Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Purpose and objectives of the study, planned results
- 3. Research and development overview
- 3.1 Overview of international sources
- 3.2 Overview of national sources
- 3.3 Overview of local sources
- 4. Features of strategic development of SES in an unstable external environment
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The development of the state's economy is influenced by many negative environmental factors and creates problems for stable development. The combination of these factors contributes to a decrease in the development of the economic system, therefore, internal problems are increasing. In such conditions, the role of the state in ensuring the sustainability of regional development is increasingly increasing, as a basis for creating stability of the socio-economic development of the country as a whole and improving the standard of living of the population. The master's thesis examines the managerial approach to the socio-economic development of the region, the principles of forming a system of strategic management of the development of the region, the features of strategic management of socio-economic development of the region and ways to overcome negative trends.
1. Theme urgency
In the modern world, there is a situation when planning the sustainable strategic development of socio-economic systems is one of the main types of work of the leadership of a region or country. Given the instability of the external environment in view of the enormous changes that have occurred in the world order system since the beginning of the XXI century, they require an adequate response to them in order to ensure a decent and safe life for residents of the state or the hotel region.
Effective development and implementation of the strategy requires managers to respond flexibly and adequately to changes in the external and internal conditions of the functioning of the socio-economic system. This is important because it is the population that is the main driving force in the economy of the state and the region.
The above conditions ensure the need to consider socio-economic systems, methods of their creation and improvement and management from a strategic point of view.
2. Purpose and objectives of the study, planned results
The purpose of this work is to review and analyze the process of strategic enterprise management and methods for improving the management system.
The tasks that need to be completed to achieve this goal are:
- to determine the essence and content of socio-economic systems;
- to highlight the features of the external environment of the functioning of socio-economic systems;
- to identify the features of the strategic development of SES in an unstable external environment.
The objectof the study is the processes of forming a strategy for the development of socio-economic systems.
The subjectof the study is the methods of strategic management of the socio-economic system.
3. Research and development overview
In the scientific literature, the topic of strategic development of socio-economic systems is disclosed quite widely. Various authors, both domestic and foreign, have touched on this topic in their scientific research over the past 20 years, since the changing situation in the global economic system often forced the development of new methods and planning systems.
3.1 Overview of international sources
Different scientists characterized socio-economic systems in different ways and gave them different definitions.
A comparison of these definitions is given in table 3.1.
Table 3.1 – Comparison of SES definitions
| Author | Definition |
|---|---|
| Gaisina A.V., Nusratullin V.K. [4] | The socio-economic system is a system that implements the unity of social and economic relations in society, consisting in subordinating the goals and objectives of the development of production to the interests of the general population in meeting their diverse needs. |
| I.B. Beregovaya [1] | The socio-economic system is an integral set of interrelated and interacting social and economic institutions (subjects) and relations regarding the distribution and consumption of tangible and intangible resources, production, distribution, exchange and consumption of goods and services. |
| L. G. Batrakova [2] | The socio-economic system is a set of interrelated and in a certain way ordered elements of the economy, it is a set of mechanisms and institutions for making and implementing decisions concerning production, income and consumption within a certain geographical area. |
| P.Ya. Baklanov [1] | Spatial combination of population groups, facilities and organizations of economy, infrastructure, service and management within a certain territory (from a separate settlement to a socio-economic area as a whole), together with their various relationships with each other and with the territory. |
| Kalyakina I.M., Nomerchuk A.Ya. | SES is understood as a system localized in the economic space. It has historical, geographical, spiritual and economic boundaries, can be embodied in state-political entities or in other organizations. The main properties of socio-economic systems are considered to be integrity, hierarchy and integrativity. |
As you can see, various scientists, in general, put forward similar definitions of the socio-economic system.
3.2 Overview of national sources
Drevitskaya I.Yu. (Associate Professor of the Department of Donetsk National University) in her work highlights patriotism as a factor in the development of the socio-economic system of the state. In an era of rapidly changing forms of socio-economic systems, devastating global economic crises and universal threats of a different kind (from armed conflicts to viral diseases), the correct use of information technology (information as the main value of modernity) allows you to take an advantageous place in the competitive race. These technologies stimulate the development of educational institutions, which are designed to supply the state economy with highly educated and qualified personnel, ensure the creation of jobs and the development of innovative areas of economic activity with high added value of products produced within the country, as well as the growth of domestic demand, maintain a stable and high exchange rate of the national currency and the welfare of the population. [5]
The lecturer of the Department of Enterprise Economics of DonNU Zavgorodnyaya Yu.V. in her works considered the socio-economic system – the agricultural sector. [6]
3.3 Overview of local sources
At Donetsk National Technical University, Associate Professor of the Department of International Economics Shavkun G.A. is studying the peculiarities of the development of socio-economic systems in an unstable external environment. The author fully shares the definition of the stability of the socio-economic system formulated by B.K. Yesekina and S. Sapargali: «the ability to effectively use, autonomously modify the resources of its development, continuously increase the indicators of its positive change without increasing or minimizing the costs of basic, non-renewable resources». [9]
Sharnopolskaya O.N. (Associate Professor of the Department of «Economic Theory and Public Administration» of Donetsk National Technical University) explores methodological approaches to the study of anti-crisis development of socio-economic systems.
According to the author, the peculiarity of the development of socio-economic systems in a crisis is the need to predict uncertainty in the future, which is characterized by a variety of environmental factors, the dynamics of processes, qualitative changes in the system. It is the assessment of the degree of influence of uncertainty factors that should become the basis in the methodology of strategic management of anti-crisis development. [10]
After analyzing the various approaches to this definition, we can generalize. Socio-economic systems are complex structures consisting of economic, industrial, technical and social structures created in the sphere of production, distribution, exchange and consumer results of human activity. They represent a set of subjects interconnected by economic, social, political, and environmental relationships. Such systems include enterprises (organizations), localities, industries, clusters, regions, countries. The main feature of socio-economic systems is that an integral part of their functioning is a person.
4. Features of strategic development of SES in an unstable external environment
In order to consider the strategic management of socio-economic systems, it is necessary, first, to define the very concept of «development». The general definition that unites the features of all these spheres of activity is as follows: «development is a progressive movement, evolution, transition from one state to another, that is, the transition of something into a qualitatively different state».
Thus, speaking about development, it should be borne in mind that this process is always necessary and mandatory, since any system sooner or later finds itself in a situation where changes become important for the continuation of the existence of this system. However, such a process is not always controllable.
Development can occur evolutionarily or revolutionarily. Evolutionary development refers to the process of gradual changes in a particular system over a certain period of time, when the system, adapting to the influence of external factors, acquires new properties that allow it to continue its activities more efficiently.
Revolutionary development is understood as a rapid, profound change of the system, often by breaking the early state of the system, destroying the foundations on which this system operated. In itself, a revolutionary change often suggests that the leadership of this system, in whatever form it existed, could not cope with a crisis situation or difficult circumstances of the external environment, which led to the need for immediate changes. Revolutionary development is often associated with acute conflicts within the system, various costs and the fact that changes are carried out under the influence of circumstances momentary, which means they are not planned and prepared, which negatively affects the actions of the system in general.
The difference between these types of changes is presented in table 4.1.
Table 4.1 – Types of changes occurring in the system
| Type of changes | Duration | Personality |
|---|---|---|
| Evolutionary | Fast, instant | Qualitative, not changing the nature of the system as a whole |
| Revolutionary | Stretched over time | Qualitative, leading to a change in the entire nature of the system |
The key difference between strategic development is that this type of development is systemic in nature. The changes planned in the system can be both evolutionary and revolutionary, depending on what is currently a priority for the leadership of the socio-economic system. [7]
Thus, we can deduce the definition of strategic development.
Strategic development is a logically justified and time- and resource-balanced change in the state of the system, occurring in accordance with a pre-developed plan and subordinated to the unified strategic goals of the system, based on an assessment of the state of this system and the state of the external environment in which it operates, indicating the sequence of actions necessary to implement and implement changes. Strategic development consists in the ability to model the situation, the ability to identify the need for changes, the development of the strategy itself, as well as the ability to implement the strategy. At the same time, strategic development is a system of actions necessary to achieve the set goals, often in conditions of limited resources. In addition, strategic consists of both well-thought-out purposeful actions and actions that are a reaction to an unforeseen development of events.
Regarding the strategic development of SES, it should be borne in mind that SES differ greatly from each other in size, functions performed and scale of activity. Depending on this division , SES are classified into:
- Micro-level SES, which include individual enterprises;
- Meso-level SES, which include regional socio-economic systems;
- Macro-level SES, which include states and interregional socio-economic systems, as well as supranational–level systems. [3]
This division is shown in the figure 4.1.
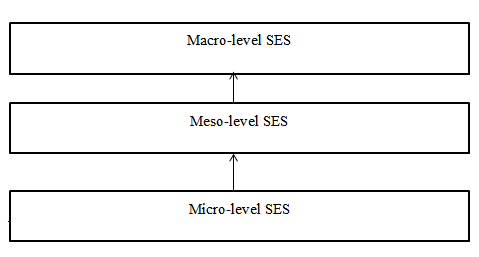
Figure 4.1 - Division of socio-economic systems by level
The type of connection shown in the figure, which can be conditionally designated as a bottom-up connection, suggests that SES relate as follows: micro-level SES form a socio-economic system of the region at the Meso-level. In turn, regional SES form the socio-economic system of the state level.
Transnational corporations (TNCs) can be singled out separately, which, being enterprises, due to their extensive and complex organizational structure, have the characteristics of all types of SES.
Considering that SES of all levels operate in constant connection with the external environment, they, like all other systems, are subject to its changes in all respects, and when strategically managing such systems, all crisis phenomena should be taken into account and respond to them in a timely manner.
So, among the many factors affecting the activities of SES at all levels, three main groups can be distinguished:
- Factors characterizing the economic environment as a sales and supply market. These include:
- the monetary and financial system with which the SES interacts;
- monetary and fiscal policy;
- inflation rate;
- import policy;
- participation in international economic organizations.
- Factors characterizing the labor force used. These include:
- socio-economic development of the region;
- investment attractiveness of the region;
- regional legislation in the field of social and labor relations;
- regional programs aimed at the development of labor potential;
- regional social partnership programs;
- demographic situation;
- migration situation;
- structure of professional education;
- activities of public professional organizations and employers' associations.
- Factors characterizing the state of the finances of organizations and the financial market as a whole:
- form of specialization;
- concentration and diversification of production;
- currency exchange rate;
- the value of shares and securities.
These factors are presented more clearly in figure 4.2.
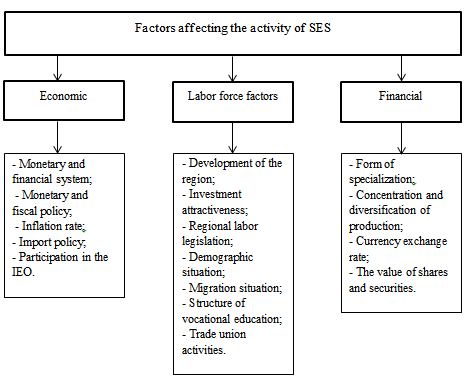
Figure 4.2 - Factors affecting the activity of socio-economic systems
Taking into account the influence of all the above factors, as well as the peculiarities of the local mentality, culture, political and economic systems, the management of SES at any level develops a long-term development plan, in which reserves are laid, the volumes of which are calculated in accordance with the assessment of the instability of the external environment using the Ansoff matrix.
With the help of these resources, anti-crisis funds are formed, acting as a kind of "airbag" in case of situations that the SES is not able to cope with on its own. For micro-level SES, i.e. enterprises, reserve capital acts as such a "safety cushion". The funds for this come from the following sources:
- deductions from the net profit of the organization;
- due to the property contributions of the founders;
- due to retained earnings at the end of the financial year.
In the meso–level SES (region), reserves are formed from the region's own profits, as well as with the help of state budget allocations and subsidies.
In macro-level SES (states), state reserve funds are formed, which are designed to ensure the receipt of funds to the budget in the event of crisis phenomena and events of various nature.
The instability of the external environment is primarily characterized by the inability to assess the risks arising in it. However, there should always be reserves in the SES, which will become insurance in case of unforeseen situations of different scales. [8]
Conclusion
Summarizing all of the above, we can conclude that the socio–economic system (SES) is a complex structure consisting of economic, industrial, technical and social structures created in the field of production, distribution, exchange and consumer results of human activity.
The external environment is a set of active economic entities, economic, social and natural conditions, national and interstate institutional structures and other external conditions and factors operating in the environment of the enterprise and affecting various areas of its activities.
The instability of the external environment is primarily characterized by the inability to assess the risks arising in it.
The unique features inherent in SES include:
- integrity;
- hierarchy;
- complexity;
- greater inertia;
- high degree of reliability of operation.
The factors of influence of the external environment include:
- economic factors;
- political factors;
- social factors;
- environmental factors;
- international factors.
Thus, the development of socio-economic systems is closely related to the conditions of the external environment in which its functioning takes place. Using environmental assessment methods, the SES management can navigate the situation and create an action and development plan to respond to any situation.
Operating in an unstable external environment, SES face many different threats and factors that are extremely important to correctly assess the conditions and circumstances of the events. Assessing such factors as the environmental, economic, social, technological situation, as well as environmental factors, choosing the most important of them from the point of view of the SES management, the management develops an action plan for a given situation in a tactical, and then in a strategic perspective.
References
- Бакланов П.Я. Территориальные социально-экономические системы в региональном развитии / П.Я. Бакланов // Тихоокеанский институт географии ДВО РАН, Владивосток. - 2016. Режим доступа: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=29809079.
- Батракова, Л.Г. Эволюция социально-экономических систем / Л.Г. Батракова. // Ярославский педагогический вестник. – 2018. Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/evolyutsiya-sotsialno-ekonomicheskih-sistem.
- Волынский А. И. - Мезоуровень как объект исследования в экономической литературе современной России / А.И. Волынский // JIS. - 2017. Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/mezouroven-kak-obekt-issledovaniya-v-ekonomicheskoy-literature-sovremennoy-rossii.
- Гайсина, А.В., Нусратуллин, В.К. Социально-экономические системы и их типы / А.В. Гайсина, В.К Нусратуллин // Институт экономики финансов и бизнеса, Башкирский государственный университет. - 2018. Режим доступа: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=37000100.
- Древицкая И.Ю., Карабанов С.А. Патриотизм, как фактор развития социально-экономической системы государства / И.Ю. Древицкая, С.А. Карабанов // Проблемы развития социально-экономических систем: Материалы Международной научной конференции молодых уч?ных и студентов (Донецк, 16-17 апреля 2020 г.). – 2020. Режим доступа: http://repo.donnu.ru:8080/jspui/bitstream/123456789/4708/1/3264_DL9L.pdf.
- Завгородняя Ю.В. Особенности управления стратегическим потенциалом сельскохозяйственных предприятий / Ю.В. Завгородняя // Вестник Института экономических исследований. – 2020. Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-upravleniya-strategicheskim-potentsialom-selskohozyaystvennyh-predpriyatiy.
- Калякина И.М, Номерчук А.Я. Управление социально-экономической системой / И.М. Калякина, А.Я. Номерчук // Естественные и математические науки в современном мире. - 2018. Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/upravlenie-sotsialno-ekonomicheskoy-sistemoy.
- Папин, С.Б. Развитие организации в нестабильной внешней среде / С.Б. Папин // Российское предпринимательство. - 2007. Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/razvitie-organizatsii-v-nestabilnoy-vneshney-srede.
- Шавкун Г.А. Особенности развития региональных социально-экономических систем в условиях нестабильной среды / Г.А. Шавкун // Вестник Камчатского государственного технического университета. – 2018. Режим доступа:https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-razvitiya-regionalnyh-sotsialno-ekonomicheskih-sistem-v-usloviyah-nestabilnoy-sredy.
- Шарнопольская О.Н. Стратегия интеграционного антикризисного развития социально-экономических систем: теоретико-методический аспект: Монография / О.Н. Шарнопольская, Е.Г. Курган, Е.А. Шумаева и др. // Донецкий национальный технический университет (Донецк) . – 2020. Режим доступа:https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=43441985.
