Abstract
Content
1 Theme urgency
2 Goal and tasks of the research
3 Development of sorbent based on expanded graphite
Conclusion
References
Introduction
In the conditions of active urban processes in industrial cities, the level of pollution of natural water with technogenic pollutants is especially increasing. A huge number of pollutants enter the reservoirs with wastewater enterprises of ferrous and nonferrous metallurgy, chemical, petrochemical, gas, coal industry, agriculture enterprises and public utilities, as well as surface runoff from adjacent areas.
The most dangerous pollutants of the aquatic environment are organic substances: phenols, formaldehyde, aromatic hydrocarbons, oils, resins, petroleum products, and heavy metal compounds: copper, zinc, chromium.
A lot of technogenic organic pollutants have a toxic effect on aquatic organisms. Insoluble hydrocarbons form a film on the water surface, which prevents the dissolution of atmospheric oxygen in water. Heavy metals have cumulative and additive properties and cause mutagenic and carcinogenic processes in organisms.
1 Theme urgency
The existing methods of purification of industrial wastewater do not reach a satisfactory level of water quality at minimal cost. Therefore, the actual task is to improve such processes.
Application of adsorption technologies for the removal of pollutants is of particular importance.
Search and investigation of sorbents that based on available materials with low cost is of considerable interest. Thermally expanded graphite (TEG), obtained from natural graphite, can be used as such material.
Thermally expanded graphite is a promising sorbent material. Its advantage over other sorbents is large porosity, large specific surface area and low cost.
2 Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of the study is to develop a method for obtaining a sorbent from natural graphite for the purification of wastewater from organic pollutants and heavy metals.
Objectives of the study:
- development of a method for processing graphite to produce thermally expandable graphite compounds;
- examination of the structure and physicochemical properties of the obtainedcompounds;
- investigation of the sorption properties of the sorbent based on thermally expanded graphite.
The object of the study is natural graphite and a sorbent obtained as a result of its processing.
The subject of the study are the structural features, physicochemical properties of graphite intercalation compounds (GIC) and thermally expanded graphite obtained on the basis of synthesized GIC.
The work is expected to produce the following results:
- determination of the optimal way of processing graphite to produce a sorbent based on it;
- investigation of the sorption capacity of the resulting thermally expanded graphite in relation to aquatic environmental pollutants;
- development of a method of using the developed sorbent in technological processes of water purification.
- Двадненко, М.В. Адсорбционная очистка сточных вод / М.В. Двадненко, Н.М. Привалова, И.Ю. Кудаева, А.Г. Степура // Современные наукоемкие технологии. – 2010. – №10. – С. 214-215.
- Телегин, Л.Г. Охрана окружающей среды при сооружении и эксплуатации газонефтепроводов / Л.Г. Телегин, Б.И. Ким, В.И. Зоненко. – М.: Недра, 1988. – 64 с.
- Климов, Е.С. Природные сорбенты и комплексоны в очистке сточных вод: Монография. / Е.С. Климов, М.В. Бузаева. – Ульяновск: УлГТУ, 2011. – 201 с.
- Алыков, Н.М. Очистка воды природным сорбентом / Н.М. Алыков, А.С. Реснянская // Экология и промышленность России. – 2003. – № 2. – С. 12–13.
- Никитина, Т.В. Очистка вод от нефтепродуктов и ионов тяжелых металлов сорбентами на основе отходов волокнистых материалов и графита: автореферат диссертации кандидата химических наук: / Т.В. Никитина. – Иваново, 2011. – 16 с.
- Черныш, И.Г. Физико-химические свойства графита и его соединений / И.Г. Черныш, И.И. Карпов, Г.П. Приходько, В.М. Шай. – К.: Наукова думка, 1990. – 200 с.
- Убеллоде, А. Р. Графит и его кристаллические соединения: Пер. с англ / А.Р. Убеллоде, Ф.А. Льюис. – М.: Мир, 1965. – 249 с.
- Ярошенко, А.П. Высококачественные вспучивающиеся соединения интеркалирования графита – новые подходы к химии и технологии / А.П. Ярошенко, М.В. Савоськин. // Журнал прикладной химии. – 1995. – Т. 68. – Вып. 8. – С. 1302-1306.
- Фиалков, А.С. Углерод, межслоевые соединения и композиты на его основе / А.С. Фиалков. – М.: Аспект-Пресс, 1997. – 718 с.
- Forsman, W.C Chemistry of graphite intercalation by nitric acid / W.C. Forsman, F.L. Vogel, D.E. Carl, J. Hoffman. // Carbon. – 1978. – Vol. 16, № 4. – Pp. 269-271.
- Song, K.M. On lower-nitrogen expandable graphite / K.M. Song, H.J. Dun // Mater. Res. Bull. – 2000. – Vol. 35, № 3.- Pp. 425-430.
- Финаенов, А.И. Адсорбенты на основе терморасширенного графита / А.И. Финаенов, А.С. Кольченко, А.В. Яковлев, Э.В. Финаенова, и др. // Вестник Саратовского государственного технического университета. – 2011. – Т. 2. – № 1. – С. 45-52.
- Яковлев, А.В. Применение терморасширенного графита для очистки воды от ионов Cr (VI), Ni (II), Fe (II) / А.В. Яковлев // Вестник СГТУ – 2005. – № 4 (9). – С. 85-89.
- Солдатов, В.С. Физико-химические и сорбционные свойства терморасширенного графита / В.С. Солдатов, Т.А. Коршунова // Весці Нацыянальнай акадэміі навук Беларусі. Серыя хімічных навук – 2012. - № 3. – С. 82-86.
- Никитина, Т.В. Очистка вод от нефтепродуктов и ионов тяжелых металлов сорбентами на основе отходов волокнистых материалов и графита: Автореф. дис. канд. хим. наук: 03.02.08 / Энгельсский технологический институт. – Иваново, 2011. – 16 с.
- Темирханов, Б.А. Новые углеродные материалы для ликвидации разливов нефти / Б.А. Темирханов, З.Х. Султыгова, А.Х. Саламов, А.М. Нальгиева // Фундаментальные исследования. – 2012. – Т. 2. № 6. – С. 471.
- Чесноков, Н.В. Сорбционные свойства композитов на основе терморасширенных графитов / Н.В. Чесноков, Б.Н. Кузнецов, Н.М. Микова, В.А. Дроздов // Рос. хим. ж. – 2006. – Т. 1, № 1. – С. 75-78.
- Яковлев, А.В. Применение терморасширенного графита в процессе водоочистки и водоподготовки / А.В. Яковлев, А.И. Финаенов, Е.В. Яковлева, Э.В. Финаенова // Журнал прикладной химии. – 2004. – № 11. – С. 1833-1835.
- Войташ, А.А. Разработка сорбента для очистки сточных вод от органических загрязнителей на основе соединений тройного интеркалирования графита / А.А. Войташ, Ю.Н. Ганнова, Ю.В. Берестнева. / ХI Международная научная конференция аспирантов и студентов «Охрана окружающей среды и рациональное использование природных ресурсов» (13-14 апреля 2017 г., Донецк). – Донецк, 2017 г.
- Темердашев, З. А, Исследование сорбционных свойств углеродных материалов при очистке вод от органических загрязнителей / З.А. Темердашев, Т.Н. Мусорина, Н.В. Киселева // Защита окружающей среды в нефтегазовом комплексе. – 2007. – № 3. – С. 3-5.
3 Development of sorbent based on expanded graphite
|
The graphite used was a purified natural graphite GT-1 from Zavalie Graphite Works, Ukraine. Nitric acid (98 wt%) was chosen as the main intercalant. To improve the stability of graphite nitrate, it was modified (co-intercalated) with organic compounds: 1,4-dioxane, ethyl formate, acetic acid, ethyl acetate, dimethylacetamide or a mixture of substances in a ratio of 1 : 1 by volume. These substances showed a good ability to stabilize graphite nitrate [19]. Graphite nitrate cointercalation compounds were synthesized in the thermostatic reactor at 20 °C. Nitric acid was added to the sample of natural graphite. The mixture was stirred for 10 min. Cointercalant (an organic compound or two compounds in equal amounts) was then added, and the mixture was stirred again for 10 min. Nitric acid and cointercalants were used at 0.6 and Sheme of production of TEG is present on Fig. 1 |  Figure 1 – TEG production scheme |
The thermal expansion coefficients (Kv) of graphite nitrate and its cointercalation compounds were determined by the thermal shock mode of heating. A stainless cuvette was placed into a muffle furnace preheated up to 900 °C. About 0.2 – 0.25 g of the product was inserted into the heated cuvette and kept in the furnace for 120 s. Then the cuvette with expanded graphite was removed from the furnace, the contents were gently transferred to a graduated cylinder and obtained graphite foam volume was measured.
The thermal expansion coefficient for all samples was determined from the equation:
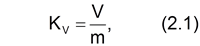
where Kv – the thermal expansion coefficient,
V – the graphite foam volume, cm3;
m – the initial mass of the sample before heating, g.
The obtained values of Kv for the test samples shown in Table 1.
Table 1 - The thermal expansion coefficients of test compounds
| Intercalants | Kv, cm3/g | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| HNO3 | - | - | 249 |
| HNO3 | Acetic acid | - | 354 |
| HNO3 | 1,4-dioxane | - | 260 |
| HNO3 | Ethyl acetate | - | 273 |
| HNO3 | Dimethylacetamide | - | 125 |
| HNO3 | Ethyl formate | - | 318 |
| HNO3 | Ethyl formate | Acetic acid | 378 |
| HNO3 | Ethyl formate | 1,4-dioxane | 357 |
| HNO3 | Ethyl formate | Ethyl acetate | 340 |
| HNO3 | Ethyl formate | Dimethylacetamide | 242 |
On the basis of the obtained values of the expansion coefficient, the method for treating graphite nitrate with ethyl formate and acetic acid, which makes it possible to achieve the greatest expansion volume of graphite crystals (378 cm3/g) was chosen.
The microstructure of the expanded graphite was investigated with scanning electron microscopy (SEM). SEM image of the expanded graphite is present on Fig. 2

Figure 2 - SEM images of initial graphite (a), graphite nitrate cointercalated with acetic acid and ethyl formate (б), and of expanded graphite (в)
The sorption capacity of the expanded graphite to benzene, engine oil and heavy oil was determined. Our results along with those for expanded graphite from the bisulfate graphite modified with H2O2 [20] are listed in Table 2.
Table 2 - The sorption capacity of the expanded graphite
| Pollutant | Sorption capacity, g per 1 g of the expanded graphite | |
| expanded graphite from the bisulfate graphite modified with H2O2 | expanded graphite from the nitrate graphite modified with ethyl formate and acetic acid | |
| Heavy oil | 55 | 62 |
| Engine oil | 50 | 43 |
| Benzene | 35 | 71 |
Thus, there is an increase in the sorption capacity of the investigated TEG relatively to heavy oil and benzene, in comparison with the TEG that is traditionally used for water purification. From the data obtained it can be concluded that it is expedient to use the developed sorbent for purification of industrial wastewater and reservoirs in case of emergency hydrocarbon spills.
Conclusions
It can be concluded that the studies on improving the methods of sorption water purification are relevant. Thermally expanded graphite is an easily accessible material with a high sorption capacity and the ability to regenerate. The listed characteristics make relevant further studies on the use of TRH as a sorbent.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: July 2018. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
