Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Theme urgency
2 Relations with academic programs, plans, themes
3 Objectives and tasks of research
4 Prospective cientific novelty of the results
5 Review of developments and research on the topic
6. A description of the deliverables and work
6.1 Next generation networks
6.2 Existing load balancing algorithms
6.3 Mathematical model development
6.4 Delay equirements
6.5 Link selection criterion
6.6 Models’ algorithm
6.7 Simulation results
7 Further research directions and objects
Conclusions
Bibliography
Notes
INTRODUCTION
- multiservice - various types of data regardless of the used transfer technologies;
- dynamism - a flexible and dynamic change of the band provided the data depending on the current needs of the user;
- intelligence - the ability to control the parameters of data transmission without user intervention;
- multi-statement - the possibility of involvement of several operators in the provision of services;
- scalability - increase network capacity without significant changes in network topology, system management and control.
At this stage of development of telecommunications networks were formed requirements, which requires a modern communications network
It should be noted that the existing circuit and packet switching communication networks is not correspond the above criteria. And thus it prevents the introduction of new services. At the same time increase the volume and variation of service connection may be quite negative impact on quality of service for existing services and for networks in general.
All this is forcing into account the availability of multimedia services in planning ways of traditional networks toward creating the next generation networks.
(the content)
a Background
Modern multiservice networks are deployed in all major areas intensively expanding subscriber base, launching new services. Recently gaining popularity of interactive applications, which are different from traditional data services requirements for communications channels. This all leads to a tightening of quality requirements of service, and forced to revise the existing approaches to building networks, operating principles of equipment, as well as introduce new methods to control and manage the network.
(the content)
2 Relationship with academic programs, plans, themes
Masters qualifying work completed during 2010-2011. According to the scientific direction of the department "Automation and Telecommunications Donetsk National Technical University.
(the content)
3 Objectives and tasks of research
3.1 Objectives of the study
The objectives of this research is to study and analyze traffic in multiservice networks, construction of a model router with the ability to balance the flow of data and its research and development of algorithms for traffic management and development of the optimality criterion of the system load balancing on the transport network.
3.2 Idea of work
The idea of work is to use information about type of traffic and the characteristics of communication channels for managing the flow of data for optimum load distribution on the transport network, while maintaining an acceptable quality of service. And also use the resulting model to develop an effective control algorithm (the development of criteria and choice of optimization method)
3.3 The main objectives of the study
To implement the idea and the goal of master's work should solve the following tasks:
- examine methodological and theoretical material on the methods of traffic management, optimization techniques, to choose the best;
- develop own model of the router for traffic control;
- develop a traffic balancing algorithm guided by the study of theoretical information, the selected mathematical tools and results of modeling.
3.4. Subject of study
The subject of this study is a mathematical model of the router and developed on the basis of its traffic balancing algorithm
3.5. The object of the research
Object of the research is the characteristics of service quality for different types of traffic and the parameters of the communication channels.
3.6. Methodology and Methods
In this research, to investigate the router using the method of mathematical modeling
(the content)
4 Prospective scientific novelty of the results
Novelty of these master's works is the following: increased quality of service in multiservice networks by developing algorithms for dynamic load distribution channels and their assessment of the current state, efficiency utilization of available network resources.
(the content)
5 Review of developments and research on the topic
The issue of methods of load balancing in multi-service telecommunications networks pertains to the requirements of service quality. This issue is addressed by both domestic and foreign scholars and specialists. Providing services to the subscriber with the stated quality parameters considered Olifer NG, Semenov A., Vladimir Vishnevsky
Companies producing telecom equipment CISCO Systems, Motorola, Nokia, Siemens Networks, Huawei Technologies and others are pioneers in introducing new techniques and mechanisms for regulating the quality of services in telecommunications networks.
Quality issues in multiservice networks engaged in such foreign experts: Srinivas Vageshn, P. Ferguson, D. Heymann and others.
(the content)
6 Description of received and expected results of work
Work on this topic began with a preliminary research of requirements for quality of service in multiservice networks, of network transport protocols and data analysis capabilities of flow control of data; review the concept of NGN (New Generation Network);
6.1 Next generation network
Next-generation telecommunications network (NGN - Next Generation Network) - a multiservice communications network, the core of which is IP-based network to support full or partial integration of voice, data and multimedia. Implements the principle of convergence of telecommunications services. This concept of building a communication network provides for the granting of unlimited set of services with the flexibility of their management, personalization and the creation of new services through the harmonization of network solutions, realization of a universal transport network with distributed switching, the imposition of the functions of providing services to the network termination units and integration with traditional communication networks. Benefits of NGN networks: For the operator:
- build a universal network;
- increase profitability by increasing the number of additional multimedia services;
- optimal use of existing resources by sharing the load between the nodes in the network;
- the flexibility to change the configuration, build capacity and upgrade;
- simpler deployment and management at the expense of universality;
For Users
- independence from transfer technology;
- flexible set of variations, volume and quality of services provided;
- mobility of receiving services.
For any number of network users the NGN is required to solve problems of traffic management. By design, this network involves the simultaneous existence of many different types of flows. Each of these flows requires unconditional respect for some transmission parameters and allows for some concessions on other issues.Therefore, during periods of network congestion can cut back to one stream of bandwidth for the other - to increase the delivery time, and for the third, for example, ignore the integrity of transmitted data. Multiservice network must have a more complicated control system than traditional management systems and networks. It should ensure the simultaneous provision of a diverse array of network services and network transfer heterogeneous traffic. For the effective management of traffic should have the necessary hardware and software that enable fast and flexible to provide any service to the user. In this paper, we simulated the process of managing traffic to external networks from this, having several ways to access the outside world.
6.2 Existing algorithms for load balancing
Spillover (Overflow algorithm)
One of the channels is taken as basic. For this channel is determined some limit value of load. Upon reaching this load for a certain period (10 ~ 600 seconds) begins to use the following link. Once the download of the main channel drops, new session will open on it.
Example of application of this algorithm: back-channel is more expensive, it’s used as an extra.
Weighted Round Robin
Determined by the load factor for all channels. The ratio is determined for a number of user sessions.
For example, the ratio channel_1: channel_2 = 3:1. This means that the number of open sessions across multiple channels will be 3:1, respectively. In this case, the real distribution of loads (utilization of the channel) is not analyzed.
Least Load First
This algorithm determines the loading of the outbound flow, incoming and outgoing or incoming flow at the current time, and then - recycling channel in accordance with the maximum bandwidth. The new session opens in the less loaded channel.
None of the proposed algorithms do not use data on the nature of incoming loads.And also, the choice of route is determined by only one parameter - the bandwidth, hence can not control the transmission quality for each type of traffic.
6.3 Development of mathematical model
The object model is a computer network in which access to other networks (the Internet, remote corporate networks) is carried out through a "broad router". It uses several alternative routes for communication with the outside world. Router problem - to estimate the parameters of communication channels (channel congestion, through-delay) and type of traffic, choose the most profitable option of load distribution between the lines, while maintaining an acceptable quality of service.
Each traffic type is characterized by its requirements to the parameters of the communication channels. If voice traffic is picky about the delay and its rejection, the transfer of data - distortions and packet loss. Therefore, for each type of transmitted data is useful to introduce the so-called utility function, which is assessing the appropriateness of the communication channel for transmission of traffic at the moment.
For voice traffic dependent utility function U on the available bandwidth b will have the form (6.1)
 (6.1)
(6.1) where, Bmin - minimum bandwidth required for the operation of the codec used and the protocol voice communications.
Video transmission in real time is similar in characteristics to the voice, but when using adaptive coding and control jitter delay allowed a significant reduction in bandwidth. Analytical expression of the utility function has the form (3.2):
 (6.2)
(6.2)  (6.3)
(6.3)
Bmax - maximum required capacity.
ε - the ratio of the maximum required bandwidth to a minimum.
The least bandwidth intensive is the transfer of data (files, email, etc.).
Utility function for this type traffic looks like (6.4):
 (6.1)
(6.1) Plots the utility functions for different types of traffic on the bandwidth shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.
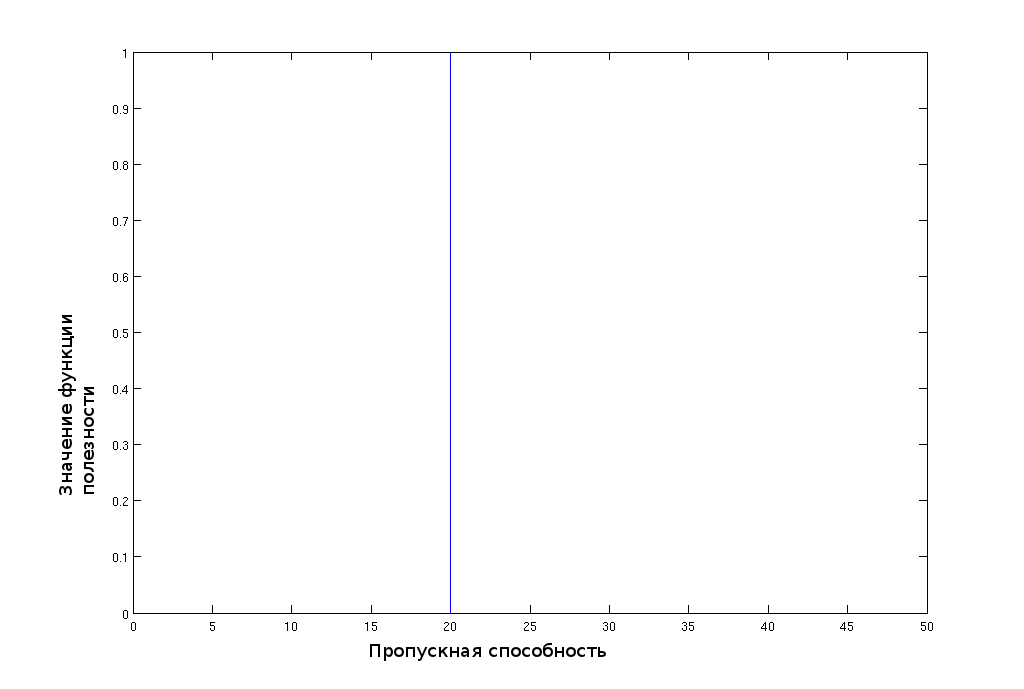
Figure 1. Utility function of bandwidth for VoIP traffic.
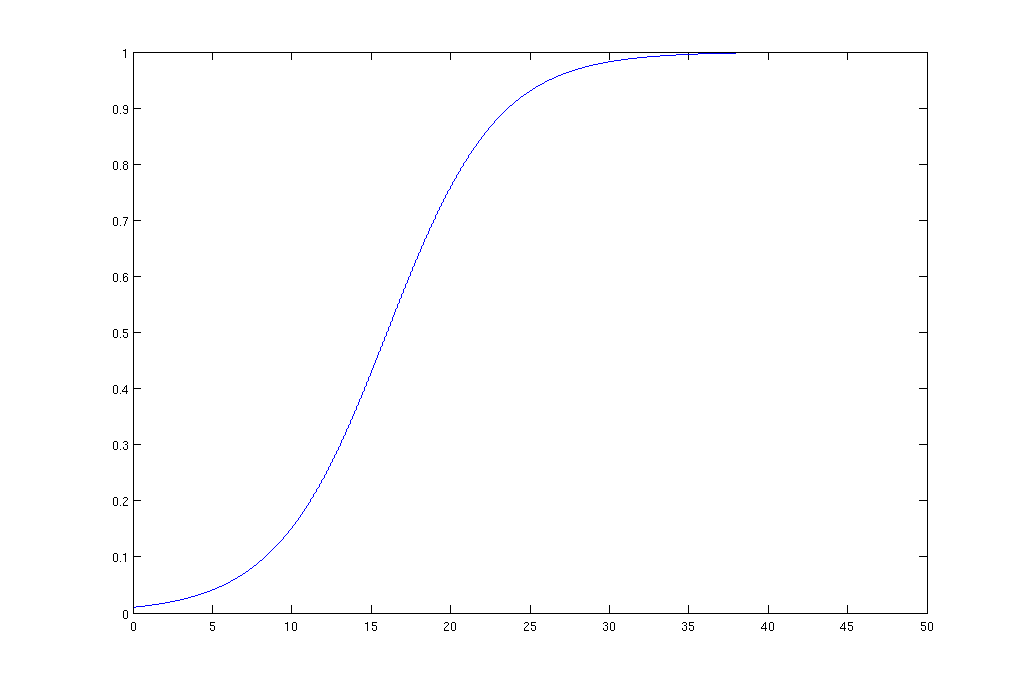
Figure 2. Utility function of bandwidth for IPTV traffic.
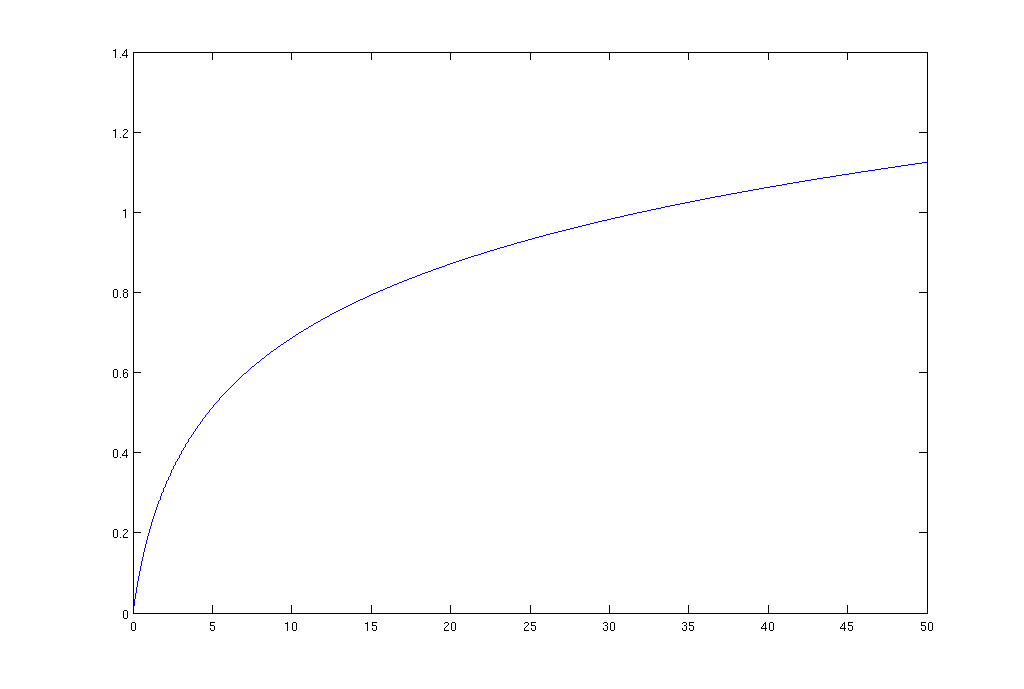
Figure 3. Utility function of bandwidth for file transfer traffic.
6.4 Requirements for the delay
Significant impact on the quality of service has delayed delivery of data. As well as for capacity, quality of service dependency on the delay of each traffic type has its own. The most critical delays is streaming voice and video (especially when using algorithms with a large aspect ratio). On the recommendation of ITU-T G.114 for voice quality is above average pass-through delay should be less than 400ms. To send video data acceptable delay is 1000ms. The dependence of the utility function of the delay in the communication channel can be described analytically as (6.5):
 (6.5)
(6.5) where,
 (6.6)
(6.6) τmax - the maximum allowable delay.
ε - the ratio of the maximum delay to a minimum.
Utility function of the delay is shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. The schedule depends on the size of the utility function through the delay for VoIP and IPTV.
For file transfer delay is not so critical, so this option for this type traffic do not count.
6.5 Link selection criterion
Choice of communication channel for the incoming data will take into account the utility functions, which are described above. Assessment of quality for each incoming flow (session) is estimated criterion:
In the designed model, the choice of channel for which communication is carried out Ksessii greatest. Evaluation of the quality of each channel at a given time is defined as the sum of the ratings of sessions:
 (6.8)
(6.8)  (6.8)
(6.8) 6.6 Algorithm model
The algorithm of the model shown in Figure 5:
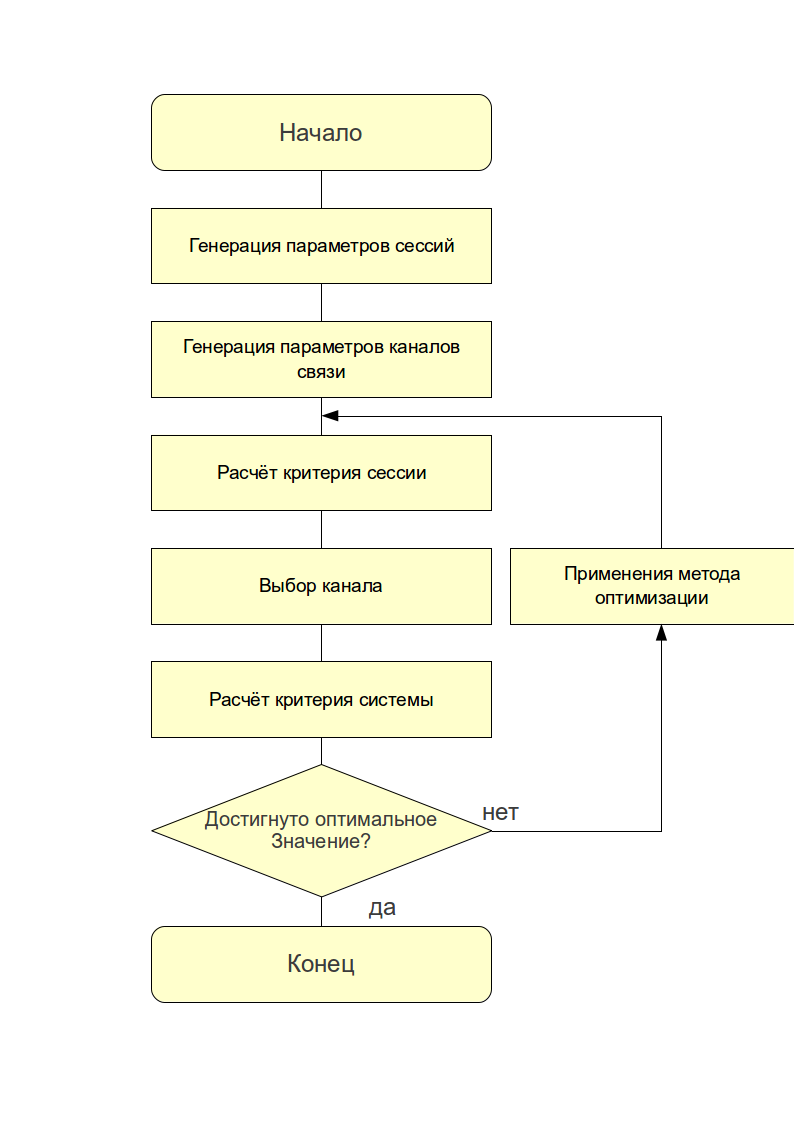
Figure 5. Block diagram of the model load balancing.
The algorithm begins by initializing the parameters of the simulated system: namely a random generated sequences for the sessions initiated by users (the type of data transferred, duration of transmission) are generated by random sequences for the state of communication channels (through delays and their standard deviation, loss, malfunction). Further, the calculation is performed for the proposed criterion based on the value of which is estimated the system. If the evaluation system is unsatisfactory, then performed further optimization of the system configuration.
The proposed model was implemented with the programming environment MatLab ( source code version 0.1b )
7 Direction and objects of further research
In the future we plan to develop a mathematical model using stochastic optimization methods (method of ant colonies, the method of neural networks), to compare the proposed methods and also to select the optimal one of the areas of research is the complement of the optimization criterion, to account for a greater number of traffic parameters and communication channels that allow the construction of more flexible load balancing. Another important stage of work will be to develop a feasibility criterion for system optimization based on already established.
CONCLUSIONS
During this work were analyzed methodological and theoretical material on how to control traffic optimization techniques. Proposed a formalized selection criteria communication channel based on its parameters and traffic characteristics. Developed a basic algorithm of balancing techniques based on the proposed criteria.The directions for further research aimed at adapting the techniques developed for practical application in terms of real multi-communications networks.
References
1. Крылов В.В. Теория телетрафика и ее приложения./В.В. Крылов, С.С. Самохвалова. – СПб.: БХВ-Петербург. –2005. – 288 c
2. Vegesna S. IP Quality of Service./Srinivas Vegesna. – Cisco Press. – 2001. – 368 p
3. Норенков И.П. Основы автоматизированного проектирования: Учеб. для вузов./И.П.Норенков – М.: Изд-во МГТУ им. Н.Э. Баумана, 2000. –360 с.
4. ITU-T Recommendation Y.1540/Y.1541. Network perfomance objectives for IP-based services. Geneva: International Telecommunication Union.[Электронный ресурс] – 2006./- Режим доступа к статье: http://www.itu.int/rec/dologin~type=items
5. Олифер Н., Олифер В. Базовые технологии локальных сетей./Н.Олифер, В.Олифер – Центр Информационных Технологий, 1999
6. Семенов Ю.А. Telecommunication technologies - телекоммуникационные технологии (v3.3, 10 мая 2010 года) [Электронный ресурс]/Ю.А. Семенов./- Режим доступа к статье: http://book.itep.ru
7. Type of Service in the Internet Protocol Suite; RFC-1349, July 1992 [Электронный ресурс]/P. Almquist./- Режим доступа к статье: http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1349.txt
8. Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field)in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers; RFC-2474, December 1998 [Электронный ресурс]/K. Nichols./- Режим доступа к статье: http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2474.txt
9. Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6); RFC-1883, December 1995 [Электронный ресурс]/S. Deering, R. Hinden./- Режим доступа к статье: http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1883.txt
10. Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6); RFC-2460, December 1998 [Электронный ресурс]/S. Deering, R. Hinden./- Режим доступа к статье: http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2460.txt
(to the contents)
Notices
During writing this abstract master's qualifying work is not completed yet. Date of final completion: Dec. 1, 2011 Full text of the work and materials on the subject of the work can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after this date.
(to the contents)
