Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. The essence of crisis management
- 2. The system of crisis management personnel
- 3. The use of outplacement in the crisis
- Conclusions
- References
Introduction
In the crisis conditions of the market economy country a special place is the practical application of technologies of personnel management that improve the socio-economic efficiency of enterprises.
Crisis periods are common to all companies, both national and foreign. But if Western business has accumulated rich experience in overcoming the problems developed a number of effective technology of the way out of the crisis, the subjects of the national economy have no such experience yet. Often, companies are taking measures to crisis management, but mainly in the area of financial management.
Nevertheless, has long been known that the social and psychological problems directly affect the appearance of symptoms of the crisis is not less economic and logistical problems, and in some cases more.
Crisis management now includes the management of marketing, finance, production, personnel and information. In modern conditions it becomes a central element of the staff, their interests, needs and attitudes. After all, it is people who enliven and generate enterprise system.
The current level of international relations is characterized by high dynamics of the latest HR-technologies. This trend requires new concepts, a new look at the opportunities and strategies to achieve it's by our enterprises. World experience shows that the use and further development of progressive principles of crisis management personnel in the practice of enterprises should serve as a powerful lever for their development, and to prevent the appearance of symptoms of the crisis. Therefore, it becomes urgent implementation of optimal strategies for the implementation of these management methods, corresponding to the established international practice.
1. The essence of crisis management
In the conditions of the permanent changes of the factors external financial environment and internal conditions of the financial activities increases the probability of occurrence of periodic crisis enterprise, which can show itself in different ways.
One of the manifestations of a financial crisis companies, bear the greatest threat to the functioning and development. In this regard, all the more urgent study of the financial crisis - its causes, its prevention capabilities and features of financial management in a crisis. In order to prevent crisis using crisis management now [5, p. 62].
The issues of crisis management and functioning of the enterprise in unstable environments engaged in both foreign and domestic scientists particular Balueev I. P, Bryukhovetskaya N. E, Zaitsev N. A, Blank I. A, Galchinskiy A. S., Ligonenko L. A, Tereschenko O. M., Altman A, Barton D., Richard J., Helfert S., Holt R., Shelde D. and others. However, the existing theoretical developments and approaches to solving this problem covering only certain aspects of crisis management companies, so there is a need for its complex study and research.
Crisis management is the process of using forms, methods and procedures aimed at the socio-economic recovery of the financial and economic activity of an individual entrepreneur, enterprise, industry, the creation and development of conditions for the way out of the crisis.
The crisis of the financial and economic activities of economic entities, tactical crisis and a solvency crisis. The cause of all crises is the management (improper, unprofessional, abuse or outright fraud as a result of theft or raiding, manipulation, conspiracy, acts of corruption) is aimed at prosecution purposes outside the objectives of the project (state ministries, corporations, firms, institutions) [3].
The objective of crisis management is to prevent the appearance of symptoms of the crisis and the development of measures for the organization of activities in unstable conditions. That is crisis management - is the formation of such an enterprise management system that ensures its effective operation at a certain level of risk. The professionalism of the leaders in these conditions is manifested not only in the use of the entire complex known management tools (including the methods of organization of business processes), but also in the ability to predict the course of events external environmental factors of the enterprise.
For the implementation of crisis management in the enterprise is often created a special team of highly qualified managers, which is endowed with special powers in the adoption and implementation of management decisions, as well as adequate financial resources.
Crisis management starts with understanding the reasons that led to the crisis. The main causes of the crisis are shown in Figure 1.1 [14, p. 23].
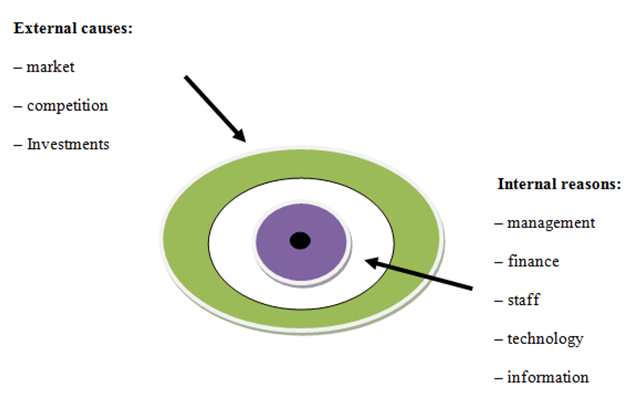
Figure 1.1 – The main causes of the crisis in the enterprise
The list of crisis factors also includes a number of indicators: unemployment, inflation, consumer ability of the population, the economic policy of the state, the activities of foreign companies, labor motivation, innovative climate, quality of Marketing and others.
Successful strategic planning depends on the real conditions in the enterprise. If the assumption prove false or shift occurs in an unexpected direction, the plan is not likely to work. Then the situation could escalate into a crisis.
Crisis financial management now realizes its main objectives through the implementation of certain functions, such as general and specific. General functions of crisis management is to finance the formation of effective information systems for support of alternatives of management decisions; the implementation of effective control over the implementation of management decisions on the financial recovery of the enterprise.
The specific function - a diagnosis of the symptoms of the crisis of the enterprise; restoration of financial stability; elimination of insolvency; ensuring financial balance in the process of enterprise development; the development of an overall strategy of financial improvement of the enterprise. The mechanism of anti-crisis financial management based on the general principles inherent in the management processes, and the specific features associated with the anti-crisis procedures to bring the company out of an extreme situation [7, p. 301].
In a developed and stable economy, increasing the level of specialization is one of the main factors of production efficiency. Accordingly, changing the characteristics of the employee. In times of economic crisis, when interrupted economic relations, specialization contrary worsen the viability of the enterprise.
The problem of crisis management insolvent enterprises stems from the very nature of the country's economic reforms. The impact on the company via the institution of bankruptcy allows you to rebuild not only the work of the enterprise, but also to improve the financial and economic climate of other economic entities to reduce the volume of non-payments.
The specifics of crisis management is to define such rules and management procedures, which could stabilize the situation and to bring the company gradually from the crisis. The use of specific tools and management compounded gain of unpredictable consequences of managerial decisions.
There are methods of forming anti-crisis stability [6]:
- The methods enhance financial stability by managing liquidity and the structure of assets and sources of funds.
- The methods of cost management through the optimization of fixed and variable costs.
- The methods of revenue management by main activity, and operating income is realizable.
- The methods of crisis management personnel.
In conclusion, it should be noted that it would be wrong to think the crisis has only a negative phenomenon. It has a positive side. Crises provide opportunities that are not available at other times. The positive aspects of the crisis include:
- The emergence of leaders.
- Accelerating change.
- The discovery of hidden problems.
- Change command more professional.
- Display of new competitive opportunities.
So the skill out of the crisis is to find the positive aspects for the enterprise and gain a favorable effect in the right direction.
2. The system of crisis management personnel
In the crisis conditions of market economy in our country are particularly important issues of practical application of modern technologies of personnel management that improve the socio-economic efficiency of any production. The market economy imposes on professional development managers more demanding than planned.
The manegement od the people is the most difficult task for any leader. In modern conditions the potential of the human being came to be regarded as essential for increasing productivity and management gradually began to understand what they are responsible for a person in the workplace, for the disclosure of its potential for the benefit of the company and for its own good.
Crisis management personnel means not only the formal organization of work with the staff (planning, selection, selection, placement, and so on. F.), But a combination of factors and socio-psychological, moral character - a democratic management style, caring attitude to the needs of man, taking into account its individual characteristics, and others.
Human resource management in unstable conditions is designed to take into account a whole range of issues of adaptation of the employee to the external and internal conditions of functioning and development of the organization. Particular attention should be paid to the analysis of motivational systems, their ability to shape and direct in accordance with the challenges facing the organization. This also should include the problem of interaction between the leaders of the organization with the trade unions and employment agencies, security personnel, development of new approaches to the priority values. Important within the organization - are employees and outside - consumers of products. It is important to turn the minds of staff to the consumer, not to please the chief; for profit, rather than squandering; to the innovator, not hardened mechanical executor; go to social norms, based on a solid economic foundation, not forgetting the spirituality and morality [2].
The system of crisis management personnel is a collection of sub-systems of general and line management, a number of functional subsystems, specializing in the implementation of similar functions and relationships between them [15, p. 33].
The subsystem of general and line management provides: management of the organization as a whole, functional management and production units. Functions of this subsystem perform: Manager (Manager) of the organization, his deputies, heads of functional and production departments, their deputies, masters, foremen. The structure of the personnel management system depends on the size of the organization, its geographic location, nature of the activity and other factors. In small and medium-sized firms, one subsystem may serve several functional sub-systems in emerging and crisis conditions, the organization may be canceled one subsystem and the other created a set of new features, there are other structural - functional transformations.
The concept of crisis management staff urges leaders of the organization to focus on the strategic perspective directions of work with the staff, such as mass retraining employees of the organization in connection with the transition to new technologies; rejuvenation of personnel by attracting young professionals and encouraging early retirement of persons not "fit" in the new requirements and is not capable of mastering modern methods of work; development of principles of staff employment when their mass release and attract the general workers to participate in management of the organization, and others. [16, p. 56].
An important strategic direction of crisis management personnel is an effective use of human resources marketing. It provided a number of ways: searching for promising students since the first years of universities and colleges, which provided the opportunity to work in the organization of the holidays, scholarships due to its resources, help in practical training, preparation and protection of diploma works; cooperation with the public employment service; the use of private firms in the selection and training of managers and other personnel; interaction with the staff leasing is carried out, that is sent to a temporary worker "rental"; Organization prognostic research on training and retraining of skilled workers organization.
Market relations and changes in the organization of the crisis is reflected in the change in the individual systems of values ??that people bring to the workplace. Their installations are starting to change under the influence of these changes varies in different age groups. The inevitable revision and values ??of the organization, promotion of other more important in the new socio-economic conditions. This requires in particular to take into account when developing a new human resources policy in the organization.
Each company creates its own set of values ??that give it personality. Especially important are the values ??assume the character of basic principles that underlie its "ideology". They usually are reflected in the mission and goals affect the rethinking of the functions associated with the strategy determined by promising up and coming action plans [1].
Thus, the personnel policy aimed at creating such a system of work with shots that would seek to obtain not only economic but also social impact, subject to applicable law. In a crisis, personnel policy had to be transformed. Features her organization associated with limited financial means, inevitably arrangements associated with the closing of a number of social development programs and staff reductions, an increase in social and psychological tension. The main ideological credo crisis management personnel policy - survival with minimal losses human capacity and ensure the best possible social protection of personnel.
In a market economy, the competitiveness of the organization is determined by how it reacts flexibly to any change in the external environment, how sensitively captures the changing needs of the market as ready for constant changes. In these circumstances requires a fundamentally new type of worker: skilled, initiative, prone to innovation, ready to make their own decisions and take responsibility for them, which binds their personal goals with the goals of the organization, which works focused on long-term cooperation [10].
The strategic objective of crisis management personnel is also the formation of an appropriate organizational culture of the enterprise. The mastery of the latest management technologies is impossible without the development of the foundations of organizational and cultural approach, giving the integral understanding of the functioning and development of different types of organizations, taking into account the psychological and socio-economic mechanisms of human behavior in complex crises.
The effectiveness of anti-crisis activities of enterprises depends on their willingness and ability to master the principles of strategic management. On the verge of a crisis, the company must solve two very difficult problems. You must select the priority actions of the many alternatives that are difficult to quantify, and guide the team in the right direction.
The problems caused by the crisis factors, most clearly seen in relation to managerial staff. Traditionally, these issues are addressed in two ways. The first group of problems is related to the mastery of management personnel skills in market conditions. For a long time at the domestic enterprises of their activities in the costly mode if you have access to resources and state guaranteed purchase of products (services). In a market economy, the need to think about saving resources, reducing the cost of, the needs of consumers, and others.
The second group of problems is connected with the decentralization of the company. This increases the level of independence and responsibility of the majority of managerial staff requires appropriate measures in the field of labor management.
In the context of the structural crisis in the first place stands the task of mastering the crisis management personnel management [12]. Crisis trends perceived by people in very different ways (both in time and depth perception). As international and domestic experience, there is the problem of late perception of crisis in the mass consciousness.
This factor may have negative consequences. Instead of anti-crisis objectives and actions related to the stabilization of the priority industries, in terms of perception of late become very popular setting unrealistic targets. Therefore, the formation of a false stereotype in practice prevents the survival of the real economy. In order to ensure effective anti-crisis measures need to be clear about the likely future state of the environment in which the company operates. Most managers are beginning to work effectively, provided that the information consistent with the target of their past experiences. If there is the opposite situation of their experience, they often ignore it and consider the erroneous [1].
If the conditions of the activities of qualitative change, the model of successful action, which takes into account only the experience, becoming a serious threat to adapt to the new reality of the enterprise.
However, the process of crisis management associated with high levels of uncertainty and incomplete control. In such circumstances, the intuition is rated higher formal logic and experience, along with the wish to become a non-standard actions and paradoxical. Modern anti-crisis measures introduced significant changes in the value of the activities of various departments. Thus, the transition from production-oriented to focus on the main sales space previously occupied by industrial units, goes in the financial and marketing activities. Accordingly, there are threats to the status of individual services and managers. At the same time managers and departments, whose position may suffer as a result of the crisis factors, trying to reduce or not to recognize the impact of these factors on the company. Thus, they try to maintain a high position, which is obtained in completely different conditions [11].
Typically, these employees represent the type of thinking that brought success in the past. So often create obstacles to the anti-crisis thinking, confident that they are doing for the good of the company.
Thus, the crisis will not help thinking of the real survival of the company, if the leaders with such thinking without sufficient impact across the enterprise.
It is important to realize the objective of crisis tendencies, inevitable at this stage of the operation of the national economy. Understanding the events and their dynamics in the short term it is necessary to base the development of appropriate anti-crisis measures. For this purpose it is necessary to actively shape the crisis thinking.
3. The use of outplacement in the crisis
In recent years, many scientists point out that it is the staff determines the strategic success of any company and acts as a basis to ensure its competitiveness and identifies areas for further development. Of particular importance in this situation becomes the competence of the head to respond to existing and direct their actions in crisis management personnel, improve the efficiency of staff in a downsizing. Therefore, the use of staff as an effective tool struggle with the crisis today is very important.
Today, in the post-crisis state of the majority of the world business activity is characterized by instability and uncertainty. One of the consequences of the deteriorating financial condition of enterprises have a need for the release of staff.
The release of the personnel - a kind of administrative activity, providing a set of measures to comply with legal regulations and organizational and psychological support from the administration for dismissal of employees. This is the final stage in the process of formation of the organization's personnel [5, p. 578].
The release of personnel is a necessary measure, when it is not rational to retrain staff to keep a man on flexible working hours (reduction of working hours), in which case you can use the method of outplacement. This method is today especially important, as it allows the company to maintain its good reputation and not to destroy your brand in such a difficult situation, as the release of the personnel.
The study of the problems involved in such scholars as: L. Balabanov, Kibanova A. Klim D. Konyaeva A. Yu Odegov, Sardak A. and others. At the same time, given the current situation in the world, the issue takes on a new urgency.
Given the studied approaches, we propose the following definition of outplacement – a combination of various measures aimed at reducing the negative consequences (physical and mental) for the dismissed or laid-off employees by the employer, including his further employment. Outplacement program can be divided into two parts: an analytical and practical. The first part involves an analysis of the labor market, the valuation of the candidate on the market, to develop a plan for further action to find work, learning search technology.
The second part – a merchandising, direct representation of the candidate or the employer company. The biggest mistake companies and individuals who use outplacement program – self-employment of 100%. This program does not give such guarantees. In order for a person found work again, to coincide many factors that can not always depend on the recruiting company. The program's objective – to help people find their way in the labor market, help to assess themselves and to learn how to position yourself. The agency takes over these obligations, plus professional assistance to the candidate.
According to recruiters, counseling and psychological care is much more important than the direct employment, especially if the person is not looking for a similar, but more interesting position, place higher.
employment does not depend on the recruiter, and on the active position of the candidate. Successful candidates who are outplacement program usually parallel themselves looking for a job. Candidates must be active. Tasks of the Agency – to give people the right direction. Normally, the standard outplacement program is designed for no more than 1 year, and more often for six months. This term, according to experts recruitment agencies, it should be enough for high-quality employment. During this period a person gets used to search for work, he begins to behave confidently, understand its place and value in the market.
On the other hand, during the year, any company undergoing a period of passivity and activity in the recruitment of personnel, and hence the search for work is less dependent on market conditions. Of course, if a person gets a job after six months or three months, the program will automatically stop. The main problem most people who fall under the outplacement program, not ready for release. And, then, and unwillingness to further the search for work. The program gives effect only if the person wants to prepare for a job search.
Bidder ready to various twists his professional fate, the interview can be seen at once, because it thinks its future for years to come. Therefore, you should never ask the company provides some programs for laid-off employees for its wine.
may be considered only outplacement services, including consulting, along with the help of technical and information support. Because not all job seekers have free access to the Internet, the ability to use e-mail and fax. In the Western centers, outplacement, for example, applicants have only to provide the resources above, but for a period of outplacement allocated permanent jobs where they can send their hours resume by fax, look vacancies online or phoning potential employers, offering their services.
In the event of any enterprise crisis management it goes into crisis management. Its special feature is the presence of many of the problems, actions, procedures that do not occur, and accordingly are not applicable guidance for enterprise management in a stable situation. If they are not met, the company may be premature panic among the staff, which will accelerate the "death" of the enterprise, and otherwise he has a chance to "survive".
In order to enhance the capacity of crisis management need to be aware of and understand the role this process could play outplacement, as a measure of crisis, conflict-free, "polite", "soft" downsizing [6]. It is proposed to carry out research to use a visual model that through the mechanisms of visualization will help facilitate the understanding of the eastern side of HR processes, crisis management and outplacement.
The visualization as a method of knowledge or activate creative thinking since ancient times allows people to use the mechanism of spatial thinking. Due to spatial thinking man is a constant recoding of his images, that is, the transition from spatial images of real objects of their semi-graphical representation of three-dimensional to two-dimensional images and back. Using the visualization object in the study, design and development of mathematical models help researchers see the final version of the management of complex production processes or as an abstract figure, which is difficult to visualize, but which then helps the researcher to obtain new knowledge about the object under study. Also simplifies the visualization and reduce the time for the transmission of thought-images from one person to another or visually compare multiple thought-images in selecting the optimal solution to any management tasks. You can also say that imaging is an intermediate link between the creation of thought-image and its materialization as the thought-creates the image of a man, and it is engaged in the materialization of the other.
Outplacement can be seen as a process and as a means. Key meanings invested in the concept of "outplacement" shown in Fig. 3.1.

Figure 3.1 – Outplacement model from the perspective of the business process and a set of tools that allow it
(animation: 5 frames, 5 cycles of repeating, 199 kilobytes)
Outplacement as a process reflects the principles and procedures of employment procedures of candidates for dismissal from the company, the exchange of management information between the management and the candidates (that is, as it happens), a set of actions to be performed at the same time and their sequence. Thus, outplacement can be viewed as a specific set of business processes associated with counseling, labor market research, employment, etc.
The process of liberation and employment can be divided into two sub-process. One is performed by management (autpleyserami) and includes the development of strategies of liberation campaign financing to reduce personnel, outplacement candidates, their advice, as well as studies of the labor market, the formation of the company's reputation, etc. Autpleyser – a fellow HR-service personnel engaged in the liberation of his subsequent employment in other enterprises on favorable terms dismissed.
The other processes are performed directly candidates for dismissal, and they include training, workshops, consultations, choice of place of employment of the possible positions, selecting appropriate compensation for dismissal, resume, interview, etc.
When use the term outplacement in the semantic understanding of the process, in this case, also use such a thing as "soft dismissal from employment" – is the direct execution of actions for the exchange of information between elements of the communication process.
Outplacement as a tool – a set of components required for the start of the process and participate in the release candidate, then there are those that this process is provided, as well as those that come as the end result of outplacement. Thus, agents are established norms (rules, instructions, regulations) the interaction between the leadership and candidates for dismissal within the enterprise, the public opinion of the company outside of it, its image and reputation, moral and psychological climate in the enterprise, the strategy of liberation, delivery methods psychological support, as well as a system of methods and forms of counseling.
As a conclusion, it should be noted that the use of outplacement is particularly popular in our region. This is due to the fact that the economy has always focused on the Donbass coal industry, which is associated with the need for energy and raw material base technology heavy industries: iron and steel, energy, chemical industry, as well as the needs of the population in the fuel and household needs. The special features of the functioning of the coal industry is their limited life, which is due to coal reserves are set aside for the production of a mine. In this regard, these companies periodically suffer restructuring, changes in the level of concentration of production, reorganization, liquidation. Derivatives of these processes is often a reduction in staff. It was at this point outplacement method will be very useful, because will increase the level of employment in the region and reduce tensions on the labor market. Application outplacement can become the "lifeline" instrument of personnel policy, which will bring the company out of the crisis, creating a favorable platform for the effective operation in the future by maintaining a positive reputation.
Conclusions
Improving living standards, improve the foreign policy, economic growth and other important figures of modern society is largely determined by the financial situation of enterprises in various industries, as well as the opportunities of which they possess.
At the same time, the market conditions enterprises are the most vulnerable in the event of crises. Factors bankruptcy of domestic enterprises are derived from the depth of the crisis state of the national economy. To prevent possible financial complications using the appropriate mechanisms for crisis management strategies, particularly among which is the system of crisis management personnel.
Employees directly involved in the development and implementation of crisis strategy. From staffing and staff development directly determines the final result of the activity of the organization. Therefore, in a structural crisis in the first place stands the task of mastering the employees of the enterprise crisis management.
It displays the possible solutions to the problems of the crisis can be attributed to the method of outplacement personnel management. Experience has shown that implementation of HR processes through outplacement brings undeniable benefits. Description of their actions makes it possible to analyze them in the system, to see too much and, conversely, to add necessary to build a logical and simple control scheme. Evaluating the effectiveness of its operation will allow to constantly improve the quality of management and, of course, to save time and resources.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the critical state of economic actors at all levels have a negative effect on the economy. Therefore, the successful implementation of anti-crisis measures in enterprises directly affects the achievement of sustainable economic growth and welfare of the population, which determines the urgency of solving the problems of their early implementation.
References
- Балдин К. В. Антикризисное управление. Учеб. пособие. – М.: Гадарики, 2011. – 271 с.
- Васюкова В. А. Стратегическое управление персоналом в условиях кризиса. Учеб. пособие. – М.: НГТИ, 2008. – 345 с.
- Грязнова А. . Антикризисный менеджмент. Учеб. пособие. – М.: «ЭКМОС», 2001. – 368 с.
- Демчук О. Н., Ефремова Т.А. Антикризисное управление. Учеб. пособие. – М.: Флинта, 2009. – 256 с.
- Егоршин А. П. Управление персоналом: учебник для вузов. – Новгород: НИМБ, 2003. – 720 с.
- Клим Д. Аутплейсмент как красивое расставание. – М.: Я – перший, 2010. – № 1–2. – 338 с.
- Климова Н. І. Стратегічні цілі фінансового управління в умовах нестабільної економіки // Вісник Університету банківської справи Національного банку України. – 2009. – № 1 (14). – С. 66-67.
- Коротков Э. М. Антикризисное управление. Учеб. пособие. – М.: ИНФРА-М, 2007. – 620 с.
- Литовченко О. Ю. Концептуальні основи механізму антикризового фінансового управління підприємством // Вісник економіки транспорту і промисловості. – 2012. – № 39. – С. 302.
- Минаев Э. С., Панагушин В.П. Антикризисное управление. Учеб. пособие для вузов. – М.: ПРИОР, 1998. – 432 с.
- Мостенська Т. Л. Ризики в системі антикризового управління // Вісник ЖДТУ. – 2009. – № 1 (51). – С. 34.
- Муравьев А. И., Крутик А.Б. Антикризисное управление // Теория и практика менеджмента. – 2002. – С. 432.
- Стецюк Н. М. Антикризисное управление. Учеб. пособие. – Хабаровск: ДВГУПС, 2007. –37 с.
- Терещенко О. О. Антикризове фінансове управління на підприємстві. Навчальний посібник. – К.: КНЕУ, 2006. – 268 с.
- Чумак В. Г. Менеджмент персонала. Учеб. пособие. – Ростов н/Д: Феникс, 2003. – 72 с.
- Шепеленко Г. А. Антикризисное управление производством и персоналом. Учеб. пособие. – М.: Феникс, 2003. – 230 с.
