CONTENTS
1 Topic importance
Continuous casting machines function in stationary conditions and demand a perfect machine regulation and control systems for such maintenance regime. Deviation from the best regime of casting, caused by different disturbances, might decrease productivity, deterioration of metal quality and rise the number of emergency situation. Regulation and control systems of continuous casting machine promote elimination of disturbances
and provide the most rational regime of casting and safety work of unit.
2 Aim and objectives of work
Automatic control system of velocity of ingot extension must prevent emergency conditions. Consequently, automatic control system (ACS), must control extension of ingot with given velocity, with optimal thermal conditions of mold and secondary cooling zone.
3 Review of existing and projected results
For this purpose automatic control system of extension of ingot velocity in continuous casting machine is implemented on the basis of microcontroller (MC), which ensures possibility of direct input of signals of various feedback control (independent from type of signal: discrete, analog or impact) with the next soft- engineering processing inside the MC. Transition of uncontrolled system of driving actuator to
regulate ones
there was provided. This makes it possible to appreciably refine the performance specification of equipment, property and range of control of process variable, expand dexterity o f system and to low down power consumed by engine, so appreciably to economize electric energy.
The most effective automation of the process is on the channel of velocity of regulation of ingot extension, because this channel is the less inertial and this allows to have an influence on difficult physical process that take place in mold.
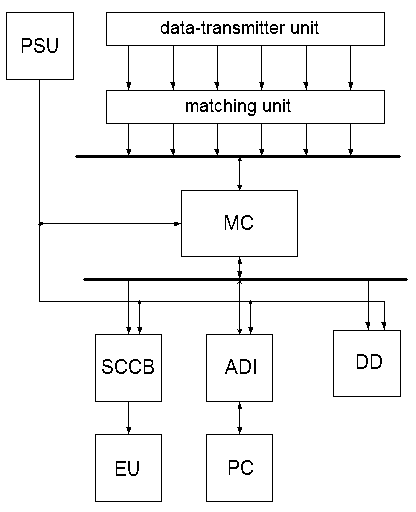
Figure 1 shows structural scheme of automation of the process of extension of ingot.
Figure 1 - Structural scheme of automatic control system (ACS)
PSU - power supply unit;
MC - microcontroller;
SCCB - signal conditioner with control block;
ADI - dissemination of information adapter;
DD - display device;
EU - execution unit
Signals from conversion element are transformed to voltage and enter to ADC (analog-to-digital converter) built-in MC. There the monitored signal is encoded to binary code. Then these signals are analyzed in the MC and the control signal is generated to the actuating unit.
Signal conditioners with PC (personal computer) support distance control of developed facility, it means downloading of monitored information to the dispatcher's panel and definition of reference value of velocity from dispatcher's panel.
Formation of velocity rate level of given extension occurs by selection from memory array of MC of this value for the reason of information from sensors of extension rate of ingots, temperature of liquid steel, hot metal line in the mold, expenditure of cooling water on the secondary cooling zone, temperature of ingot scum, expenditure of lubricant on the mold.
The grade of steel is defined by operator. When there is a signal of disagreement command is generated to appropriate alteration of ingots extension rate.
Summary
So analysis of continuous casting process as automation object there was made. On the basis of coverage of well-known engineering solutions and demands which are lodged to plant automation system, there was developed automatic control of system extension rate of ingots which satisfies given technical and technological demands.
1. Ефимов В.А. Специальные способы литья. – М: Машиностроение,1991. - 734с.
2. Краснов Б.И. Оптимальное управление режимами непрерывной разливки стали. – М.:
Металлургия, 1975. - 310с.
3. Беленький А.М. Автоматическое управление металлургическими процессами. – М.:
Металлургия, 1989. - 379с.
4. Глинков Г.М. Контроль и автоматизация металлургических процессов. – М, Металлургия, 1989. - 287с.
5. Ш.М. Марголин Электропривод машин непрерывного литья заготовок - М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1987. - 374с.
6. Беленький А.М. Автоматическое управление металлургическими процессами. – М.: Металлургия, 1989. - 356с.
7. Дюдкин Д.А. Современные машины НРС. – К.: Наукова думка, 1989. - 197с.
|
© 2008 Bobita Tatyana
© 2008 DonNTU
|