Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Approbation
- 2. Design studio management system
- 3. Threats to the confidentiality of information resources
- 4. Data leakage prevention technologies
- 5. Introduction of DLP technologies into the design studio management system
- Conclusions
- List of sources
Introduction
The current economic situation has significantly intensified the competitive struggle of companies for market positions, and sometimes for survival. Some companies, developing anti-crisis strategies, have significantly reduced the expenditure part for some items of their business. Often, information security falls under cost reduction. However, savings are fraught with leaks of personal data and confidential information, which can harm the business as a whole.
Falcongaze analysts claim that half of the risks that the company may face are internal threats. During a crisis, the indicators of internal threats can rise up to 60%. The thing is that in times of economic instability, there are cases of rotation and even dismissal of personnel. For this reason, disgruntled employees are trying to either resell important information to competitors, or destroy databases, considering them their own work. [ 1 ]
It is worth noting that the activity of the design studio has always been associated with the processing and storage of a large amount of confidential data. The workflow of the design studio is carried out through a system that processes and stores information about current and implemented projects, about employees and their employment, about personal data of customers.
To prevent information security incidents, it is critically important to introduce DLP technologies (Data Leak Prevention) into the design studio's management system, which will allow analyzing the movement of data both inside and outside the corporate network, preventing the leakage of important information, according to established rules and policies.
The aim of the work is to update the security issues of confidential data in information systems and the introduction of technologies to minimize the relevant incidents.
1. Approbation
Presentations on this work were held at conferences:
- Modern information technologies in education and scientific research (СИТОНИ-2021).
- Software engineering: methods and technologies for the development of information and computing systems (ПИИВС-2022).
- Intelligent information systems. Theory and practice (ИИС-2022).
2. Design studio management system
A design studio is an organization engaged in the creation of websites and corporate styles, the distinctive features of which are the simultaneous management of several projects and constant contact with various customers to clarify, coordinate and calculate the ordered services.
The organizational structure of the design studio in question includes employees of the following positions: art director, project manager, marketer, programmer, designer, accountant, lawyer, system administrator. The company operates with huge amounts of data: both the results of the work of employees, as well as reporting and statistics.
Programmatically, the system is implemented by a general-purpose scripting language, intensively used for the development of PHP web applications, a free open-source web framework Laravel, a free relational database management system MySQL and a software stack WAMP.
An infological model has been designed to visualize data exchange flows within the system. It is a human-oriented and DBMS-independent domain model that defines the totality of information objects, their attributes and relationships between objects, the dynamics of changes, as well as the nature of information needs. [ 2 ]
The infological scheme of the design studio is shown in Fig. 1:
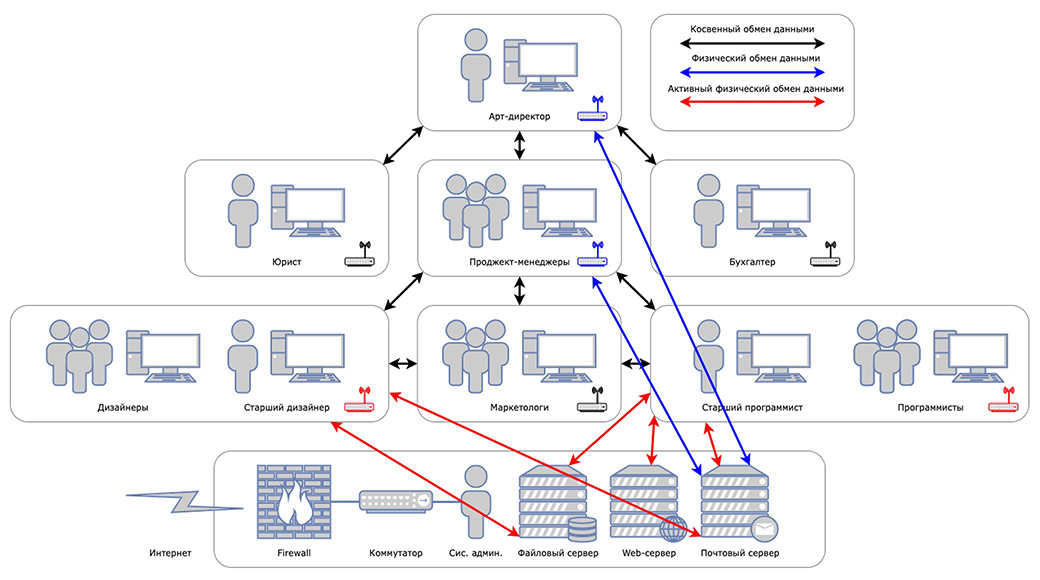
Figure 1 – Infological diagram of the design studio
The presented infological diagram shows the flow of information between the participants of information processes. At the physical level, the web server, file server, and mail server are connected to the Internet via a firewall-protected communication channel. Then, using wireless access points over a local network, different departments access the servers.
A large number of employees and the volume of connections of different types of data exchange increase the likelihood of threats to the confidentiality of information resources.
3. Threats to the confidentiality of information resources
Sources of threat to the security of confidential data can be both competitor companies and intruders, as well as employees together with the company's management bodies. The purpose of any threat is to affect the integrity, completeness and availability of data.
Threats can be external and internal. External threats are attempts to gain access to data from the outside and are accompanied by hacking of servers, networks, employee accounts and reading information from technical leakage channels (acoustic reading using bugs, cameras, pointing at hardware, obtaining vibroacoustic information from windows and architectural structures).
In turn, internal threats imply illegal actions of the staff, the working department or the management of the company. As a result, a system user who works with confidential information can give out information to outsiders. In practice, such a threat is more common than others. An employee can provide secret data to competitors for years. This is easily implemented, because the security administrator does not qualify the actions of an authorized user as a threat.
Since internal information security threats are related to the human factor, it is more difficult to track and manage them. Incidents can be prevented by dividing employees into risk groups.
An unauthorized access attempt can occur in several ways:
- Through employees who can transfer confidential data to outsiders, take physical media or gain access to protected information through printed documents.
- With the help of software, attackers carry out attacks that are aimed at stealing login-password pairs, intercepting cryptographic keys to decrypt data, unauthorized copying of information.
- Using hardware components of an automated system. For example, the introduction of listening devices or the use of hardware technologies for reading information at a distance (outside the controlled area). [ 3 ]
To prevent theft, modification and dissemination of confidential information, the use of appropriate integrated software solutions is strongly recommended.
4. Data leakage prevention technologies
Information leakage protection technologies are based on the identification, prevention, registration and elimination of the consequences of information security incidents or events that violate the regulated information security protection procedures.
As part of ensuring the information security of a design studio, special attention should be paid to protecting confidential data from internal threats. Thus, a secure digital "perimeter" should be created around the company's management system, which will analyze all outgoing, and in some cases incoming information.
Controlled information should be not only Internet traffic, but also a number of other information flows: documents that are carried outside the protected security circuit on external media, printed on a printer, sent to mobile media via Bluetooth, etc.
Since the Data Leak Prevention system must prevent leaks of confidential information, it necessarily has built-in mechanisms for determining the degree of confidentiality of a document detected in intercepted traffic. As a rule, two methods are most common: by analyzing the special markers of the document and by analyzing the contents of the document. Currently, the second option is more common, because it is resistant to modifications made to the document before sending it, and also makes it easy to expand the number of confidential documents that the system can work with.
The principle of operation of DLP systems is to analyze all traffic that is located within the protected corporate network. The introduction of a DLP system helps to control incoming and outgoing data flows and block unauthorized attempts to transfer important corporate data.
DLP works on the principle of data-centric security. It does not mean protecting servers, software or networks, but controlling the security of data that is processed in the system. According to this principle, all information flows are divided into three categories:
- Data-in-use – all the information that users work with (creating and editing documents, media content).
- Data-at-rest – information that is statically stored on users' end devices and in public places.
- Data-in-motion – data in the process of movement, transmitted information flows (transactions, authorization information, server-client requests, and others).
In addition to its main task related to the prevention of information leaks, DLP systems are also well suited for solving a number of other tasks related to the control of personnel actions.
DLP systems are most often used to solve the following non-core tasks for themselves:
- Monitoring the use of working time and working resources by employees.
- Monitoring the communication of employees in order to identify the "underhand" struggle that can harm the organization.
- Control of the legality of employees' actions (printing fake documents, etc.).
- Identification of employees who send out resumes for the prompt search of specialists for the vacant position. [ 4 ]
When implementing a DLP system, it is important to adhere not only to the principles of information protection, but also to the norms of legislation. Monitoring compliance with the rules of working with confidential information should not violate the personal rights of users, so it is worth abandoning actions that can be regarded as surveillance. Additionally, it is necessary to provide control mechanisms for system administrators who have access to all types of data. In order to avoid dissatisfaction and indignation in the team, it is recommended to include items in the general information about the operation of the system, where it is clearly indicated the goals of implementing DLP control and describe how the use of the information protection system contributes to the financial well-being of the company. It should be emphasized separately that the head of the design studio has the right to protect the trade secrets of the organization, and computers and other equipment provided to the employee are the property of the company, and any protection system can be used to protect the property. [ 5 ]
To ensure the maximum possible protection of information during the implementation of DLP, all recommendations should be followed and several protection blocks should be used at once. This will create a cost-effective, working protective circuit. The implementation of the DLP system should be carried out in stages from preparation to design and configuration of components to work under load in the company.
5. Introduction of DLP technologies into the design studio management system
Before the DLP implementation process, it is important to carry out preparatory procedures. The process of preparing the company for the installation of a security system consists of an audit of information security, risk assessment and settlement of legal issues. An audit implies an assessment of the real degree of information protection. At this preparatory stage, there is a search for possible channels of vulnerabilities in this ecosystem.
In addition, as part of the introduction of DLP technologies into the design studio management system, it is necessary to conduct a survey of information flows, which includes:
- Assessment of the level of security when working with internal documents of the company.
- A detailed study of all the technical resources of the company, from servers to network streams.
- Creating a list of data that belongs to a group of information with restricted access.
- Development of access control rules.
- The study of the processes of processing, creation, transmission and storage of information within the company.
Risk assessment and creation of access control rules are mandatory steps at the stage of implementing a cost-effective DLP system. Risks are assessed along with a survey of potential leakage channels. Depending on the probable damage, a decision is made on the need to protect the leakage channel. [ 6 ]
Thus, we will describe the functioning of the design studio management system for creating access control rules – a set of rights that the system user receives depending on the position held. In Fig. 2 shows a diagram of the use cases of the system being developed, which includes functions available to the administrator, employees and clients of the design studio:
- Functions available to the administrator: adding employees, assigning employees, changing employee data, changing the development stage, viewing order data, filling out a brief, adding a project, changing customer data.
- Functions available to the client: changing customer data, filling out a brief, viewing order data.
- Functions available to an employee: changing employee data, changing the development stage, viewing order data.

Figure 2 – Diagram of use cases
(animation: 4 frames, 1 playback cycle, 139 kilobytes)
In order to prevent the possibility of unauthorized access to confidential information, it was decided to use separate personal accounts to implement the separation of rights of users of the system.
In turn, to ensure the security of the entire system, special attention should be paid to the issue of reliable storage and encryption of authentication data from the created personal accounts of users. To prevent the risks associated with data leakage and to ensure the information security of the company, first of all, cryptographic protection methods are used through data encryption.
As part of the protection of confidential information, the design studio should use a cryptographic algorithm with a high rate of encryption and decryption (by generating replacement tables).
It is worth noting that for a design studio where data security is among the business priorities, the introduction of DLP is the optimal choice. Successful DLP integration will allow you to control all information flows, as well as identify and eliminate security threats in time.
Conclusions
The abstract describes the problems of information security incidents. The problem of leakage of confidential information has been updated. The developed infological scheme for visualization of data exchange flows of the design studio is presented. The process of implementing Data Leak Prevention technologies into the company's management system is considered. The functioning of the system for access differentiation depending on the positions of design studio employees is analyzed. The question of the need to use cryptographic protection of personal data in the management system is raised. The importance of carrying out further work for the integrated information security of the design studio is emphasized.
At the time of writing the abstract, the master's work has not yet been completed. Final completion: May 2023. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after the specified date.
List of sources
- Azone-IT – DLP-системы — элемент информационной безопасности [Электронный ресурс]. Режим доступа: https://www.azone-it.ru/... – Загл. с экрана.
- Studbooks – Инфологическая модель предметной области [Электронный ресурс]. Режим доступа: https://studbooks.net/... – Загл. с экрана.
- ЦБИС – Основы информационной безопсности [Электронный ресурс]. Режим доступа: https://цбис.рф/... – Загл. с экрана.
- Searchinform – Информационная безопасность. Защита данных с помощью DLP-системы [Электронный ресурс]. Режим доступа: https://searchinform.ru/... – Загл. с экрана.
- Spravochnick – Внедрение DLP-системы на предприятии [Электронный ресурс]. Режим доступа: https://spravochnick.ru/... – Загл. с экрана.
- Searchinform – Информационная безопасность. Внедрение DLP-систем [Электронный ресурс]. Режим доступа: https://searchinform.ru/... – Загл. с экрана.
- Герасименко В. Основы защиты информации Текст. // В. А. Герасименко, А. А. Малюк. — М.: МИФИ, 1997, — 539 с.
- DisserCat – Совершенствование инструментальных средств выявления утечек инсайдерской информации в финансово-кредитных организациях [Электронный ресурс]. Режим доступа: https://www.dissercat.com/... – Загл. с экрана.
- Sethuraman H. Master Thesis – Data Loss/Leakage Prevention // H. Sethuraman, M. Abdul Haseeb – Lulea University of Technology, 2012.
- Sallot D. R. Implementing a (DLP) Data Loss Prevention Management Solution // D. R. Sallot – ASIN: B01MSWJYN5, 2016.
