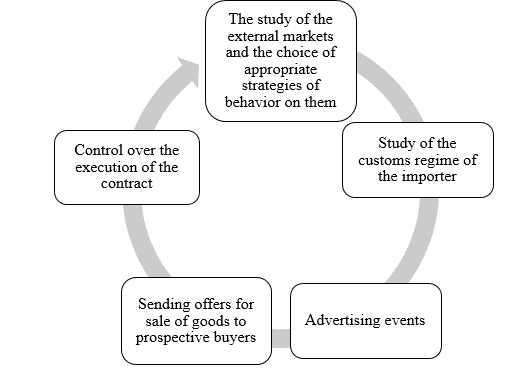
Fig. 1.3 — Stages of implementation of export transactions
Therefore, foreign trade requires some necessary marketing and management operations. The mechanism of foreign economic activity of each enterprise operates in this particular for the individual enterprise institutional and legal framework, which is formed by the national legislation of the countries, international standards, General and for various spheres of international relations, the statutes of international organizations and associations, etc. Therefore, the structure of the mechanism regulating the activities of the enterprise at the international level can be considered as a set of its foreign economic policy and a system of levers (instruments) of influence on the practical implementation of this policy [6]. FEA enterprises–is part of their overall activities, designated as a set of production and economic, organizational, economic and operational and commercial functions of the enterprise in accordance with the foreign economic relations of the state, contributing to the entry of the enterprise to the foreign market and participation in foreign economic operations, directions, forms and methods, which are summarized in accordance with the production process for the purposes and objectives of the enterprise, its functioning and development. The improvement of foreign economic activity opens up additional resources, for example, the exploitation of the potential of international cooperation of production, independence in the implementation of their corporate plans.
2.Internal and external environmental factors affecting the foreign economic activity of industrial enterprises
The meaning of the production activity of each enterprise is to acquire economic (material) interest. At the same time, the desire to obtain the maximum result is limitless. However, any company always has a restrictive framework in the possibility of using the necessary resources (material, labor, financial, etc.) for one reason or another. One of the main tasks of the company's management is the resolution of this contradiction. And in this foreign trade enterprises is not so bad. The influence of internal and external factors is paramount [7]. Every enterprise exists and operates in a particular environment, and the environment reacts accordingly to any of its actions. There are no separate enterprises from the outside world. The company exists only through interaction with the outside world, i.e. with the external environment. There is always a mutually beneficial relationship between the enterprise and the external environment. Because only through such interactions, the company can replenish the necessary production resources and sell their goods. At the same time, environmental factors are not controlled by the company and its services.
Issues of grouping factors have been studied by many scientists. For example, faminsky I. P., Ignatov V. G., Alebastrova L. N. allocated internal and external environment of the enterprise.
The external environment is factors that are beyond the competence of the organization itself, but have the ability to influence it. The external environment in which the organization resides is not in a static position, constantly changing. Changing taxes and laws, the ruble, changing consumer tastes and the very structure of markets, fashion dictates its terms. The ability of the organization to respond to all these challenges and to respond competently to the actions of the external environment is one of the main guarantees of its success. The influence of external factors on the foreign economic activity of the enterprise has an even more significant effect. For example, traders are faced with additional factors related to activities in other countries and, accordingly, in other conditions. In this regard, the following groups of factors are distinguished: economic, political, socio–cultural, technological. The structure of the external environment is shown in Fig. 2.1 [8].
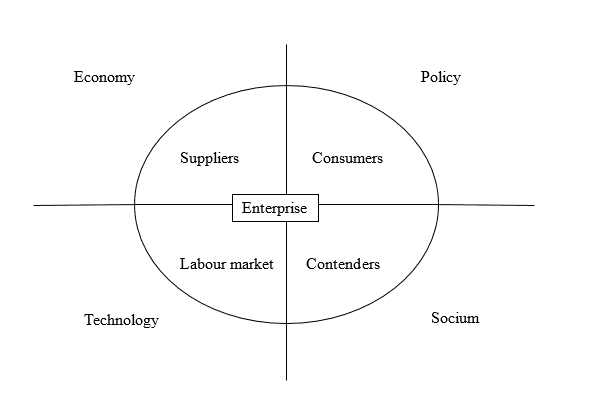
Fig. 2.1 — Structure of environmental factors of the organization.
Chuev I. N. he supported the generally accepted grouping of factors, but divided them into two groups: direct impact and indirect impact and brought his concept of the external environment of the enterprise. Its wording is as follows. The external environment of the enterprise is all the factors and conditions that are formed regardless of the existence of the enterprise and have a significant impact on it. Environmental factors many economists divide into two groups – micro and macro, or direct and indirect effects. Factors of microenvironment or direct impact are those factors that can have a direct impact on the work of the enterprise, they constantly interact with the enterprise: suppliers of resources, consumers, competitors, labor resources, the state, trade unions, shareholders (if the enterprise is a joint stock company). Factors of indirect influence do not have a direct effect on the work of the enterprise, but the need to take them into account is the correct development of the strategy of the enterprise itself [9]. The most important indirect factors:
- political and legal factors. Various legislative and governmental factors that can make significant adjustments to the opportunities and threats to the organization's activities. When analyzing the external environment, there is the greatest influence of such factors as: adjustments in tax policy, the relationship of business representatives with the government; the balance of political forces; patent law; environmental legislation; the state budget; antitrust laws; monetary policy, etc. This also includes factors of intergovernmental relations. For example, economic sanctions. The same group includes factors of the world economy. Such as WTO, Eurasian Union, etc.
- economic factors – rates of inflation or deflation, employment of labour, international balance of payments, interest and tax rates, size and dynamics of gross domestic product, labour productivity, etc.as a rule, the change or stability of some of these indicators have the opposite effect on different enterprises: for one group of enterprises it may pose an economic threat, and for another–new prospects. For example, a decrease in purchase prices for products of the metallurgical industry is perceived as a threat for metallurgists, and for Metalworking enterprises as a benefit [10];
- social and cultural factors influence the way and priorities in our life, work, consumption and have a great influence on all enterprises and organizations. The most significant socio–cultural factors affecting the activities of the enterprise are: birth rate; mortality; migration; life expectancy; disposable income; lifestyle; level of education; demand; attitude to work; attitude to rest; population's reaction to the quality of goods and services, population's demand for quality of life; customs and traditions existing in society; value priority; national mentality, etc.;
- technological factors are the scientific and technical direction of the external market development. These factors play one of the most important roles in the development of society and are the main sources of productive and social progress. The impact of technological innovations on the enterprise is manifested in its desire to get ahead of competitors through the operational application of R & d achievements. Revolutionary technological changes, discoveries, for example, the introduction of mobile phones, computers, the Internet, new modes of transport, etc.into everyday life, represent a great potential and, accordingly. serious threats to Laggards, the impact of which managers should be aware of and assess [11].
Regarding the participants of foreign trade, there are factors that limit the implementation of foreign economic activity of enterprises:
.gif)
Fig. 2.2 — impediments to foreign trade
The complexity of the analysis of the external environment of the enterprise is especially its factors. Analysis of the external environment of the enterprise is complicated by the fact that the main characteristics of environmental factors are their uncertainty, complexity, mobility, and their interdependence. Thanks to the improvement of infrastructure, as well as the intensive development of technologies, the external environment of enterprises exposes it to an increasing impact, which requires management to significantly increase the speed and depth of the analysis of the external environment, and adjust its own strategy, in accordance with the increasing threats from the external environment. Under the influence of events occurring outside the enterprise, in the external environment, managers have to change the structure of the internal environment, adapting it to the changed conditions. The internal environment of the enterprise is part of the overall environment that is located within the organization. It has a constant and direct impact on the life of the enterprise [12].
The internal environment forms the technological and managerial climate of the enterprise and is a product of management work. The analysis of the internal environment is necessary and carried out to detect strong and weak links in the work of the enterprise in order to correct and strengthen weaknesses in time and, at the necessary moment, to use external conditions to acquire additional advantages over competitors. In addition, it is necessary to identify in time the weak links that can not withstand external influences and increase the threat to the enterprise. The internal environment of the enterprise consists of such parts as: production, Finance, marketing, personnel management, organizational design. The need to analyze the internal environment can be explained by the following arguments:
- the user must know about the strengths and weaknesses of potential of the enterprise in the competitive struggle for markets, and this requires information on the status of the internal environment;
- analysis of the internal environment makes it possible to formulate more clearly the tactical objectives and strategic goals of the organization [13].
The main segments of the internal environment of the enterprise are:
- production (in foreign interpretation – operations management): structure, volume, productivity; product range; supply of raw materials and materials, degree of stocks, speed of their consumption; availability of equipment and its degree of operation, unused capacity; environmental technologies; quality supervision; patents, branding, etc.;
- personnel: number of employees, professionalism, productivity, staff turnover, labor costs, interests and requests of employees;
- management organization: administrative model, management methodology, management level, work capacity and interests of top management, qualification, reputation and status of the enterprise [14];
- marketing, which includes all operations related to production and sales planning, including: product range, market share, distribution and sales channels, marketing budget and its execution, marketing plans and programs, sales promotion, advertising, pricing;
- Finance – the most truthful source, which reflects all the business activity of the enterprise. Financial analysis makes it possible to identify, understand and evaluate the aspect of difficulties at the qualitative and quantitative level;
- culture and image of the enterprise – create an image of the enterprise; good reputation of the enterprise allows to attract highly skilled workers, to stimulate consumers to purchase goods, etc. [15].
Management is obliged to properly dispose of its own resources of the enterprise, professionally manage the process of production, sales, etc., that is, all segments of the internal environment. In order to manage all these capacities productively, it is necessary to learn not only to identify the effects of multiple factors on production efficiency, but also to anticipate and manage them. There are several options for the classification of environmental factors. One of them involves combining them through some common features – such as the presence of common goals, modification of resources, the correlation of the organization with the external environment and so on. Chechevitsyna A. N. decided to group the factors of the internal environment in the following way
Table 2.1–Grouping of internal environment factors of the organization
| Classification criterion | Name of factor |
| 1. Having common goals | Goals, shared values |
| 2. Resource conversion | Personnel, technology, financial system, information system, business processes |
| 3. Dependence of the organization on the external environment | Style of organization, strategy |
| 4. Division of labour | Personnel skills, tasks |
| 5. Unit formation | Structure |
| 6. Need and existence of a governing body | Authority |
| 7. Other | Organization culture |
Table 2.1 concludes that this approach focuses mainly on one criterion – the transformation of resources. This is due to the fact that the enterprise is created to convert resources into the final result [16]. In addition to this classification, you can apply the fragmentation of factors into objective and subjective. A number of objective factors of the internal environment include: structure, goals, objectives, technology, financial system, information system, strategy, business processes, as well as personnel, etc. A number of subjective factors determined by the characteristics and relationships of people in the organization: shared values, organizational style, staff skills, power, culture of the organization, etc.In addition, assessing the organization as a transforming system, all factors can be divided into three groups: input (resources); output (results); transformation process (production) [17]. There are other classifications of internal factors. It should be understood that in management internal variables should always be investigated only in the relationship. All internal factors are interdependent and affect each other. As a result, we see that the financial success of the company is formed under the influence of a huge number of factors, both external and internal. External factors are not controlled by the organization, but the management should have the ability to diagnose the transformation of the external environment and professionally adapt the internal resources of the enterprise to external changes. Therefore, in order to effectively respond to all changes in the external environment, it is necessary to continuously monitor, analyze, make forecasts and develop the necessary decisions. The main problem in the analysis of the environment – the variety of factors of its components, as well as many variations of each factor. For constant control of the external environment, analysis and forecast of possible scenarios, it is necessary to form a special monitoring and analytical structure at the enterprise.
3. Methods of assessing the effectiveness of foreign economic activity of industrial enterprises
In defining economic efficiency, economists tend to see two distinct differences in the "cost" and "resource" approaches to efficiency. However, the designation of its essence in their works, almost identical. Such an interpretation of the concept of efficiency is available in the studies of foreign authors. K. R. McConnell and S. L. BRU in "Economics" gave the following definition of production efficiency: "we want to get the maximum return with a minimum of costs from the available limited production resources" [18, p. 23.].
For both economic science and practical use, it is necessary to be able to calculate efficiency. Therefore, there are questions about the criteria and indicators of economic efficiency. "Criterion" is a Greek word, in the dictionary of S. I. Ozhegov it is defined as a measure of evaluation, judgment. Enterprises engaged in foreign trade, it is necessary to adjust the methods of assessing the results, due to the following reasons:
- Costs are recorded in the national currency, while the result–in the currency of other States;
- if the company carries out several types of activities, it is necessary to develop methods for calculating costs;
- higher probability of risk, which in turn causes additional costs associated with insurance of its activities;
- the implementation of state regulation of foreign trade activities, first of all tariff methods;
- the peculiarities of the various types of FEA [19].
A special place is taken by the assessment of the effectiveness of foreign trade, The entire system of indicators is usually divided into two categories:
- Effect measures, which are defined as the modulus of the difference between results and costs, expressed in the appropriate monetary units.
- Performance indicators, which are determined by the ratio of the value of the results to the value of costs and are specified in relative units.
When calculating indicators, it is necessary to withstand the following conditions:
- the principle of thorough accounting of all components of costs and results. It is necessary to fully reflect all the results of activities to monitor the productivity of decisions;
- the principle of comparison with the basic version. To assess the effectiveness of the need to determine the basis of comparison of the result;
- the principle of bringing costs and results in a comparable form. The indicators to be compared should be comparable;
- the principle of guidance costs and results occurring at different times, at the same time. Compliance with this principle is one of the most fundamental provisions of the theory of efficiency evaluation [19].
Economic efficiency of exports. This indicator of the economic effect of the export operation is calculated as follows:
.png)
Where ЭЭэкс — the economic effect of exports, RUB.;
О вф — foreign exchange earnings of the enterprise, RUB;
В р — ruble revenue from the mandatory sale of part of the currency to the state, RUB
Зэкс — the company's costs associated with exports, RUB.
.png)
Where Зэкс — indicator of economic efficiency of export, RUB. / RUB.
In its content, this indicator is identical to the concept of profit. The indicator of economic efficiency of export is calculated:
From an economic point of view, the indicator of efficiency is profitability, i.e. the result that we have for each ruble of costs. A necessary condition is the excess of this indicator 1. In order to make a more objective decision on the export of products, the export efficiency index of the Ээкс is compared with the efficiency indicator of production and sales of products in the domestic market of Эви:
.png)
Where Зви — indicator of efficiency of production and sales of products in the domestic market, RUB. / RUB. ;
О экс — the volume of exports in domestic prices, RUB.;
Сп.экс. — production cost of export goods;
Зр.вн. — costs for the sale of export products within the country, RUB.
To carry out an effective export transaction it is necessary to perform the following ratio:
.png)
Economic efficiency of imports. There are several types of imports: for own consumption or for sale in the domestic market. The economic effect of imports on domestic consumption of imported products is calculated:
.png)
Where ЭЭисп — indicator of economic effect of imports of products for own use, RUB.;
Зи — total costs for the purchase and use of alternative imported products, RUB.;
.png)
Where ЦПп.в. — purchase price (manufacturing costs), RUB.;
Эр.в. — operating costs for the entire period of use of products, RUB.;
ЦПимп — the price of consumption of imported products (costs for the entire period of use of imported products), RUB.;
.png)
Where Цп.и. — costs associated with the acquisition of goods in the foreign market, RUB.;
Эр.и. — operating costs for the entire period of imported products, RUB.
The economic sense of the indicator of economic effect calculated by the formula (1.1) is that it shows what profit (loss) the importer will have if he acquires imported products instead of purchasing (manufacturing) products alternative to imported ones.
If ЦПимп > Зи, it symbolizes the amount of profit (loss), which will receive the importer, if he instead of imported products will acquire (produce) products, alternative to import. The economic efficiency of imports for own use is calculated as follows:
.png)
A necessary condition for effective imports in this case is Эимп > 1. The economic meaning of this indicator – how many times more effective imported products alternative. The economic efficiency of imports for resale in the domestic market is calculated:
.png)
Where ЭЭимп — indicator of the economic effect of imports, RUB.;
Цр.и. — еhe sale price of imported goods less costs associated with the sale, RUB.;
Цп.и. — the purchase price of imported goods (costs associated with their acquisition), RUB.
The economic meaning of the indicator of the effect of imports of goods, calculated by the formula (1.9) – what profit (loss) will have the importer after the resale of imported goods. The indicator of economic efficiency of import and sale of goods in the domestic market is calculated by the formula:
.png)
The economic meaning of the indicator of efficiency of import of Eimp calculated by the formula (1.10) – how many rubles of revenue the importer receives per ruble of costs associated with imports. A necessary condition for effective imports is the ratio: Эимп > 1.
A kind of commodity exchange operation is the operation with tolling raw materials (tolling). The result for the enterprise processing foreign raw materials with payment for processing of finished products will be the cost of the finished product. Costs for the enterprise–the processor of raw materials will be the costs directly connected with processing and delivery of raw materials and sending of finished goods. In the same way it is possible to calculate indicators of economic efficiency of other forms of activity of the enterprise in the foreign market. At the same time, it is important to methodically accurately calculate the costs and results of the activities carried out in the foreign market. Participating in foreign economic activity, the company faces tough competition in the foreign market. Success in the work, in this case, can guarantee only the most advanced management methods. Successful work should be understood as a financial gain, expressed in the appropriate monetary units, for the enterprise, for the products sold, services rendered, work performed, etc. Insufficiently complete calculation of costs and results can distort the final result of evaluating the effectiveness of an action or decision.
4.Methods of improving the efficiency of foreign economic activity of metallurgical enterprises
Today, there is no uniform definition of efficiency among modern economists. L. I. Abalkin wrote that "production efficiency means nothing, like getting a certain result in the unit of the resources used" [21, p. 53]. L. E. Manelski said: "Efficiency means the efficiency, effectiveness. If you try to give the briefest description of the effective management, it is possible to present it accurately and succinctly as follows: to achieve great results at minimal cost. A prerequisite for effective management is the rapid growth of end results of production compared to cost, due to which these results are achieved" [22, p. 9].
"The term economic efficiency refers to the situation in which it is impossible to make any changes to better meet the desires of the other person, causing damage to the satisfaction of the desires of another person" [23, p. 13]. This definition is known in Economics as Pareto efficiency. Efficiency according to V. Pareto justifies the criterion of social welfare, which includes both improving the performance of the economic entity, and the search for an effective state of the market.
Improving the efficiency of foreign economic activity of the enterprise involves an increase in the volume and profitability of import or export supplies and reducing the costs of their organization. The Foundation of a successful import–export operation and the extraction of maximum profit by the company, according to the results of its execution, is a carefully developed and well–established plan for the foreign economic transaction. A reasonable model of international delivery is a series of operations or a scheme of foreign economic transaction. The basis of this plan is primarily the analysis of the foreign market, the choice of the most popular product, the choice of a foreign partner, a well–thought–out strategy for the development of relations with this partner, the optimal scheme of cargo delivery and legal customs clearance.
Trust relationships between companies arise with long–term cooperation, full understanding and openness of relations. In each case, discounts in the price of goods, deferred payment or any other preferential regime can be provided. However, the presence of a reliable partner should not be a reason to abandon the regular monitoring of other foreign markets and suppliers. Since the change of a foreign supplier is also an option to reduce the cost of supplies. To reduce the cost of delivery and insurance (a significant cost item in the export–import operations of products) it is required to develop an optimal delivery scheme, considering all possible options and get the best price from the carrier, freight forwarder and insurance company.
One of the main principles of effective foreign economic activity is a completely legal customs clearance. Probably, there are opportunities for cheaper import–export transactions, but the risks of losing time, money and cargo greatly reduce the effectiveness of such foreign economic supplies. A significant item of expenditure is the cost of the Department of foreign economic activity in the organizational and economic structure of the enterprise. It is necessary to decide whether to abolish this Department and include it in another structural unit (for example, economic Department) or there is an opportunity to transfer the organization of export–import operations of the company specializing in this activity. Now there are outsourcing companies able to maximize the efficiency of foreign economic activity. Their tasks include:
- search function for foreign suppliers or buyers;
- negotiating with potential partners;
- development of a draft international contract;
- elaboration of the optimal logistics chain of product delivery;
- selection of the optimal range of goods;
- detailing and coordination of codes of the commodity nomenclature of foreign economic activity on the range with customs authorities;
- calculation of the cost of goods for the buyer;
- preparation of the entire list of actions to be performed during the foreign economic operation;
- formation of the list of expenses and terms of payment.
Customers receive a ready–made plan for the organization of export delivery, which allows to minimize the risks of customs clearance, reduce the cost of transportation and storage of goods in stock, minimize the time of registration of permits (certificates and declarations of conformity, etc.) for exported products [24].
There are other ways to develop the efficiency of foreign economic activity of enterprises: modernization of fixed assets, improvement of production technology; investment in R & d, improving the quality criteria of manufactured products by bringing it to international standards; increase in knowledge–intensive products; trade in patents and licenses; the use of advanced methods in marketing; attracting foreign investment; the use of modern efficient forms of production, improving the skills of personnel; Association of domestic enterprises in unions.; state support and stimulation of foreign economic activity of enterprises, creation of a unified foreign economic information base by the state.
Methods of improving the efficiency of foreign trade in the foreign market, depending on the direct participants of foreign trade. However, to know what to do and implement it in life – these are two big differences. Let us consider in more detail the possibilities of Russian enterprises in improving their efficiency of foreign trade.
1. It is necessary to invest in R & d, advanced technologies that will help reduce the cost of products and improve their quality. The processes of improving the quality of intellectual resources and updating the scientific base, the formation of mechanisms for encouragement and stimulation should come to the fore. For more effective use of these resources it is necessary to use "breakthrough" innovations. In a highly competitive environment, these innovations will allow Russian enterprises to significantly expand their segment in international markets.
Fixed assets form an important component of the material and technical base of enterprises and play a huge role in the implementation of key areas of their activities. With them are associated many of the challenges of the modern Russian economy: the high moral and physical wear and tear, resulting in a lack of competitiveness, the incomplete utilization of productive capacity, increased tax burden. All these factors affect the competitiveness of products, especially when the company enters the foreign market. The implementation of these areas depends largely on the available material and technical base and the possibility of updating it. The main shortcomings of the depreciation policy of Russia are:
- small investments in fixed assets due to depreciation (20–25%). This indicates a lack of motivation of enterprises to increase their own investment resources;
- a high degree of depreciation of fixed assets of enterprises (40 – 45%) and there is a tendency to increase it;
- insufficient use of depreciation potential as an investment source. This is a consequence of the application of the linear method of depreciation calculation by the dominant majority of enterprises;
- the possibility of using accelerated depreciation methods is not considered;
- depreciation charge management system not implemented;
- there is no relationship between depreciation and financial policy of the enterprise;
- insufficient methodological guidance of the process of forming depreciation policy and determining its productivity.
In the depreciation policy of the group is present especially noticeable omissions: depreciation policy standardized for all branches of economy and regions; not due to a clear preference for businesses and prospects of application of it tools in the innovation goals, and others [25].
In the developed world, depreciation is the main source of financing for investment projects, accounting for up to 70 per cent of total investment, while commercial loans and other sources account for no more than 40 per cent. These proportions are due to the high returns to the state, which instead of a reduced tax burden on business opens up a new, more efficient source of investment for the economy and exercises enhanced control over investment processes. Accelerated depreciation of fixed assets will significantly increase the volume of investments, accelerate the pace of high–tech development of industry sectors, and generally improve the efficiency of the domestic economy. As a result, the reduction of the tax burden on business in the medium term will be compensated by the increased efficiency of the industrial sector [26].
2. In time to switch to the production of demanded products, professionally conduct market research of demand in the foreign market and, in case of favorable or unfavorable conditions, in time to develop new markets. The main role of strategic marketing–the definition of economic opportunities, ie opportunities that will unlock the potential of the enterprise with available resources. Also, the objectives of strategic marketing are: the definition of goals, the formation of a development strategy, as well as the optimal structure of the product portfolio.
3. Regularly and to the necessary extent to carry out promotions of their products and their company. Advertising in the modern world implements a binding function: it integrates four marketing participants–the enterprise itself (advertiser), an advertising Agency, an advertising object and a consumer into an integrated information and production operation. Advertising starts the process of information exchange.
4. Constantly engaged in improving the management of the enterprise. The correct choice of management strategy, which is aimed at solving the following tasks: prioritization of tasks in accordance with the chosen strategy; establishing a correspondence between the chosen strategy and the management organization (the formation of the relationship of powers, functions, rights and responsibilities; between management and ensuring their work by technical means, information).
An important factor for effective competition is the timely adjustment of the strategy when the external environment changes. This factor is formed through the use of modern methods of business process management including all stages of the product life cycle. When using the scenario method of planning, it is possible to determine the possible options for the development of market conditions. Identification and analysis of risks of each scenario allows to choose the best strategy, the implementation of which will create conditions for the formation of competitive advantages of the enterprise [27].
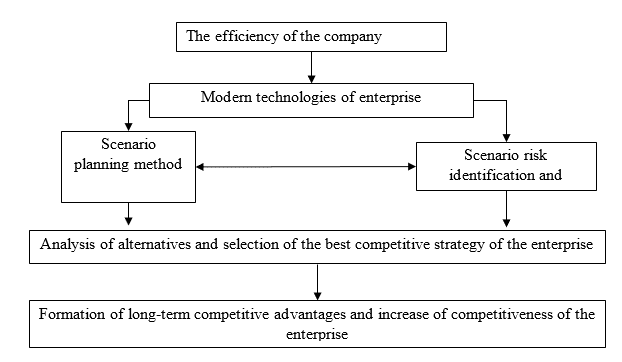
Fig. 3.1 — the Mechanism of formation of effective activity of the enterprise
5. Management of large–scale business without the use of information systems today is impossible to imagine.
E–Commerce (e – commerce) – is forcing many commercial processes, in the case of their execution electronically. At the same time, the information goes directly to the addressee, bypassing a series of unnecessary mediation services. The definition of e–Commerce includes not only the infrastructure focused on the Internet, but also the international exchange of metal trade: London metal exchange, new York "Nymex" and "Comex", etc. [28].
Today, Internet services not only contribute to the rapprochement of the seller and the buyer, but also are an effective means of reducing the costs of suppliers and consumers, as well as reduce the time of the buying and selling process and improve its quality.
Key factors of efficiency of foreign economic activity of the industrial enterprise are long–term relations with foreign consumers, understanding and satisfaction of their requirements, providing them with convenient conditions of purchase. In this way it is necessary to move to more efficient foreign economic activity. The implementation of the above measures will have a positive impact on the efficiency of export–import operations of the economic entity and the final results of its activities. Thus, it can be stated that the foreign economic activity of enterprises has the following opportunities for development:
- modernization of production facilities, application of the latest technologies in industrial enterprises;
- scientific and technical capacity building, R & d expansion and implementation of their results in the production process, software improvement and development;
- increasing the competitiveness of products, improving their quality to international standards and higher;
- increase in the number and range of science–intensive products in total production and exports;
- improving the quality and professionalism in the marketing of foreign economic activity of economic entities;
- involvement of foreign and domestic investments in production development;
- improvement of management and development of new effective technologies of management and business organization, improvement of the level of qualification of the personnel of the enterprise;
- development of state support and assistance to foreign economic activity of Russian enterprises, formation of a unified state network of foreign economic information.
The high standard and competitiveness of the goods produced by the enterprise is a guarantee of stable demand and active expansion of the range of consumers.
Conclusion
FEA of an industrial enterprise is a production and economic activity that is associated with the movement of goods, technologies, capital across the state border. Countries are included in international trade, specializing in certain services and goods for the following reasons: there is no country on Earth that is able to produce absolutely everything that its consumers need; lack or lack of necessary resources in their own country.
In the international division of labour, countries specialize in a number of factors. This is facilitated by differences not only in climatic conditions, but also in the provision of natural, productive resources: labor, management, investment, and it is also important to combine these conditions that the country has. All these differences lead to the fact that the production of such goods is cheaper in some countries and more expensive in others. In the course of foreign economic activity, enterprises apply foreign trade prices. Prices are grouped on the basis of the applications: the rates of the unified country, or waist of the regional (regional, local).
FEA enterprises–a segment of their range of activities, referred to as a set of production and economic, organizational, economic and operational and commercial functions of the enterprise in accordance with the foreign economic relations of the state, contributing to the entry of the enterprise to the foreign market and participation in foreign economic transactions, methods, forms and directions of which are summarized in accordance with the production process for the purposes and objectives of the enterprise, its functioning and development.
The external environment is factors that are beyond the competence of the organization itself, but have the ability to influence it. Environmental factors many economists divide into two groups – micro and macro, or direct and indirect effects. Factors of microenvironment or direct impact are those factors that can have a direct impact on the work of the enterprise, they constantly interact with the enterprise: suppliers of resources, consumers, competitors, labor resources, the state, trade unions, shareholders (if the enterprise is a joint stock company). Factors of indirect influence do not have a direct effect on the operation of the enterprise, but the need to take them into account is the correct development of the strategy of the enterprise, they include: political, social, economic, technological.
The internal environment forms the technological and managerial climate of the enterprise and is a product of management work, it includes the following elements: production, Finance, marketing, personnel management, organizational structure. The financial condition of the company is formed under the influence of a large number of factors, both external and internal. External factors are not controlled by the organization, but the management must recognize changes in the external environment and be able to adapt internal resources of the enterprise to them. Therefore, in order to effectively respond to all changes in the external environment, it is necessary to constantly monitor, analyze, make forecasts and develop the necessary decisions. The main problem in the analysis of the environment – the variety of factors of its components, as well as many variations of each factor. For constant control of the external environment, a special structure should be created in the organization. Conducting foreign economic activities, the company falls into the conditions of fierce international competition. In these conditions it is possible to work successfully, only applying modern methods of management. Successful work should be understood as a monetary, cost estimate of the received benefit for the enterprise: money for the delivered products, performed works and services, the cost of the received goods, works, services, etc. As a result, we see that the financial success of the company is formed under the influence of a huge number of factors, both external and internal. External factors are not controlled by the organization, but the management must recognize changes in the external environment and be able to adapt internal resources of the enterprise to them.
Therefore, in order to effectively respond to all changes in the external environment, it is necessary to constantly monitor, analyze, make forecasts and develop the necessary decisions. The main problem in the analysis of the environment – the variety of factors of its components, as well as many variations of each factor. For constant control of the external environment, a special structure should be created in the organization. For both economic science and practical use, it is necessary to be able to calculate efficiency. Therefore, there are questions about the criteria and indicators of economic efficiency. A special place is taken by the assessment of the effectiveness of foreign trade, The entire system of indicators is usually divided into two categories:
1. Effect measures, which are defined as the modulus of the difference between results and costs, expressed in the appropriate monetary units.
2. Performance indicators, which are determined by the ratio of the value of the results to the value of costs and are specified in relative units.
When calculating indicators, it is necessary to withstand the following conditions:
- the principle of comparison with the basic version. To assess the effectiveness of the need to determine the basis of comparison of the result;
- the principle of bringing costs and results in a comparable form. The indicators to be compared should be comparable;
- the principle of guidance costs and results occurring at different times, at the same time. Compliance with this principle – one of the most fundamental provisions of the theory of performance evaluation.
Improving the efficiency of foreign economic activity of the enterprise involves an increase in the volume and profitability of import or export supplies and reducing the costs of their organization. The basis of success of import and export deliveries and profit maximization of the company is correctly organized and in detail worked out scheme of implementation of the foreign economic transaction. One of the main principles of effective foreign economic activity is fully legal customs clearance. Probably, there are opportunities for cheaper import–export transactions, but the risks of losing time, money and cargo greatly reduce the effectiveness of such foreign economic supplies. A significant item of expenditure is the cost of the Department of foreign economic activity in the organizational and economic structure of the enterprise. Now there are outsourcing companies able to maximize the efficiency of foreign economic activity.
There are other ways of improving the efficiency of foreign economic activity of enterprises: renewal of assets, modernization of production technology; investments in research and development, increasing the level of product quality by bringing it to international standards; increase of science–intensive products; trade of patents and licenses; the application of advanced methods in marketing; attracting foreign investments; application of modern and effective forms of organization of production, high qualification of the personnel; the merger of domestic enterprises in the unions; state support and stimulation of foreign economic activity of enterprises, creation of a unified foreign economic information base by the state. Fixed assets form an important component of the material and technical base of enterprises and play a huge role in the implementation of key areas of their activities. With them are associated many of the challenges of the modern Russian economy: the high moral and physical wear and tear, resulting in a lack of competitiveness, the incomplete utilization of productive capacity, increased tax burden.
Accelerated depreciation of fixed assets will significantly increase the volume of investments, accelerate the pace of high–tech development of industry sectors, and generally improve the efficiency of the domestic economy. As a result, the reduction of the tax burden on business in the medium term will be compensated by the increased efficiency of the industrial sector Today, Internet services not only contribute to the rapprochement of the seller and the buyer, but also are an effective means of reducing the costs of suppliers and consumers, as well as reduce the time of the buying and selling process and improve its quality. Thus, it can be stated that the foreign economic activity of enterprises has the following opportunities for development:
- modernization of production facilities, application of the latest technologies in industrial enterprises;
- scientific and technical capacity building, R & d expansion and implementation of their results in the production process, software improvement and development;
- increasing the competitiveness of products, improving their quality to international standards and higher;
- increase in the number and range of science–intensive products in total production and exports;
- improving the quality and professionalism in the marketing of foreign economic activity of economic entities;
- involvement of foreign and domestic investments in production development;
- improvement of management and development of new effective technologies of management and business organization, improvement of the level of qualification of the personnel of the enterprise;
- development of state support and assistance to foreign economic activity of Russian enterprises, formation of a unified state network of foreign economic information.
The high standard and competitiveness of the goods produced by the enterprise is a guarantee of stable demand and active expansion of the range of consumers.
References
- Попов С. Внешнеэкономическая деятельность фирмы. Москва. — 2002. — 397 с.
- Стровский Л.Е. Внешний рынок и предприятие. — М.: Финансы и статистика, 2003. — 310 с.
- Современные подходы к дефиниции «внешнеэкономическая деятельность» [Электронный ресурс] — economy.nayka.com.ua›?op=1&z=4902
- Условия поставки (Инкотермс) [Электронный ресурс] — https://www.qdpro.com.ua/catalogue/15020000
- Дегтярева О.И., Полянова Т.Н., Саркисов С.В. Внешнеэкономическая деятельность. Издательство: Дело, 2004. — 32 с.
- Механизм внешнеэкономической деятельности предприятия [Электронный ресурс] — https://studopedia.ru/1_86083_mehanizm-vneshneekonomicheskoy-deyatelnosti-predpriyatiya.html
- Внешнеэкономическая среда и ее влияние на функционирование предприятия [Электронный ресурс] — https://mirznanii.com/a/169853/vneshneekonomicheskaya-sreda-i-ee-vliyanie-na-funktsionirovanie-predpriyatiya
- Внешние и внутренние факторы, влияющие на финансово-экономическое состояние предприятия [Электронный ресурс] — https://studfiles.net/preview/4169061/page:17/
- Внешняя и внутренняя среда предприятия [Электронный ресурс] — http://pepelontyfera.ru/vneshnyaya-i-vnutrennyaya-sreda-predpriyat/
- Анализ стратегических факторов внешней среды организации [Электронный ресурс] — http://works.doklad.ru/view/PgEJOgeAx9g.html
- Международные отношения: Внешнеэкономическая деятельность «НЛМК» [Электронный ресурс] — https://uchil.net/?cm=57958
- Факторы и механизм влияния макросреды на внешнеэкономическую деятельность промышленного предприятия [Электронный ресурс] — http://www.dslib.net/economika-xoziajstva/faktory-i-mehanizm-vlijanija-makrosredy-na-vneshnejekonomicheskuju-dejatelnost.html
- Факторы влияния на развитие внешнеэкономической деятельности предприятий [Электронный ресурс] — https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/faktory-vliyaniya-na-razvitie-vneshneekonomicheskoy-deyatelnosti-predpriyatiy
- Факторы влияния на развитие внешнеэкономической деятельности предприятий [Электронный ресурс] — https://cyberpedia.su/1x3fa5.html
- Основы внешнеэкономических знаний / Под. ред. И.П. Фаминского. — М.: Международные отношения, 2001. — 278 с.
- Внутренняя среда организации и организационная культура как важная ее составляющая [Электронный ресурс] — http://sdamzavas.net/1-33948.html
- Внутренняя и внешняя среда организации [Электронный ресурс] — http://gendocs.ru/v7509/%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8_%D0%BF%D0%BE_%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B8
- Макконелл, К.Р. Экономикс: принципы, проблемы и политика: в 2 т.: пер. с англ. / К.Р. Макконелл, С.Л. Брю. — 11-е изд. — М.: Республика, 1992. — Т. 1. — 399 с.
- Оценка эффективности внешнеэкономической деятельности предприятия [Электронный ресурс] — http://lectmania.ru/2x2bb7.html
- Анализ внешнеэкономической деятельности [Электронный ресурс] — https://studme.org/1280052810449/ekonomika/analiz_vneshneekonomicheskoy_deyatelnosti
- Абалкин, Л.И. Конечные народнохозяйственные результаты: сущность, показатели, пути повышения / Л.И. Абалкин. — М.: Политиздат, 1982. — 278 с.
- Кунельский, Л.Э. Как ускорить рост эффективности / Л.Э. Кунельский. — М.: Политиздат, 1988. — 223 с.
- Доллан, Э.Дж. Микроэкономика / Э.Дж. Доллан, Д.Е. Линдсей: пер. с англ. В. Лукашевича [и др.]; под общей ред. Б. Лисовика и В. Лукашевича. — СПб., 1994. — 498 с.
- Краткий внешнеэкономический словарь-справочник / под ред. В.Е. Рыбалкина. - [2-е изд., перераб. и доп.]. — М.: Международные отношения, 1991. — 256 с.
- Сравнительный анализ амортизационной политики зарубежных стран и России [Электронный ресурс] — https://vuzlit.ru/639850/sravnitelnyy_analiz_amortizatsionnoy_politiki_zarubezhnyh_stran_rossii
- Направления совершенствования амортизационной политики в России [Электронный ресурс] — http://popecon.ru/otrivki/367-napravlenija-sovershenstvovanija-amortizacionnoi-politiki-v-rossii.html
- Инновационное развитие России. Возможности и перспективы [Электронный ресурс] — http://lib.rin.ru/authors/vjacheslav-baranov
- Повышение эффективности внешнеэкономической деятельности предприятия [Электронный ресурс] — http://www.coolreferat.com/%D0%94%D0%B5%D1%8F%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8C
