Advantages and disadvantages of using programmable building kit lego in learning of robototechnics
Автор: Grebneva D
Источник:Электронный научный журнал «Наука и перспективы» №2, 2017. Режим доступа: http://nip.esrae.ru/
Abstract
The article analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of using Lego educational robotics kits in the educational process. The review of the finished projects from Lego Education Ev3 and their possibilities for studying simple mechanisms and basic algorithms for controlling robots is given. To the main lack of use of programmable Lego constructors in the educational process, the author refers to the desire for unnecessary simplification of work, which can lead to the illusion of simplicity of working with microelectronics in students.
Lego robotic constructors are one of the most popular tools for teaching robotics to schoolchildren of all age categories.
For younger students, it is suggested to use the Lego EducationWedo set, which includes building elements, a motor, a tilt sensor and a distance sensor.
For primary and high school students, an educational Lego MindStorms constructor has been developed, the current version of which is called Lego MindStorms Ev3.
The advantages of using Lego MindStorms Ev3 in the educational process include:
- Availability of free Lego EV3 Basic software;
- Microsoft Small Basic Ev3 text-based programming environment, specially designed for programming training;
- easy installation;
- Friendly interface;
- Russian language support;
- a built-in reference system with a guide to the assembly and programming of several robot models
- a large number of working examples.
Projects of robotic devices built out of Lego MindStorms Ev3 can be divided into three large groups:
- Standard model robots developed by experts from Lego Education, the description comes with the software as a learning project (robot-truck, crane, sorter etc.).
- More models of robots submitted by specialistenregister in the field of microelectronics and robotics (printer, walking robot, clock, etc.)
- Individual projects for the robotics students designed for the performance of any specific problem.
With the help of already developed projects in robotics, you can study simple mechanisms and basic algorithms for controlling a robot: the organization of movement, the basics of computer vision, and other tasks that can be solved not only in robotics, but also in other related subject areas (physics, mathematics, technology, etc.).

Figure 1 – Examples of developed Lego Ev3 projects
Thus, the student can study robotics along the path of increasing complexity: working with basic models, studying author's models of robots to expand knowledge and get acquainted with the ideas of various types of robots, creating their own development.
Without denying the positive aspects of using Lego Education kits in the educational process, we note, however, that it is impractical to limit ourselves only to these constructors in teaching robotics for a number of reasons.
1. The child sees the result, but does not see the system behind the result – the blocks remain "black boxes" for him, which function in an incomprehensible "magic" way for him. As can be seen from Fig. 1. All the microelectronic elements of the Lego software block are "hidden" in the case. For comparison, a drawing of the Arduino program block with open microelectronic elements is shown next to it.
Figure 2 – Comparison of the appearance of Lego and Arduino programmable blocks
2. The construction elements of the Lego constructor, the assembly schemes of the proposed robots are simplified so that every child can easily cope with the task. At the same time, students are not required to work with basic things – such as a ruler, compasses, soldering iron, hacksaw, hammer, screwdriver, etc. In other words, the work of assembling and programming robots from Lego is quite far from the reality that is presented in industry, in production.
To illustrate this problem, we can compare the assembly schemes of a Lego-based robot trolley and an Arduino-based one [1, 2]. The instructions for assembling a Lego robot trolley take 107 pages and describe each step up to how to insert the battery into the programmable unit. The image of the robot parts as realistic as possible (no diagram), there is no explanatory text and names of parts (part names are presented separately in the user manual [3]). The instructions for assembling the robot cart from Arduino take 4 pages. The assembly process is shown schematically, there is an explanatory text, the names of the parts. A comparison of the elements of the instructions for assembling robots based on Lego and Arduino is shown in Figure 3.
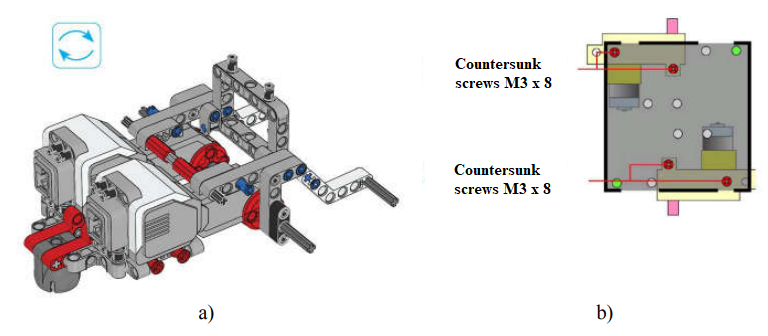
Figure 3 – Description of the steps for assembling a robot cart from Lego (a) and Arduino (b)
Thus, Lego robotic constructors can be used at the stage of introducing students to robotics, but with an emphasis on the fact that these are really only "the first steps into robotics". It should be emphasized that the development of Lego is a huge work of engineers who took care of the simplicity of the designer. If possible, you should organize excursions to enterprises where automated and robotic systems are used to form a holistic perception of students about the subject area of robotics. The next stage of studying robotics can be working with the Arduino designer, which is more close to the real work of an engineer.
List of the literature
1. Инструкция по сборке робота-тележки Educator Vehicle [Электронный ресурс].
URL: http://robotsquare.com/wpcontent/uploads/2013/10/_educator.pdf (дата обращения 10.02.2017)
2. Руководство по практическим занятиям POP-BOT mobile robot kit.[Электронный ресурс].
URL: http://static12.insales.ru/files/1/469/1106389/original/popbotxt.pdf
3. Руководство пользователя Lego MindStorms Education Ev3 [Электронный ресурс].
URL: http://soiro.ru/sites/default/files/lego_ev3_rukovodstvo_polzovatelya.pdf (дата обращения 10.02.2017)