Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study, expected results
- 3. The mechanism of influence of the employer on the educational program by means of professional standards
- 3.1 Creation of the competence model of the graduate in the direction of training 27.03.02 Quality Management
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The main trends in the development of most countries are the transition of the economy to a post-industrial type, associated with the creation and introduction of new technologies in all spheres of society, changes in the structure of employment, globalization of economic ties and increasing competition.
Today, in the world of new information technologies and new business processes that provide leadership and competitiveness, employees have to regularly transform not only the scope of their competencies, but also the competencies themselves, acquiring completely new knowledge and skills. At the same time, graduates have to retrain already in the workplace, as coming to the production, they knowingly possess unsuitable for effective work skills.
The reality Is that the economy has changed technologically and structurally, the processes associated with globalization have begun. In these conditions, at all levels, the imbalance between the requirements for workers in real time and the qualifications of professions developed at a very different time has become increasingly noticeable.
1. Theme urgency
In today's conditions, vocational education cannot develop as a closed system. Educational institutions are faced with the need to have a clear order from consumers of educational services in terms of the number (target order) and quality of vocational education of graduates, that is, the implementation of the objectives of vocational education makes it necessary not only to maintain established contacts between educational institutions and employers, but also their development.
Interaction with employers is a complex process, the purpose of which is to train personnel focused on innovative activities in the socio-economic sphere of the region. Unfortunately, the current system of training does not fully meet the requirements of employers and only partially meets the rapidly changing requirements of the time. Among the problems that complicate the interaction of educational institutions and employers are the following [1]:
- contradictions between the development of the labor market of specialists and the ability to meet these requirements in the vocational education system;
- discrepancies between the dynamics of growth of labor market requirements to the level of professional competence of a specialist and the lack of consistency of these requirements with graduates of educational institutions;
2. The purpose and objectives of the study, expected results
The aim of the study is to find ways to solve the problem of isolation of education from the employer, to develop a tool to influence the content of educational programs using professional standards.
To achieve this goal, the following objectives were set:
- research prospects of interaction between employers and educational institutions;
- develop guidelines to improve the quality of educational services by changing the content of educational programs.
The practical significance of the results obtained is to develop recommendations and proposals to improve the effectiveness of improving the educational program written on the basis of a professional standard.
3. The mechanism of influence of the employer on the educational program by means of professional standards
Modernization of the vocational education system has caused the need to form a field of active interaction of various stakeholders in the development of education of the parties: authorities, educational institutions, students, employers, members of the public, business, professional communities [5].
Joint activities to develop basic educational programs, which will allow joint efforts to determine the requirements for the level of education of General cultural and professional competencies of graduates and to develop curricula taking into account the requirements of the regional labor market and the potential of the educational institution. Undoubtedly, the employer engaged in hiring and placement of staff knows better than anyone else what kind of personnel is needed to carry out certain professional functions.
When designing basic educational programs, it is necessary to jointly carry out functional analysis by describing the work activity, its functions and results, which allows you to quickly take into account changes in technology and organization of work in the regional labor markets, where graduates will get in the future. Functional analysis begins with the establishment of the requirements of employers to the standards of activity in a particular professional area (profession) in order to determine the present and future industry requirements for different categories of personnel.
When developing an educational standard, an educational institution, through questionnaires and expert surveys, should form a list of competencies that, in the opinion of employers, graduates of specific specialties and educational areas should have [8].
Thus, the employer becomes the priority partner of the educational organization, and building a dialogue is the key to the quality of educational programs, the demand for graduates in the labor market.
The Relevance of requirements, mobility of content, system nature and modular structure distinguish the professional standard from all documents used in the practice of personnel management and labor market regulation in the past.
Professional standard – multifunctional normative document defining within a specific type of economic activity (field of professional activity) the requirements for the content and working conditions, qualifications and competencies of employees at different qualification levels [9].
The range of stakeholders in professional standards is quite wide. This document integrates the interests of business, the employee, the state and the education system.
The generalized scheme of stakeholders in the professional standard is presented in figure 1.
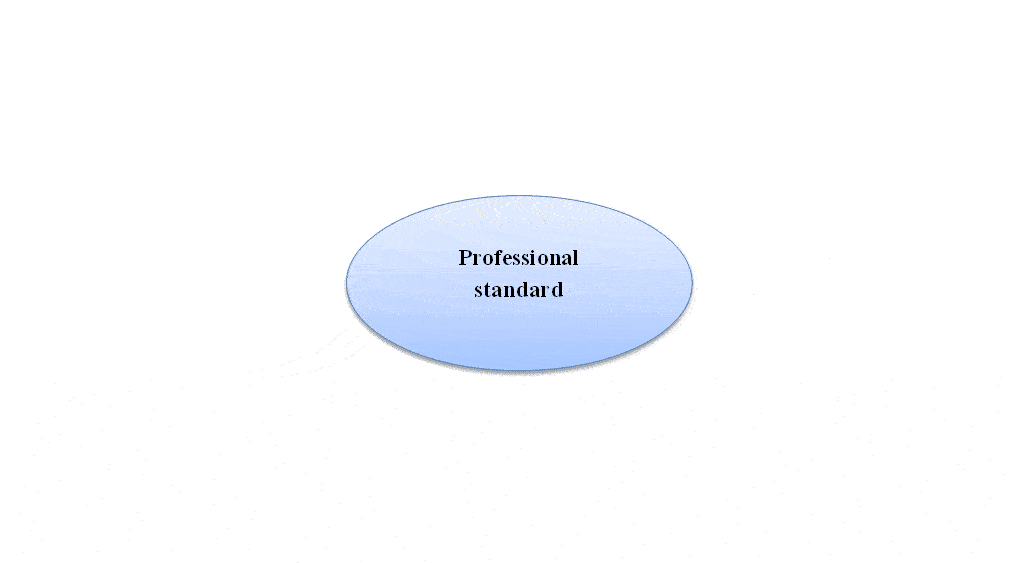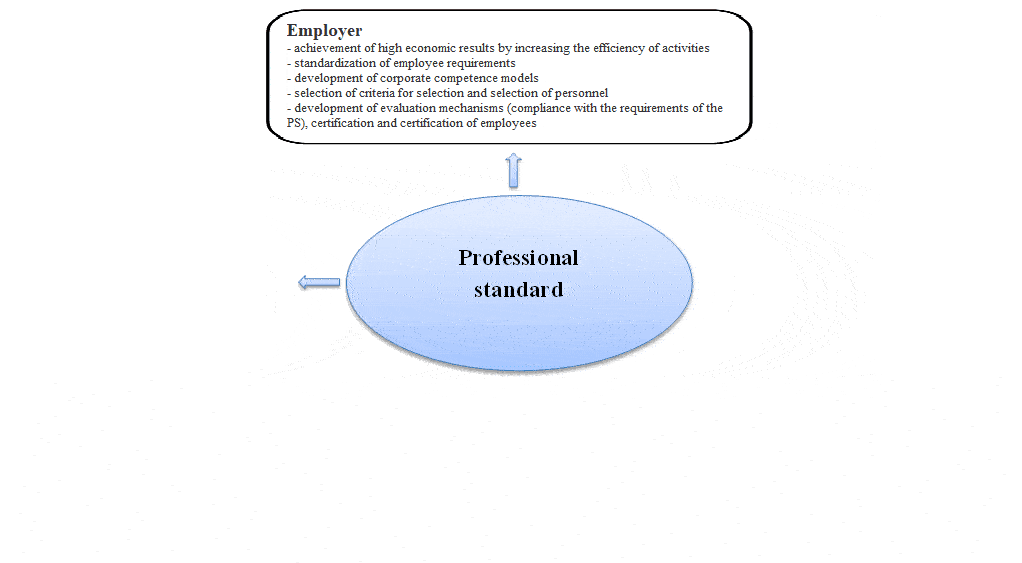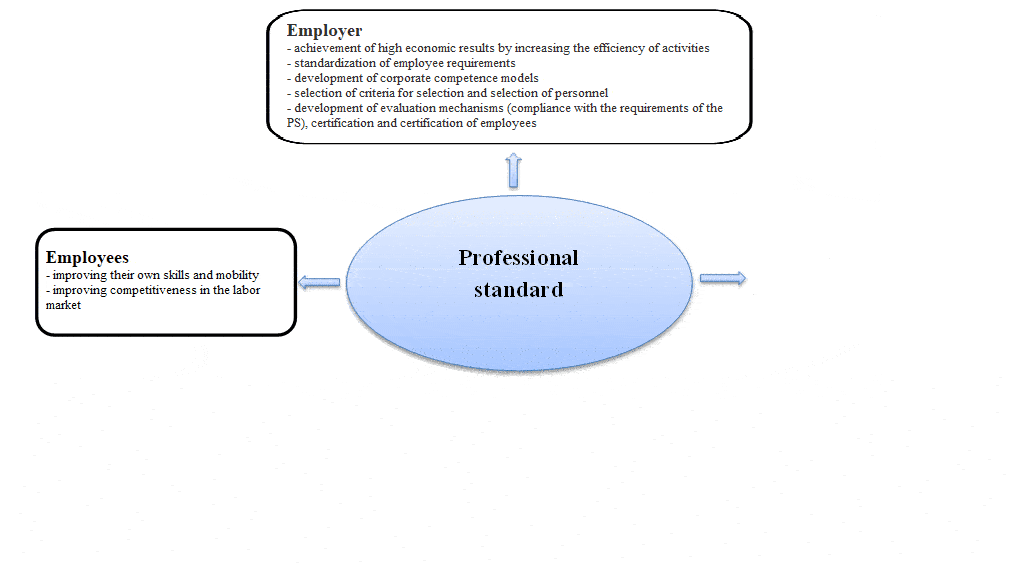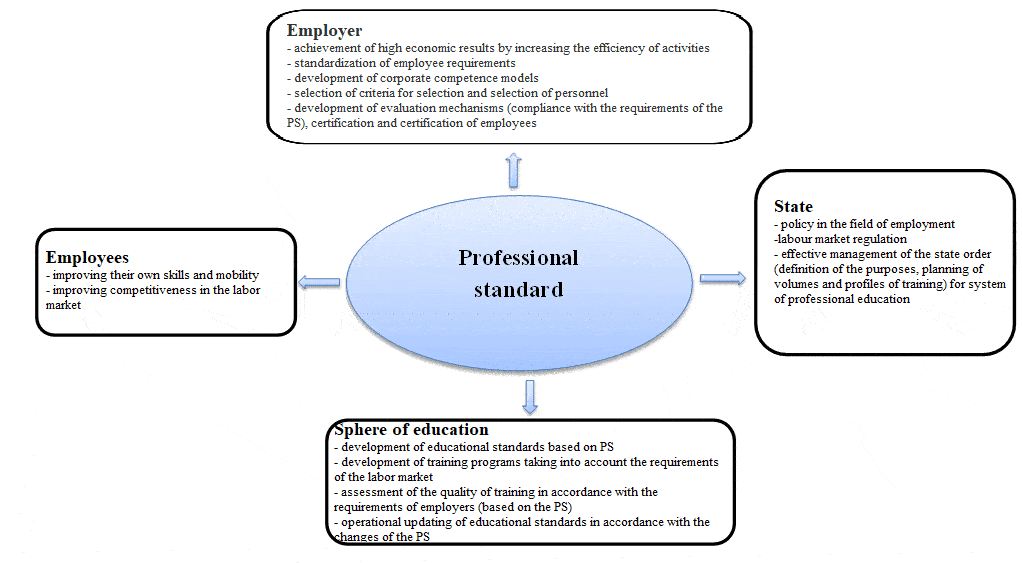
Figure 1 – Range of stakeholders in the professional standard
(animation: 9 frames, cycles of repeating – 6, 119 kilobytes)
The new educational standards will contain professional and vocational competencies that reflect the knowledge and skills that meet the requirements of employers. That is, a graduate of an educational institution will have the competencies necessary for the labor market and the employer; the employer will receive an employee trained at his request, which determines his competitiveness, and the educational institution will become in demand among applicants.
3.1 Creation of the competence model of the graduate in the direction of training 27.03.02 Quality Management
To create a model of graduate competence, it is necessary to determine the choice of professional standard. Currently, as part of the implementation of the direction 27.03.02 Quality Management, applicable are two PS:
-
product quality Specialist
; -
Internal auditor
.
Further analysis was conducted for compliance with the requirements of the professional standard and the requirements of the educational orientation of the programme with the aim of forming a model of competencies of graduates, most prepared to professional activity and has the necessary knowledge in the field of quality management.
As a result of comparison of the above documents, labor functions were identified, the acquisition of which requires PS, but are not reflected in professional competencies. The analysis revealed the need to improve the basic educational program in terms of the formation of additional activities, Production and operational activities
and relevant professional and specialized competencies (SC), the ability to identify and analyze consumer requirements for products (services) – SC-1; ability to carry out work to ensure customer satisfaction & ndash; SC-2.
At the next stage of the work of the working group, a model of graduate competencies was formed, presented in figure 2.
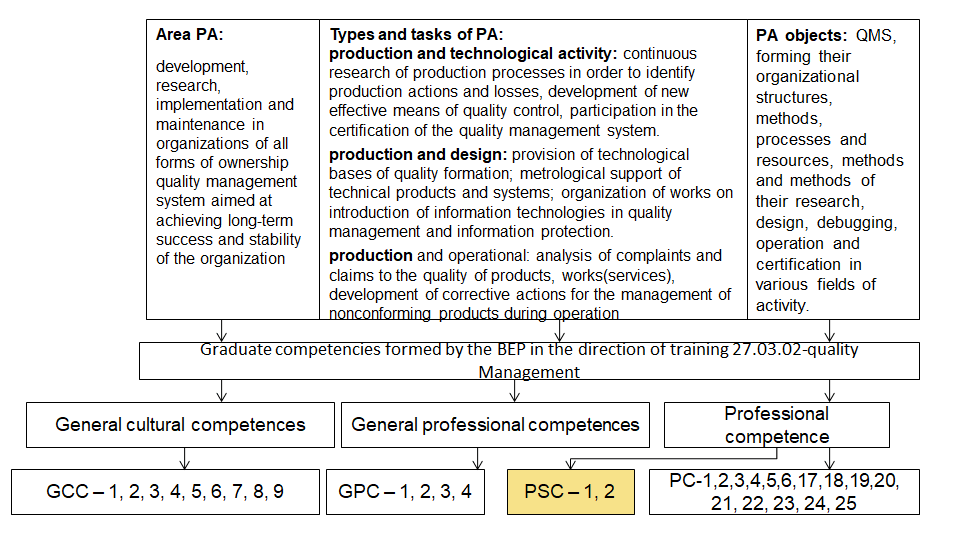
Figure 2 – Competence model of the graduate in the direction of training 27.03.02 Quality management
Thus, at this stage, the task was completed: the development of a model of graduate competencies, taking into account the PS, which resulted in the formulation of additional activities and professional and special competencies, resulting in the formation of a model of graduate competencies in the direction of 27.03.02 & ndash; quality Management.
Conclusion
The study revealed that the employer's assessment is an indicator of the quality of educational services, so the educational institution should focus on its requirements. One of the main unifying element in the formation of the list of professional competencies, taking into account both the requirements of employers and the requirements of educational standards is the professional standard.
Creating educational programs based on professional standards will improve the quality of educational services with the release of competitive young specialists with sufficient professional skills and competencies, functions that should have a graduate in their area.
Also, this development will ensure more complete compliance of qualified employees with the requirements of employers, which, ultimately, should lead to increased efficiency of production or business process. Improving the professional level of employees has a significant impact on labor productivity, reducing the cost of employers to adapt workers in employment, as well as on the competitiveness of workers in the labor market.
This masterʼs work is not completed yet. Final completion: Jule 2020. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Реутов Н. Н. Взаимодействие высшей школы и работодателей в современных условиях как фактор подготовки конкурентоспособного специалиста // Электр. журн.
Оригинальные исследования
. Вып. №3, Июнь. - Дымарская О. Я. Профессиональное образование и рынок труда: опыт и перспективы взаимодействия // Россия реформирующаяся: Ежегодник 2005 / Отв. ред. Л. М. Дробижева. М.: Институт социологии РАН, 2006. – С. 174—184.
- Лукичев Г. А. В поисках эффективного взаимодействия высшего образования и работодателей // Экономика образования. – 2005. – № 4. – с. 5-21.
- Боброва Т. А. Современная система высшего образования Российской Федерации: основные проблемы и пути их решения // Молодой ученый. – 2018. – №45. – С. 127-130.
- Чернякова М. М. Модернизация учреждений образования как необходимое условие развития социальной политики// Современные технологии управления. ISSN 2226-9339. – №1 (25). Номер статьи: 2509. Дата публикации: 2013-01-08 [Электронный ресурс]. — Режим доступа: https://sovman.ru/article/2509/.
- Кривых С. В. Методические рекомендации по разработке учебных планов по ФГОС ВПО / С. В. Кривых, А. Н. Строганова. СПб.: НОУ
Экспресс
, 2011. - Байденко В. И. Компетентностный подход к проектированию государственных образовательных стандартов высшего профессионального образования (методологические и методические вопросы): методическое пособие. – М.: Исследовательский центр проблем качества подготовки специалистов, 2005.
- Никитина Е. А. Междисциплинарные знания и формирование универсальных компетенций профессиональных кадров для наукоемких отраслей: российский технологический журнал / 2013, – с. 186-191.
- Олейникова О. Н., Муравьева А. А. Профессиональные стандарты: принципы формирования, назначение и структура. Методическое пособие. – М.: АНО Центр ИРПО, 2011. – 100 с.[Электронный ресурс].Режим доступа: https://www.profiz.ru/sr/4_2015/profstandarti/.
- Азарова Р. Н., Борисова Н. В., Кузов Б. В.// Один из подходов к проектированию основных образовательных программ вузов на основе компетентностного подхода //Материалы XVII Всероссийской научно-методической конференции
Проектирование федеральных государственных образовательных стандартов и образовательных программ высшего профессионального образования в контексте европейских и мировых тенденций
.
