CONTENT
- INTRODUCTION
- BASIC APPROACHES TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE FINANCIAL STATE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT PROCEDURE
- OPTIMIZATION MECHANISM OF THE ENTERPRISE FINANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
- CONCLUSIONS
- LIST OF REFERENCES
INTRODUCTION
The development of market relations has led to an increase in the role of enterprise finance. The state of the company's financial resources becomes a factor determining the financial results of its activities. Quantitative and qualitative parameters of the financial condition of an enterprise determine its place in the market and the ability to function in the economic space. All this led to an increase in the role of financial management in the overall process of managing the economy.
Approaches to assessing the financial condition and economic security, as well as indicators reflecting their level, allow timely identification of shortcomings in the conduct of financial and economic and production and economic activities of an enterprise.
The subject of the research is methods of optimization of financial condition as factors of economic security.
The object of the study is optimization of the financial condition as a factor of economic security.
The purpose of the research work is to study the methods of financial condition as a factor in the economic security of an enterprise
Research objectives:
- Consider the essence and content of the enterprise financial management system;
- Describe the economic security of the enterprise;
- To study the influence of financial condition as a factor in the economic security of an enterprise.
BASIC APPROACHES TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE FINANCIAL STATE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
In a market economy, financial flows are the main object of management at any enterprise, since every economic decision is directly or indirectly related to the movement of funds. Therefore, most managers in one way or another have to interact with financial services in the process of implementing their functional tasks.
In this regard, knowledge of the basics of the financial management system today is necessary for every middle and top-level manager for a deeper and more comprehensive understanding of the problems facing his enterprise and for the effective performance of his functions.
There are four stages in the formation and development of the financial management system as a science.
First stage. The need for a conscious, purposeful activity to manage economic and economic processes in the West arose a long time ago. However, it began to be realized in theory and practice only in the 1850s. (this time can be considered the beginning of the history of financial management).
Second phase. The beginning of the second stage of development of the financial management system in the West was characterized by the end of industrialization. Enterprise growth rates accelerated. It was necessary to make systematic changes in the use of resources. New methods of financial management were constantly developed. Therefore, the main tasks of the financial management system during the transition from the first stage to the second included the development of criteria, indicators and benchmarks that could ensure the effective use of resources. These criteria were initially of the most general nature and allowed the management of the enterprises to determine the general foundations of the strategy for the development of financial management.
Stage three. In the early 1930s. in the West, the financial management system gradually moved to the third stage of its development. The world crisis of the 1930s. caused serious economic difficulties for many economic entities in most countries: a decline in production, bankruptcy. Many small, medium and even large enterprises faced financial difficulties, the number of financial obligations for which they could not provide payments grew. This period was characterized by high rates of inflation, massive bankruptcy of enterprises, low investment activity of business entities.
The current stage is characterized by the progressive economic development of most countries, the active integration of individual national economies into the world economic system, and the beginning of the processes of economic globalization. The role of financial markets in the activities of large companies and industrial and economic complexes has increased dramatically. Previously, financial resources acted as an intermediary in the exchange or acquisition of economic resources.
The level of economic security of an enterprise is based on how effectively the enterprise turns out to prevent hazards and eliminate losses from negative impacts on various aspects of the economic security of the enterprise.
Thus, in theory, all the necessary definitions, objectives, principles and directions of the financial management system have been developed. This enables finance professionals to develop an effective financial management system for the enterprise.
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT PROCEDURE
The financial management system at the enterprise is interconnected with the planning of economic activities and is based on other indicators of the plan. However, drawing up a financial plan is not a simple arithmetic recalculation of production indicators into financial indicators.
In the process of developing a financial management system, the following are determined: costs of products sold, proceeds from sales, cash savings, depreciation, the amount and sources of financing for investments planned for the planned period, the need for working capital and sources of its coverage, distribution and use of profits, relationships with the budget , off-budget funds, banks.
The financial management system is the determination of the directions of a variety of products and goods that are in demand and ready for sale, the choice of financial sources and the distribution of financial resources, as well as control over the implementation of certain financial measures (payments, budget execution, payment of employees).
In the process of developing a financial management system, the following methods can be used:
- Normative method;
- Balance method;
- Calculation and analytical method;
- Methods of economic and mathematical modeling;
- Direct counting method.
Any of the above planning methods is based on the existing relationship between profits, sales and costs. Let's characterize the listed methods.
The normative method is based on a system of norms and standards used to calculate a number of indicators of the financial plan.
Balance sheet method of planning financial indicators is to link the planned income and use of financial resources, taking into account the balances at the beginning and end of the planning period by building balance ratios. The use of this method is advisable when planning profit distribution, forming accumulation and consumption funds. The balance method is traditionally used when developing a chess table.
The calculation and analytical method is based on the analysis of the dynamics of retrospective data and an expert assessment of the predicted change in the planned financial indicator. This statistical method is widely used in planning the amount of profit and income, determining the amount of deductions from profit to the accumulation fund, consumption and reserve fund.
Methods of economic and mathematical modeling make it possible to establish a quantitatively defined relationship between the planned indicators and the factors that determine them. The economic and mathematical model can express the functional dependence of a financial indicator on a number of factors influencing it.
The direct counting method is the most common. It is used, as a rule, with a small range of products. In the most general form, profit is the difference between price and cost, but when calculating the planned profit, it is necessary to clarify the volume of products from the sale of which this profit is expected.
In modern conditions, the direct account method can be used when planning profit only for a very short period of time, until prices, salaries and other circumstances change.
Thus, the end result of planning is planning decisions, which is the basis for the subsequent purposeful activities of the enterprise.
OPTIMIZATION MECHANISM OF THE ENTERPRISE FINANCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
The main goal of any enterprise is to generate as much profit as possible. This requires that the proceeds from the sale of their own products exceed the costs of its production. But, in order to start producing and selling something, you need initial capital. It can be obtained from some external source in the form of a loan.
This process reflects the mechanism of borrowing, that is, obtaining and using borrowed funds for financing. But the activities of the company that took out a loan will be effective, from a financial point of view, only when the profit from borrowed funds exceeds the interest paid on this loan.
The second most important point in financial management is deciding how to spend money. To this end, the company draws up a financial plan that should ensure an efficient investment of funds for the growth and prosperity of the company, as well as achieving the best ratio between cash inflow
and cash outflow
. This is commonly referred to as cash flow planning
.
The main source of funds is the company's income, i.e. what the company receives from its activities: the sale of products, the lease of property, interest from investments in other enterprises and activities, etc.
If the costs of the enterprise are less than the expected profit, then it makes sense to undertake such an investment.
Internal sources of own funds are: authorized capital, reserves accumulated by the enterprise, other contributions from legal entities and individuals (targeted funding, donations, charitable contributions, etc.)
Domestic financing implies the use of equity capital, which, according to sources of formation, has the following structure, shown in Figure 1.
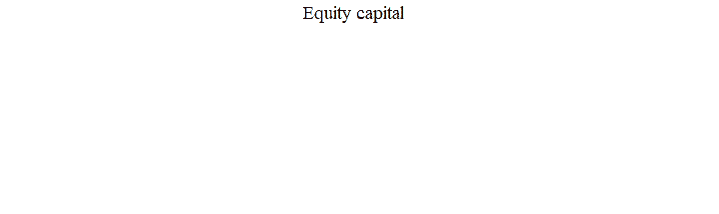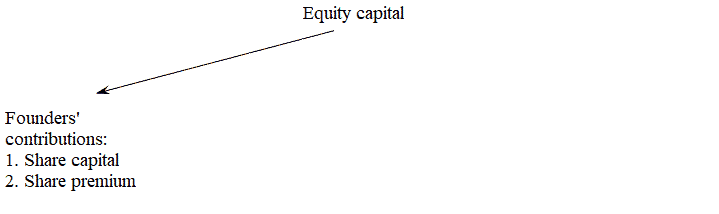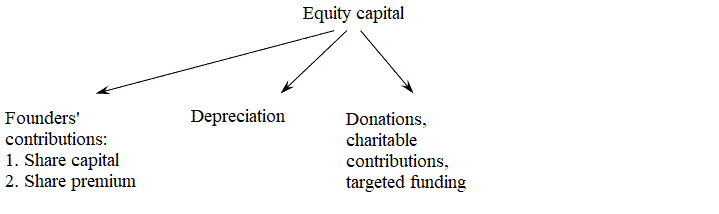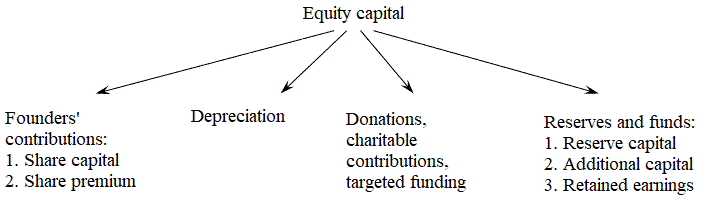
Figure 1 – Equity components (animation: 5 frames, Infinite repetition, 33 kilobytes)
The components of external financing are shown in Figure 2, its source - debt capital.
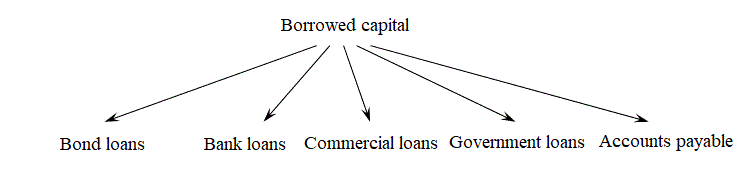
Figure2 – Debt capital components
External sources of borrowed funds include: bank loans; borrowed funds; funds from the sale of bonds and other securities; accounts payable.
On the basis of the above concepts and theoretical definitions, the financial service of business entities should formulate its own financial mechanism.
The financial mechanism of an enterprise is an integral part of the economic mechanism; a set of methods and forms by means of which the company provides itself with the necessary funds.
An example of a typical structure of a financial mechanism is shown in Figure 3.
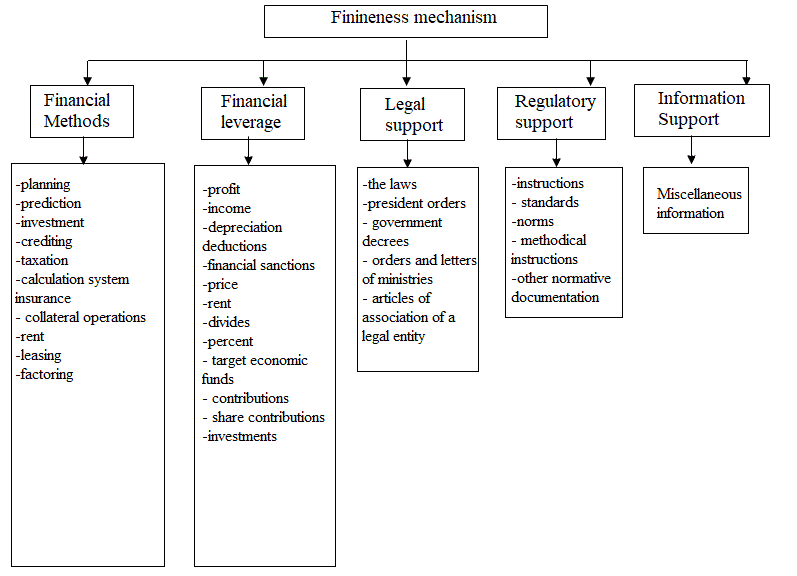
Figure 3 – Financial mechanism structure
In a broad sense, a financial mechanism is a set of methods for organizing financial relations used by society in order to ensure favorable conditions for economic development.
Thus, the main purpose of the enterprise is primarily to generate income. All sources of income are the financial resources of the enterprise, which are used to fulfill financial obligations to banks, insurance organizations, suppliers of materials and goods.
CONCLUSIONS
The level of economic security of an economic entity directly depends on its financial condition, the assessment of which is based on performance indicators and depending on the emerging external and internal dangers and risks of their occurrence. With certain actions or inaction on the part of business entities, various levels of economic security of the organization are revealed.
Thus, in theory, all the necessary definitions, objectives, principles and directions of the financial management system have been developed. This enables finance professionals to develop an effective financial management system for the enterprise. By economic security, it is advisable to understand the security of public relations, the readiness and ability of the institutional units of society to develop measures to block or neutralize possible or emerging threats, the implementation of these measures in order to develop the domestic economy and maintain the socio-political stability of society.
LIST OF REFERENCES
- Балабанов И. Т. Основы финансового менеджмента. Как управлять капиталом? – М.: Финансы и статистика, 1996. – 384с.
- Бригхем Ю., Гапенски Л. Финансовый менеджмент: Полный курс: В 2-х т. / Пер. с англ. под ред. В.В. Ковалева. – Санкт-Петербург: Экономическая школа, 1997. – т1. – 497 с.
- Герчикова И. Н. Менеджмент: Учебник. – 3-е изд., перераб. и доп. – М.: Банки и биржи, ЮНИТИ, 1997. – 501 с.
- Крейнина М. Н. Финансовый менеджмент / Учебное пособие. – М.: Дело и Сервис, 2008. – 304 с.
- Балабанов И. Т. Риск – Менеджмент. – М., 2003. – С. 196.
- Балиашвили Д. У., Волкова С. А., Волкова Т. А. Методика комплексной оценки экономической безопасности предприятия с учетом макро- и микроэкономических факторов // Экономика. Инновации. Управление качеством. 2015. № 3. С. 68–70.
- Фирсов И. В. Методологические основы принятия решений в системе обеспечения экономической безопасности в современных условиях, проблемы и пути их решения // Безопасность бизнеса. 2016. № 3. С. 3–8.
- Глустенков И. В. Экономическая безопасность организации // Вестник Международного института экономики и права. 2015. № 2. С. 77–81.
- Громыко А. Ю., Москаленко С. Г. Методика оценки интегрального показателя экономической безопасности предприятия // Актуальные проблемы социально-гуманитарного и научно-технического знания. 2015. № 2. С. 41–43.
