Abstract
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Integrated approach to resource consumption in the enterprise
- Conclusion
- References
- To improve the definition of the economic category of resource-saving based on the analysis of author's studies;
- Systematize the classification of natural resources of the enterprise;
- Analyze tools and factors affecting the level of resource consumption in the enterprise;
- Develop aimed at assessing the use of natural resources in the enterprise;
- Form a set of proposals for the formation of tools that optimize the consumption of resources and increase the efficiency of their use in the enterprise.
- Accounting for natural resources in each area of the economy;
- Complex use of natural resources by improving their extraction and use;
- Reducing the economic costs of resource management;
- Reducing resource consumption;
- Careful attitude to non-renewable resources, for example, mineral resources;
- The expedient placement of the population, industry, agriculture, fishing, etc.;
- Restriction in some regions of the population;
- The organization of reserves, reserves, monuments of nature, etc.
Content
Introduction
The most important problem of the modern economy is the limited resources and at the same time the need to improve the efficiency of the enterprise. For the effective operation of the enterprise, the optimization of resource consumption is extremely important, as a qualitative basis for management decisions.
1. Theme urgency
This direction is especially important, since the production of products accounts for the largest share of material resources, due to which, based on the practical experience of foreign countries, up to 80% of total resource savings are achieved. Also at the heart of the activities of any enterprise is the need to plan consumption of all categories of resources, thereby ensuring the competitiveness of the enterprise and products.
the result of such management is the practical implementation of resource-saving policies, within the framework of which a set of measures aimed at improving the efficiency of the enterprise through the rational use of natural resources is determined.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of the work is the development of theoretical provisions and the justification of scientific and applied recommendations for organizational and economic regulation of resource consumption at enterprises, taking into account their production and economic activities.
The object of work is the process of consumption of natural resources in the enterprise.
The subject of the research is the scientific and methodological aspects of the justification and practical use of tools for organizational and economic regulation of the process of resource use in the enterprise.
Main tasks of the research:
3. Integrated approach to resource consumption in the enterprise
In recent years, the authors of scientific papers emphasize the importance of rational use of resources, which is explained by the fact that the gross domestic product of the state is created by more than three quarters due to the use of resource potential, and resource stocks in turn are depleted, which creates certain conditions for restrictions for their use in future periods.
In other words, making up the natural base of production, they represent the most important budget-forming and capital-intensive asset of national wealth. Due to their extraction, use and export conditions for the progressive development can be created [1, p. 246]
Management of natural resources is a set of targeted impacts on the management object in order to ensure the consumption of material resources at a competitive level, which, in essence, is a resource saving. Resource saving is a process of rationalizing the use of raw materials, fuel and energy and other types of resources in the national economy on the basis of the introduction of the results of scientific and technological progress, optimizing economic ties, strengthening the economy regime, and applying progressive management methods that increase the efficiency of resource use. In general, the rationalization of the use of material resources is an increase in the level of their useful use, expressed in a decrease in the specific consumption of materials per unit of output with an increase or preservation of quality and technical level of products [2, p. 116].
There are a number of different classifications of natural resources. In particular, natural resources are divided into exhaustible and inexhaustible, reproducible and non-produced. This classification is optimal in structure, i.e. sufficiently fully reflects the entire range of resources available in nature from the point of view of the peculiarities of their ecological and economic use and existence.
В мировой практике принята следующая классификация всех минеральных ресурсов [4]:
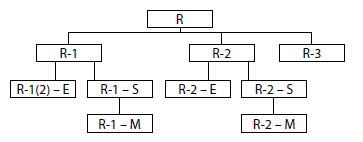
Figure 1 – International Classification of Natural Resources
R – common resources;
R-1 – resources in the fields studied with reliability, allowing to establish conditions of occurrence, morphology and quality of minerals (error can reach 50%);
R-2 – resources are estimated preliminary, the error can exceed 50%;
R-3 – undiscovered resources used to select areas of prospecting and to assess the prospects of certain areas;
R-1(2) – Е – resources that can be operated in a single country or region under the existing socio-economic conditions and available technology;
R-1(2) – S – the remainder of the resources that are not currently of interest, but may be suitable for development in the future;
R-1(2) – М – resources of interest in the near future.
Index 1 fixes proved and reasonably guaranteed reserves, index 2 - previously estimated and possible reserves and resources.
In the domestic practice, it is customary to distinguish four categories of reserves according to the degree of their exploration and quantitative certainty: A, B, C1 and C2. Reserves of category A are the most explored with precise definite limits of occurrence and are completely prepared for extraction. As a rule, the reserves of categories A and B are used to fulfill the current plans for the development of the national economy. The remaining categories of stocks (C1 and C2) are used to justify projects for determining capital investments in the construction of enterprises for extraction and processing of mineral raw materials, are taken into account in the development of long-term tasks, to justify general long-term plans, for geological exploration planning [3, pp. 53-54].
Activities to plan the use of natural resources require overcoming the historically established utilitarian approach to environmental management, as today they are mainly carried out in the interests of individual leading consumers. The existing planning system does not ensure the solution of problems of nature management in their unity with the processes of development of social production.
Environmental protection activity appears in the form of predefined activities that are disjointed. As a result, the facts of exploitation of certain useful properties of nature by some branch of the economy become frequent, leading to environmental degradation. A similar situation is observed in the use of secondary resources, the consumption of which is not taken into account when addressing such closely interrelated economic and social problems as the rational use of natural resources, improving the quality of the environment, and the involvement of consumption wastes into the economic circulation. All of them are considered and solved in isolation from each other [1, p. 250].
Of great importance is the integrated approach to the use of natural resources, which includes the solution of the following main tasks [5, pp. 29-30]:
Of great importance is the use of natural resources and engineering protection of the environment through the development of cyclical closed technologies, resource-saving, low-waste and non-waste technologies, biotechnologies, reuse of material resources (recycling), recycling and detoxification of waste, creating low-polluting technologies for processing and using raw materials.
The problem of saving and efficient use of resources at many enterprises is that with the growth of the volume of resources used in the industry, there is a need to reduce the unit costs of production with an increase in the output of commodity products from a unit of processed raw materials and its rational use. At the same time, the problem of efficient use of material resources is most actual for domestic enterprises, since they are the main type of resources consumed by enterprises in the production process and constitute the largest value in the structure of production costs, thus having a significant impact on the amount of profit, the level of profitability and production efficiency generally [6, pp. 427-428].
Conclusion
Thus, resource-saving is an important reserve for increasing production efficiency, which in itself indicates the need for a thorough analysis of the enterprise's activities and consideration of all possible factors. Resource saving allows to significantly raise the level of quality of goods and services, as well as positively affect the state of the environment when introducing innovative technologies that a priori have a more progressive structure of resource consumption. Innovative resource-saving policies, combined with environmental and economic aspects and clear control in all areas and at various stages of production, are a complex and costly process, which, however, with a correctly selected set of measures and their sequence can yield positive results.
- Попова Альфия Рафаиловна Формирование механизма управления природными ресурсами России // Вестник ВолГУ. Серия 3: Экономика. Экология. №2, 2008. – С.246-252
- Каленюк А. А. Повышение конкурентоспособности промышленного предприятия на основе управления ресурсосбережением // Вестник Саратовского государственного социально-экономического университета. №4, 2009. – С.116-118
- Мосейко В.В., Варлачева Н.В. Экономическая классификация природных ресурсов // Вестник ТГПУ. №9, 2007. – C. 52-54
- Никитин В. С. Теория и методы прогнозной экономической оценки минерально-сырьевых ресурсов.- М.: Наука, 1988.
- Мельников А. В., Мельников В. Н. Особенности управления ресурсами окружающей среды методами экологической кибернетики // Вестник АГТУ. Серия: Рыбное хозяйство. 2010. №1. – С.29-31
- Шумак Ж. Г., Орешникова О. В. Проблемы ресурсосбережения на предприятиях мясоперерабатывающей промышленности в контексте их инновационного развития // Молодой ученый. – 2013. – №5. – С. 427-430
