Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance and objectives of the research topic
- 2. The reasons and necessity for the introduction of distance learning. Advantages and disadvantages
- 3. Studying the technical possibility of conducting classes. Distance learning technologies
- 4. The impact of distance learning on the quality of student academic performance
- 5. Substantiation of the idea of forming the course
Applied Geodesy
for distance learning - Conclusions
- List of used literature
Introduction
One of the technologies recognized and successfully developing in the global educational space is distance learning technology.
Distance learning is a form of education that has appeared quite recently, and has become more relevant due to the COVID–19 pandemic and other adverse factors. It is based on the educational interaction of teachers and students who are far from each other, which is implemented using telecommunications technologies and Internet resources. The use of such a form of education is associated with a number of positive consequences, such as: reducing student tuition costs, forming a unified information infrastructure of an educational institution, the possibility of expanding the student body and security issues. These features, combined with the low cost of deploying and maintaining the system, make distance learning a convenient addition to traditional forms of learning, and also allow you to organize fully distance courses.
Distance learning is playing an increasingly important role in modernizing education. According to Order No.816 of the Ministry of Education and Science
of the Russian Federation dated 08/23/2017 On the use of distance learning technologies
, final control of learning using distance
learning technologies can be carried out both face-to-face and remotely [1]. The State Duma of the Russian Federation is considering draft amendments to the law
on education related to distance learning.
1. Relevance and objectives of the research topic
The relevance of the topic lies in the lack of educational and methodological support for independent extracurricular work of students. Therefore, the direction
and actual purpose of this research work is to study the process and problems of presenting the course Applied Geodesy
for distance learning based on modern digital technologies.
In accordance with this, the main objectives of the study can be determined:
- To consider the reasons and necessity of introducing distance learning into the curriculum. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages.
- To study the technical possibility of conducting classes.
- To investigate the impact of distance learning on the quality of education when it is impossible to conduct face-to-face classes.
- To substantiate the idea of presenting the course
Applied Geodesy
for distance learning.
Based on the work carried out, conclusions should be drawn about the expediency of conducting a distance learning course in conditions where it is impossible to conduct face-to-face classes.
2. The reasons and necessity for the introduction of distance learning. Advantages and disadvantages
The law does not establish a specific list of reasons for distance learning in the case of choosing such a form of education for students, since it is precisely this choice that ensures a person's right to education, taking into account his opinion and interests. It is important that the choice of distance learning be justified precisely by the fact that it will be better for yourself.
As relatively recent events have shown, distance learning can become a forced form of education due to the sanitary and epidemiological situation and the peculiarities of the spread of the new coronavirus infection (COVID–19). The introduction of distance learning as a compulsory form of education is permissible on the basis of an appropriate administrative act, and not in oral form [2].
So, in March 2020, the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation recommended that all educational institutions temporarily transfer students to distance learning, if necessary. This decision was made after a meeting of the operational headquarters for the prevention of the spread of coronavirus infection COVID-19 [3].
– Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 273-FZ dated December 29, 2012 On Education in the Russian Federation
(articles 13, 16, 17, 18, 28, 30, 41)[4];
– Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the conditions and organization of education in educational institutions 2.4.2.2821-10[5];
– Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated August 23, 2017 No. 816 On Approval of the Procedure for the Use of e-learning, distance learning
technologies by organizations engaged in educational activities in the implementation of educational programs
[1].
The introduction of distance learning, as elsewhere, has its advantages and disadvantages, which are shown in Figure 1.
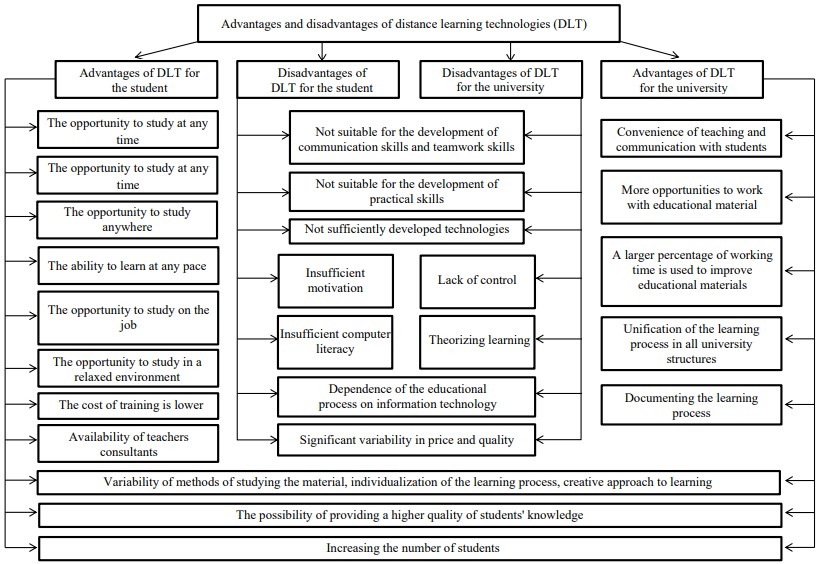
Figure 1 – Advantages and disadvantages of distance learning
Analyzing the diagram in Figure 1, it can be concluded that distance learning technologies have a number of advantages for both students and universities.
To get an overall picture of students' attitudes towards distance learning, a student survey was studied. The survey was conducted in May-June 2020 among 800 Russian students [6]. The survey results are shown in Figure 2.
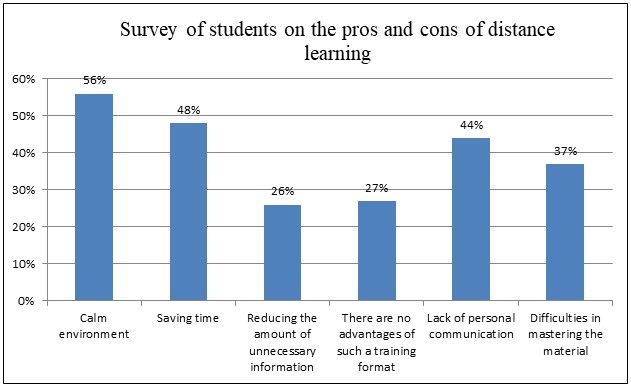
Figure 2 – Student survey on the pros and cons of distance learning
This is primarily due to the weak spread of distance education in our country, the low quality of the technologies used, as well as the lack of awareness of the population about the benefits of distance learning.
3. Studying the technical possibility of conducting classes. Distance learning technologies
In 2015, our country developed Methodological recommendations for the implementation of additional professional programs using distance learning technologies, e-learning
and online form
, which regulated the concepts of fully distance learning
and partial use of distance learning technologies
for additional professional education[7]:
– Fully distance learning implies the use of such a learning mode in which the student masters the educational program completely remotely using a specialized remote shell (platform), the functionality of which is provided by the organization. All communications with the teaching staff are carried out through the specified shell (platform).
– A model in which there is a partial use of distance learning technologies in the implementation of additional professional programs, face-to-face classes alternate with distance ones.
Among the technologies used in the process of distance learning, the most widespread are[8,9]:
– case technology – this is a form of distance learning based on providing students with information and educational resources in the form of specialized sets of educational and methodological complexes using various types of information carriers (cases);
– Internet technology – this is a method of remote transmission of information based on the use of global and local computer networks to provide students with access to information educational resources and to form a set of methodological, organizational, technical and software tools for the implementation and management of the educational process, regardless of the location of its subjects;
– telecommunication technology - This is a technology based primarily on the use of satellite data transmission and television broadcasting, as well as global and local networks to ensure the interaction of students with the teacher and among themselves and students' access to information educational resources presented in the form of digital libraries, video lectures and other learning tools.
A particularly important factor in the typology of distance learning institutions is the combination of pedagogical techniques and methods used in the educational process. By choosing the method of communication between teachers and trainees as a criterion, such methods can be classified according to the following criteria[10]:
– Teaching methods through the interaction of the student with educational resources with minimal participation of the teacher or other trainees. The development of such methods is characterized by a multimedia approach, this is when educational resources are created using a variety of means: printed, video materials, audio, and what is especially important for electronic educational institutions – educational materials delivered over computer networks. This is, first of all [11]:
a) interactive databases;
b) electronic journals;
c) computer training programs.
– Methods of individualized learning and teaching, which are characterized by the relationship of students with each other. Such methods are implemented in distance education mainly through technologies such as telephone, voice mail, and e-mail. The development of tele-mentoring mediated by computer networks is an important component of the educational process in e-learning institutions.
– Methods based on the presentation of educational material to students by a teacher or an expert, in which students do not play a major role in communication.
– Methods characterized by active interaction between all participants in the educational process. The importance of such methods and the intensity of their use increases significantly with the development of educational telecommunication technologies. In other words, interactive interactions between students, and not just between the teacher and the students, become an important source for gaining knowledge. The development of these methods is associated with the holding of educational collective discussions and conferences. Audio, audio-graphic and video conferencing technologies make it possible to actively develop such methods in distance education.
Currently, the following distance learning models are successfully used (see Figure 3) [12,13].
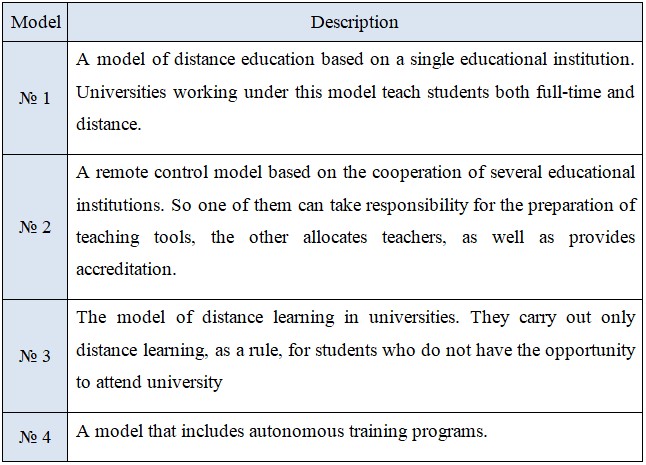
Figure 3 – Distance learning models
The educational technologies most suitable for use in distance learning include (see Figure 4) [14]:
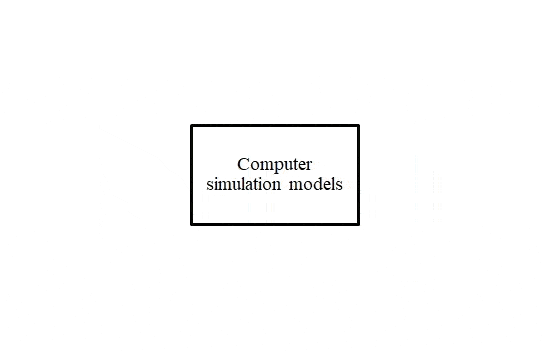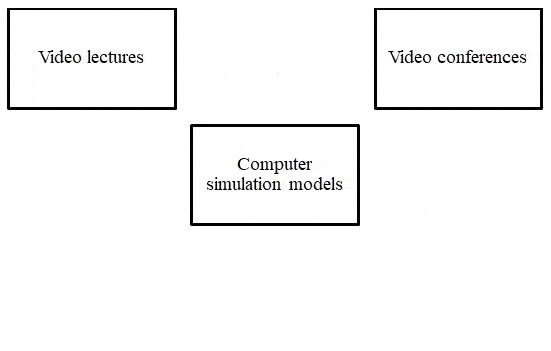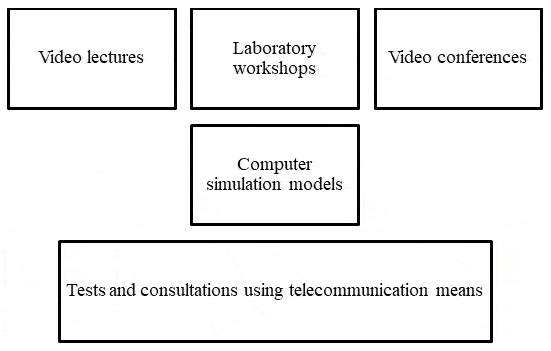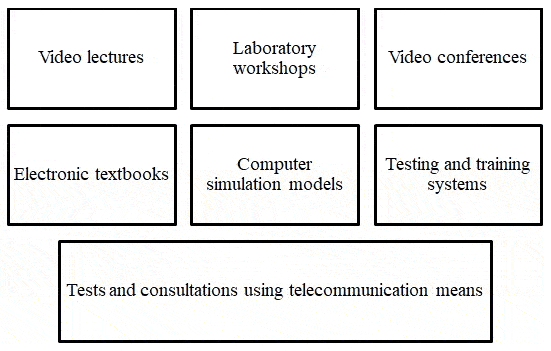
Figure 4 – Educational technologies adapted for distance learning
(animation: 7 frames; 5 repetition cycles; 54 kilobytes)
During the organization of joint educational programs, distance learning network technologies become important, since they allow the principle of distribution of educational resources and human resources to be most widely implemented.
In all the variety of e-learning tools, 5 groups can be distinguished [15]:
a) author's software products;
b) learning management systems;
c) content management systems (content of training courses);
d) educational content management systems;
e) freely distributed LMS\LCMS.
4. The impact of distance learning on the quality of student academic performance
The concept of quality
is a multidimensional category that includes, along with economic, social, cognitive and cultural components of education and is perceived as
a universal integrative characteristic of educational activity and its results [16].
Many researchers have recently been studying the question of the quality and possibilities, advantages and disadvantages of distance education, as well as analyzing the attitude of students and teachers to the restrictions that have arisen in the context of the pandemic [17,18].
The National Research University Higher School of Economics, together with Tomsk State University, conducted an online survey in April and May 2021 in order to assess the degree of satisfaction among students with the distance learning format (35 thousand students from more than 400 universities in Russia participated in the survey). According to the results of the study, which are published on the RBC website, It can be said that initially students did not see any problems with the transition to distance learning, but by the summer more students began to experience various difficulties: problems with self-organization and motivation, lack of communication, loneliness and depression [19]. Some students note that it is more difficult to ask questions to a teacher in a distance format.
Teachers of the A.I. Herzen Russian State Pedagogical University conducted a longitudinal study, which showed that, in the opinion of students, the quality of acquired knowledge and skills deteriorated during distance learning, motivation to study decreased, and the academic load increased. It is also noted that in the presence of already formed educational competencies and external incentives, for example, financial, it is easier to adapt to new conditions [20]. It is especially difficult for first-year students to study remotely, since the learning environment, teaching methods, assessment criteria, etc. are completely new to them. Whereas senior students quite easily accepted the new learning format and the results of their knowledge assessment have not changed much. [21].
At Kursk State Medical University, the analysis of learning outcomes showed even an increase in student academic performance. However, the author notes that this trend rather speaks not about real knowledge, but is a consequence of an unfair attitude to study, since at the moment there are no or difficult to implement mechanisms for quality control of student assignments [22].
The result of some surveys is shown in the form of diagrams (see Figure 5).
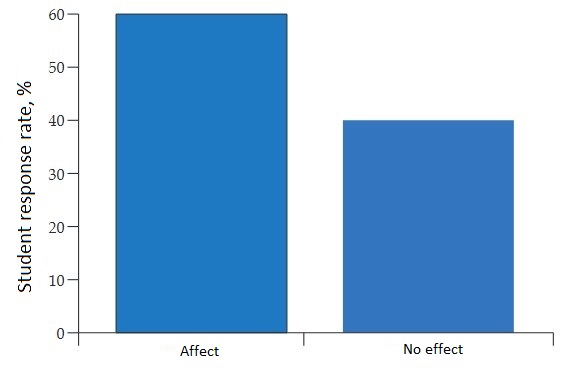
Figure 5 – The degree of influence of DL on the quality of education
Here are the results of a survey of students about what form of education they prefer (see Figure 6).
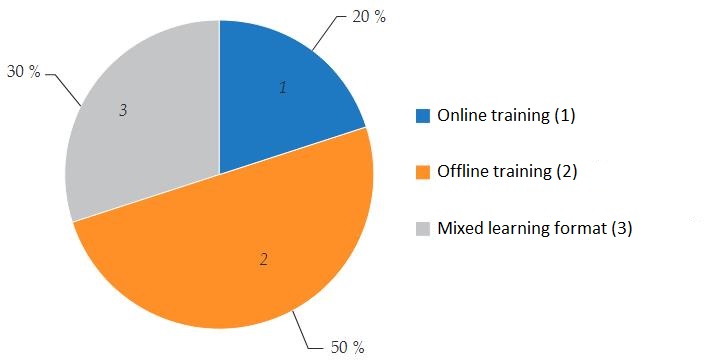
Figure 6 – Learning offline or online: student preferences
One of the factors of improving the quality of education in the system of higher professional education is the widespread introduction of modern information technologies, including multimedia and virtual. Modern information technologies in combination with pedagogical technologies can significantly increase the effectiveness of the educational process; achieve the solution of the main task: the development of students' cognitive skills, critical and creative thinking, the ability to independently construct their knowledge and navigate the information space.
Distance learning can have a positive impact on the quality of a student's education, increasing their creative and intellectual potential due to self-organization, the desire for knowledge, the ability to interact with computer technology and make responsible decisions on their own; formation of student's independence; their cognitive motivation, the development of skills to extract information from a variety of sources, the development of skills in project activities, high-quality performance of labor-intensive research or creative work due to the expansion of time frames, ergonomics and cost-effectiveness [23].
5. Substantiation of the idea of forming the course Applied Geodesy
for distance learning
Directly forming a distance learning course in the discipline Applied Geodesy
will allow students to study the discipline program independently, in the absence of opportunities
to attend classroom classes [24]. It will help the student to form a clear understanding of the methods of topographic and geodetic support for various national
economic tasks, including during the construction, reconstruction and operation of real estate located in urban areas, using modern digital technologies..
In the task of the distance course, you can freely display the study of the main types of engineering and geodetic works in topographic and geodetic surveys, the creation and correction of topographic plans, for solving engineering problems in land management and cadastral works in production and technological, design and survey, organizational and managerial and research activities [25].
Having studied the main aspects of distance learning in this work, as a result, it can be concluded that the formation of the course Applied Geodesy
for distance learning based
on modern digital technologies has many advantages and rational justifications. We will note some of them using the information provided in this research paper:
– The relevance of the topic: Geodesy is an important industry that is used in various fields such as civil engineering, cartography, geological research and much more. Modern digital technologies such as global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), laser scanning and geographic information systems (GIS) are an integral part of modern geodesy. Therefore, teaching students these technologies through distance learning, especially at a time when it is very difficult to attend classroom classes, is relevant and useful.
– Accessibility of education: Distance learning can significantly increase the availability of education for students who do not have the opportunity
to attend traditional educational institutions or live in remote regions. In the modern world, where digital technologies make it possible to provide high-quality education online,
the formation of the course Applied Geodesy
for distance learning will attract more students and provide them with relevant knowledge.
– Interactivity and hands-on learning: In modern digital technologies, there are many opportunities to create interactive and hands-on activities. They allow students to gain real-world experience working with geographic information systems, perform data analysis and perform practical tasks. Modern digital technologies also make it possible to provide feedback and evaluate student performance more effectively.
– Support and updates: The distance learning course can be developed in a format that allows you to regularly update and supplement materials in accordance with the latest achievements in the field of geodesy and modern digital technologies. This is especially important for such a rapidly developing industry as geodesy, where new methods and tools are constantly emerging.
– Effectiveness and efficiency of training: Several studies have shown that distance learning can be just as effective, if not more so, than traditional teaching methods. Students can study materials at their convenience, at their own pace, and have access to a variety of educational materials and resources.
These advantages and rational justifications confirm the expediency of forming the course Applied Geodesy
for distance learning based on modern digital technologies.
This will ensure wider access to education, increase the efficiency and effectiveness of student learning, and prepare them to work with modern digital technologies,
which is relevant and in demand in the modern world.
Conclusion
Given the combination of all factors affecting the impossibility of conducting face-to-face classes, this is, at the moment, the only way to resume (extend) the educational process in our region.
Upon completion of the development of the master's thesis, it is planned to provide a theoretical block on the formation of the course Applied Geodesy
for distance learning at based
on modern digital technologies, with the subsequent practical implementation of the task and summing up the results with the formulation of conclusions on research work.
At the time of writing this abstract, the master's thesis has not yet been completed. The final completion is scheduled for May 2024. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after the specified date. You can contact us by e-mail: kirill.zelenin.23@mail.ru
List of used literature
- Приказ Министерства науки и высшего образования РФ от 23.08.2017 №816
Об утверждении Порядка применения организациями, осуществляющими образовательную деятельность, электронного обучения, дистанционных образовательных технологий при реализации образовательных программ
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://normativ.kontur.ru/document?moduleId=1&documentId=300600 // Загл. с экрана. - Онлайн Школа.
Какие могут быть причины для дистанционного обучения?
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://onlineschool-1.ru/faq/pravovye-voprosy/kakie-mogut-byt-prichiny-dlya-distancionnogo-obucheniya// Загл. с экрана. - Образовательная социальная сеть nsportal.ru.
Нормативно-правовая база дистанционного обучения
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://nsportal.ru/shkola/distantsionnoe-obuchenie/library/2022/06/15/normativno-pravovaya-baza-distantsionnogo // Загл. с экрана. - Федеральный закон от 29.12.2012 №273-ФЗ
Об образовании в Российской Федерации
(статьи 13, 16, 17, 18, 28, 30, 41). – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_140174/ - СанПиН 2.4.2.2821-10
Санитарно-эпидемиологические требования к условиям и организации обучения в образовательных учреждениях
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://rg.ru/documents/2011/03/16/sanpin-dok.html - ТАСС.
Российские студенты рассказали о плюсах и минусах дистанционного обучения
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://tass.ru/obschestvo/9032425 – Загл. с экрана. - Методические рекомендации по реализации дополнительных профессиональных программ с использованием дистанционных образовательных технологий, электронного обучения и в сетевой форме. Направленные письмом Министерства образования и науки РФ от 21 апреля 2015 г. № ВК-1013/06. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://sudact.ru/law/pismo-minobrnauki-rossii-ot-21042015-n-vk-101306/ Загл. с экрана.
- Берг О. Тренинги и обучение // Кадровый вопрос. – 2013. – № 10
- Кислухина И.А.
Использование дистанционных образовательных технологий в системе высшего образования: проблемы и перспективы
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/ispolzovanie-distantsionnyh-obrazovatelnyh-tehnologiy-v-sisteme-vysshego-obrazovaniya-problemy-i-perspektivy - Малков В.В.
Обзор способов реализации дистанционных образовательных технологий
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/obzor-sposobov-realizatsii-distantsionnyh-obrazovatelnyh-tehnologiy/viewer - StudFiles.
Методы дистанционного университетского образования
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://studfile.net/preview/8979628/page:4/ // Загл. с экрана. - В.И. Снегурова
Модели дистанционного обучения в системе среднего образования
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.unibob.ru/upload/files/18.pdf - П.В. Сысоев, Н.И. Хмаренко
Модели дистанционного обучения
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/modeli-distantsionnogo-obucheniya/viewer - Сайко Е.В.
Информационные технологии в дистанционном обучении
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/informatsionnye-tehnologii-v-distantsionnom-obuchenii-1/viewer Выбор системы дистанционного обучения
Готская И.Б., Жучков В.М. Кораблев А.В., Ргпу им. А.И. Герцена. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://geum.ru/next/art-7815.leaf-2.php- Мухаметзянова Г.В.
Профессиональное образование: Проблемы качества и научно-методического обеспечения
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=19999085 - Джумагулов, Э.К. Пути решения проблем дистанционного обучения / Э.К. Джумагулов // Alatoo Academic Studies. – 2020. – № 4. – С. 54–59. – DOI 10.17015/aas.2020.204.06. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=44744101
- Мандель, Б.Р. Дистанционное образование: дорога к истине вымощена парадоксами / Б.Р. Мандель // Ректор ВУЗа. – 2021. – № 5. – С. 48–63. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://panor.ru/articles/distantsionnoe-obrazovanie-doroga-k-istine-vymoshchena-paradoksami/59840.html
- РБК.
Студенты назвали основные проблемы онлайн-обучения
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://www.rbc.ru/society/19/08/2020/5f3bbdae9a7947d167de1a41 Загл. с экрана. - Панферов В.Н., Безгодова С.А., Микляева А.В.
Динамика отношения студентовк дистанционному обучению (результаты лонгитюдного исследования)
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://dzen.ru/a/YwjadBHaV2Vhfmpk Загл. с экрана. - Панферов В.Н., Безгодова С.А., Микляева А.В.
Оценка качества взаимодействия с преподавателями студентами в условиях временного перехода на дистанционное обучение: результаты лонгитюда
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://psyjournals.ru/nonserialpublications/dhte2020/contents/dhte2020_Panferov_Bezgodova_Miklyaeva.pdf - Чиркова В.М.
Влияние дистанционной формы обучения на успеваемость и посещаемость иностранных учащихся в период пандемии
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/vliyanie-distantsionnoy-formy-obucheniya-na-uspevaemost-i-poseschaemost-inostrannyh-uchaschihsya-v-period-pandemii
- Буланова-Топоркова М.В., Духавнева А.В., Кукушкин В.С., Сучков Г.В.,
Педагогические технологии: учебное пособие для студентов педагогических специальностей
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://djvu.online/file/jJj4fRxcwb7bQ- Pandia.ru. //
Программа учебной дисциплины
. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://pandia.ru/text/77/226/25507.php Загл. с экрана.Прикладная геодезия
- Геодезические работы при землеустройстве: учеб. пособие по направлению подготовки 21.03.02
Землеустройство и кадастры
/ Е.С. Денисова. – Пенза: ПГУАС, 2016. – 116 с. – [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://library.pguas.ru/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/1728/УП%20%20Денисова%20для%2021.03.02%20ЗиК%20РИО.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y - Буланова-Топоркова М.В., Духавнева А.В., Кукушкин В.С., Сучков Г.В.,
