Abstract
The content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Overview of research and development
- 4. The conceptual basis of equity accounting
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Equity is one of the most used economic categories. It is the basis of creation and development of enterprises in the process of operation ensures that the interests of the state, owners and staff. Any organization of industrial or other commercial activity must have a certain capital, represents a collection of material assets and funds, financial investments and costs of acquisition of rights and privileges necessary for the implementation of its economic activity.
1. Theme urgency
In a market economy increases the need for reliable accounting and reporting information on the activities of economic entities. Capital is one of the strategic goals of management and the important object of accounting. Effective capital management is impossible without the study and further improvement of methodology and organization of accounting and financial reporting.
A critical component of the information system of capital management is accounting, the data of which are not only information about the state and change the state of objects of control but also audit database.
The need for improvement of methodology of accounting and analysis of own capital of the organization occurs in the transition to international financial reporting standards (IFRS). As a result, in the present time there is a question of methodological standardization and the integration of elements of own capital of the organization.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of the study is to identify gaps and inconsistencies in the accounting of equity and the development of specific recommendations for improving accounting and audit of equity.
Main tasks of the research:
- The study of the conceptual foundations and environment to standardize the treatment of equity;
- The discovery and generalization of theoretical aspects and practical experience of accounting of equity in terms of the standardized environment of the DPR;
- The discovery of the main features of audit of equity;
- The identification of the main directions of improvement of accounting and auditing of equity.
Research object: Business transactions related to the formation and changes of equity in enterprises of different ownership forms.
Research subject: a set of theoretical, methodological and practical issues of accounting and audit of operations with its equity.
3. Overview of research and development
Supporters of political economy A. Smith and D. Ricardo equated to the accumulated capital to work. They believed that the accumulation of capital is essential to production growth. A. Smith took to the capital part of reserves, intended for the subsequent production and income. In his opinion, in conditions of simple commodity production labour is the only source of value. From the point of view of David Ricardo, "capital is accumulated labor, or all that is involved in the production", and in the opinion of the founder of the school of the physiocrats francois Quesnay, "capital is not money, but the means of production, which can be purchased with money" [1].
According to Nassau William Senior, capital is a combination of three factors: land, labor and substance. Natural resources are the material of its content, and the content is a rejection of its industrial use, the labor is the same — a method of storing and formation [2].
John Stuart Mill was considered the capital of that part of the property of the entrepreneur (industrialist), which forms the Foundation for the implementation of the new production. In his writings he wrote: "Capital is first accumulated materialized labor product advanced for the purchase of means of production and labor" [2].
According to Jean Baptiste "Capital is one of the factors of production that forms in the accumulation process, i.e. through the employment of a larger number of products generated than was consumed in the production process" [3].
The notion of capital, according to prominent researcher and historian of accounting Raymond de Ruwer was introduced in accounting by the need to separate accounting of funds deposited by several participants. He believed that the appearance of the capital account simultaneously led to the emergence of double-entry method [4].
A comprehensive analysis of the content of the capital held in their scientific works, Marx, who, unlike his predecessors, considered the capital as the sum of the accumulated values, in his opinion, capital is not a thing but a relation, a self-reproducing value [5].
According to Marx the source of capital is surplus value, which is formed of surplus employees in the manufacturing sector. Marx also believed that "capital is not simply the sum of the material and produced means of production, Capital is converted into capital of the means of production that are themselves so are not capital as gold or silver themselves money" [6].
Outstanding neoclassical, the famous English economist of the XX century, Alfred Marshall, the main feature of the capital considered its ability to create income. This ability is due to the productivity of capital as a factor of production [7]. Campbell McConnell and Stanley Brue, the concept of "capital" is identified with the investment resources available produced means of production — all kinds of tools, machines, equipment [8].
Obviously, all opinions about the economic nature of capital have the right to exist and are mostly the same. Therefore, considering the nature of capital, mostly Western economists noted that the material content of capital presents it as a factor of production and social form of capital is its ability to create profit.
A key moment in the development of the concept of "equity" was his Association with the obligations into a single category of "source" in the theory of Russian scientist N. S. Lunsky [9]. He has developed the broadest interpretation of the liability, in accordance with which asset is the assets of the organization, and the passive – the sources of these funds, such as debt and equity:
Many interpretations of capital testify to the diversity, complexity and contradictions of this category. Its economic content, specific forms of change with qualitative changes in productive forces and relations of production. Modern society gives rise to a new theory of value and capital.
4. The conceptual basis of equity accounting
Equity is an abstract value of the property, other than his current or realizable value, but because it does not reflect the current value of the rights of the owners of the enterprise (firm). The amount of own capital significantly influences the rating in accounting assets and accounts payable, which was used in the creation of enterprises, although accidentally it may be the same as the total market value of the shares or the amount that can be obtained from the sale of the net assets or the whole enterprise. Equity is the basis for the establishment and functioning of economic activity of any enterprise, it is one of the most significant and important indicators, as does the following:
- autonomy and power - the amount of equity determines the degree of independence and influence of its owners at the enterprise;
- responsibility and protection of the rights of creditors reflected in the balance sheet equity is for external users, the measure of relations responsibility at the company, as well as protecting lenders from loss of capital;
- long - term lending is available to the company indefinitely;
- credit is a credit, under other equal conditions, preference is given to companies with less payables and large private capital;
- reimbursement of damages - temporary damages to be repaid at the expense of own capital;
- the allocation of income and asset shares of individual owners in the capital is the basis for allocation of the financial result and the liquidation of the company.
The equity is formed in two ways: by making the owners of the business cash and other assets, and the accumulation amount of profit that remains in the enterprise [10].
Equity has 8 components (fig.1).
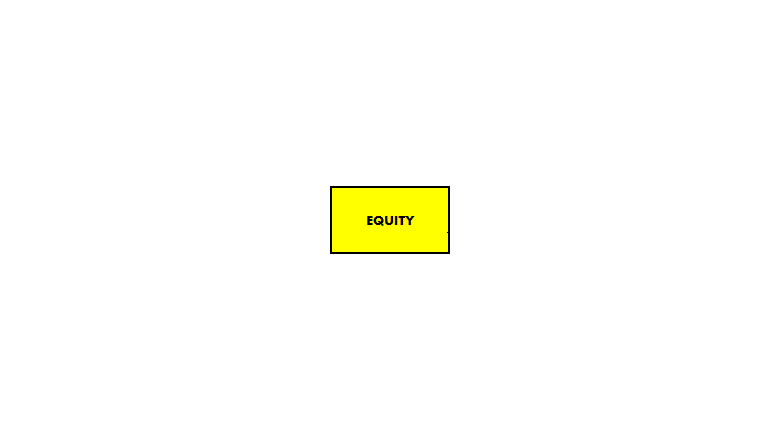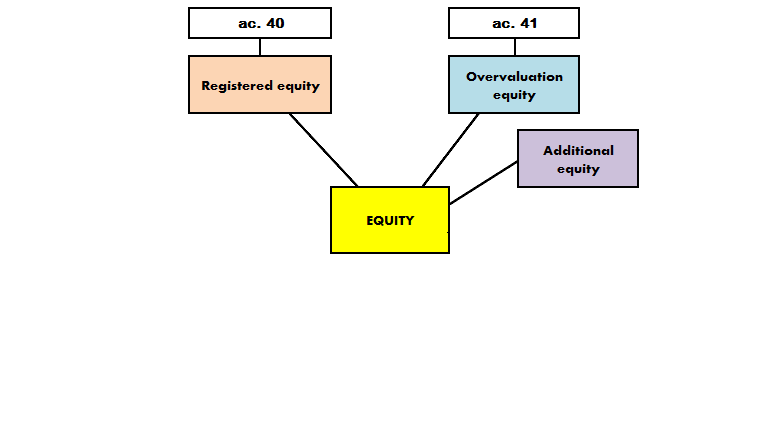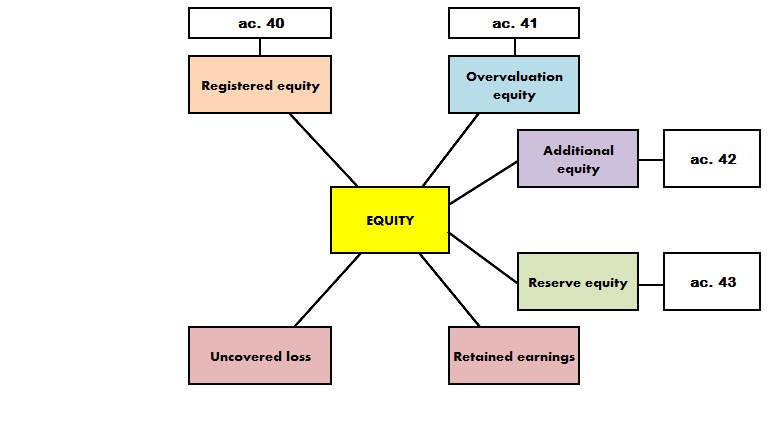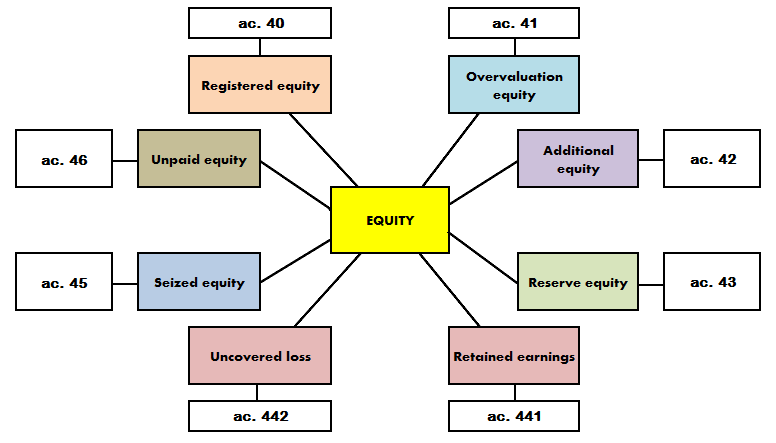
Figure 1 – Structure of equity
(animation: 15 frames, 10 cycles of repeating, 121 kilobytes)
As a methodological basis for calculating the size of the current capital of the company is required to apply the basic balance equation (fig.2):
Figure 1 – Basic balance equation
At the organization of accounting of operations with its own capital it is necessary to adhere to existing legal documents. At the legislative level the order of reflection of equity in the statements embodied in NSA № 1 "General requirements to financial reporting" [11]. The organization equity is a non-stop process, targeted selection and application of the most efficient tools and techniques of collecting and processing accounting information and reporting on the availability, the formation and use of funds, reserves and financial results.
Accounting principles transactions with equity are based on common accounting principles, in particular on the principle of recognition of assets and liabilities, income and expenses and the requirements of corporate law and securities legislation.
Conclusion
At the present stage of economic development capital is one of the key economic and accounting categories. The value of equity of any company is often decisive to establish whether the company can continue as a going concern, and how these activities provided their own, and not borrowed sources of financing. Disclosure of information on the status and changes of equity in reporting allows management personnel to assess the financial independence of the enterprise and directions of subsequent management decisions, and users to draw conclusions about the level of skills of managers to manage the resources entrusted to them and trust other entities.
Equity plays a pivotal role in the financial security of the enterprise. The company needs to analyze its own capital as it helps to identify the main components and to determine the impact of their changes for financial stability.
Various errors in the accounting of equity capital lead to distortions in the financial statements, which in turn entails the adoption of wrong economic decisions. To avoid such situations in the enterprises conducted the audit.
References
- Кенэ Ф. Избранные экономические произведения / пер. А. В. Горбунова, Ф. Р Каплан, Л. А. Фейгиной. М.: Соцэкгиз, 1960. - 487 с.
- Кириленко В. В. История экономических учений: учеб. пособие / под ред. В. В. Кириленко. Тернополь: Экономическая мысль, 2007. - 233 с.
- Сэй Ж. Б. Трактат по политической экономии. М.: Дело; Академия народного хозяйства при Правительстве РФ, 2000. - 232 с.
- Рувер, де Р. Как возникла двойная бухгалтерия / де Р. Рувер: под ред. Н. Вейцмана.; пер. с англ. А. Мухина – М.:Госфиниздат, 1958. – 67 с.
- Маркс, К. Капитал: в 3 т. – Т. 3 / К. Маркс. – М.: Политиздат, 1988. – 750 с.
- Маркс, К. Капитал: в 3 т. – Т. 1 / К. Маркс. – М.: Политиздат, 1988. – 750 с.
- Маршалл А. Принципы экономической науки: в 5 т. // пер. с англ. М.: Прогресс, 1993. Т. 1. - 416 с.
- Макконнелл К. Р., Брю С. Л. Экономикс: принципы, проблемы и политика. 11-е изд. / пер. с англ. М.: Республика, 1992. - 400 с.
- Лунский, Н.С. Краткий учебник коммерческой бухгалтерии / Н.С. Лунский. – 3-е издание – М., 1913. – 316 с.
- Славьюка Р.А. Финансы предприятий: Учеб. пособие. - Киев: ЦУЛ, 2002. - 460с.
- Національне положення (стандарт) бухгалтерського обліку 1 "Загальні вимоги до фінансової звітності", затверджене МФУ від 07.02.2013 р. № 73.-[Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://zakon4.rada.gov.ua...
