Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. A review of research and development on the topic
- 4. A mathematical model for the analysis of transients in the system of own needs
- 5. The main content of work
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
With all the changes in the electric circuit: turn off, short circuit, fluctuations in the value of any parameter, etc. – it arises transients, which may not occur instantly, as there is no instantaneous change in energy stored in the electromagnetic field of the circuit. Thus, the transition process due to the mismatch between the size of stored energy in the magnetic field of the coil and the electric field of the capacitor to its value for a new state of the chain.
Transients can occur large overvoltage, overcurrent, electromagnetic waves that can disrupt the operation of the device until its failure. On the other hand, transients are useful practical applications, for example, in various kinds of electronic generators. All this necessitates the study of methods of analysis of nonstationary modes of operation of the circuit.
1. Theme urgency
Calculated schemes of electric power stations of high power and electricity supply systems of industrial enterprises can arrive at significant size and to have a complex topology. So, for example, scheme of direct-current of one power units by power 800 MVt has 105 knots and 130 branches, has radial, circular areas.
In the most perspective domestic firms which are engaged in planning and building of energy objects for the calculations of currents of KZ the used programs of calculation are on PEVM. But such programs have a high cost.
In educational institutions, industrial calculation program, as a rule, can not be used because of their high cost. On the other hand they have a closed structure and can not be effectively used in the learning process.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
- The work purpose
- Idea of work
- The main probems of the researches
- The subject of the research
- The object of the research
- Methodology and methods of researches
In connection with the reconstruction of equipment on the electric stations appears necessity of permanent calculation short circuit currents. In a number of cases calculation schemes are difficult enough and there is a necessity of automation of process of calculation for them currents of KZ. The purpose of work is perfection the software department Electrical stations
associated with the calculation of short circuit currents.
Calculation of currents of KZ for the schemes of electric connections with dif-ferent classes of tension(to and higher 1 kV) on variable and on a direct current on a single computer technology with the use of matrix methods of nodal poten-tials.
Modernization of methods and algorithms of the programs of calculation short circuit currents of KZ with the purpose of increase of their functional possibilities and reliability of calculations.
Subject matter are the software products having the opened algorithm, whose implementation is made in the automation package MathCad mathematical calculations.
Methods and algorithms of calculating short circuit currents in electrical schemes alternating and permanent current.
In this work is used the followings methods:
a) methods of matrix analysis;
b) the method of nodal potentials in the classical kind and using the matrix of nodal resistances.
3. A review of research and development on the topic
The programmatic complex ENERGYCS for designing power systems Ivanovo State Power University.
The model, which is used to calculate the short circuit current, satisfies the most stringent requirements for the calculations to select the settings of relay protection. Currents of branches are brought to its nominal voltage. This takes into account the exact values of the coefficients of transformation of transformers and change in resistances of transformers winding when switching branches RPN and MSDSCalculation of the nodal voltages of a short circuit is produced by the method of Gauss, on tensions of knots are calculated currents in branches. For a calculation the emf at the initial moment of short circuit for the system, for generators, for synchronous and asynchronous motors are used in the program voltage in the steady state preceding the emergence of a short circuit, - the results of the calculation of the steady mode, taking into account of voltage regulators and the mode of active and reactive power. Actually, a complete calculation of the steady mode is produced for every calculation of currents of short circuit. The module of ENERGYCS TKZ is unconnected with the module of ENERGYCS UR and can be used quite independently. To obtain comparable results can turn on the program, in which the emf is calculated at nominal parameters - the results are consistent with obtained by other means (eg, manually or using other programs). However thus possible to get the overpriced or understated values of currents of short circuit. For today a programmatic complex ENERGYCS allows to decide the followings tasks within the framework of calculations of currents of short circuit:
- a calculation of initial values of currents of three-phase short circuits is in difficultly reserved networks;
- calculation of initial values of currents of single-phase to earth short circuit;
- calculation of initial values of currents of diphasic on earth short circuits;
- calculation of initial values of currents of diphasic without earth short circuits;
- calculation of currents in the cables of lines at short circuits on earth and estimation of their thermal firmness;
- calculation of capacitive currents of single-phase earth fault in networks with isolated neutral;
- calculation of shock of short circuit currents at three-phase the short circuit in accordance with ГОСТ 27514-87 [1];
- calculation of values periodic and aperiodic constituents of current of KZ at a given time;
- calculation of virtual value of current of three-phase KZ in the moment of disconnecting;
- calculation of integral of Joule in the moment of disconnecting, and also thermally equivalent and equivalent onesecond currents of short circuit;
- construction of vector diagrams of currents and voltages for arbitrary nodes and arbitrary branches network.
The program allows for a given point of the short circuit to consider the distribution of currents and voltages in all branches of the circuit, bring in the tables or on the schemes values of the maximum values of short circuit currents the phases, the currents in all phases of currents on symmetrical components, as well as to construct a vector diagram of currents for the chosen branch and vector diagram of voltages for the selected node.
During the calculation of asymmetrical short circuit at a given point the chart of a zero sequence is formed automatically. Forming of scheme is carried out on is based
- topological structure of a design scheme;
- information about the scheme groups connections the windings of the transformer and its mode of neutral;
- information about mutual influence of VL, passing in general corridors taking into account geometry of pendant of wires on support;
- information on the availability and method of grounding, grozozaschitnykh wire.
The results of calculations can be shown out directly on a chart or in tables. Final documents can be formed with the use of MS Word on the basis of the beforehand provided templates.
The program provides several options for presenting the results of the calculation of TDF(токов кз).
The first version determines the node, in which should consider the possibility of short circuit. get as a result, currents is a short-circuit currents in the site for three-phase, two-phase, one-and two-phase short circuit on the ground, and the importance of surge current and constant decay time of the free component. For every type of KZ distributing of currents is determined in all branches, and for all knots are remaining tensions (Fig 1).

Figure 1 – The results of the calculation of current distribution (TDF) for a short circuit at one point
In the second variant the program executes the calculations of TKZ for the great number of the indicated a nodal points of the scheme. In this case on a scheme can be shown out only values of currents in the selected knots, and in a table are currents in all selected knots and joinings to them branches. Except for the initial values of currents of KZ for all types of damages, in the table displays the regime parameters for the evaluation of the thermal and dynamic actions of the three-phase short circuit currents, ie for each branch adjacent to the node to the CP displays the results of the calculation of surge current, the Joule integral, thermally equivalent and equivalent odnosecond currents (Fig 2).

Figure 2 – The results of the calculation of TDF during a short circuit at several points
For the calculations of currents of KZ with the purpose of determination of setpoints of relay protection a foreseen the calculation of currents,flowing through a given branch of a short circuit in a given set of nodes. The example of table is resulted on a fig 3.

Figure 3 – Short-circuit currents in the control branch
The calculations of currents of earth-fault for networks with isolated neutral are produced a topological method in the same module and can be shown out on a chart or in tables along with the results of calculations of TKZ.
The example of calculation of TKZ for the system of own needs of thermal elektrostan-cii is rotined on a fig 4.

Figure 4 – Example of calculation of TDF for the system's own needs [2]
4. A mathematical model for the analysis of transients in the system of own needs
In fig. 5 the schematic diagram of electric system with asynchronous and synchronous electric motors is represented.

Figure 5 – Initial schematic diagram of the electrical system (animation: 5 frames, 5 cycles, 238 kilobytes)
The settlement scheme make on the basis of the set schematic diagram of electric system and equivalent circuits of its separate elements which with some simplifications are used in this work.
The settlement equivalent circuit is presented by resistance (active, inductive), resistance of switches, the KZ shunt, a grounding conductor and resistance of a stator of asynchronous and synchronous electric motors in capacity of 4000 and 6000 KW respectively.
For the description of the asynchronous engine we will use its double-circuit equivalent circuit which allows to consider rather precisely the phenomenon of replacement of a current in a rotor. Let's use a known method of receiving parameters of a double-circuit equivalent circuit on the basis of catalog data [3].
Salient Pole synchronous engines,for the purpose of possibility of ensuring asynchronous start-up are supplied with the starting winding which cores are put in polar boots of a rotor and electricly incorporate among themselves, and also to cores of the next polar boots. The so-called full starting winding in axes d and q and an excitement winding on an axis d is as a result formed.

Figure 6 – Equivalent circuit of the salient pole synchronous engine on an axis d [2]

Figure 7 – Equivalent circuit salient of the pole synchronous engines on an axis d [2]
Parameters of a winding of excitement:

where:
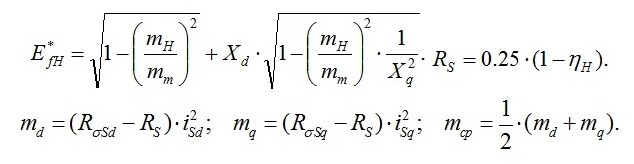
Mathematical modeling of transients is made for instant values of currents and tension. For this purpose we will use Ohm and Kirkhgof laws according to which it is required to work out the differential equations for currents and tension of branches and knots of the set scheme. Algorithms of calculations we will make on the basis of matrix methods.
5. The main content of work
At power plants and large power systems, power industry design schemes can achieve significant size and have a complex topology. Fig. 8 shows the electrical circuit supplying one of the mines of Donbass.

Figure 8 – Diagram of power supply one of the mines of Donbass
Fig. 9 shows a simplified equivalent circuit.

Figure 9 – Topologically equivalent circuit of a power supply circuit of one of the mines of Donbass
In this work considered software products with the opened construction of algorithms realization of which is executed in the package of automation of mathematical calculations of Mathcad.
As with the a manual calculation of short circuit currents at the first stage of works is formed calculation electric chart and the corresponding equivalent circuit of substitution. For the her elements from of the reference books or other sources take the required input data.
The equivalent circuit of substitution numbered at a small scheme, or symbolic identification of nodes. Are marked and the directions of currents in the branches.
In the program of calculation of currents of KZ a calculation chart appears the entrance matrix of description of branches V. In this matrix has an amount of lines equal to the number of branches of a design scheme, and a few columnsIn the first and second from them disposes-numbers or denotations of knots from which the current of branch goes out and in which this current is included. Resistances of branches are disposed in a next column. If necessary (in the case of different sizes) early as one column disposed E.M.F. branches. So, for example, in the schemes of main electric connections of power-stations size E.M.F generators can be about 1.2, and E.M.F. electric motors – 0.9.
The algorithms of the programs of calculation short circuit currents are built on the method of nodal tensions in the matrix form of record
 (1)
(1)
where Uu – vector of nodal voltages, Yu – a square matrix of nodal conductivities, Iu – vector of nodal currents.
Matrix Yu at the following
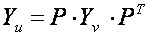 (2)
(2)
where P – the matrix of connections of nodes with branches , diagonal matrix of conductances of branches, Zv – vector resistance, branches, which must be obtained from the input matrix V.
Vector Iu from of EMF can be found as
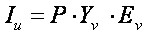 (3)
(3)
where Ev – vector EMF branches.
The matrix of connections R in the case of numerical numbering of nodes, her can be created using the following user function FormP
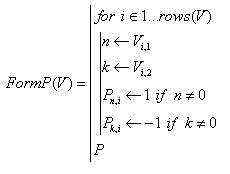 (4)
(4)
In the case of symbolic indexing of nodes in the above functions FormP will be changed conditional statements on the followings:
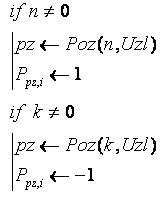 (5)
(5)
In the operators (5) is used function Poz for to determine the node number site for its symbolic notation in the vector Uzl.
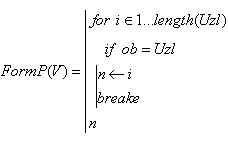 (6)
(6)
Vector of Uzl in the case of one level of tension of the nodes of a design scheme, for example in the schemes of alternating and permanent current by tension less than 1 kV, formed automatically from these denotations of knots of matrix of description of branches V by dint of the next function of Formuzl

Figure 10 – The function FormUzl to create a vector Uzl
At the calculation of scheme with a few degrees of voltage in As the input is formed the matrix of description of knots of Ub is formed, in which to on disposed columns: denotation of knot, sizes of middle base tensions, own tvv and complete tpv terms of disconnecting of switches and calculation term of action of relay defence of trz. Under ГОСТ 27514-87. Short circuits in electrical installations [4] calculations of the total values of periodic components of short circuit currents can be obtained using the input resistance of the scheme relative to the corresponding point of BB. Such resistance can be obtained by inverting the matrix of nodal conductivitie
 (7)
(7)
They are in the corresponding diagonal a elements of matrix of Zu. The current short-circuit in the i node
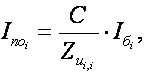 (8)
(8)
where C=1÷1.1 – equivalent EMF calculation scheme, Iб – base current, Uб – base voltage.
The magnitude of Zu can also be found according to [1] the time constant at each node of a design scheme as
 (9)
(9)
where w0 = 314.15 – synchronous angular frequency network
 (10)
(10)
Shock instantaneous values of current of KZ.
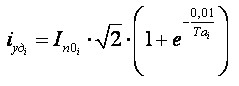 (11)
(11)
Thermal impulse of current of KZ.
 (12)
(12)
In those cases, when necessary to know spreading of currents of KZ in branches scheme, or when size E.M.F. sources considerably differ between itself the calculation of currents of KZ in the separate knot of Nk is executed in the following sequence: in the knot of KZ is entered the shunt of KZ with the large value of conductivities, for example
 (13)
(13)
Then there are the voltage at the nodes of (1) and short-circuit currents of branches, as
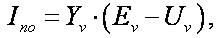 (14)
(14)
where Uv – stress vector branches.
The total a value of the periodic component can be obtained as
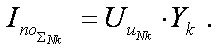 (15)
(15)
Calculation of asymmetrical KZ in obedience to a rule Shchedrin the point of KZ de bene esse a removed at the value of shunt of KZ and after him symmetric KZ is examined. The magnitude of the shunt is determined by the resultant resistance of the circuit feedback and zero sequence.To find these resistances are formed matrix describing the branches of these schemes V2 and V0. Then, it formed the matrix of nodal conductances and resistances, as shown above for the direct sequence schemes. In the corresponding diagonal elements of these matrices are the resultant resistance of the circuit with respect to the relevant sites. Asymmetrical short-circuit current in the i-node is determined on the following expression.
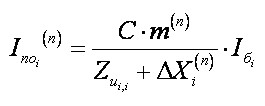 (16)
(16)
where m – conversion factor between the current direct sequencing and by the current of KZ especially phases Calculation of short circuit currents in electrical installations AC voltage less than 1 square.
Feature of these calculations is
- a accounting the active resistance of all elements of the scheme;
- a accounting the resistance of the electric arc;
- execution of calculations in the units named;
- binding calculation of three-phase and single-phase short circuit;
- account the additional resistance of the circuit elements: current transformers, contact connections, spools releasers and other.
In general, the algorithm is not significantly different from that described above [4].
Conclusion
As a result of implementation of this work can be done the followings basic conclusions:
On the basis of the developed methods of machine calculation of currents of KZ the program of calculation is modernized on PEVM in the environment of mathematical package of Mathcad, which has the followings advantages before analogues:
- it is possibility of calculations of symmetric and asymmetrical currents of KZ;
- it is introduction of index numeration of branches.
The executed comparisons of calculations of currents of KZ on the developed program with the best world analogues gave positive results.
On this program there were the executed calculations of currents of KZ for some power-stations of the Donetsk region.
The program is inculcated in the educational process of department of ES at implementation of the course and diploma planning.
*When writing this abstract master's work is not yet complete. The full text of work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his supervisor in January 2016.
References
- ГОСТ 27514-87. Короткое замыкание в електроустановках. Методы расчета в электроустановках переменного тока напряжением свыше 1кВ – М:.Издательство стандартов, 1988
- Николай Ильичев, Вячеслав Серов, Анатолий Кулешов, Ольга Михалева Программный комплекс EnergyCS для проектирования электроэнергетических систем.: CADmaster #36/1.2007 (январь-март) // Электротехника
- Скрипник О.І., Коновал В.С. Діалоговий автоматизований комплекс дакар-2002 – новий рівень інформаційного забезпечення електроенергетичних систем.: Журнал
Вісник
Національного університетуЛьвівська політехніка
№ 460 2002 року - Крючков И.П., Неклепаев Б.Н., Старшинов В.А. Расчет коротких замыканий и выбор электрооборудования. М.: Академия, 2006.
