Quick navigation
I. Introduction
In short, we need to investigate the vector control system in an AC drive, then tie this drive to an electric vehicle. After that it is necessary to study the intensity of solar radiation (energy) for a certain region. From the point of view of these observations, to assess and draw conclusions in which cases our virtually created electric vehicle will turn into a solar cell, and will operate on solar panels, and only from consumed solar energy. And also, in which cases it will simply be an electric car, powered by an alternating current network.
II. Selection of solar panels
Solar cells created with the use of gallium arsenide (a combination of gallium and arsenic) are the most optimal option for solar energy, even despite its exceedingly high cost, since we are interested, first of all, the high efficiency of the installation. Gallium arsenide is a semiconductor with the same solar energy properties as silicon, but more efficient in terms of performance. That is why the solar cells on its basis are characterized by a much greater efficiency (up to 44%) [1].
III. The transformation of solar energy into mechanical energy [2]

This structure includes:
- Solar panels, which, in turn, directly convert solar energy into electrical energy, thanks to the photoelectric effect.
- Solar battery controller providing normalization of battery output voltage, charging of batteries and (optionally) supply of low-voltage direct current to the load.
- Electrochemical accumulators storing energy during its excess and supplying it to the system during a shortage period with insufficient illumination of photocells or with a temporary increase in consumption. Also, the accumulated energy reserve allows you to move at night or in conditions of strong clouds.
- Inverter, which provides conversion of direct current from batteries and photocells to an alternating current.
- An electric motor, which is installed more directly directly on the drive wheels, in order to avoid loss of power during transmission. The control unit, which deals with the distribution of the received energy (the excess accumulates in the battery) and the regulation of the parameters of the solar battery (cooling, orientation in the sun).
IV. Investigation of a vector control system based on AD with a rotor. Selection of the electric motor
Vector control, also called field-oriented control (FOC), is a variable-frequency drive (VFD) control method in which the stator currents of a three-phase AC electric motor are identified as two orthogonal components that can be visualized with a vector. One component defines the magnetic flux of the motor, the other the torque. The control system of the drive calculates the corresponding current component references from the flux and torque references given by the drive's speed control. Typically proportional-integral (PI) controllers are used to keep the measured current components at their reference values. The pulse-width modulation of the variable-frequency drive defines the transistor switching according to the stator voltage references that are the output of the PI current controllers [3].
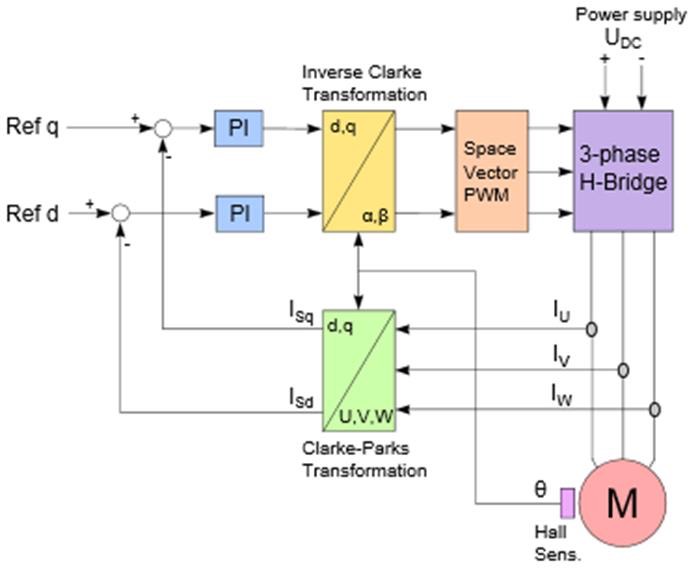 Figure 4.1 - Vector control structure
Figure 4.1 - Vector control structure
a. Results of the study:

Figure 4.2 – VC - system in Matlab
In this paper, we created and investigated the vector control system and obtained such results:
 Figure 4.3 – Oscillograms wm, isq, isd
Figure 4.3 – Oscillograms wm, isq, isd
Oscillograms, where the speed (wm) the instantaneous (isq) and the flow-forming (isq) components coincided with the calculated ones. Thus, we checked and proved the relevance of the vector control system.
V. Conclusion
As a result of research work, materials on issues related to the topic of master's work were collected and studied. The intensity of solar radiation was studied using the example of the Russian Federation. Arsenide-gallium solar cells were chosen because of the results of the research, because they have the highest efficiency - 44%. The system of converting solar energy into mechanical was fully studied. And also a study of the VC - system was carried out, using the example of an asynchronous electric motor.





