Abstract
- Introduction
- 1. Formulation of the problem
- 2. Analysis of previous studies and publications
- 3. The main results of the study
- 4. Conclusions
- List of references
Introduction
Analysis of the pharmaceutical market indicates that the Russian Federation is a net importer for the global pharmaceutical market. The development and production of high-quality generic medicines and innovative products will increase the export potential of the industry and ensure the competitiveness of medicines in the markets of developing and developed countries.
1.Formulation of the problem
The pharmaceutical industry is a highly profitable and high-tech industry, and it occupies a special place in the global economy, since about 80% of the population uses at least once a year certain drugs (drugs), and for certain categories of the population, the constant use of drugs is vital [8]. Stable increase in world population from 6.9 billion people. in 2009, up to 7.6 billion people. In 2018, the demand for food and pharmaceutical products is growing. According to UN forecasts, the world's population over 60 will be 2.1 billion. by 2050, while the share of this age category will be 34% in Europe, 27% - North America, 25% - Latin America and the Caribbean, 24% - Oceania and Asia, and 10% in Africa [2]. High rates of population aging in developed and developing countries will lead to a serious increase in the global pharmaceutical market, which actualizes issues related to optimizing health care costs, state support and protecting the national pharmaceutical industry in all countries of the world. Evaluate «Evaluate Pharma» by 2022 they forecast an increase in the global pharmaceutical market to 1.5 trillion. US dollars, R&D expenses up to 182 billion US dollars, which will provide 50% increase in sales of pharmaceutical products. On average, in 2018, the costs of R&D by global pharmaceutical manufacturers amounted to about 15% of the profit of the entire industry. The main groups of drugs developed and sold on the pharmaceutical market until 2024 will be antitumor and dermatological drugs [13]. In 2000–2018 years 30% of all pharmaceutical products were produced in advanced economies, while there has been an increase in drug production in emerging economies [11]. For the Russian Federation (RF) in the context of the sanctions policy of the countries of Europe and the USA, as well as the geopolitical situation in the world, the development of its own pharmaceutical industry will not only have a high socio-economic significance, but will also be one of the components of national security. In this regard, it is necessary to analyze the pharmaceutical industry of the Russian Federation on the basis of which to identify prospects for its development in the global pharmaceutical market.
2. Analysis of previous studies and publications
IQVIA, a company, deals with the issues of expertise in order to develop health care and improve the quality of life of people in the world«Frost & Sallivan» conducts market research and analysis of the development of the global pharmaceutical market; assessment and forecast of the global pharmaceutical market is carried out by an international analytical company«Evaluate Pharma».In the Russian Federation, such studies are carried out by the analytical agencies DSM and Deloitte. The issues of the functioning and development of the pharmaceutical industry are reflected in the works of Russian scientists Witter S., Dorovsky A.V., Balashov A.I., Romakina N.A., Ovcharova E.G., Mironenko N.S., Marchenko Yu.O. and foreign researchers Leopold K., McKee M., Redwood G., Wigl M., Volger S., Mossialos E. Taggart J., Arts D., Cavanos P., et al. The importance of R&D in the pharmaceutical industry was highlighted by foreign researchers Grassmann O., Cohen F. J., Scherer F. M., and Russian researchers I. Karachev, V. Mysachenko and others.
3.Key findings
The global financial crisis that began in 2008 did not adversely affect the development of the global pharmaceutical market[11]. In 2001, the global pharmaceutical industry’s revenue amounted to $ 390.2 billion; since 2009, the indicator has consistently demonstrated an average annual growth of 5.3%[10].According to an international analytical company«Evaluate Pharma», In 2017, the global pharmaceutical market capacity amounted to $ 1.2 billion.[13],which is 3.6% more than in 2016 (Fig. 1).
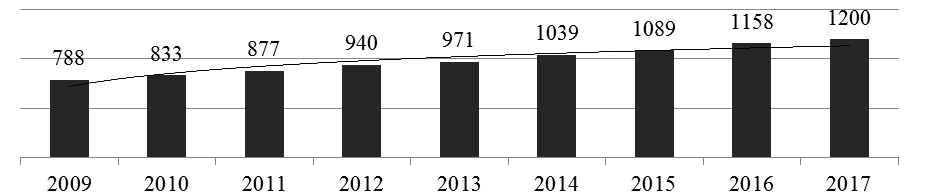
Picture 1 — World pharmaceutical market in 2009–2017, billion US dollars[13].
The leading centers of the pharmaceutical industry are traditionally the USA, Europe and Japan, where more than 20 of the world's largest pharmaceutical manufacturers are concentrated (Pfizer, MSD, Jonson & Jonson, Abbvie, Takeda, Astellas, etc.)[14].The main geographical tendency of the modern pharmaceutical market is the constant shift of its balance from countries with developed economies to countries with developing economies. For example, the Chinese pharmaceutical market in 2017 amounted to 165 billion US dollars, ranking second in the ranking of countries in terms of the pharmaceutical market after the United States (456 billion US dollars). The Japanese pharmaceutical market is confidently in third place in the global pharmaceutical ranking and amounts to $ 120 billion.[13].
Key indicators of the global pharmaceutical market indicate that countries with developing economies, which are united by IMS Health into a group, have a significant impact on its development.«Pharmerging Markets», including 21 countries where the leaders of the Russian Federation, China, Brazil and India. So, in 2017, the group showed the highest growth rates in the pharmaceutical market—14.6% compared to 2016, while the market size in monetary terms amounted to 415 billion US dollars, reaching 33.8% of the global market [15].Taking into account that original and generic drugs are distinguished in the product structure of the pharmaceutical market, in developing countries generic drugs prevail in the pharmaceutical market, and in countries with developed economies innovative products are growing. At the same time, the global market for generic drugs shows an increase, which is projected«Evaluate Pharma» will continue until 2020 (Fig. 2).

Figure 2 —Global Generic Medicines Market 2014–2020, billion US dollars[13].
*– data for 2020 are forward-looking.
In 2017, in the geographical structure of the market, 41.8% of generic drugs were represented by the United States and European countries, while 58.2% were countries with developing economies. Given the global trends in the pharmaceutical market, by 2020 the share of developed countries will be about 35.5%, which is due to increased demand in developing countries for generic drugs, the share of which is projected at 78%, while in developed countries 69% will be original Drugs[14].
In the world ranking of countries in terms of the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation takes 14th place, while in terms of population it is one of the ten leading countries[12].Consumption of pharmaceutical products per capita in the Russian Federation in 2017 amounted to 2.13% of all expenditures, which corresponds to the 11th position in the ranking of states for the consumption of pharmaceutical products by the population [8].In 2018, the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation amounted to 1,682 billion rubles, which is 2.6% higher than in 2017 (Fig. 3). In dollar terms for 2010–2018 years there has been a decrease in the drug market capacity since 2014, due to the devaluation of the ruble, which affected the negative dynamics of the pharmaceutical market in foreign currencies. The exception was 2017, when there was a strengthening of the Russian currency against the dollar and the euro. However, according to DSM Group experts, the aggregate figures for 2010–2018 years demonstrate the beginning of the transition of the pharmaceutical industry of the Russian Federation to an innovative stage of development [12].Russia entered Pharmerging Markets and the growth rates of its pharmaceutical market in the next five years are expected by DSM Group experts to be higher than in European countries, which indicates the possibility of increasing the capacity of the Russian pharmaceutical market and improving its position in the global market.
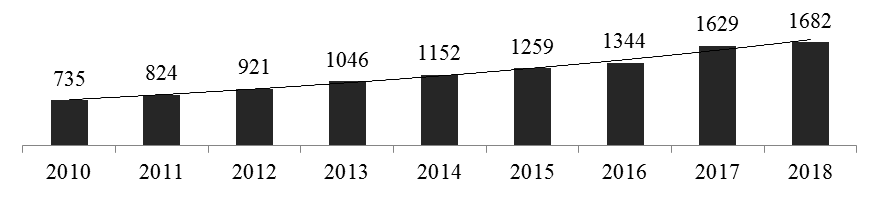
Рисунок 3 — The pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation in 2010–2018, billion rubles [12].
Program «The development of the pharmaceutical and medical industries for 2013– 2020 years» became one of the most successful among industry programs of the Russian Federation[1]. became one of the most successful among industry programs of the Russian Federation [5]. Investing in the industry made it possible to open more than 70 production sites with contract manufacturing of drugs, organize 12 pharmaceutical clusters, create holdings and strategic alliances with foreign pharmaceutical enterprises. As a result, Russian pharmaceutical manufacturers not only took a leading position in terms of sales in the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation, but also increased export volumes of products. In 2018, a number of production sites were launched with a maximum depth of localization of pharmaceutical production, which will allow the manufacture of drugs in a full and closed cycle. For the period 2013–2017 years the production was transferred to GMP standards, drugs were marked and a unified monitoring system for their quality was introduced. As a result, in 2017, more than 70% of pharmaceuticals were manufactured in accordance with GMP standards.[12],which allow you to sell pharmaceutical products on the world market, which increases its competitiveness. At the same time, some Russian pharmaceutical companies have not switched to using the GMP standard so far, since only large manufacturers can afford production modernization, while small and medium-sized companies are forced to work only for the domestic market [6].
Since 2016, within the framework of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), which includes the Russian Federation, there is a single market for the circulation of drugs and medical devices, which introduced a unified registration procedure for drugs and a single market information system that allows pharmaceutical manufacturers to register drugs according to the rules of the integration association[8].It should be noted that in 2018 the formation of a unified control and regulation system for the EAEU pharmaceutical market, which allows Russian pharmaceutical manufacturers to sell goods on the markets of the participating countries, has ended.
Also in 2017, the Eurasian branch of ISPE (The International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering) was opened, which will harmonize the standards for the turnover of pharmaceutical products of the Russian Federation with world standards and increase the volume of pharmaceutical exports to eurozone countries to expand international cooperation in the field of exchange of scientific capital [6]. An additional measure to increase the share of Russian drugs in the world market is a special investment contract (SPIC) that regulates the investor’s obligations to develop industrial production within the stipulated time and the stability of tax and regulatory conditions for investment activities. It should be noted that already in 2018, six contract pharmaceutical companies of the Russian Federation became the owners of SPIC [12].
Traditionally, the commercial sector prevails in the structure of the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation, which forms the main trends in its development. In 2018, retail pharmacy sales of medicines amounted to 5.3 million packages in the amount of 991 billion rubles, which is higher by 4.6% than in 2017 in value terms and by 3.9% in kind. In 2018, the share of original drugs on the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation did not change compared to 2017 and amounted to 36% in value terms, therefore, consumers continue to give preference to generic drugs. In general, in 2018, in the Russian pharmaceutical market in monetary terms, the prescription and over-the-counter drug groups were sold equally. At the same time, the main sales volume of over-the-counter drugs was carried out in the commercial segment of the pharmaceutical market, while in the hospital segment, 94% are prescription drugs. The share of drugs of foreign production at the end of 2018 did not change in relation to the previous year and amounted to 70.2% in monetary terms and 39.4% in kind[12].
In 2018, the top 20, according to the results of the occupied share in the retail pharmacy sales of the Russian Federation, was mainly represented by pharmaceutical multinationals of Europe and the USA. In total, the top — of 20 manufacturers account for 54.3% of the pharmacy sales of drugs in value terms. Of the Russian enterprises, it included only three manufacturers, the maximum share of which is «Отисифарм» — 3,4%, «Фармстандарт» — 2% и «Валента Фарм» – 1,5%. In real terms, the leaders in pharmacy sales are Russian manufacturers Фармстандарт
– 7,5%, «Отисифарм» – 3,5% и «Озон» – 3,3%. In 2018, about 300 new brands were launched on the Russian pharmaceutical market, of which 143 were produced in Russia. In physical terms, in 2018, the leaders in retail pharmacy sales were drugs of groups A, C, R, N, D (according to the ATC classification), which amounted to 71.1% of the volume of pharmacy sales [12].
The state import substitution program in the pharmaceutical industry of the Russian Federation is being implemented through the development of Russian drugs; as a result, there is a negative trend in the import of pharmaceutical products, starting in 2013.(рис. 4).
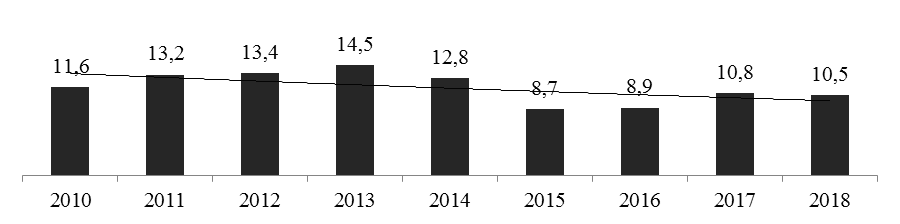
Рисунок 3 —Import of medicines to the Russian Federation in 2010-2018 in billions of US dollars[7].
So, in 2018, the volume of drug imports amounted to 10.5 billion US dollars, which is 27.6% lower than the same indicator in 2013. At the same time, the geographic structure of imports to the Russian Federation to non-CIS countries makes up 98% [18].The Russian Federation continues to be a net importer of products for the global pharmaceutical market. So, in 2018, the export balance amounted to—$ 9,706.2 million[7].
More than 90% of drugs manufactured in the Russian Federation are made from imported pharmaceutical substances. In 2018, the import of substances was carried out from 42 countries and amounted to 82 billion rubles, which is 32% higher than the same indicator of the previous year. The increase in the indicator was due to the import of goods of a higher price category. In the geographical structure of imports in value terms, Chinese-made substances prevail, which tend to increase. So, if in 2017 they amounted to 18%, then already in 2018. — 20%. The total import of substances from European countries in value terms in 2018 amounted to about 64%, France remains the leading import country. An analysis of the import of pharmaceutical substances of the Russian Federation indicates the dependence of manufacturers on currency fluctuations of the ruble and the sanctions policy of European countries, which has an effect on rising prices and, accordingly, reducing the competitiveness of goods [12]. To maintain the competitiveness of the industry, the Government of the Russian Federation is developing measures to support national manufacturers of pharmaceutical substances, including tax incentives, subsidies and subsidies. So, PAO Фармасинтез
plans to invest $ 200 million in the production of pharmaceutical substances with the launch of the plant in 2021. In addition toФармсинтеза
,A number of Russian pharmaceutical manufacturers plan to launch production of drugs with the maximum depth of production localization.
The export of pharmaceutical products of the Russian Federation shows stable dynamics in 2010–2018 years (рис. 5).
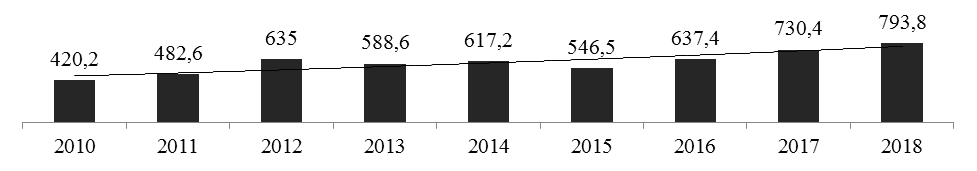
Рисунок 3 —Экспорт фармацевтической продукции Российской Федерации в The export of pharmaceutical products of the Russian Federation shows stable dynamics in 20102010–2018, mln.USD[7]*
*- compiled according to the data of the Customs Service of Russia, product group 30«Pharmaceutical products».
In 2014–2015 years there was a decrease in exports by 12% in dollar terms, while the volume of exports in real terms showed an annual increase, since the ruble exchange rate for the same period fell by 60%. In 2018, the volume of exports of finished drugs amounted to $ 793.8 million, which is 8.6% higher than in 2017. The geography of pharmaceutical product exports also remains stable. Most often, finished dosage forms are exported by manufacturers of generic drugs, while the original drugs leave the basis for imports. [12].Analysis of drug exports shows that the post-Soviet countries remain the main buyers of Russian medicines. In 2018, the countries of the European Union accounted for about 1% of total exports, while the CIS countries and the EAEU accounted for 71.2% of the total volume. USA, Belarus 101,701 thousand US dollars and Uzbekistan 86,200 thousand US dollars. At the same time, there is a tendency towards the beginning of the development of European markets and regions of Asia and Latin America. Also, you should pay attention to a significant increase in exports in 2010–2018 years to the UK, Latvia, Lithuania, China, Cuba, Iran and Turkey, which indicates an improvement in the quality of Russian pharmaceutical products [7].
The cost of production of generic drugs in the Russian Federation is higher than in developed countries because the industry uses imported pharmaceutical substances and equipment. The existing system of international drug certification limits the possibility of optimizing production costs, primarily for enterprises engaged in foreign economic activity. At the same time, the development and production of innovative pharmaceutical products does not guarantee the successful entry of drugs into the international pharmaceutical market, dominated by multinationals[4].The innovative development of the pharmaceutical industry of the Russian Federation should be carried out with state support for the development of innovative drugs and pharmaceutical substances, which are significantly underfunded in comparison with developed countries. It is advisable to use for this a system of government orders for development in the field of oncology, dermatology, diabetes, as well as for the treatment of orphan diseases. It is necessary to provide state support to manufacturers of pharmaceutical equipment with international certification of goods, which will reduce the cost of the process of switching to GMP standards and their implementation in medium and small pharmaceutical enterprises. It should be noted that the increase in drug exports from the Russian Federation will be associated with high-quality generic drugs, since the development and production of innovative pharmacological products takes on average 7 – 10 years, therefore, the export of innovative products of the Russian Federation to European markets – a long-term issue.
According to the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation, deductions of national pharmaceutical manufacturers for R&D are 1–2% from industry profits, and investments in marketing innovations are almost 3 times higher than the level of investment in R&D [11]. Consequently, a business model has been formed in the Russian Federation focused on the promotion of goods, and not on improving their quality. These circumstances indicate the need to develop a system of incentives for pharmaceutical manufacturers to increase R&D expenses, which will be expressed in subsidies and subsidies, the establishment of special customs duties for the import of raw materials, materials and equipment, as well as tax benefits for the period of commercialization of innovative drugs. The incentive system should be aimed at manufacturers who have switched to GMP standards or are preparing for this process, which will not only improve the quality of products, but also expand sales markets in developed countries. Despite the high consumption of original drugs in developed countries, high-quality generic drugs will be in demand to optimize government spending on health and insurance companies that incur losses associated with reimbursement of insurance payments in case of loss of life and health.
The establishment of a common pharmaceutical market for the CIS countries and agreements with the BRICS, APEC, and SCO countries will accelerate the development of the pharmaceutical market of the Russian Federation, since the pharmaceutical production sector is underdeveloped in the countries participating in these international associations and is absent in some countries [9].Most of the member countries of these associations belong to rapidly developing countries, where generic drugs are mainly consumed, which will allow to increase export volumes of pharmaceutical goods of the Russian Federation in a short time, as well as organize contract manufacturing. Against the backdrop of the ongoing global financial crisis, the devaluation of the national currencies of a number of developing countries, drugs of European and American production will not be able to compete in price with goods of Russian pharmaceutical manufacturers. Preferences within the framework of the single pharmaceutical market of the CIS will increase competitiveness and strengthen the image of Russian pharmaceutical products as high-quality generic drugs.
4.Conclusions
Based on an analysis of the development of the Russian pharmaceutical market in the context of world realities, the need to reduce the gap between the Russian Federation and developed countries in the development and production of competitive innovative products and high-quality generic drugs by increasing the level of drug development and production technologies is revealed. The need for the transition of the pharmaceutical industry from a marketing orientation to a production one by establishing maximum allowable costs for advertising products and a minimum amount of R&D contributions is noted. The feasibility of providing state support to pharmaceutical manufacturers of drugs, pharmaceutical substances and manufacturers of pharmaceutical equipment is justified. The importance of developing a mechanism for stimulating the export activity of manufacturers by creating preferences for them through participation in international integration associations, as well as promoting the development of pharmaceutical manufacturers with international product certification, has been proved.
Список литературы
- Государственная программа «Развитие фармацевтической и медицинской промышленности на 2013- 2020 годы». - UPL: http://minpromtorg.gov.ru/common/upload/files/docs/.
- Всемирная организация здравоохранения. - https:// http://www.who.int/.
- Зязева, Н.Н. Современное состояние, условия и перспективы развития мирового фармацевтического рынка / Н.Н. Зязева // Российский внешнеэкономический вестник. – 2015. – № 12. – С. 118-129.
- омовцева, О. А./ К вопросу о классификации экономических кластеров // О. А. Ломовцева, С. Ю. Соболева, А. В. - Научные ведомости Белгородского государственного университета. История. Политология. Экономика. Информатика. – 2015. – №1 (198), Вып. 33/1. – С. 55–60.
- Мамедьяров, З.А. Тенденции и перспективы российской фармацевтической отрасли и применимость мирового опыта / З.А. Мамедьяров // МИР (Модернизация. Инновации. Развитие). – 2017. – Т. 8. –№ 4. – С. 772–780.
- Новосельцева, Е.Г. Российский фармацевтический рынок: состояние и перспективы развития в рамках интеграционных процессов / Е.Г. Новосельцева, Ф.С. Сенина // Волгоградский научно-медицинский журнал. – 2016. – № 2. – С. 11-14.
- Таможенная служба Российской Федерации. - UPL: http://www.customs.ru/.
- Тенденции фармацевтического рынка России – 2017. Система прослеживаемости лекарственных препаратов: дополнительные затраты или возможности? / Deloitte. 2017. - 32 с.
- Чистяков, Е. Интеграционный потенциал СНГ и его роль в развитии мирохозяйственных связей / Е. Чистяков, В. Шульга // Экономист. – Москва. –2013. –№ 6. – С. 12-17.
- Шабалина, Л.В. Перспективы инновационного развития фармацевтической отрасли Донецкой Народной Республики. / Л.В. Шабалина, Н.Ю. Маслий. // Материалы 4-й Международной научно-практической конференции «Инновационные перспективы Донбасса», г. Донецк, 22-25 мая 2018 г. – Донецк: ДонНТУ. – 2018. – Т. 5: 5. Актуальные проблемы инновационного развития экономики Донбасса. – С. 151-155.
- Шабалина, Л.В. Перспективы развития российской фармацевтической отрасли на мировом рынке / Л.В. Шабалина, Н.Ю. Маслий. // Материалы XIV-й Международной научно-практической конференции «Экономика и маркетинг в XXI веке: проблемы, опыт, перспективы», 23–24 ноября 2017 г., г. Донецк, ДонНТУ: [посвящ. 90-летию кафедры «Экономика и маркетинг»: материалы] / редкол.: А.А.Кравченко [и др.]. – Донецк: Изд-во ДонНТУ. – 2017. – С. 601-607.
- DSM Group. - UPL: http://www.dsm.ru.
- Evaluate Pharmaю - UPL: http://www.evaluategroup.com.
- Frost & Sallivan. - UPL: www.frost.com.
- Shiva S. Introduction to logic design / S. Shiva. – CRC Press, 1998. – 628 pp.
- IMSHealth. - UPL: http://www.imshealth.com/. .
