Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study, the planned results
- 3. Review of research and development
- 3.1 Overview of international sources
- 3.2 Review of national sources
- 3.3 Local Source Overview
- List of sources
Introduction
The object of computerization is the transport dispatch system. Dispatch systems successfully used in various transport companies. These systems solve the problem of controlling the position of transport means, level of their loading, amount of fuel and other indicators. Such systems allow you to identify situations of unfair use of the property of transport companies, for example, the use vehicles for non-official purposes; gasoline discharge; and timely detection of emergency situations. All this, ultimately, leads to lower losses for transport companies.
1. Relevance of the topic
Currently there are many different commercial systems and solutions that allow you to solve transport dispatching tasks. However, these systems are not widely used in our region. This is mainly due to the high cost and complexity of implementation. Therefore, the relevance of this topic. in solving these problems.
2. The purpose and objectives of the study, the planned results
The purpose of this work is to study the possibility of implementing a simple transport dispatch system, winning at the price of existing solutions.
For this it is necessary: ??to explore the subject area, analyze existing methods for solving such tasks, highlight their strengths and weaknesses, choose the most promising solutions for this tasks, analyze the results of their application and select the best of them.
Formed a number of tasks to achieve the goal:
- Justification and choice of platform for the implementation of the hardware.
- Justification and choice of platform for visualization of results.
- Designing a system and tools for receiving and storing data.
The main objectives of the study:
- Determining a vehicle's geo-location at a specific frequency
- Determining the time for each geography
- Writing data to a non-volatile drive
- Transfer data to removable storage
- Visualization of data in a readable form
| Task | Ex. data | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Detection | Image | Deciding on the presence (and possibly on the number) of persons in the image, determining their position |
| Recognition | Single Face Fragment | Candidates from the existing database, the key features of which are close to the current data fragment. |
Object of study : design of a transport dispatch system
Subject of research : study of the possibility of minimizing the cost of the system
When building a monitoring system, the following features should be considered: complicating the task:
- The system must be difficult to access for unauthorized modification
- Being connected to the vehicle's battery, the system must be subject to a surge voltage test. at the time of starting the engine
- The system should not consume energy when the engine is off
3. Review of research and development
Background to the emergence of vehicle monitoring solutions
First of all, it is connected with the continuous process of integration of all types of transport with telematic systems, technological progress and increased safety requirements. It is worth highlighting the industry automakers, as they become more and more interested in producing cars, which go on sale with an integrated monitoring system. Telematics is one area information technology, which is designed to monitor and continuously monitor transport, improve fuel efficiency, ensure maximum safety for drivers and pedestrians.
Monitoring of transport began its development in the west. When the cost of a mobile phone dropped to acceptable for use on a large scale (mid-90s), mobile electronics manufacturers began to look for new markets. But a new market in the form of monitoring of transport did not appear immediately, since accuracy of determination of coordinates was important for monitoring. Namely, determining the location of a position with minimum error for civilian purposes was impossible, because the original GPS was developed as exclusively military project for accurate guidance of rockets to fixed and then to mobile objects in the air and on the ground. And only in 2000. deception of accuracy canceled by decree US President Bill Clinton It is exactly 2000 that can be considered the starting point in the development of transport monitoring.
In the early 2000s, the first devices began to appear that could be installed on transport and to track A little later, these devices began to be delivered to Russia. The second problem that got in the way of large-scale use of transport monitoring? this is a cellular network coverage GPRS. That is why the first car terminals transmitted coordinates in SMS messages. And in the software Ensuring the dispatcher could observe the "point on the map", which indicated the location of the car. But since then, a lot of time has passed, and transport monitoring systems in the Russian Federation and in the West have made great strides, choosing their own development paths. Maybe in something even copying each other. [1]
Modern business conditions pose new and new challenges for companies. Now for profit is no longer enough just to make the best transport route. It is necessary constantly track vehicle coordinates to dynamically respond to rapidly changing road conditions. Development of transport infrastructure and provision of navigation for all types of transport impossible without modern reliable information about the objects of the earth’s surface that it creates and provides geodesy and cartography. This information is very important for the organization of transport on all types transport, first of all, when solving the issue of navigation support of transport (practically it is 80% the total amount of development of various navigation systems). [2]
Navigation systems
Conceptually, vehicle tracking is as follows:
- The tracker installed in the car receives a signal from one or several navigation systems, not only satellite, but also global wireless network services. To do this, the device must have GLONASS / GPS / LBS-modules that automatically calculate the coordinates of the object by the location of the satellites and closest cell towers. [8]
- Telemetry and other data (for example, audio recording, event “accident”) are collected in the tracker's memory. Then the information is transmitted in packets at fixed time intervals over GPRS channels via the Internet to telematic server with special software and / or via SMS notifications to a mobile device the owner. [8]
The system of satellite monitoring of vehicles allows not only to determine the current location of the vehicle with accuracy up to 2.5 meters, but also view the history of its movement, as well as perform a number of other functions. So, modern tracking devices allow voice communication with the driver, to conduct audio monitoring. environment, receive notifications about the consumption of gasoline or the deviation of the car from a given route. GPS and GLONASS positioning systems whose capabilities are used in trackers have more similarities, rather than differences, but the nuances are still there. In addition to state ownership, they differ:
- Methods of using radio frequencies: in GLONASS - more secure FDMA (the principle of "dedicated line"), but also more resource intensive; GPS is less secure and stable CDMA (coded multiple access), but while more economical.
- The principle of satellite arrangement: the Russian satellite constellation is independent of the rotation of the Earth; American - requires continuous synchronization and adjustment of the satellite orbit; domestic system currently working in 3 planes of 8 satellites, the US - in 6 planes of 4 satellite All systems also have backup satellites.
- Accuracy in different latitudes: due to the higher orbit of Russian satellites, they provide greater than GPS, accuracy in the northern latitudes, in particular, in the area of ??the Scandinavian countries.
- Signal accuracy: today it is 3–6 meters in GLONASS, 2–4 meters in GPS, but this is explained extremely insufficient grouping of domestic satellites, which is continuously increasing. TO mid-2020s, GLONASS plans to reduce the error of only up to 10 cm.
All of the above means that a modern satellite vehicle monitoring system should use both navigation systems at the same time. Trackers that work with both GLONASS and GPS modules allow improve the overall accuracy of object detection (up to 1.5–3 meters) and achieve stable and high-quality work even in difficult conditions of modern cities with dense high buildings, which greatly complicates passing signals from navigation satellites. [3]
3.1 Overview of international sources
OnStar Vehicle Monitoring System
The system was developed by OnStar Corporation, founded in 1995. At the very beginning of the formation of the company sold individual devices that were available only to owners of certain car models. By 2005, the range of supported devices has expanded to include Audi, Subaru, Volkswagen, and others. To this the time the device entered into mass production and integrated into cars already at the assembly stage. In 2006, the project had about half a million users. At the moment, this number is 4,000,000, with a cost of one device about $ 200 [4]
The system uses CDMA communication channel, provided mainly by Verzion Wireless in the USA and Bell Mobile In Canada. GPS is used to determine the location. Information from the sensors is automatically transmitted to call centers. This allows you to immediately notify the rescue and law enforcement of the accident location organs. In addition, the system, using a GPS sensor, allows you to track a stolen vehicle. Also available possibility of obtaining information on speed, fuel consumption and driving direction. This allows conclusions about the style of driving a car. This information is used by insurance companies to calculate cost of individual insurance policies. New car models are equipped with a remote system. engine stop. After such a stop, the car can only be started after entering a special secret code. [4]
NEXCO Central Traffic Management System
The system is developed by Japan Highway Public Corporation. The principle of operation is global monitoring traffic on the main highways of the country. At the moment, the system covers about 2000 km of roads. The system is centralized. The traffic control center is located in Tokyo. Datacenter handles huge the amount of data received from road sensors with a minute interval. This ensures maximum real picture of the traffic situation. There are 744 access points on the roads that allow you to work emergency telephone channels and sensors to transmit the necessary information about the traffic situation. [6]
For data transmission, a global IP network is used, with the help of which information from sensors is transmitted traffic control center monitors. Global data transmission is provided via fiber optic communications This allows you to quickly handle calls and incoming data. This system is running in parallel with the current in April 2012. Server space is 90% smaller than the old system, therefore, there is significant energy savings. [6]
ECall Japan
Since the mid 1980s. On all roads of the country, an intelligent transport system was launched, designed to implement full automation of traffic management. All cars began to install special onboard navigation and communication equipment with which control is provided location and condition of the vehicle.
The transmission of control signals, as well as duplex communication with the driver, is performed by the dispatch service rapid response called ECall.
As a result of the success of the system, mortality on the roads of Japan has decreased significantly, in 2009 amounted to 5 thousand people. Authorities plan to reduce the death toll to zero. [4]
3.2 National Sources
System of global monitoring of transport ERA GLONASS
A significant decrease in the market growth rate was noted by almost all the participants of the conference “Sharks M2M business "ended in January 2014. According to the reporting data of the Analytical Center, the same Omnicomm, by the end of 2013 in Russia 1.5 million units of various vehicles and special equipment were equipped with transport telematics systems. [7]
The system ERA GLONASS
is designed in accordance with the order of the Government of the Russian
Federation and is intended to reduce road fatalities and injuries by speeding up the alert of emergency
services response to accidents and other emergency situations.
The system will include navigation and telecommunications terminals that will start to be massively installed on vehicles starting in 2013 and the corresponding infrastructure covering all subjects RF (Fig. 1). To ensure the efficiency of the system on the territory of the Russian Federation, the Government of Russia reserved special telephone codes that will be used to communicate with emergency information receiving centers. [9]
It is supposed to legally oblige all car owners to install onboard equipment by 2020, the cost of which will
be about 3 thousand Russian rubles. The fee for using the system is not charged will be ERA GLONASS
will be compatible with similar services to be created in countries Customs Union, as well as the European
Union. [7]
The system for identification and monitoring of road objects is based on radio frequency technology short-range identification (RFID) in combination with satellite navigation systems GLONASS and GPS. The project solves the tasks of vehicle monitoring, remote control of documents and identification objects of transport infrastructure. [10]
3.3 Local Sources
Creating a system for automated management of the city’s freight traffic
A draft technical and software approval of carrier’s operational plans at the level of the city’s administration is the “single transport city”. Today in cities almost there is no unified transportation management system, which leads to these problems. Known in using three models of transportation management - decentralized, centralized and mixed.Consider each of the models of urban transportation management systems in terms of application modern computer automation. The centralized system will work as follows. After forming with manufacturers and distributors of all applications for the delivery of products to trade enterprises the data is transmitted to the central server of the city coordination center for transport, where it also arrives information on operating modes of warehouses and trade enterprises of the city, data on available vehicles with their characteristics from carriers and distributors, data on changes in urban transport network (Fig. 3). Further, the server generates, according to the available data, the delivery routes taking into account dislocation of transport of carriers and transfers them to the control centers of carriers for execution.
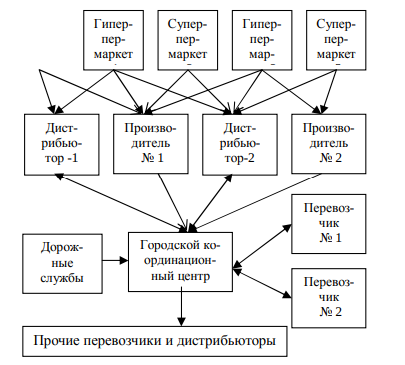
Fig. 1 - Structure of information links of the urban transit system
The advantage of this scheme is the modeling of routes, taking into account all the influencing factors and obtaining the most optimal loading pattern of highways, the greatest service to all participants in the system. The disadvantage of such a system is dependence on the level of organization of work of all members of the system - development routes does not start until all applications and data are received. Certain mode synchronization required works of all warehouses, enterprises. Also, the entire transportation system is highly dependent on computer network works. Therefore, in this form, local systems of individual distributors are working today, but as a result we come to the above problems in the city scale. [5]
Ñïèñîê èñòî÷íèêîâ
- https://habr.com/ru/post/241109/
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sistemy-monitoringa-transportnyh-sredstv-na-osnove-glonass-gps.pdf
- https://www.kp.ru/guide/sistemy-sputnikovogo-monitoringa-avtotransporta.html
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/analiz-sistem-avtomatizirovannogo-monitoringa-avtomobilnogo-transporta-i-upravleniya-dorozhnym-dvizheniem
- http://masters.donntu.ru/2014/fknt/baryshev/library/article8.pdf
- https://globalposition.org/vse-novosti/778-wialon-priznan-liderom-sredi-sistem-monitoringa-transporta-v-rossii-i-stranax-vostochnoj-evropy
- http://controlauto.ru/issledovaniya-rossiiskogo-rynka-monitoringa-transporta/
- http://space-team.com/about_company/
- http://www.acg.in.ua/vse-o-gps-monitoringe/
- http://www.resurscontrol.by/news_test.php?id=149
