Abstract
content
- Introduction
- 1. ANALYSIS OF BUILDING DESIGN
- 1.1 General description of the design object
- 1.2 Analysis of the existing telecommunications network, and the rationale for the transition to NGN
- 2. Synthesis of networking concept
- 2.1 Selecting the network topology
- 2.2 Selection of technologies for the provision of telephony services in the access layer
- 3. IP-network design
- 3.1 The distribution of IP addresses to network
- 3.2 Testing the backup route
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Conditions for the formation of the market in Lebanon is determined to modern telecommunications operators specific tasks aimed at accelerating the implementation of important social and economic problem - Information cities and towns of all sizes, the entry to the global information infrastructure. Field of telecommunications is constantly updated, is in need of constant development and investment.
Until recently, the telephone and data networks of large cities in our country have been completely analog. After the de-monopolization of the market and the emergence of various private enterprises connection problem in providing various telecommunications services to new subscribers. Furthermore, existing subscribers have started load more than it was previously (development ²nternet, multimedia services, increasing the average talk time). These changes also affected the city of Beirut. Every year in Beirut subscriber density increases, due to the volume of information that is transmitted through the information and communications infrastructure is increasing every year and sets new requirements for the quality of services.
Along with the increasing number of communication services changed their quality - from a simple telephone service for multimedia services that will be provided by integrated digital communications networks.
Principles of construction of analog networks are not suitable for digital because of the inconsistency indicators of current and future resources and communication systems. Furthermore, the construction architecture of analog and digital networks differ in orientation with regard to the developers of the development of network services based on the architecture and functionality of the digital telephone network to access converged NGN.
Modern telecommunications network not only to ensure the establishment of a common person connections, but also give them access to additional services. The use of technology ADSL data can be a wonderful solution to this problem for customers who already have a phone line. The implementation of such a system in connection to allow users to rapid exchange of information while reducing the cost of telecommunications. For new customers the operator can offer connectivity in the last mile technology Ethernet.
In this paper, we developed the basic solutions for the modernization of the telecommunications network operator «OGERO» to access the network NGN.
The aim of this work - the development of the project for the modernization of the telecommunications network g.Beyrut administrative center for providing advanced telephony services and transmission dannyah and the transition to a network NGN. To fulfill this goal should be to solve the following problem:
- To analyze a design object model to develop an information network.
- Put the requirements for network services and quality of services.
- To calculate network traffic for telephony and data access layer, core, calculate the load on the transport channels in the areas of access to resources on the network and to other networks.
- Select implementation technology network access and kernel-level data and provide voice services.
- Develop structural and functional network diagram, provide a description of the network nodes and channels, as well as the interfaces and protocols.
- Select hardware solutions for the construction of a corporate network.
- Develop a SCS, the wiring and to configure basic equipment.
- For the analysis of the results of design to simulate the network segment, to assess the functioning of its basic characteristics.
- To calculate the economic indicators of the project implementation.
- Put requirements for the protection and security of the company that will provide telecommunications services.
1.ANALYSIS OF BUILDING DESIGN
1.1 General description of the design object
In this paper, the design of the NGN network is performed for the central area of Beirut (Lebanon). During the design will upgrade the existing telecommunications network operator «OGERO».
Beirut - the capital and largest city of Lebanon, a major sea port. Beirut is not only the capital of Lebanon, but also financial and banking center in the country and the region as a whole. In Beirut, the most important banks and commercial organizations in Lebanon, and offices of many international organizations.
Also in the economy of Beirut plays an important role seaport, which is one of the most important ports in the eastern Mediterranean. Port of Beirut serves except Lebanon and Syria, Iraq and Iran. Annually through the port passes over 3,000 ships. Port of the Lebanese capital related road or rail connection to Damascus, Baghdad, Tehran and Haifa.
The economy of Beirut diversified. In her present and sufficiently large publishing companies, banks, trading and industrial enterprises.
Among the industrial enterprises of the textile in Beirut, skin enterprises and enterprises in the food industry. Many of the companies are small and medium-sized businesses, which is prevalent in Beirut. The main export products of enterprises Beirut are fruits (citrus, apples, etc.), olive oil, silk - raw and wool.
In addition to government organizations located in Beirut offices of many international organizations such as the Commission for Economic and Social Policy in Western Asia, United Nations, International Labour Organization, UNESCO, and others.
Map of the administrative center of the city is represented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.Design District
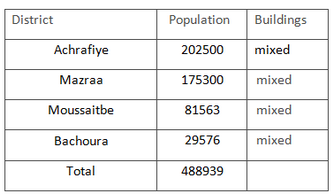
Population distribution by area of Beirut is presented in Table 1.
Table 1.Distribution of the population of the city by districts
In Beirut, there is a national telecommunications operator «OGERO» and mobile operators «Libancell» and «Cellis» and many small regional operators of cable television and data services, Internet.
1.2 Analysis of the existing telecommunications network, and the rationale for the transition to NGN
The greatest among the operators are taken in a «OGERO», which covers the largest part of the subscribers of the city. The operator provides services to the population analog phones, ADSL-Internet speeds of up to 2 Mbit / s. Thus, the existing network can not meet the need for residents of the city with modern telecommunication services.
Distribution subscriber telephone network Beirut built on the principle of the cabinet without the use of technology multiplexing subscriber lines. Analog subscriber lines, in most cases the pulse dialing method, but in some cases (modern equipment) can be used as a tone and pulse dialing.
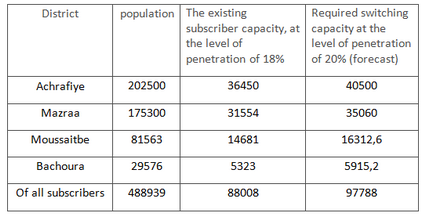
The maximum capacity of the existing telephone network is 90,000 subscribers, the number of used numbers - 87492 . The level of market penetration of services - 18%, while the telephone is available capacity is almost used up. The network uses a physically obsolete equipment. In addition to the replacement of equipment will increase the network capacity, namely its subscriber capacity. According to the results of the analysis of the demand for NGN services novih the population identified the need to provide digital telephony services, expanding the list of additional services, and bringing the level of penetration in the period 5-10 years to 20% with the possibility of increasing the capacity of the network in the future.
Telephone network of the city is included in the transportation network of Lebanon on the Rights of the individual node area.
The distribution of the PSTN subscriber base by area is shown in Table 2.
Table 2.Distribution of the PSTN subscriber base by districts Beirut
The profitability of traditional telecom operator «OGERO» reduced. The cause of the declining trend in the profitability of the traditional business of the operator due to the fact that the conventional fixed-line service is in demand only in the segment of low-income and non-demanding users. And most solvent customers need is not just a call, but to have a network connection to access numerous opportunities and services.
The supply side access to the Internet Service Provider can not provide the speed, which now need to subscribers for broadband access, because the maximum speed for the majority of users that can provide operator in Beirut - 2 Mbit / s. In addition, the city, there are small providers that provide access to the network ²nternet with speeds up to 10 Mbit / s (home network), but they do not provide telephony services and ²PTV, and multiservice networks are not.
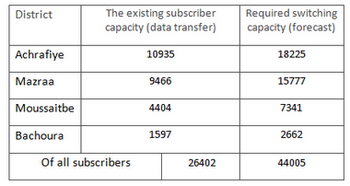
The number of subscribers who use data services is 30% [5] of the number of telephone subscribers by districts. The operator plans to increase the number of users of data services to 45%.
The number of existing and prospective customers for data services predstavlenav Table 3.
Table 3.Distribution of subscriber data services by districts
Thus, the telephone network, the Beirut enough "digitalized". Inter-station communication to a greater extent "digitalized" using digital trunks. In addition to using the technology of the equipment E1 SDH.
With increasing number of subscribers in a network of beams SL becomes large, the capacitance decreases, and their use. Capacity of the telephone network now reaches more than 80% load. The density of subscribers will increase as the level of market penetration of telecommunication services.
In terms of reliability, network control and normal docking data systems used by more than two types of CSK, which negatively affects the management of the network and, accordingly, on the management of traffic.
The topology of the backbone network organization - mixed. Each district communication is the center of a star topology, from which derive the channels and connected to a communication of another district on the base topology "point to point".
Such networks are used by dedicated digital and analog lines. Each type of topology of the access network in the district - the "star", the center of which is the central area of the router for data transfer and district PBX for telephony. The last level in the hierarchy of the organization is a telecommunications network, end users - residential subscribers, offices, government organizations.
Thus, the main features of the existing network is:
- telephone network load of 80%;
- congestion data network 75% at maximum unwarranted access speed of 2 Mbit / s;
- low level of digitalization;
- almost exhausted the installed capacity of the network access to telephony;
- lack of quality service QoS makes it impossible to provide services in real time (video, IP telephony, and others).
Thus, the capacity of the existing telephone network Beirut needs to expand, moreover, to the development of data networks subscribers require operators to expand the range of services and cost reduction in noises. These needs can be satisfied subscribers with the following design decisions:
- The modernization of the telephone network through the establishment of a new modern digital switching equipment;
- The transition to IP technology All over the transport layer (IP Backbone) between the support equipment and outside switch modules to reduce the cost of connecting lines;
- Increase channel capacity and transmission power switching data network equipment.
With the modernization of the urban segment of the phone system is important not only to ensure the establishment of a common person connections, but also give them access to additional services. The implementation of modern communication system will provide people and businesses the opportunity for rapid information exchange, while reducing the cost of telecommunications.
2. Synthesis of networking concept
2.1 Selecting the network topology
As the switching systems in the network will be used by modern station 5ESS Rel.16.1 5E-XC Softsw³tch.
5ESS switching system is a versatile phone system with distributed control. Versatility 5ESS terms of use on the communication networks is provided: a modular architecture, hardware and software, a wide range of capacities AL; possibility of direct access to the network at the level of the synchronous transport module STM-1 (Synchronous Transport Module), as well as G³gab³t Ethernet; presence of various interstation interaction methods, in particular the OCS and 7 S³gtran (MEGACO). All of these parameters are used to TK. In the upgraded network switching system will be composed of PBO and 3 offsets MMRSM with a maximum capacity of 50,000 subscribers each. Subscribers of the area where it is found PBO will be incorporated directly into the SM.
After analyzing the possible options for the network topology, and given the geographical aspects of the area and the location of the possibility of switching nodes, we conclude that in order to achieve scalability and performance, is the most reasonable topology "Ring" at the transport layer, and the hybrid hierarchical "tree-Star" at the level of access .
The advantage of this topology is that, compared with other topologies it has better fault tolerance, as it includes all the best qualities of these topologies.
In this project the backbone network will be organized in a ring that will integrate the transport network routers. To transport network routers will be included switching equipment - vinosnye switching modules MMRSM and support equipment SM / CM. Network access and distribution, in turn, will be represented by a tree-topology star - callers will be connected to busbars of streets, houses and porches, which will include a R²SLU to MMRSM. Through SM / CM exits to the AMTS and PSTN transport network SDH. To transmit the user data to be included in DSLAM, which are connected to the access routers. Access routers will be included in the core routers.
Core router will be included in a large ring that unites the districts of routers and networks of higher-level (field and national scale) of it is provided access to the Internet.
2.2 Selection of technologies for the provision of telephony services in the access layer
Based on the fact that the city of Beirut at the operator already has a well-developed telephone network subscriber access, the modernization of the equipment replaced will only switching telephone network and the customer will have no significant changes.
Legacy telephony access layer may be provided on the protocols V 5.1 and V 5.2.
V5 - Technology access to the network. Standards V5 (V5.1-ETS 300 324-1 and V5.2-ETS 300 347-1) should provide an interface between the access network and the telephone exchange to support narrowband communication services. V5 series standards specify the requirements (electrical, physical, procedural, and protocol) for network connections and central offices. The access network - a system between the terminal equipment and MMRSM member R²SLU that replaces part or all of the local distribution network. It provides a common interaction with devices such as analog PSTN phone, analog or digital PBX, ISDN terminal equipment of basic and primary access network edge equipment and line equipment which is rented. It also provides multiplexing of introduction, and the output data. The access network is responsible for recognition of tone bursts access analog signals, their duration, and frequency of the voltage pulses for ringing tone, as well as specific characteristics of the sequence signal. ATS is responsible for managing calls by providing switching forming tone bursts dialing numbers decoding and so on.
There are two types V5: V5.1 and V5.2. V5.1 protocol operates on a stream of E1 whereas the V5.2 protocol operates on a group of E1 (up to 16). Both of these protocols may use time slots 15, 16 and 31 for transmitting signals (of course, limitations on the distribution of signals over time intervals).
V5.1 interface operates in one flow for E1 data channels and control channels. It supports the following services: connection to the PSTN, ISDN basic access and leased line. Data channels are set in advance. Therefore, this interface can only support up to 30 channels of communication with the PSTN or 15 channels of ISDN basic access.
V5.2 interface can operate on a group (up to 16) E1. Therefore, it can support up to several thousand channels of data. This is because the data channels are allocated dynamically on request, and is also supported on the group call concentration flows. The concentration factor, as usual, is about 8. Due to the possible existence of multiple channels V5.2 enables the identification of the individual channels, which allows you to check the integrity of the stream. Some streams may be blocked for maintenance or when the characteristics of the data environment below satisfactory. In addition, this protocol is composed of security protocols designed to protect the signaling links, by switching the control channel of the stream to another defective defective stream. This protocol supports ISDN PR² in addition to all the services supported by V5.1.
The main advantages of the protocol V5.2:
- V5.2 is more of a service protocols, namely, channel assignment protocol, security protocol and protocol control channel.
- V5.2 uses additional reserve time slots to increase the security of communication.
- V5.2 can support up to 16 E1.
- The network layer interface V5.2 includes the following service protocols:
- protocol destination bearers (SCD);
- paths Management Protocol Interface (LINK Control);
- security protocol (Protect³on Protocol).
Thus, in total, at the level of access between the terminal equipment and MMRSM member R²SLU choose protocol V 5.2.
3. IP-network design
3.1 The distribution of IP addresses to network
Cproektovannaya multiservice telecommunication network has 44,005 subscribers with data services. The whole network is divided into 4 sections with a nodal point in each area. In order to optimize for each service area has been allocated its subnet. Addresses of network users will be given a dynamic DHCP-server.
To arrange a layer addressing the projected highway network needs to allocate address space for the organization of two-point networks, which are connected by global routes on a "point to point". To address the access level needed 4 subnets with 17-19 bit-mask. At the core level required mask 15. It is also necessary to allocate addresses for servers in the DMZ. Selected addresses of networks are presented in Table 4. Address to access the network resources - in Table 5.
Òàáëèöà 4. Ðàñïðåäåëåíèå àäðåñíîãî ïðîñòðàíñòâà çîí îáñëóæèâàíèÿ
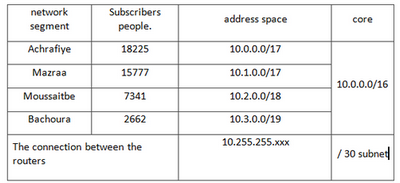
Table 5. Distribution of the address space area access to network resources
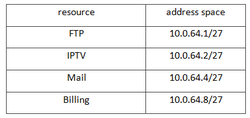
3.2 Testing the backup route
For each piece of equipment you need to set up your configuration file, which will include the address of network interfaces and routing tables, as well as some additional information. So check it out first create a model of the network - it is from the company C³sco is a software tool - Packet Tracer 5.3.2. Packet Tracer program offers several basic models of communication equipment and core technologies that are most widely used in corporate networks territorial. The model is not built in "full scale" and a little "lite", showing only part of the access network. Configure basic network nodes to carry out the program of Packet Tracer. The network model is shown in Figure 2.
Multiservice telecommunication network is divided into two levels: the level of access and trunk level. Main level is constructed of 4 routers that are connected to the ring and have access to core routers. At the level of access users is access via PPPoE.
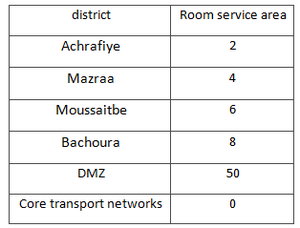
The telecommunications network will be divided into service areas for setting dynamic marshruizatsii OSPF. Each service area will have a corresponding service area, as shown in Table 6. DMZ zone will have a coverage area of 50. The transport network will have a core service area of 0. In the service area router ports include respective different levels, as shown in Figure 2.
Table 6.Distribution of the zones of OSPF routing
When you configure the NAT router must take into account that the subscribers of different tariff models have different access rights to services. Online access to a particular service is defined by the access list.
Thus, it is necessary to configure the access lists from the problem. Table 7 shows the classes of users access rights to the servers.
Table 7. Permissions classes of users to servers
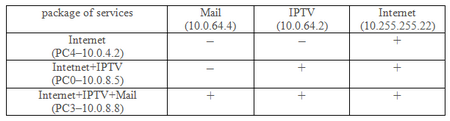
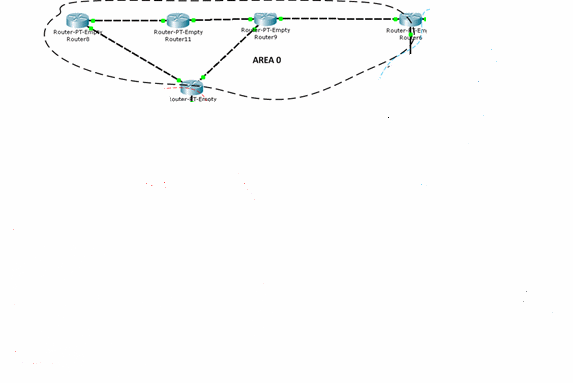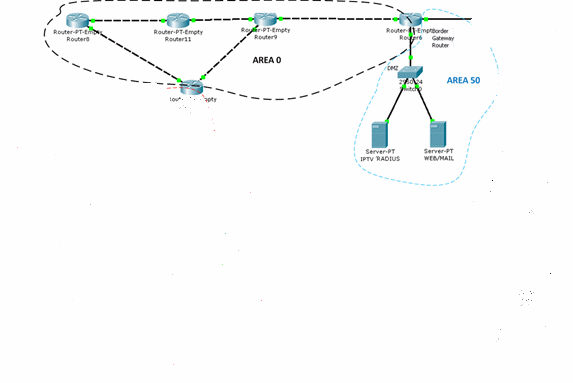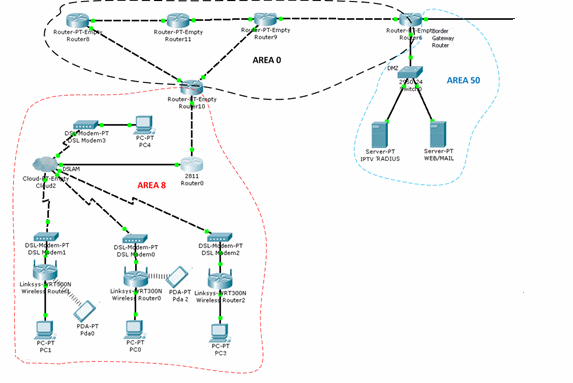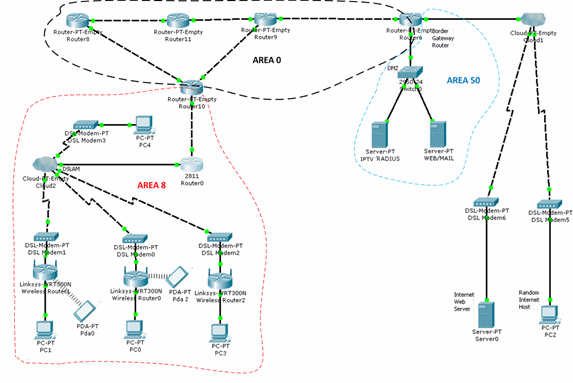
Figure 2. Model of a network in Packet Tracer
Conclusion
In this work, a design of NGN network for the administrative center of the city of Beirut. During the design was upgraded existing telecommunications network operator «OGERO» based on modern technology and IP switching center of a new generation 5ESS (Release 16.1 (5E-XC) Softsw³tch). In the developed network of subscribers to such services will be provided:
- Classic telephony;
- The Internet;
- ²PTV;
- Data transmission.
Services will be provided to the following categories of subscribers:
- Subscribers residential sector;
- Business subscribers;
- Subscribers administrative sector.
Calculation of traffic showed that the transport network (IP Backbone) between MMRSM and PBO will be based on the capacity of the channels 30 Gbit / s. At the direction of the GRO-AMTS must proklyuchit 21 channel E1, or 1 * STM-1 (63 E1). You must be connected to the PSTN 2 * STM-1 (2 * 63 E1). Internet needs to channel 10 Gbit / s.
Analysis of possible solutions for the construction of topological network showed that for scalability and performance, the most reasonable topology looks like a "ring" at the transport layer and a hybrid hierarchical "tree-star-star" level of access.
By the routers will be connected to the transport network switching equipment - vinosnye switching modules MMRSM and support equipment SM / CM. Network access and distribution, in turn, will be presented topology "star-tree-Star" - callers will be connected to busbars of streets, houses and porches that through R²SLU will be included in MMRSM. Through SM / CM exits to the AMTS and PSTN transport network SDH. For data subscribers are connected to the DSLAM, which are connected to the access routers. Access routers will be included in the core routers.
At the level of access between the terminal equipment and MMRSM member R²SLU selected protocol V 5.2. For data services chosen technology ADSL 2 + on the "last mile" and Ethernet (G³gab³t Ethernet) connection-level DSLAM access router. The transport network will be based on technology G³gab³t Ethernet.
Support equipment operates MMRSM means S³gtran protocol. To optimize the data transmission in the network to be used routing protocol OSPF.
For the construction of the transport network data most flexible and versatile, supporting the required number of ports and is easily integrated into the IP network provider is the equipment of C³sco, namely routers C³sco 7609 at the kernel level, 2811 at the access level. Based on the fact that the network has used DSLAM Huawe³ 5300, to upgrade the network equipment that we choose the same vendor, but with more capacity and more modern, namely Huawe³ DSLAM 5603.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2013. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Olifer VG Olifer NA Computer networks. Principles, technologies, protocols. - M. Peter, 1999. - 672s.
- LA Ponomarenko Shchelkunov VI, Sklyarov AY The tools of design, simulation and analysis of computer networks: Studies. allowance. - Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 2002. - 508.
- MO Chumak. 5ESS digital switching system and the features of its design: uch.posobie. - Delhi: UDAZ - 1998 p.
- Yuri Filimonov Construction of multi-service networks Ethernet. St. Petersburg.: BHV-Petersburg, 2007. - 592s.: Il.
- Marder NS Modern telecommunications. - M. IRIAS., 2006 - 384 p.
- V. Velichko, EA Subbotin, V. Shuvalov, AF Jaroslavtsev. Telecommunication systems and networks. Volume 3. Multi-service networks. Textbook. In three volumes. - M: Hotline Telecom, 2005.-592 p.: Ill.
- Metodichn³ vkaz³vki to graduate proektuvannya for student³v spets³alnost³ 7.092401 "Telekomun³kats³yn³ system is the network" (zm³st, structure, rules of registration). / UKL.: V.². Bessarabia, VO Popov, R. Fedyun that ³n. - Donetsk, Donetsk National Technical University, 2003, 26 p.
- Dokumentats³ya through the settings obladnannya f³rmi Cisco www.cisco.com
- Computer networks / YA Kulakov, GM Lutsk - K., Junior, 1998. - 384s.
- A.Retana, D.Slays, R. White. The principle of proektuvannya corporate IP-based networks. "V³lyams", 2002. - 368 p.
- A. Tanenbaum, Computer Networks. - St. Petersburg: Piter, 2003
- Overview produktoov and solutions company Cisco Systems / G. Bolshakov, etc. - Kiev: Cisco Systems, 2002. -84c.
