

Byeze Vladimir
Faculty Computers Sciences and Technologies
Department Automated Control Systems
Speciality «Information Control System»
Subsystem route optimization trucks in a warehouse
Scientific adviser: Telyatnikov Oleksandr
Subsystem route optimization trucks in a warehouse
Introduction
The problem of definition of a comprehensible variant of placing of the goods in a warehouse isn't new to trade and logistics system. Its essence consists in definition of optimum places of storage of the goods.
Working out of the decisions directed on optimization of placing of the goods in a warehouse, is made in two stages.
At the first stage it is required to collect the data about the goods, to define the list optimum for the given assortment of places of storage, and also to calculate necessary quantity of places of storage. At drawing up of the general lay-out of a warehouse it is expedient to consider forecasts concerning assortment, sales volumes of these or those goods, increase in stocks of the seasonal goods.
On the basis of the calculated quantity of places of storage, and also taking into account used technology of processing of cargo, types and quantity of racks are defined, the detailed plan of premises with placing of racks and pallets is made.
At the second stage it is necessary to develop algorithm of placing of the goods in a warehouse which will allow:
- To provide storage of the goods with observance of demanded storage conditions and personnel access;
- To reduce time for goods selection;
- To reduce distances of passage of loaders on zones in the course of selection;
- To reduce total distances of passage of the goods on a warehouse;
- To provide uniform loading on technological zones and the warehouse personnel;
- To reduce turns in technological operations.
As a rule, in the warehouses using the automated control system, the rigid binding of names of the goods to storage places isn't made. Dynamic placing according to which the control system of a warehouse chooses a cell practises.
Definition of rules of storage in information system is followed by instructions for the name of the goods of parameters Ђa storage modeї and "area". The Same parameters are established and in cells. Thus, cells for placing of unit of storage are defined at full coincidence of the given parameters. For storage unit the regular, non-staff and critical area of placing can be set. At impossibility of placing in regular places of storage the system tries to place in non-staff, and then in critical places of storage.
Criteria of optimization of such problem are:
- The minimum distance of transportation of the goods;
- Choice of the nearest loader to a shipment place.
Urgency
The various methods are developed, offering to solve this problem, however it is actual, as at present goods placing not ideally and sometimes occupies a lot of time.
Practical value
Placing of the goods plays a key role a warehouse in optimization of warehouse processes. How the goods are placed in a warehouse, preservation of its quality, and speed of selection depends also.
The review of researches on a theme
For all types of warehouses it is possible to allocate some general principles and optimization methods:
- With reference to a warehouse the rule of Pareto will sound as follows: 80 % of a turnover of goods give 20 % of the goods. For revealing of these of 20% the AVS-ANALYSIS (drawing 1) is spent. Its essence consists that the total of the sold goods of each kind for long enough period of time (quarter, half a year or year is counted up).
- Also in any warehouse it is necessary to develop an optimum route of movement on a warehouse at goods statement on storage and selection of the order or to develop a movement order on a warehouse.
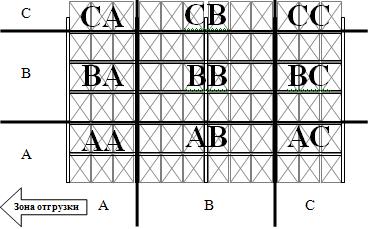
Drawing 1 Ц Placing of the goods on racks of a zone of storage depending on frequency of selection (the grouping is spent by the ABC-method)
The basic results
Is available n points of shipment in which the arrived goods, their names are concentrated Nm1,Е,Nmn and quantity A1,Е,An. Also are available m*k*p cells B 1,1,1 , Е, B m, k, p for goods placing. Also there are two types of the loaders, the first type can place the goods on height 1, Е, p 1 , and the second on height 1, Е, p. Also the location of each loader in warehouse M j, o , j=1, Е, m+n is known; o=1, Е k. It is necessary to make the plan of placing of the goods in a warehouse.
Let's define for each zone of the shipment, what places of placing are intended for the arrived goods (drawing 2), and Clark-Right's method we will receive routes.
For calculation of distances between the chosen places d ij , i=1, Е, m, the formula (2) is used:
 , (2)
, (2)
Where I i , I j Ц number of a rack of places i and j; J i , J j Ц number of a cell of places i and j; Lp Ц aperture distance between racks; Ly Ц width of a cell; k Ц quantity of cells in a rack.
For calculation of distances from a shipment zone d ij , i=0, the formula is used (3):
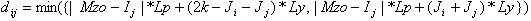 , (3)
, (3)
Where M zo Ц rack number opposite to which there is a shipment zone.
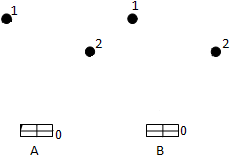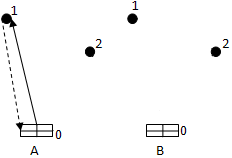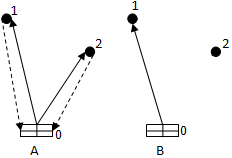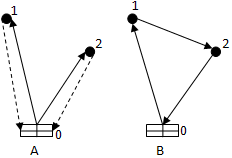
Drawing 2 Ц Routes
There are two ways of transportation of cargoes a radial route «A» and a ring route «B» (drawing 2). The difference between a route «A» and «B» (4), is called a meter prize.
sij = (2d01 + 2d02)-( d01 + d02 + d12)=d01 + d02 Ц d12 (4)
Under the formula (5) meter prizes pay off sij.
sij = d0i + d0j Ц dij (5)
The received values are brought in table 1 where distances between points dij (the right top part of a matrix) and meter prizes sij (the left bottom part of a matrix are presented).
Table 1 Ц the Matrix of distances and meter prizes
| Matrix of distances between points (dij) | ||||||
| Matrix of meter prizes (sij) | 0 | d01 | d02 | d03 | Е | d0r |
| d10 | 1 | d12 | d13 | Е | d1r | |
| d20 | d21 | 2 | d23 | Е | d2r | |
| s30 | s31 | s32 | 3 | Е | d3r | |
| Е | Е | Е | Е | Е | Е | |
| sr0 | sr1 | sr2 | sr3 | Е | r | |
After algorithm performance there are movement routes (drawing 3). Then between loaders the found routes are distributed and brought by it in turn.
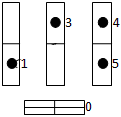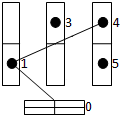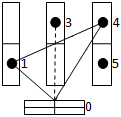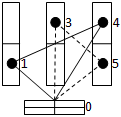
Drawing 3 Ц Places of placing of the goods
Conclusion
In comparison with full search the decision error the given method doesn't surpass on the average 5-10 %. Advantages of a method are its simplicity, reliability and flexibility that allows to consider variety of the additional factors influencing the final decision of a problem, but the most important advantage is its high speed of a finding of routes.
Literature
- Ћиндерс ћ. –., ‘ирон ’. ≈. ”правление снабжением и запасами: Ћогистика [“екст] : пер. с англ. - —ѕб.: ѕолигон, 1999
- ќптимизаци€ размещени€ товара в распределительном центре [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://www.axelot.ru...
- –азработка системы складировани€ центре [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://virgos.ru...
- Tuning a Parametric Clarke-Wright Heuristic via a Genetic Algorithm [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu...
- јЋ√ќ–»“ћџ –≈Ў≈Ќ»я “–јЌ—ѕќ–“Ќџ’, —≈“≈¬џ’ «јƒј„ » «јƒј„ ќ Ќј«Ќј„≈Ќ»» [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://www.agta.ru...
- Clarke & Wright's Savings Algorithm [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://www.hha.dk...
- «адача о кратчайших пут€х [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://algolist.manual.ru...
- ќптимизаци€ размещени€ товара на складе фармдистрибьютора [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://www.lobanov-logist.ru...
- ћаршрутизац≥€ транспортних перевезень методом ларка-–айта ≥ њњ автоматизац≥€ в MS Excel [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://studentbank.ru...
- ќптимальное размещение ресурсов на складе [Ёлектронный ресурс]. - –ежим доступа: http://edu.dvgups.ru...
While writing the given abstract the master's work has not been completed yet. The work completed is December, 2011. The text of master's work and materials on this topic can be received from the author or her research guide after the indicated date.