RUS
| UKR
||
Master's
portal of DonNTU

Pavlo Pashchevskyi
Faculty: Computer Science and Technology
Speciality: Information control systems and technologies
Scientific adviser: docent, PhD Tamara Zhukova
About
author
Development of computer subsystem for planning and prognosis of production release
Maintenance
Introduction
Topicality
Aim of the work
The main task of development and researches
The subject of development and research
The object of development and research
Methodology of researches
Practical sence of the got results
Describtion of the developing subsystem
Review of the researches of the topic in DonNTU
Review of the researches of the topic in Ukraine
Review of the researches of the topic in the world
Raising of task of optimization
Decision of planning task by genetic algorithms
Neuron networks for the decision of prognostication task
Conclusion
References
In today's market relations planning all economic activities of enterprises and firms is an important prerequisite of free enterprise and the production, distribution and consumption of resources and goods. In a world of limited productive resources market planning to use them is the basis of economic freedom as producers of goods and services and consumers of material goods. In a market where existing prices for all products and resources are set free by the competing manufacturers and consumers, each company or firm decides what products and how much they should produce in the upcoming planning period. Planning of activities was now the economic basis of free market of individuals and labor groups, small and large companies, different companies and organizations, all businesses and economic entities with different ownership forms. The planning process provides the necessary balance between production and consumption of products, size of market demand for goods and services and the volume of their supply firms and enterprises. The producers themselves tend to the fullest satisfaction of our products and services to all existing customers, the market needs which are essentially future production plans of enterprises and companies.
The stable financial state of industrial enterprise, which operating in a market economy, can be well-to-do on condition of permanent perfection and development of production with the purpose of products issue, proper to dynamically changing demand of users. Providing this accordance is possible only on the basis of the effective planning of the production program of industrial enterprise.
An enterprise forms the production program on the basis of government order, orders of users and consumer. Thus, the production program of industrial enterprise determines a possible volume production and sales to the products in the planned period, proper on a nomenclature, assortment and quality to the requirements of users.
Also it should be noted continuously growing requirement in prognoses. Actuality of upgrading of prognosis researches increases. It requires more deep study and development of basic problems, arising up in prognostication.
From foregoing it is possible to say about actuality of theme of master's degree work, that the production program of enterprise is inalienable part for effective activity of industrial enterprise.
The purpose of creation of subsystem of planning and forecasting of products issue is a theoretical ground and development of instruments and methods of planning and forecasting of products issue in the conditions of instability and indefiniteness, providing adaptation of the planned indexes to the change of parameters of external and internal environment.
The tasks of development and research are predetermined by the purpose of work and consist of that:
- To give the concept of the production program of enterprise (PPE)
- To prospect the theoretical and methodical going near planning of the production program of enterprise in the conditions of indefiniteness.
- To expose and systematize factors, having influence on products issue of enterprise and reflecting of a particular branch specific.
- To define the period of planning of the production program based on the exposed of a particular branch conformities to law of demand on the products of enterprise.
- To execute the analysis of criteria and methods of planning and forecasting of products issue of enterprise.
- To develop the computer subsystem of planning of products issue of enterprise, which adequately taking into account basic conformities to law of production and realization of products.
The article of development and research is a computer subsystem of planning and forecasting of release of products which will allow to make on an enterprise optimum prognosis and on its basis plan of products issue.
A research object in this work will be a process of planning and prognostication of issue of products in the conditions of "SV-Plast" lyd. - enterprise than produces polyethylene pipes for cold water
Methodological basis of research was made by positions of analysis of the systems, methods of planning of the production program of enterprise, methods of mathematical statistics, economics and mathematics methods and models, expert methods, methods of acceptance of administrative decisions in the conditions of indefiniteness. Neuron networks, giving good results in the conditions of incomplete or surplus, partly contradictory information of high-cube, and genetic algorithms, adequately taking into account basic conformities to law of production and realization of products on the basis of processes of natural selection, are chosen for development of computer subsystem of planning and forecasting of products issue.
Practical meaningfulness of the got results consists in development of subsystem of scheduling and forecasting of products issue, which will be created in conditions and taking into account the specific of the Ukrainian economy (seasonal vibrations of demand, instability in economy).
Essence of prognostication and planning of issue of products consists of ground of aims and methods of their achievement on the basis of exposure of complex of tasks and works, and also determination of effective methods and methods, resources of all kinds, necessary for implementation of these tasks and establishment of their co-operation. Planning is one of major condition of organization of effective work of enterprise. Planning engulfs basic directions to economic activity, such as sales, purchases, production, management money facilities in co-operation between itself. Planning leans against prognostication of demand, analysis and estimation of present resources, prospects of development of enterprise.
Optimization of structure of raw material at planning of issue of products is the substantial source of backlogs of increase of sum arrived. Logically to suppose that an enterprise is advantageous to increase the stakes of those wares which bring in a maximal income. But always it should be remembered about the row of limitations, not allowing to give up less cost-effective products:
1) potential demand on products is dynamic enough and differentiated in time and space. Those wares and trade marks which are claimed presently now can lose the consumer attractiveness through some intervals of time;
2) capital production assets need permanent exploitation, adjusting and service. Outages of equipment are an always unfavorable factor for a production.
The plan of issue of products determines:
a) quantitative indexes of production;
b) volume of output, which depends on the followings factors of products:
- initial size of available production capacities;
- amount and type of the equipment, his productivity, possibility of the best use, plan of repair;
- amounts of working hours in the planned period;
- assortment of products (orders of clients), which depends on a season (time of year), fashion and necessities of population;
- resources of raw material and limits of expense of it on unit of products and his quality.
For every period, engulfed by a plan, it is necessary to define two variables: production volume in this period; amount of resources in-use in this period. The plan of issue of products reflects a nomenclature and assortment productions of goods in accordance with the plan of realization, obligations of enterprise and economic conditions.
Planning and forecasting of the produced products includes the decision of row of tasks. Foremost, demand is forecast on products, produced by an enterprise. A nomenclature, assortment and volume of output of products, is further planned in accordance with a prognosis. A nomenclature of production is a list of wares (finished products, ready-to-cook foods, etc.), subject to making on an enterprise in the planned period. The assortment of products characterizes correlation of specific scales of separate types of wares in the general issue of products. A nomenclature, assortment and volume of the products made an enterprise, is set on the basis of the centralized task on supplying with major kinds to the products and brief-case of orders of enterprise taking into account his specialization. Agreements are thus taken into account on deliveries, celled by an enterprise.
The nomenclature of the produced products can suffice vast, an enterprise is equipped by plenty of equipment of different type and setting. In this case it is expedient to perfect the structure of issue only of that products specific gravity of which in the general volume of output is high enough.
The necessary condition of increase of amount of production of certain wares is universality of equipment for their production. The plan of issue of products can influence on the size of a number of costs, including: costs of storage of the prepared products; costs of conduct of brief-case of the set aside orders; costs, related to extracurricular work or outage of workers; costs, related to the transmission of part of works to the subcontractors.
The task of optimization of structure of raw material at planning of issue of products must decide on every industrial enterprise which is interested in maximization of income from a sale to the produced products.
For the normal functioning of computer informative subsystem of planning and prognostication of issue of products the followings entrance documents are needed:
- report on realization of commodities from storage of the prepared products for a previous month, quarter, year (planned period);
- information about products on beginning of the planned period;
- invoices on materials;
- bills of charges;
- technological maps;
- calculations on produced goods;
- brief-case of orders;
- information about the production capacity of enterprise.
For the computer subsystem of planning and prognostication of issue of products output documents will be:
- prognosis of issue of products on a certain period;
- plan of issue of products on the basis of prognosis.
All got output documents in this subsystem are used in future and can be entrance documents in other, contiguous subsystems. In particular a plan of issue of products is basis for the calculation of the coordinated plans of production subdivisions, workshops of basic production and providing services. In the number of other information there are reports, queries, diagrams. There is statistical information in them which can be used by a statistical department.
Planning and forecasting production was investigated in the work of her master's Solodukha Olga "Development of a computer subsystem for planning and prognosis of production in the sewing business," Doty "" [1], and Ismail Hassan Hascer "Development of a computerized system for demand forecasting and production of textile products in Syria. "[2]
Studies on for planning and prognosis of production release such economists: M. Alekseev, IA Bokun [3] DA Pikalova [4], VI Borisevich, MI Buhalkov [5] , VI Kuzin [6] AK Znamensky [7] O. Volkov [8] VA Goremykin, Vladimir Glukhov, AI Ilyin, SE Kamenitser [9] MV Makarenko, M. Makhalin, V. Popov, E. Utkin, V. Tsarev, RA Fatkhutdinov etc. [10] developed software for planning and forecasting output at the plant the following companies: JSC "Mark" [11], the company is "Intelligence Service", etc.
Planning and forecasting are widely covered in the works of contemporary foreign authors R. Ackoff, I. Ansoff, H. Benveniste, L. Vogel [12] J. Bigelya, G. Weie, C. Gannta, P. Drucker, W. Doring, M. Porter, F. Taylor, A. Fayolle, P. Fulmer, G. Ford, and others. [13] Also, foreign firms are developing software products for planning and forecasting production. These firms include: "1C», «Consistent Software» [14], etc.
For planning and prognostication of issue of products the methods of analysis of the systems, mathematical design, optimization, expert estimations and new information technologies are used.
That parameter which determines the degree of perfection of decision of arising up problem comes to light for the decision of task of optimization. This parameter is usually named an objective function or criterion of quality. In economic tasks it, as a rule, maximization of income. The aggregate of sizes which determine an objective function is further set. Finally, all limitations which must be taken into account at the decision of task are formulated. After it a mathematical model, consisting in establishment of analytical dependence of objective function from all arguments and analytical formulation of concomitant to the task of limitations, is built. So, let it is set as a result of formalization of the applied task, that objective function
 , (1)
, (1)
where great number X is generalization of limitations, it is named in a number of feasible solutions. The creature of problem of optimization consists in a search on a great number X – great number of feasible solutions of such decision 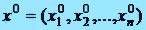 at which objective function f arrives at the least or most value (2).
at which objective function f arrives at the least or most value (2).
 (2)
(2)
As criteria of optimization choose the followings: limitations will be the maximal loading of equipment and minimum use of resources, and by an objective function – arrived maximum (3). On the basis of it get a necessity to us decision, i.e. plan of issue of products.
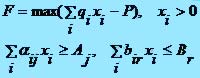 (3)
(3)
where qi is a price of i wares; xi is a volume of output i wares; P are expenses; aij is labor intensiveness of making i wares on j equipment; Ai is the maximal loading j equipment; bir is an amount of resources r, necessary for making i wares; Br is a minimum volume r resource.
Genetic algorithms are analytical technologies, created and adjusted by nature for millions of years of its existence. They allow deciding the tasks of prognostication, classification, search of optimum variants, and quite irreplaceable in those cases, when in ordinary conditions the decision of task is based on intuition or experience, but not on its strict (in mathematical sense) description.
Let some difficult function (objective function), depending on a few the variables, is given, and it is required to find such values of variables which the value of function is maximal at. Tasks are such named the tasks of optimization and meet in practice very often.
One of examples is a task of planning of issue of products. In this task variables are volumes of output of products, and a function which needs to be maximized, is total profit of enterprise. Also there is value of costs of realization of products, all expenses on every good, norms of charges and fund of time.
We will make an effort decide this task, applying known to us natural methods of optimization. We will examine every variant of issue of products (set of values of variables) as an individual, and profitableness of this variant – as adjusted of this individual. Then in the process of evolution (if we will manage it to organize) the adjusted of individuals will increase, and, will appear more and more profitable variants of plans. Stopping an evolution in some moment and choosing the best individual, we will get the good enough decision of task.
A genetic algorithm is a simple model of evolution in nature, realized as a computer program. Both the analogue of mechanism of genetic inheritance and analogue of natural selection is used in it. Biological terminology is thus saved in the simplified kind.
To model an evolutional process, we will generate in the beginning casual population, a few individuals with the casual set of chromosomes (numerical vectors). A genetic algorithm imitates the evolution of this population as cyclic process of crossing of individuals and digenesis. A life cycle of population is a few casual crossings (by means of crossing-over) and mutations as a result of which to population some amount of new individuals is added.
A selection in a genetic algorithm is a process of forming of new population from old, old population perishes whereupon.
A selection in a genetic algorithm is closely related to principles of natural selection in nature.
After a selection to new population the operations of crossing-over and mutation are again used, after again there is a selection, et cetera.
Thus, the model of selection determines how it is necessary to build population of next generation. As a rule, probability of participation of individual in crossing undertakes to his proportional adjusted. So urgent strategy of elitism, at which a few best individuals pass to the next generation without changes, is often used, not participating in a crossing-over and selection. In any case, every next generation it will be on the average better previous. When the adjusted of individuals stops to be increased, a process is stopped and as a decision of task of optimization take the best from the found individuals.
Going back to the task of construction of optimum plan, it is necessary to explain the features of realization of genetic algorithm in this case:
- Individual = variant of decision of task = set from m chromosomes of Xj, where m is an amount of wares, producible an enterprise;
- A chromosome of Xj = a volume of output of products j = 16, it is a bit record of this number.
Because the volumes of products are limited, not all values of chromosomes are possible. It is taken into account during the generation of population. The mechanisms of crossing-over (crossings) and mutation will realize elective part, and a selection of the best decisions is the gradient lowering.
That, if on some great number a difficult function is set from a few the variables, then a genetic algorithm is the program which for possible time finds a point, where a value of function is enough close to the maximally possible value. Choosing an acceptable checkout, get the best decisions which can be got for this time.
Stand a genetic algorithm generates initial population casual appearance. Work of genetic algorithm presents an iteration process which proceeds until the set number of generations or any other criterion of stop will not be executed. In every generation of genetic algorithm a selection will be realized proportionally adjusted, crossing-over and mutation.
At first, a proportional selection appoints probability to every structure Ps(i) equal to attitude of its adjusted toward total adjusted of population:
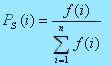 (4)
(4)
Then there is a selection (with a substitution) all n individuals for further genetic treatment, according to a size Ps(i). At such selection the members of population with high adjusted with greater probability will get out more frequent, than individuals with low adjusted. After a selection, n select individuals broke up on casual appearance n/2 pair. For every pair with probability Ps a crossing-over can be used. Accordingly, with probability 1–Ps a crossing-over does not take place and those individuals pass to the stage of mutation. If a crossing-over takes place, the got descendants replace parents and pass to the mutation.
We will define concepts now, answering mutations and to the crossing-over in a genetic algorithm.
A crossing-over is an operation at which from two chromosomes one or a few new chromosomes are generated. One-point crossing-over works as follows. At first, one of length–1 points of break gets out casual appearance. (A point of break is an area between nearby bats in a line.) Both paternal structures in this point are torn on two segments. Then, the proper segments of different parents stick together and go out two genotypes of descendants.
Since the stage of crossing-over is closed, the operators of mutation are executed. In a line which a mutation is used to, every bit with some probability changes on opposite. Population, got after a mutation, passes the stage of elite selection. This method of selection guarantees it will survive the best or the best members of population of aggregate.
Next generations are processed in like manner: selection, crossing-over and mutation.
As it applies to our put task every individual consists of array X and values of function F on variables, extracted from this array.
We use in the program a genetic algorithm, consisting of the followings steps:
- Generation of initial population, using strategy "focus", is filling of population individuals in which array cells X (bats) filled by casual appearance within the limits of scopes, certain an user.
- Choice of paternal pair by the method of roulette, i.e. method of proportional selection. Chromosomes are represented as cutting-off of lines or sectors of roulette all the same by appearance, that their size is proportional to the value of objective function. Further numbers casual appearance generate in an interval from 0 to 1, and those individuals get out as parents, random numbers get in whose segment. The numbers of chromosomes of parents must differ thus.
- A crossing-over takes place as follows: we take a casual point t on an array X (0..length–1). After it exchange parts of chromosomes (bats 0-t fill a new individual (descendant) the elements of the first paternal individual, and other elements are filled from the array of the second paternal individual; for the second descendant done vice versa). Thus, we choose fourth part of pair of parents from the initial size of population and on their basis get descendants in an amount a half from the initial size of population. We use an one-point crossing-over. Got individuals – descendants is added to population.
- All individuals execute mutation with some probability – the casual bit of array is inverted X to this individual.
- We abbreviate intermediate population on an elite chart – the again built streams replace worst parents, in obedience to the values of objective function.
- If the best decision in population dissatisfies us, then passed to the step 2.
Along with the traditional methods of prognostication today the theory of artificial neuron networks, which well showed oneself in area of management, develops stormily, wherein application of human intellect is needed, in particular at the decision of tasks of prognostication.
Neuron networks are new and very perspective calculable technology, which is giving the new going near research of dynamic tasks. Neuron networks well befit for the task of prognostication of issue of products in the conditions of incomplete or surplus, partly contradictory information of high-cube. The forecasting system uses a weekend information for the moments of time k+1, k+2 etc. as datains for prognostication on the moments of time k+2, k+3 etc.
Studies on the chosen topic, we can conclude the following: the success of any enterprise depends on a properly developed strategy production, production planning involves determining the range, scope and product release dates, based on a forecast, made ??an analysis of existing systems and subsystems in conclusion, by the urgency of a subsystem planning and forecasting of production in the company SV-Plast" ltd, a review of methods for planning and forecasting production. The analysis showed that the most suitable is the use of neural networks and genetic algorithms due to the fact that both of these methods will solve problems in which the source data may be incomplete, which is consistent with the requirements for the task.
- Solodukha OV "Development of computer subsystem of scheduling and forecasting of products issue in the condition of sewing enterprise joint-stock company of the closed type "DOTI""
- I. Hassan Hascer "Development of a computerized system for demand forecasting and production of textile products in Syria" [electronic resource]: summary / I. Hassan Hascer - Donetsk: Donetsk National Technical University, 2007. - Mode of access: http://masters.donntu.ru/2007/kita/ismail/diss/index.htm
- Бокун И.А., Темичев А.М. Прогнозирование и планирование экономики. – М.: Наука, 2002.
- Оптимизация ассортимента в условиях кризиса [Электронный ресурс]: Идеи продвижения на рынке одежды и обуви / Д.А. Пикалова //IT Manager – 2008. – Режим доступа: http://subscribe.ru/archive/ industry.lind.apparel/200811/06110801.html.
- Бухалков М.И. Внутрифирменное планирование: Учебник. – 2-е издание., испр. и доп. – М.: ИНФРА-М, 2000.
- Кузин В. И., Шахдинаров Г. М., Юрьев В. Н. Методы и модели управления фирмой: Учебник для вузов. – СПб: ПИТЕР, 2001.
- Подлазов М.К., Знаменский А.К. Экономика, организация и планирование трикотажного производства. – М.: Легкая индустрия, 1975.
- Волков О.И. Экономика предприятия. – М.: Инфра-М, 2001.
- Каменицер С.Е. Справочник экономиста промышленного предприятия. – М.: Экономика, 1974.
- Сытник В.Ф., Карагадова Е.А. Математические модели в планировании и управлении производством: Учеб. пособие для вузов. – К.: Вища шк., 1985.
- Механизм виртуозного управления [Электронный ресурс]: официальный сайт компании ООО Марка / В.Г. Бойко. – 1995–2007. – Режим доступа: http://www.virtuoso.com.ua/about_virtuoz.
- Фогель Л., Оуэнс А., Уолш М. Искусственный интеллект и эволюционное моделирование. – М.: Мир, 1969.
- Специализированная комплексная информационная система TechnologiCS [Электронный ресурс]: официальный сайт CSoft. – 2000–2008. – Режим доступа: http://www.technologics.ru/program.
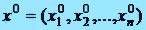 at which objective function f arrives at the least or most value (2).
at which objective function f arrives at the least or most value (2). (2)
(2)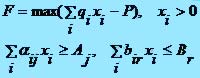 (3)
(3)
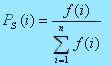 (4)
(4)