Abstract
Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. Research and Development Review
- 3. Analysis of existing WLAN networks
- 4. Implementation and maintenance of control systems, monitoring and data analysis in Wi-Fi networks
- 5. Overview of hardware for network communication
- 6. Selecting a typical hardware module for network data collection
- List of used literature
Introduction
A person in the modern world actively interacts with information in the information environment, which is at the same time a source of new information, a means of converting various data. A person constantly receives new knowledge from the information environment, creates new knowledge himself and places it in the information environment. The development of technological progress allows you to collect information using technical devices.
The Wi-Fi standard was developed on the basis of IEEE 802.11 and is used for broadband wireless communication networks. Initially, Wi-Fi technology was focused on organizing hotspots for mobile users. Wi-Fi technology has initially become the standard followed by mobile device manufacturers. Gradually, Wi-Fi networks began to use small and large offices to organize internal networks and subnets, and operators to create their own infrastructure for providing wireless Internet access based on Wi-Fi technology. Thus, at present, Wi-Fi networks are ubiquitous and often have coverage areas of entire city districts [1].
The non-profit organization Wi-Fi Alliance, which develops the Wi-Fi standard, includes more than 400 wireless equipment manufacturers around the world. The Institute of Electronic and Electrical Engineers is developing the standard itself, but they do not test various devices with this standard. This organization, rather, creates a standard for technology and principles for its use, which should be the same around the world [2].
1. Relevance of the topic
Using wireless networks, you can collect, analyze and visualize various data from sensors, sensors and surveillance cameras. This need arises in the automotive, marine and aerospace industries, which often require wireless transmission of data from vehicles under test to base stations or between two moving vehicles. Wi-Fi technology is also often used in industry and manufacturing to control measurements or to analyze remote measurements. The rapid development of technology has led to the fact that many of those who specialized in wireless technology have increased productivity and received investments and profits [3]. The need for a universal device for data collection and analysis confirms the relevance of this study. Visualization of the collected data is an important part of improving the quality of service of various services, as it facilitates the analysis process for a person.
2. Research and Development Review
The aim of the master's thesis is to improve the quality of collection, analysis and visualization of data from wireless networks by developing a hardware data collection module in a Wi-Fi network.
To achieve these goals, it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
- perform an analysis of existing WLAN networks;
- review and analyze existing technical solutions for the implementation of the system;
- explore ways to solve and determine the best way to develop a hardware data acquisition module;
- to develop and test a hardware data collection module in a Wi-Fi network;
- explore its characteristics.
3. Analysis of existing WLAN networks
There are several types of WLAN networks, which differ in the signal organization scheme, data transfer rates, network coverage radius, as well as the characteristics of radio transmitters and receivers. The most widespread wireless networks of the standard [4]: IEEE 802.11b; IEEE 802.11g; IEEE 802.11n; IEEE 802.11ac; IEEE 802.11ax.
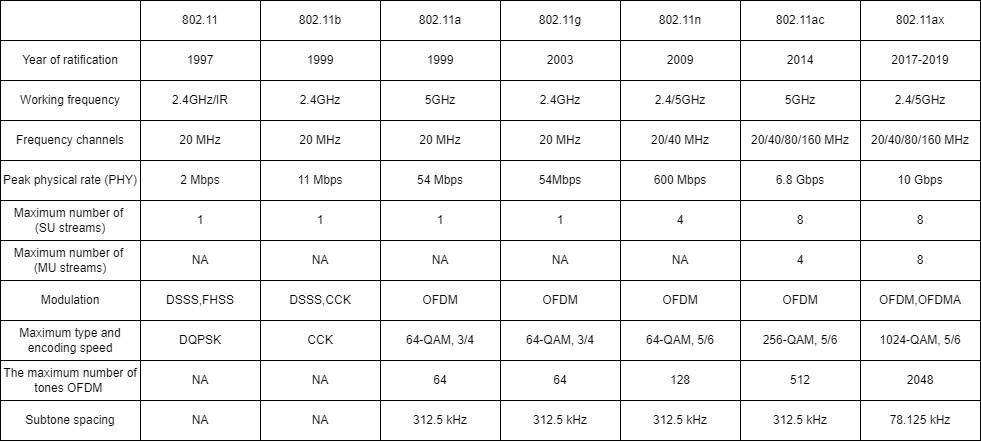
Table 1 - Comparative characteristics of WLAN networks of the IEEE standard
An example of a block diagram of using a wireless network to collect data from various devices is shown in Figure 1.
The diagram shows two devices to which sensors are connected via the RS-232 interface, and the sensors transmit information to the end device (tablet) using wireless networks.
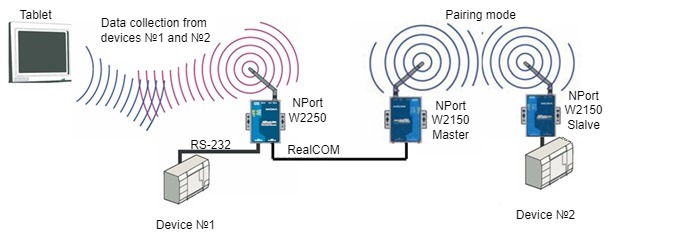
Figure 1 - An example of a block diagram of using a wireless network to collect data from various devices
4. Implementation and maintenance of control systems, monitoring and data analysis in Wi-Fi networks
The need to analyze, monitor and process various traffic in local area networks and various systems appeared in the early 2000s. Since then, various global companies have been actively creating and successfully developing traffic accounting systems in local networks, billing systems for telecom operators, projects in the field of communication networks, virtualization, and data centers.
Consider the use of software products for servicing wireless systems using the example of solutions proposed by Netams, which offers a line of several software products [5]:
- WNAM;
- WNAM Quality of Wireless;
- WNAM Radar;
- WNAM Devices.
WNAM (Wireless Network Access Manager) is specialized software for managing wireless network users. Its main task is to ensure the identification of guest Wi-Fi users in accordance with the requirements of the law (SMS, call, "Gosuslugi", voucher). WNAM is designed to be installed on the network without the use of "cloud services" and their franchises; this ensures that the collected data is securely stored, and you have full control over your own Wi-Fi identity service. Using WNAM does not provide for periodic payment for the service, and additional deductions (except for SMS payment, of your choice). WNAM integrates with your wireless equipment or access routers, directly supporting all types of residential, office and industrial Wi-Fi systems without the need to install additional devices. In addition to the functions of authorization (identification) of Wi-Fi subscribers, Wireless Network Access Manager has a flexible system of settings, designers of pages shown to subscribers, the ability to display static and targeted advertising, conduct surveys, use social network profiles, and an advanced reporting system. From a technical point of view, WNAM is installed on a physical or virtual Linux server, has a convenient web interface, stores all data in a database, and supports a failover cluster configuration.
One of the possible schemes of work is shown in Figure 2. This scheme shows the maintenance of a significant number of Wi-Fi sites (locations), each of which has a Mikrotik router with a built-in access point, or several access points behind a Mikrotik router. The latter performs the functions of a hotspot (portal of interception) and ensures the interaction of wireless subscribers with WNAM authorization servers. For ease of administration, each of the routers is connected by a VPN network to the central node of your network.
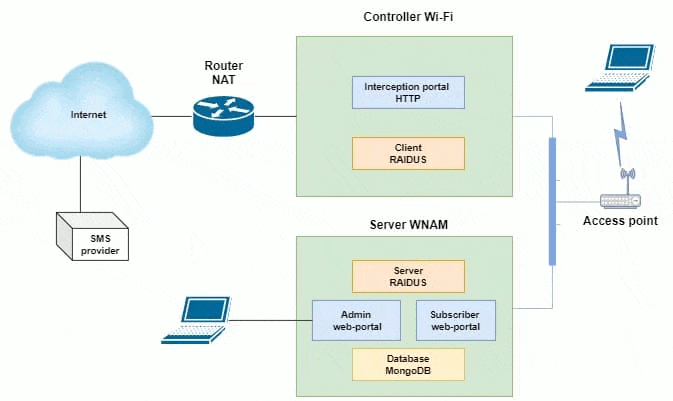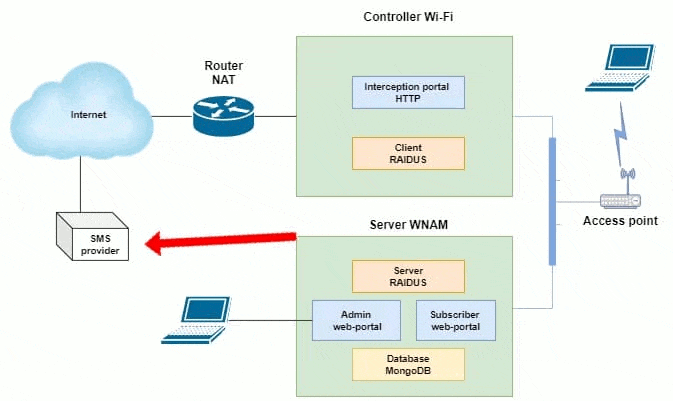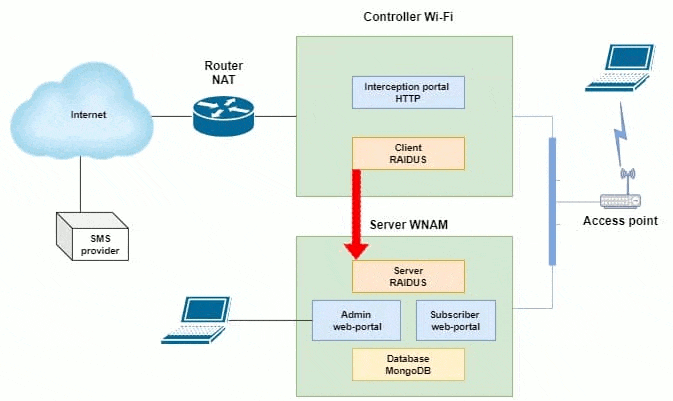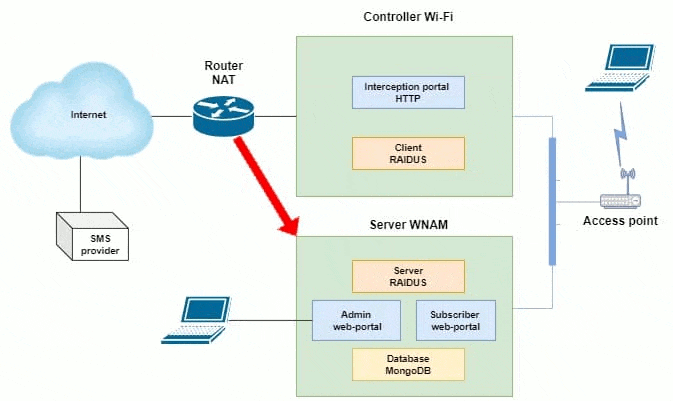
Figure 2 - One of the possible schemes of WNAM operation
(animation: 12 frames, continuous repetitions, 186 kilobytes)
WNAM Quality of Wireless is a software and hardware system for active and independent monitoring of all aspects of the state of a user's wireless network. It consists of a WNAM QoW Sensor hardware sensor and a WNAM QoW Server cloud server software that manages a fleet of such sensors.
WNAM Radar is a Wi-Fi data collection tool. All visitors carry a smartphone, the wireless module of which is constantly looking for "familiar" networks by sending special radio requests. Collecting them using WNAM Radar, you can [6]:
- receive advanced analytics on the number, frequency, duration and category of the visitor's visit;
- compare visits to each other in your different locations and times;
- build routes and "heat maps" of places with the highest concentration of people;
- associate visitor visit data with phones from the WNAM authorization system;
- etc.
WNAM Devices is specialized software for managing Wi-Fi wireless network equipment: access points and controllers. WNAM Devices supports Cisco, Huawei, Ruckus controllers, remote configuration management and AP firmware and client updates, remote monitoring and notifications, full integration with the WNAM system to build nationwide guest Wi-Fi networks, centralized control of radio air and roaming on site, configuration editing via web and via API (external system such as WNAM or CRM)
Thus, the company provides various solutions for the implementation and maintenance of systems for managing, monitoring and analyzing data in Wi-Fi networks for various types of businesses, telecom operators and advertisers.
5. Overview of hardware for network communication
To build a diagram of interaction between devices and a system that analyzes, monitors and processes various traffic in local area networks and various systems, the following equipment is used:
- Cisco WLC controllers;
- Mikrotik routers;
- controllers Ruckus ZoneDirector, SmartZone, Virtual SmartZone, SmartCell Gateway;
- Huawei controllers;
- cloud controllers (Zyxel Nebula);
- BRAS devices;
- routers based on Linux-server;
- Avaya controllers and associated access points;
- etc.
Cisco WLC controllers (wireless lan controller) provide centralized management, configuration and troubleshooting in large-scale networks of service providers. The device supports multiple deployment modes on a single controller. The controller provides exceptional visibility into application traffic using Cisco Application Visibility and Control technology [7].
A router is an OSI reference model network layer device that uses one or more metrics to determine the best path for network traffic to pass based on network layer information. The router is primarily needed to determine the further path of data sent to a large and complex network. The user of such a network sends his data to the network and indicates the address of his subscriber. Data passes through the network and, at points with a branching of routes, arrives at routers that are installed at such points [8]. Mikrotik routers are high-tech and reliable devices that have various technologies and capabilities, CLI and Web interfaces for individual configuration and can be used to solve various tasks at different levels.
Ruckus controllers from Huawei solve the minimal interoperability issues of managing and monitoring wired and wireless enterprise networks, a comprehensive portfolio of network management and control solutions that meets the performance, capacity and architecture requirements of organizations of all types and sizes. Common element: ease of configuration [9].
Devices BRAS (Broadband Remote Access Server) is a broadband remote access router. This device is remarkable in that it is located in the provider's network at the server level, while performing a number of border functions. The classic option for the interaction of the router with other nodes of the provider's network is the termination of point-to-point tunnels, including encapsulated PPPoE tunnels [10].
At the same time, the DSLAM collects the data stream from many users at one point in order to upload it to the BRAS. Client access to the network is carried out using the AAA protocol. The main tasks of BRAS are the aggregation of clients from DSLAMs using xDSL technology, the application of a quality of service (QoS) policy, and traffic routing to the provider's backbone network [11].
Avaya controllers are used to manage various functions and data generation, including using remote management of end devices (access points).
6. Selecting a typical hardware module for network data collection
Existing wireless solutions are being improved and adapted to the needs of new generation developments. In some cases, on the contrary, the emergence of fundamentally new promising technological areas dictates the need to develop unusual communications with specific requirements for power, energy savings, program control, and great autonomy [12]. To collect data in a Wi-Fi network, you can use a monolithic module that will combine all the components necessary to solve various problems of collecting and processing information. Consider such a device, using the WizFi630 module as an example. The appearance of the WizFi630 module is shown in Figure 5.
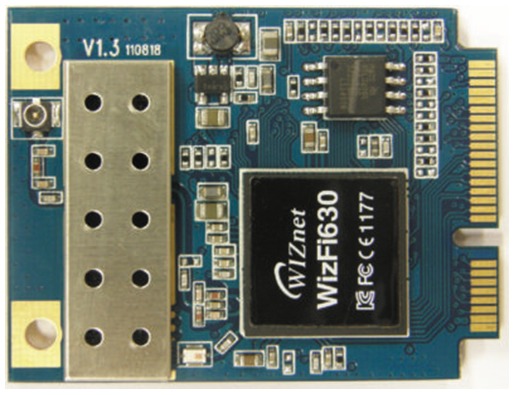
Figure 3 - Appearance of the WizFi630 module
The WizFi630 module is made in the form factor of a card with a Mini PCI Express slot. WizFi630 has three Ethernet ports and two UART ports, which allows you to provide wireless access to five devices simultaneously [13]. A U.FL connector is provided on the module to connect the antenna. The block diagram of the WizFi630 is shown in Figure 6.
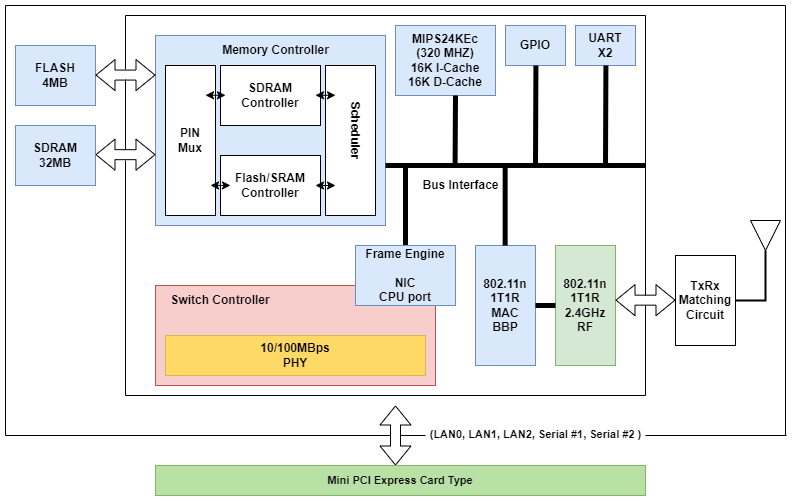
Figure 4 - Structural diagram of WizFi630
WizFi630 supports the following operating modes [13]:
- access point – in this mode, all LAN ports and the wireless interface are combined into one network. All interfaces have the same IP address space, the DHCP server function is disabled;
- client - the wireless interface is used to connect to the access point specified in the settings, all LAN (Local Area Network) ports are combined into a local network. All devices connected through the LAN ports receive a personal IP address. The module periodically sends a PING packet to the access point to check the connection;
- router – in this mode, all interfaces of the module are divided into two networks: WAN (Wide Area Network) and LAN. LAN port #0 is used to connect to an external network, the remaining LAN ports and the wireless interface are combined into a local network. The module periodically sends packets to all devices on the local network to check the connection.
- Multi Bridge - the functionality is similar to the client mode, but wireless devices can connect to the module as an access point. Thus, the wireless interface is used both to connect to an external network and to combine devices into a local network.
- Ad-hoc - the mode allows you to combine several wireless devices into a simple peer-to-peer network. In this case, all devices are connected to each other directly, without using a special access point[14].
Using the commands to control this module, it is possible to configure it for a specific task of collecting and processing the received data over a wired and wireless network.
List of used literature
- Гырдымова, Д.А. Применение протоколов шифрования в wi–fi сетях / Д.А. Гырдымова, Д.И. Зверев, Е.Л. Кротова // Международный научно-исследовательский журнал. — 2015. — №5 (36) Часть 2. — С. 70—71. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://research-journal.org/technical/primenenie-protokolov-shifrovaniya-v-wi-fi-setyax/.
- Вышел новый стандарт Wi-Fi. Рассказываем, почему теперь интернет будет намного быстрее // Медиа-ресурс Хайтек. [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:https://hightech.fm/2019/09/18/wi-fi6.
- Кравченко, Я. О. Анализа алгоритмов и протоколов маршрутизации данных в беспроводных компьютерных сетях / Я. О. Кравченко, Р. В. Мальчева // Информатика и кибернетика, 2021. - № 3(25). - С. 52-58. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа:https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=47963419.
- Стандарты WiFi // Портал 1234G.ru [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:http://1234g.ru/wifi/standarty-wifi.
- WNAM — Wireless Network Access Manager // Сайт компании NETAMS [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:https://www.netams.com/.
- Контроль качества вашей Wi-Fi сети // Сайт компании CompTek [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:https://www.wifisensor.ru/.
- Виртуальный контроллер беспроводных сетей Cisco Virtual Wireless Controller // Информационный бюллетень Cisco [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:https://network.msk.ru/files/docs/WiFi%20виртуальный%20контроллер%20описание.pdf.
- Что такое Маршрутизатор? // Сайт Network [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:.https://network.xsp.ru/3_4.php.
- Контроллеры Ruckus // Сайт компании Wireless™ (NYSE: RKUS) [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:http://ruckus-wireless.ru/controllers.
- Маршрутизатор широкополосного удаленного доступа // Портал Quick setup [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:https://qsetup.ru/marshrutizator-shirokopolosnogo-udalennogo-dostupa/.
- BRAS/BNG // Сайт компании ITGLOBAL.COM [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:https://itglobal.com/ru-ru/import-substitution/bras/.
- Мальчева, Р. В. Анализ проблем сбора данных в беспроводной локальной сети / Р. В. Мальчева, Я. О. Кравченко // Информационное пространство Донбасса: проблемы и перспективы: материалы IV Респ. с междунар. участием науч.-практ. конф., 28 окт. 2019 г. - Донецк: ГО ВПО "ДонНУЭТ", 2021. - С. 154-156.
- Бренев А.В. Wi-Fi-модуль WizFi630 компании Wiznet / Бренев А.В. // Беспроводные технологии, 2012 - № 4 [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:https://wireless-e.ru/radiomoduli/wizfi630-ot-wiznet/.
- Специальная сеть Что это за тип беспроводной сети и как она работает? // Информационная платформа Informatique Mania [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:https://www.informatique-mania.com/ru/linternet/ad-hoc-reseau/.
