 UKRAINIAN
RUSSIAN
UKRAINIAN
RUSSIAN

 UKRAINIAN
RUSSIAN
UKRAINIAN
RUSSIAN


Donetsk national technical university
In conditions of single, small or medium size lot production automation of work cycle means using flexible automation in execution of all main and auxiliary transitions in manufacture of different components. Solving of this task is provided by using numerically controlled machine tools, multi-purpose machine units used as parts of flexible machine system (FMS) and using some special system that make possible the realization of flexible man-loss technology.
While using flexible industrial systems some difficulties in utilization complete toll resources appear in FMS the level of cutting mode is set low to 60-70% regarding to the normative in suggestion that lower cutting speed and feeding guarantee mote stable work of a tool. But in reality during a low mode of operation the dispersion of tool durability is up to 200%. So we have decrease calculated value of durability period in order to guarantee target life of a tool before its changing.
The durability period for NC machines is about 10-12 minutes (but recommended in reference books – 30-60 minutes). This leads to frequent changes of valid tools.
The second problem is a wide allowance dispersion for machining because of equipment deterioration during blanking operations.
To avoid these problems while automate processing the most promising course is using adoptive control systems. That makes possible to unite outer and inner optimization and change cutting mode quantities by influencing their output parameters.
TThe aim and tasks of my master’s thesis are the following ones.
The research part:
One of the main tasks of modern mechanical engineering is working up and creation of adaptive control units for NC machines, at the same time this adaptive control unit must take into account the condition of a technological system, the characteristics of a working process and other output parameters that influence the choice of cutting process.
For non-stop cutting process control during mechanical operation with a blank in NC machine the following functional scheme of an adaptive control unit (ACU) is given (fig 1)
One of the important tasks of ACU is the definition of momentary cutting force during the processing of a blank.
Cutting force changing while the equality of all other parameters we define as:

 – fluctuaton of a blank over-measure;
– fluctuaton of a blank over-measure;
 –fluctuation of a blank space.
–fluctuation of a blank space.
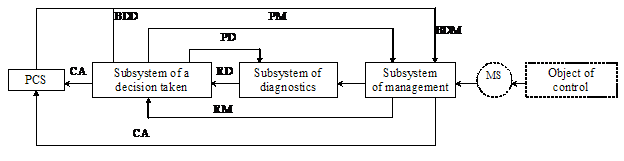
Where CA – corrective action,
BDM – basic data for manufactoring,
BDD – basic data formaking decision,
DD – programmes for diagnosys,
MS – monitoring sensor,
RD – results of diagnosys,
RM – results of monitoring,
PCS – programm-controlled system
PM – programmes for monitoring.
1) information gathering,
2) evaluation of the information and finding abnormalities established by basic data,
3) making a decision and working-out a corrective action elimionating abnormalities found,
4) an input of a corrective action/actions.
Since it is rational to take into account an instatenous value of cutting forces in an adoptive control unit, we can use a special strain reformer made in the form of a bushing with resistive-strain sensors fastened on its surface.
Next we work out a set of technological documentation for the conponent of a “cup” type and project the device for the milling operation on NC machine to obtain this device.