Abstract
Content
- 1. Basic characteristics of work
- 2. Analysis, systematization and generalization of previous research
- 3. Physical and geographical conditions of the area
- 4. The process dynamics of air pollution in the zone of influence of the waste dump for 2007-2009
- 5. The dynamics of the process of pollution of soils in the zone of influence of sludge pit during 2007-2010 years
- References
Basic characteristics of the study
The relevance of the research
The relevance of this research is in the fact that in the Donbas there were a very serious environmental situation. Donbas is the main industrial region of Ukraine, which has a large number of coal mines and coal-processing businesses that are located in close proximity to residential areas, and having a negative impact on the human health and ecological situation in general.
The main adverse factors associated with the processing of coal is the accumulation of huge masses of coal waste, which are located close to the city borders and have a negative impact on an environment. “The Mospino coal processing enterprises” includes sites with high environmental hazards: breed and dump sludge pit. Waste coal has a high concentration of a variety of toxic elements which through air and water can have an impact on different components of the environment. Areas of combustion and oxidation in the dumps can generate hazardous components such as: sulfuric acid, sulfur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen. Anaerobic conditions result a formation of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide. The combination of all this conditions is causing a danger to the environment and to people in surrounding areas, that’s why, a comprehensive study of negative processes, conditions, and their dynamics is a very relevant task to complete.
The Connection between the study and scientific programs, plans, and topics
The study was made based on materials obtained from the process of monitoring air, soils, underground and surface water in the zone of influence of coal washing waste disposal sites of LLC "Mospino Coal Enrichment Plant" in accordance with the program of environmental activities of local importance. The work is done in collaboration with GWP "Artyemovskaya hydrogeological party" Artyomovsk.
Master's study corresponds to the state of scientific program "The government ecological program of environmental monitoring" (Chamber of Ministers of Ukraine 05.12.2007 № 16761), as well as the "Strategy of Environmental Policy of Ukraine 2020". Topic of this study is connected to the regional programs: № 3/25-656 "Scientific and technological development of the Donetsk Region until 2020"; № 6/4-086 "Waste Management of the Donetsk Region for 2011-2015"; № 6/9-219 "Economic and social development of the Donetsk region in 2012 and the main directions of development of the 2013 and 2014".
Also, the need for these studies justified by a number of normative documents: “Ukrainian law Of Environmental Protection” from 25.06.91. (article 22); “Ukrainian law of wastes and land protection”; Resolution of the Chamber of Ministers of Ukraine № 391 from March 30, 1998.: "Regulations of the State Environmental Monitoring System"; Resolution of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine dated August 20, 1993, № 661: "Regulations on land monitoring".
The purpose and objectives of the study
The main purpose is to monitor the spatial and temporal dynamics in the processes of contamination, as well as determination of the level of risk and the extent of pollution in the zone of influence of the waste dump and sludge tanks, LLC "Mospino coal processing plant."
The key objectives of the study:
- Data processing of monitoring of air, soil, underground and surface water and zones of influence of the waste dump and sludge pit of Mospino LLC.
- Mapping halos pollution, construction of a set of maps that reflect the dynamics and trends of that pollution.
- Determination of the level and extent of air and soil pollution in the area of influence of the waste dump, as well as soil and subsoil, surface and underground water in the area of influence of sludge pit;
- Delimitation of zones of influence of monitoring facilities - waste dump and sludge tanks
- The study of the dynamics of the processes of environmental pollution in the areas of influence of the waste dump and sludge pit.
The object of the study
The object of ecological and geochemical study is the zone of influence of breed and dump sludge pit, LLC "Mospino Coal Enrichment Plant".
The subject of the study
The subject of the study is air, soil underground and surface water
Research Methods
- The method of systematic analysis of available information
- Field work (geological and ecological routes, a survey of the waste dump, sludge tanks and adjacent areas, sampling)
- Chemical analyzes of samples taken
- Methods of data processing with the use of statistical techniques and the use of modern software
- The Method of spatial analysis
- The Method of structural analysis
- The Method of graphical analysis.
The scientific exclusion of the results
- The study of the dynamics of air pollution due to waste dumps allowed to establish a change in the main polluting components - sulfur dioxide, ammonia and hydrogen sulfide, which is due to changes in operating conditions and dump waste conversion processes
- Soil pollution on the territory adjacent to the sludge pit directly related to the geochemical specialization of waste coal, a change in which is accompanied by changes in the spectrum of indicator elements of pollution
- The sludge pit formed a technological hydro geochemical zoning, which is set by the zone of its influence
The practical value of the study
The practical value of the study is in the complex geological and environmental assessment of the level and extent of the influence of waste dumps and sludge pit coal processing plants. Tracking the dynamics of pollution allows the change in the prioritization in environmental monitoring system, the establishment of buffer zones.
Personal contribution of the author
The author participated in the field work on monitoring of soils, underground and surface water, processed, analyzed and organized the data.
Testing results.
The results were used in the preparation of production reports. Also used in the article "Environmental problems in connection with the enrichment of coal", that is being prepared for publishing in the collection of Donetsk National Technical University.
4. The process dynamics of air pollution in the zone of influence of the waste dump for 2007-2009.
Air quality in the study area as a whole determines the relatively high regional background, typical for industrial area of the Donbas, which includes all the objects of Mospino SCP.
Emissions have a significant effect on air quality in surrounding areas and being spread by air 100 of kilometers; forming a large-scale dispersion haloes of various harmful substances.
Emissions of sulfur dioxide, carbon oxide, nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen sulfide can be carried by the dump in the process of physical-chemical, microbiological transformation of waste, accompanied by an increase in temperature inside the pf the dump. Coal wastes are composed of scattered pyrite (FeS2), which in the presence of oxygen and water is readily oxidized to produce heat. This forms an insoluble iron hydroxide (Fe2O3*n H2O) and gas - sulfur dioxide (SO2), which partly evaporates into the atmosphere, partially oxidized further forms sulfate ion (SO42-) and increases the aggressiveness of pore water waste. Raising the temperature in individual foci may lead to partial fire (or oxidation) of the organic portion of coal waste, which is in a shortage of oxygen will contribute emissions of carbon monoxide (CO). In addition, the organic portion of coal contains sulfur and nitrogen oxides which are formed in areas of the combustion of waste and released through its thickness by capillary pore system into the atmospheric air. In terms of lack of oxygen anaerobic processes are being developed, whose main product is hydrogen sulfide. Since by the oxygen saturation dump is heterogeneous, that means that even in different parts of it can appear the various processes of thermal conversion of waste. Combustion in a sufficient amount of oxygen leads to the formation of rocks burnt red color. With a lack of oxygen produced dark gray to black color rocks. Both types of burned rocks appear within the studied dump. In the period from 2007 to 2009 was studied the dynamics of the behavior of major air pollutants at the observation points (-320, 320, 640 and 1000 m) in the zone of influence of the waste dump. During laboratory research were found the concentration of dust, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen sulfide. Also were determined the main climatic characteristics: speed and direction of wind, temperature, relative humidity and barometric pressure. At the point -320 m to influence, major pollutants exceeding PDKm.r. were nitrogen dioxide (in May 2009) and dust (in July 2008). The other components in the different periods of control remain within normal values (Fig. 4.1).
In the under torch zone at a distance of 320 m from the waste dump in May 2007 and during 2008, all pollutants are remained within the standard indicators. However during 2009, the concentration of nitrogen dioxide and hydrogen sulfide exceed the MPC.
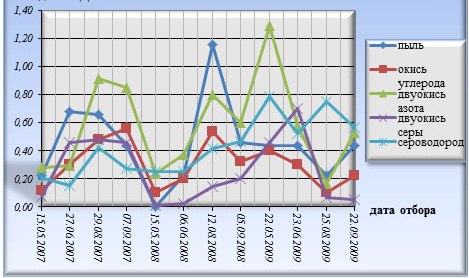
Figure 4.1 – Distribution graphs of components monitored in the air in the zone of influence of dump during 2007-2009 Checkpoint -320 m

Figure 4.2 – Distribution graphs of components monitored in the air in the zone of influence of dump during 2007-2009 Checkpoint -320 m

Figure 4.3 – Distribution graphs of components monitored in the ambient air in the zone of influence of dump during 2007-2009 Checkpoint 640 m

Figure 4.4 – Distribution graphs of components monitored in the ambient air in the zone of influence of dump during 2007-2009 Checkpoint 1000m
In the summer from June to August, there is a growth of concentration of all components monitored. Since the maximum permissible concentration observed in July 2007-2008, nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen sulfide and dust, and a gradual decline in their concentrations in August. Revealed high concentrations of sulfur dioxide in June 2007 and in July 2009, and carbon monoxide in July 2008 (Figure 4.2).
In the under torch dump area at a distance of 640 m from May 2007 and during 2008, the concentrations of all monitored components are within normal values. Only in 2009 there is maximum excess of nitrogen dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in comparison to the previous stages. In the summer the maximum permissible concentration of hydrogen sulfide and nitrogen dioxide were found only in July 2008. (Figure 4.2).
At a distance of 1000 m from the dump excess of MPC for nitrogen dioxide and hydrogen sulfide was found in May 2009.In the remaining periods of monitoring the concentration of the all controlled ingredients was within limits.
Thus, in 2009, there has been some increase in the concentrations of nitrogen dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in an observation post at a distance of 320m from dump relative to other periods of control. As the distance from the dump to the distance of 640m to 1000m concentration of all the components is gradually reduced to normal values and approaches the level of the regional background.
1. Алехин В.И., Мигуля П.С., Проскурня Ю.А. Минералого-петрографические и эколого-геохимические особенности пород терриконов Донбасса (на примере Донецко-Макеевского промышленного района) // Сб. научн. тр. НГА Украины. – Днепропетровск. – 1998. – Т. 5, №3. – с. 35-39.
2. Алехин В.И., Проскурня Ю.А. Экологические аспекты геохимии породных отвалов шахт// Сб. мат. конф. ”Актуальные проблемы геологии Украины”. – Киев. – 1998. – 53 с.
3. Изучение шахтных терриконов Донецко-Макеевского района как новых видов минерального сырья / Панов Б.С., Алехин В.И., Мигуля П.С. и др. // Отчет по НИР. – Донецк: Фонды ДонГТУ. – 1993. – 70 с.
4. Зборщик М.П., Осокин В.В. Предотвращение самовозгорания горных пород. – К.: Техніка, 1990. – 176 с.
5. Зборщик М.П., Осокин В.В. Предотвращение экологически вредных проявлений в породах угольных месторождений. – Донецк: ДонГТУ, 1996. – 178 с.
6. Панов Б.С. Некоторые вопросы экологической минералогии Донецкого бассейна // Минералогический журнал. – 1993. – Т. 15, №6. – с. 43-50.
7. Веселовский В.С., Алексеева Н.Д., Виноградова Л.П. Самовозгорание промышленных материалов. – М.: Наука, 1964. – с. 242.
8. Саранчук В.И. Окисление и самонагревание угля. – К.: Наук. Думка, 1982. – 168 с.
9. Скочинский А.А., Огиевский В.М. Рудничные пожары. – М.: Углетехиздат, 1954. – 387 с.
10. Паспорта мест удаления отходов ООО «Моспинское углеперерабатывающее предприятие», регистрационные № № 79 и 80 от 28.19.04.
11. Алексеенко В.А. Экологическая геохимия. М.: Логос, 2000. 627с.
12.Отчет о проведенной температурной съемки породного отвала, принадлежащего ООО «Моспинскоеуглеперерабатыеающее предприятие» и ГО АО ЦОФ «Моспинская». Научно-производственная внедренческая фирма «Экор-ост». Донецк, 2007.
13. Определение минерального состава и концентраций макро- и микрокомпонентов отходов углеобогащения ООО «Моспинское углеперерабатывающее предприятие». Технический отчет. ООО ПГП «Артемовская гидрогеологическая партия». Донецк. 2006.
14. Проведение экологического мониторинга в зоне влияния мест удаления отходов углеобогащения ООО «Моспинское углеперерабатывающее предприятие». Технический отчет. ООО ПГП «Артемовская гидрогеологическая партия». Донецк, 2007.
15. Проведение экологического мониторинга в зоне влияния мест удаления отходов углеобогащения ООО «Моспинское углеперерабатывающее предприятие» в 2008 г. Технический отчет. ООО ПГП «Артемовская гидрогеологическая партия». Донецк, 2008.
