Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Review of research and development
- 3.1 Overview of International Sources
- 3.2 Overview of National Sources
- 4. Methodical approaches to the analysis of the financial condition of an enterprise
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
1. Theme urgency
The relevance of the topic of the thesis
project is
due to the fact that: in modern conditions, it is necessary to
rationally
evaluate and manage the financial condition of the enterprise.
Effective
financial management aimed at avoiding bankruptcy and major financial
failures,
leadership in combating competitors, acceptable growth rates of the
company's
economic potential, growth in production and sales, maximizing profits,
minimizing costs, ensuring cost-effective operation of the enterprise
is the
main goal of successful operation of the enterprise and achievement of
their
goal.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of this study is to manage
the financial
condition of the enterprise and develop methodological recommendations
for
improving the management of the financial condition of an industrial
enterprise.
To achieve the goal in the course of the
master's
work, the following tasks are formulated and solved:
·
an
analysis of theoretical provisions on the essence of the financial
condition;
·
the
theoretical aspects of financial management of the enterprise are
analyzed;
·
methods
and models of financial management of the enterprise are characterized;
·
developed
recommendations for improving the management of the financial condition
of
industrial enterprises
The object of the research of the thesis is the
process of
managing the financial condition of the enterprise.
The subject of the study is a set of theoretical,
methodological
and practical aspects of the financial management system of an
industrial
enterprise.
Methods of research.
The methodological and theoretical basis of the research
is the
scientific works of domestic and foreign scientists devoted to the
current
problems of managing the financial condition of the enterprise. During
the
research, the following methods were used: the method of analysis and
synthesis, deduction and induction, comparison, forecasting,
statistical
information processing methods, system approach, comparisons.
Practical significance of the
results.
The result of the study is
recommendations for
improving the financial management system of the industrial enterprise.
The main content of the work
The introduction highlights the problem
of the
relevance of the topic of master's work, reveals the purpose and
objectives of
the research, shows the object, the subject, the research methods used,
and
also contains information on the practical value of the study.
3. Review of research and development
3.1 REVIEW OF INTERNATIONAL SOURCES.
The theoretical and methodological basis
of this study
was the scientific work of foreign and domestic scientists on the
assessment
and management of the financial condition of the enterprise.
Among foreign authors studying this problem, it is possible to single out works: E.I. Altman, R. Bass, R.H. Berry, R.A. Brili, B. Koil, M. Glance, V. Myuro, K. Pyroka, P. Witman and others [12]
3.2 REVIEW OF NATIONAL SOURCES.
In market conditions, the financial
condition is the
key to survival and the basis of the company's stable position. It
reflects the
state of financial resources in which an enterprise, freely maneuvering
with
cash, is able, through effective use, to ensure an uninterrupted
process of
production and sale of products, as well as to expand and update it.
The financial condition of an enterprise depends on the results of its production, commercial and financial activities. If the production and financial plans are successfully implemented, this positively affects the financial position of the enterprise, and vice versa, as a result of the underfulfilment of the plan for the production and sale of products, its cost of production increases, the revenue and profit amount decrease, and as a result - the financial condition of the enterprise and its solvency worsens.
Table 1.1 presents the views of economists on the definition of the financial condition of the enterprise
|
Author
|
Definition |
| |
|
| |
"... is the composition and placement of funds,
the structure of their sources, the speed of capital turnover, the
ability of
enterprises to repay
|
| |
|
| Sheremet A.D. |
|
| Savitskaya G.V. |
|
| |
"... this is the most important
characteristic of the economic activity of the enterprise, revealing
the
competitiveness of the enterprise, its potential in business
cooperation, it
assesses to what extent the economic interests of the enterprise and
its
partners in financial and other relations are guaranteed" [6] |
| Kovalev V.V. |
"... this is a characteristic of the
property and financial regulations of the enterprise, and the results
of its
economic activities, as well as opportunities for its further
development"
[7] |
| Belendir M.V. |
"... this is the most important characteristic of the organization, reflecting the availability of financial resources, the appropriateness and effectiveness of their deployment and use, solvency and financial stability [8] |
| |
"... this is a characteristic of the financial competitiveness of an enterprise (that is, solvency, creditworthiness), the use of financial resources and capital, the fulfillment of obligations to the state and other economic entities [9] |
| |
|
Analyzing the opinions of economists on
the concept of
the financial state of the enterprise, we can conclude that the most
accurate
definition of the financial state was presented by Savitskaya GV,
because her
opinion on the definition of the financial state most accurately shows
the
financial condition of the enterprise as a whole.
The concept of financial condition
abroad is generally
identified with financial position, financial stability. Important
indicators
at the same time are solvency, cost recovery and repayment of
obligations, the
ability to create a new product from available resources and receive
income at
the same time [11]. In the Russian and foreign approaches, the
structure of
financial analysis is also different. In domestic practice, the
components of
financial analysis differ depending on the approach of one or another
author.
The financial condition is characterized
by the
provision of financial resources necessary for the normal functioning
of the
enterprise, the appropriateness of their placement and the
effectiveness of
use, financial relationships with other legal and physical persons, and
the
financial stability of the enterprise. The ability of the enterprise to
make
timely payments, to finance its activities on an extended basis,
indicates its
good financial condition.
Thus, in order to assess the financial
condition of an
enterprise, it is necessary to assess:
1) property status, structure of its
distribution and
efficiency of use;
2) sufficiency of own and borrowed
capital for current
economic activity, rationality of its use, and also choice of strategy
for the
further development of the enterprise;
3) the achieved level in the stability of the financial condition of the enterprise, its financial independence, its own working capital, the sufficiency of fixed assets, production stocks and work in progress to ensure the competitiveness and profitability of the products.
4. METHODICAL APPROACHES TO THE ANALYSIS
OF THE
FINANCIAL STATE OF THE ENTERPRISE BY THE EXAMPLE OF JSC "Red October"
The financial condition of the enterprise is analyzed with the help of a set of methodological approaches that allow to structure and identify the interrelations of the main indicators.
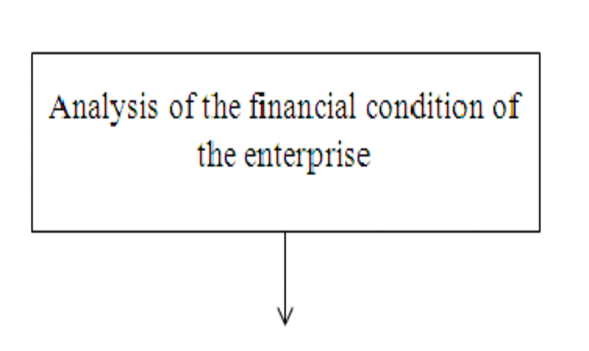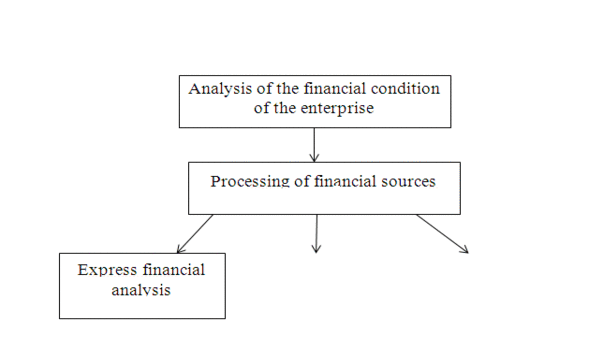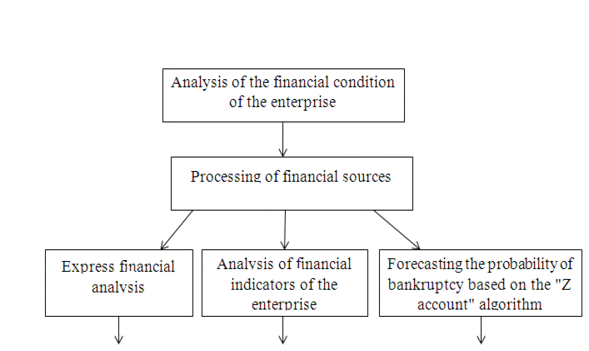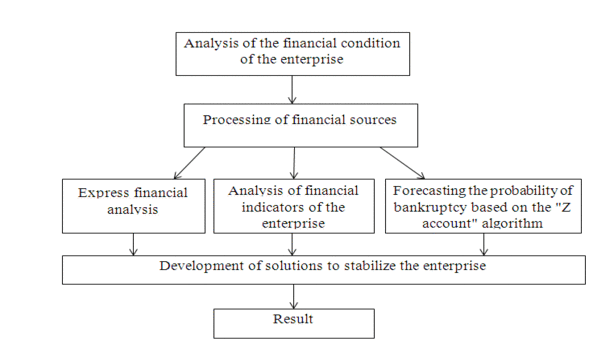
Figure 1. Analysis of the financial condition of the company
The table 4.1 Presents the main methodological approaches to the analysis of the financial condition of the company.Table 4.1 - Basic methodological approaches to the analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise
| |
|
|
| Coefficient analysis (relative indicators) |
Calculation of the ratio of individual items of
reporting company, the determination of the relationship of indicators
|
Allows for a comparative analysis of effectiveness: -to previous years - with planned indicators |
| |
Calculation of the structure of summarizing reporting items and compilation of dynamic series (percentage analysis) |
Allows you to track predict structural changes in the composition of sources of funds and the direction of their use |
| Horizontal (time) analysis |
Calculation of the structure of summarizing reporting items and compilation of dynamic series (percentage analysis) |
Allows to reveal tendencies of change of separate articles (groups of articles) of the reporting |
| Matrix Analysis |
Based on the use of a model, the elements of which reflect the interconnection of diverse but interdependent economic indicators |
The matrix model of analysis makes it possible to evaluate the decisions made in the past, as well as to justify the decisions made on the basis of interrelations and the dependence of various indicators |
Analysis of the financial condition
based on the
solvency ratios of the Red Oktober enterprise, which gives a
quantitative
description of the enterprise, is presented in Table 4.2.
Table 4.2 - Coefficients of solvency of the enterprise OJSC Red Oktober
| Indicators |
At the beginning of the reporting period |
At the end of the reporting period |
The established criterion |
| Current liquidity ratio | 1,17 |
1,95 |
Ктл=2 |
| Absolute liquidity ratio | 0,01 |
0,35 |
Кал=0,2 |
| |
0,66 |
1.12 |
Кбл=0,8 |
The matrix approach to the analysis of
the financial
condition of an enterprise is based on the use of a model, the elements
of
which reflect the interconnection of diverse but interdependent
economic
indicators. The values of the named model are determined by the
established
rules, which are dictated by the form of the balance sheet of the
enterprise,
capable of sufficiently freely transforming into a matrix where the
asset's
articles (economic means) are horizontally located, and vertically the
articles
of liability (sources of funds).
The algorithm for analyzing the
financial condition of
an enterprise through a matrix method is presented in the following
sequence:
1. An abridged form of the balance sheet
is compiled.
2. Analytical tables are formed (the
matrix balance at
the beginning of the year, the matrix balance at the end of the year,
the
difference (dynamic) matrix balance for the year).
3. Express analysis of analytical tables
is carried
out in the following directions:
- the state (structure and quality) of
enterprise
funds at the beginning and end of the period;
- Dynamics of enterprise funds for the
period;
- level of solvency and financial
stability;
- the level and rank of factors
affecting the
financial condition of the enterprise;
- conclusions are formed on the results
of the
analysis.
Let's consider the practical possibility
of using the
matrix approach to the analysis of the financial state of the
enterprise JSC
"Moscow Confectionary Factory" Red October ", which produces and
sells confectionery products.
The reduced form of the balance sheet
for 2014-2015.
is presented in Table. 4.3.
Table 4.3 - The reduced form of the balance sheet of JSC "Moscow Confectionery Factory" Red October "for 2014-2015.
|
Balance sheet items |
The analyzed period | |
| 2014 |
2015 |
|
| Balance active |
||
| Fixed assets, intangible assets (at residual value) |
2
519508 |
11
344 |
| |
4
941381 |
4
163
864 |
| |
10
042 |
141 |
| |
57452 |
|
| |
7
528
383 |
6
325
999 |
| |
1
363
292 |
1
451
951 |
| |
3
066
627 |
3
702
583 |
| |
25
000 |
1
026
500 |
| |
19
210 |
185
191 |
| |
1
993 |
50
908 |
| |
4
476
122 |
6
755
371 |
| |
12
004
505 |
13081370 |
|
Passive balance |
||
| |
784
784 |
11
023 |
| |
535 |
535 |
| |
6
478
503 |
7
067
697 |
| |
7
263
822 |
7
853
016 |
| |
0 |
800
000 |
| |
67
479 |
59
667 |
| |
67
479 |
859
667 |
| |
800
885 |
|
| |
3
817
119 |
3
470
459 |
| |
55
200 |
|
| |
4
673
204 |
4
368
687 |
| Balance |
12 004 505 | 13081370 |
The compilation of the matrix model
(Tables 4.5 and
4.6) is based on the following requirements:
1. The size of the matrix is chosen,
the articles of
the asset are reflected horizontally across the matrix, the articles of
liability are vertical. The balance line and the matrix graph are
filled in
exactly according to the balance sheet data.
2. Consistently, starting with the first
line of the
asset balance, selected sources of funds at the disposal of the
enterprise.
3. All balance results on the horizontal
and vertical
of the matrix are checked. The most important is the stage of drawing
up the
matrix - selecting sources of funds at the disposal of the enterprise
(Table
4.4).
At the same time, one should proceed
from the range of
financial rights and powers given to the enterprise, the economic
nature of its
own and borrowed funds, the economic essence of mobile and non-mobile
assets.
Table 4.4 Selection of sources of enterprise funds in the formation of the matrix
|
Means (articles of the asset) |
Sources of funds (articles of liability) |
|
Non-productive assets |
|
|
1. Fixed assets and intangible assets. |
Statutory and additional capital. Long-term loans and borrowings |
|
2. Capital investments. |
Long-term loans and borrowings |
|
|
1.Taxible and additional capital |
|
Mobile means |
|
|
|
Authorized and additional capital (balance) Reserve capital Accumulation funds and retained earnings (balance) Short-term loans and borrowings. Creditors Consumption funds and reserves |
|
|
Creditors Short-term loans and borrowings. |
|
3. Short-term financial investments. |
Reserve capital Creditors Consumption funds and reserves |
|
|
1. Reserve capital 2. Accumulation and retained earnings Credits and loans 4. Consumption funds and reserves |
Table 4.5 - Matrix Balance for 2014
| Active / Passive |
Statutory and additional capital |
Reserve capital |
Retained earnings |
Long-term loans |
Deferred liabilities |
Short-term loans and borrowings |
Commitments |
|
| |
5511,5 |
|
2503793,5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2509305 |
| |
5511,5 |
|
4691,5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
10203 |
| Capital investments + financial investments |
772569 |
|
3970018 |
0 |
0 |
197602 |
0 |
4940189 |
| |
1192 |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
1192 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
57452 |
|
57452 |
| |
|
|
|
|
10042 |
|
|
10042 |
| |
|
|
|
0 |
|
499628 |
863664 |
1363292 |
| Receivables |
|
535 |
|
0 |
57437 |
|
3008655 |
3066627 |
| Short-term financial investments |
|
|
|
0 |
|
25000 |
|
25000 |
| |
|
|
|
0 |
|
21203 |
|
21203 |
| |
784784 |
535 |
6478503 |
0 |
67479 |
800885 |
3872319 |
12004505 |
Table 4.6 - Matrix Balance for 2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
11023 |
|
2
118 045 |
|
|
|
|
2
129 068 |
| |
772
569 |
|
2
591 295 |
800
000 |
|
|
|
4
163 864 |
| |
1
192 |
|
31
734 |
|
141 |
|
|
33
067 |
| |
|
|
1
455 480 |
|
|
|
|
1
455 480 |
| |
|
535 |
|
|
59
526 |
|
3
977231
|
4
037 292 |
| |
|
|
871
143 |
|
|
67
026 |
88
331 |
1
026 500 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
236
099 |
236
099 |
|
|
784
784 |
535 |
7
067 697 |
800
000 |
59
667 |
67
026 |
4
301 661 |
13
081
370 |
Table 4.7 - Dynamic Balance for 2014-15.
| Active / Passive |
Statutory and additional capital |
Reserve capital | |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
0 |
0 |
-390440 |
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
-390440 |
| |
0 |
0 |
-1
378 723 |
800
000 |
0 |
-197
602 |
0 |
-776
325 |
| |
0 |
0 |
31
734 |
0 |
0 |
-57
452 |
0 |
-35
619 |
| |
0 |
0 |
1455480 |
0 |
0 |
-499628 |
-863664 |
92188 |
| |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2089 |
0 |
968576 |
970665 |
| Short-term investments | 0 |
0 |
871143 |
0 |
0 |
42026 |
88331 |
1001500 |
| |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
-21203 |
236099 |
214896 |
| Balance | 0 |
0 |
589
194 |
800
000 |
-7
812 |
-733
859 |
429
342 |
1
076 865 |
On the basis of the above dynamic
balance, it follows:
as a result of increasing solvency, the risk of bankruptcy of the
enterprise
decreases, positive profit dynamics are observed, short-term loans are
repaid
for the period under study, and mobile assets are financed at the
expense of
the company's own capital. At the same time negative dynamics of
financing of
non-mobile assets is observed at the expense of own funds, long-term
loans are
attracted to finance capital investments, the amount of the
enterprise's
liabilities increases. In general, the dynamic balance is positive and
the
enterprise is stable
Advantages and disadvantages of
methodological
approaches to the analysis of the company's financial condition are
presented
in Table 4.8.
Table 4.8 - Advantages and disadvantages of methodological approaches to the analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise
| Name |
Benefits |
Disadvantages |
| Coefficient |
Simplicity of calculations and elimination of influence of inflation, which is especially important in long-term analysis |
Coefficients are static, do not reflect differences in accounting methods and the quality of the constituent indicators. |
| Matrix |
Calculation of additional indicators characterizing the financial stability and creditworthiness of the organization. Receiving additional information to find out the reasons for changing the financial condition of the organization |
High labor intensity. Difficulties, connection with the selection of the source of formation of assets |
Conclusion
Thus, a financial condition is
understood as the
ability of an enterprise to finance its activities. It is characterized
by the
provision of financial resources necessary for the normal functioning
of the
enterprise, the appropriateness of their deployment and the
effectiveness of
use, financial relationships with other legal and physical persons,
solvency
and financial stability. Analysis of the financial condition of the
enterprise
is one of the key points of its assessment, as it serves as the basis
for
making managerial decisions.
Matrix balances significantly expand the
information
base of the financial express analysis necessary for making managerial
decisions. In work with the help of the matrix approach, the linking of
assets
and liabilities of the balance was determined, the structure was
calculated and
the quality of assets was determined according to the balance sheet of
the
enterprise and the sufficiency of sources of their financing, and the
financial
condition of the enterprise was confirmed by OAO "Moscow Confectionery
Factory" Red Oktober "for 2014-15.
On the basis of the above analysis, it
should be
concluded that the enterprise is financially independent and solvent.
Financing
of mobile assets is carried out at the expense of the company's own
capital.
However, there is a negative dynamics of financing of non-mobile assets
from
own funds. Based on the analysis of the Krasny Oktyabr company, it
should be
concluded that the enterprise is financially independent and solvent.
Financing
of mobile assets is carried out at the expense of the company's own
capital. However,
there is a negative dynamics of financing of non-mobile assets at the
expense
of own funds. Overall, the balance of the enterprise is positive.
When writing this essay, the master's work is not yet complete.
Final completion: May 2017. The full text of the work and materials on
the topic can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after the
specified date.
