Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Purpose and structure of the study
- 3. THEORETICAL AND METHODOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF CAPITAL MANAGEMENT IN THE ENTERPRISE
- Conclusions
- List of sources
Introduction
The enterprise's capital management system occupies a central position in modern corporate governance, representing a key mechanism for ensuring financial stability and sustainable development of the organization. In a dynamic economic environment, enterprises are increasingly paying attention to effective management of their capital as a strategically important factor for successful operation.
Against the background of uncertainty and constant changes in the business environment, the study of the enterprise's capital management system is becoming an urgent task. In this study, we focus on the theoretical and methodological aspects of this system, considering its impact on financial stability and opportunities for sustainable development of the enterprise. By analyzing the key elements of money management, we strive to identify the best approaches and tools that contribute to achieving a balance between financial stability and strategic development of the organization.1. Theme urgency
The relevance of the topic "Enterprise capital management system" is expressed in the need for enterprises to adapt to difficult economic conditions. Effective capital management is becoming a key factor for ensuring financial stability, attracting investments, optimizing costs and strengthening competitiveness. In a rapidly changing business environment, the enterprise's capital management system is an important tool for making informed financial decisions and ensuring the sustainable development of the organization.
2. The purpose and structure of the study
Analysis, evaluation and identification of the role of the capital management system in ensuring financial stability and sustainable development of the enterprise.
The structure of the study:
- This chapter provides an in-depth analysis of the theoretical and methodological foundations of the enterprise's capital management system. The key aspects are considered, including the theoretical and methodological foundations, the definition and essence of the capital management system, as well as the main indicators and methods of its analysis. A comprehensive study is being conducted aimed at understanding the role of the capital management system in ensuring financial stability and sustainable development of the enterprise.
The object of the study: the process of managing the company's capital.
The subject of the study: the company's capital management system.
- Analysis of the share of own and borrowed resources.
- Consideration of the degree of financial dependence.
- Assessment of the risks associated with the choice of a certain capital structure[7].
- Debt obligations - the amount of borrowed funds of the enterprise.
- Equity is the amount of funds owned by the owners of the enterprise.
- Total return on assets(ROA):
- Current liquidity:
- Absolute liquidity:
- Fast liquidity:
- Financial Risk Assessment: Regular analysis and assessment of the financial risk of the enterprise helps to determine the optimal capital structure. This includes assessing possible changes in the cost of capital and calculating financial stability indicators.
- Adaptation to Market Conditions: The capital structure should be flexible and able to adapt to changing market conditions. This implies a quick response to changes in rates, credit conditions and other financial parameters.
- Optimization of Capital Costs: Management should strive to minimize the cost of capital and at the same time maximize its effectiveness. This may include debt refinancing, optimizing the interest rate structure, and other measures.
- ”чет —тратегических ÷елей: —труктура капитала должна соответствовать стратегическим цел€м компании. Ќапример, если организаци€ стремитс€ к инновационному развитию, управление капиталом должно обеспечивать достаточные ресурсы дл€ исследований и разработок.
- Compliance with Laws and Regulations: Effective capital structure management also includes compliance with all applicable laws and regulations in the field of finance.
- Debt Service Strategy: The development and implementation of an effective debt service strategy, including regular payments and refinancing, helps to maintain the financial stability of the enterprise[10].
3. THEORETICAL AND METHODOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF CAPITAL MANAGEMENT IN THE ENTERPRISE
3.1 The essence and principles of the money management system
The effective functioning of an enterprise, which plays a key role in microeconomics, depends on numerous external and internal factors. Among the internal factors, the capital of the enterprise is of particular importance, which acts as a factor of production, a source of income, an investment resource, and is also an important element in the reproduction process. The capital of an enterprise is a fundamental, multidimensional and complex economic phenomenon that has not yet been fully investigated. Let's consider various scientific approaches to the definition of the concept of "capital" and present them in the table[1]
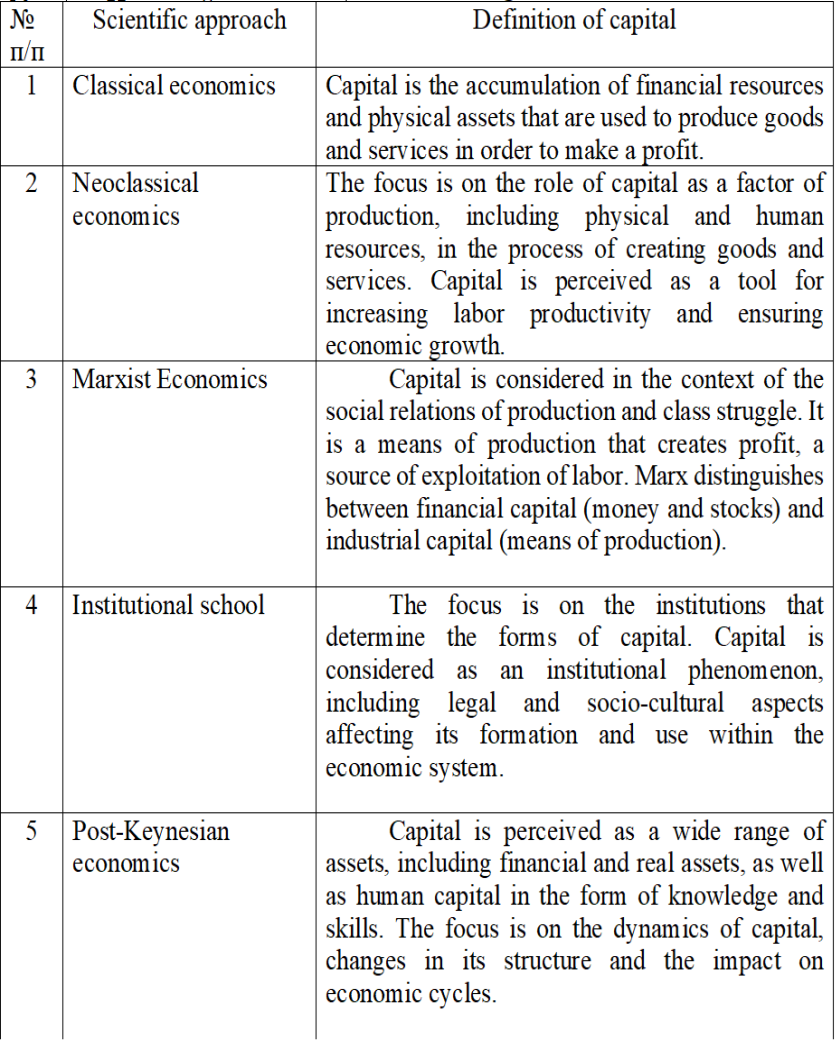
Figure 1 Approaches of various schools to the definition of the concept of "capital" of an enterprise
These various scientific approaches provide a wide range of interpretations of the concept of "capital", taking into account different aspects of its role and significance in economic theory.The principles of the capital management system cover the rational allocation of investments, effective management of working capital and fixed assets, as well as maximizing the cost of capital of the enterprise. The rational allocation of investments includes the selection of the most promising areas for capital investment, taking into account the strategic goals of the enterprise[2].
Effective management of working capital and fixed assets involves optimizing the use of current assets and ensuring their sufficiency for uninterrupted business turnover. Maximizing the cost of capital includes constant analysis of the capital structure, choosing the optimal ratio of own and borrowed funds.[3]
An effective capital management system helps to ensure the financial stability of the enterprise, increase its competitiveness and strengthen its position in the market.
3.2 Money Management Tools
In the practical field of financial analysts, generally accepted methods are widely used, combining a systematic set of tools and principles for researching the financial activities of an entity. These methods can be divided into two main groups. The first group includes methods involving a high degree of formalization, such as mathematical, statistical, econometric methods, as well as process modeling. They are based on strict analytical dependencies[4].
The second group of methods focuses on the analyst's intuition and experience, providing a logical description of analytical approaches and featuring a high level of subjectivity. This group includes methods of expert assessments, the method of comparisons, the construction of analytical tables and others. All these methods provide a variety of tools for a deeper analysis of the financial activities of the organization[5]. The types of methods are shown in Figure (2).
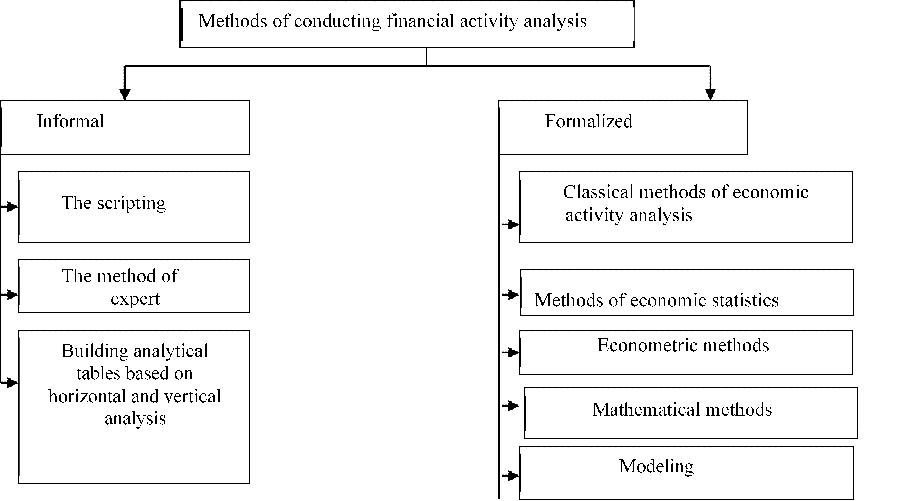
Figure 2 Ц Methods of conducting financial analysis
Capital management tools are a multi-level set of methods and techniques aimed at optimizing the use of financial resources of the enterprise. Financial analysis is an important tool for assessing the effectiveness of capital use, identifying financial risks and developing strategies for their management.
Budgeting involves the development and control of budgets, which ensures the planning of financial flows and the effective allocation of capital within the enterprise. Working capital management is aimed at optimizing inventory levels, managing accounts receivable and accounts payable, which helps to increase the liquidity of the enterprise[6].
Investment planning includes the selection and rational allocation of investments to achieve the strategic goals of the enterprise. At the same time, risk analysis and forecasting of investment returns are carried out.These tools interact to ensure effective capital management in the enterprise and contribute to achieving financial stability and sustainability.
3.3 The structure of the company's capital and the method of its calculation
The capital structure of an enterprise determines the ratio between own and borrowed funds. The methodology for calculating the capital structure includes:
The capital structure (D/E) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ \frac{\text{Debt obligations}}{\text{Equity capital}} \]
Where:
Evaluating the efficiency of using an enterprise's capital is an important aspect of financial analysis. The following indicators are used for this[9]:
\( ROA = \frac{\text{Net profit}}{\text{Average total assets}} \)
The following indicators are used to assess the company's liquidity:
\( \text{Current liquidity} = \frac{\text{Current assets}}{\text{Short-term liabilities}} \)
\( \text{Absolute liquidity} = \frac{\text{Cash}}{\text{Short-term liabilities}} \)
\( \text{Fast liquidity} = \frac{\text{ќборотные активы} - \text{Stocks}}{\text{Short-term liabilities}} \)
Effective management of the capital structure also includes making informed decisions on the allocation of resources between different sources of financing. This implies constant balanced attention to debt and equity, as well as to the choice of optimal financial instruments.
The key elements of effective capital structure management are:
The combination of these elements allows the company to dynamically adapt to changing conditions and effectively use its capital to achieve strategic goals.
Conclusions
The study of the enterprise's capital management system highlighted its central importance for ensuring financial stability and sustainable development. The revealed connection between the effectiveness of capital management, financial stability and strategic development of the enterprise emphasizes the need for an integrated approach to this system in modern business environment. The results of the study provide a basis for the development of practical recommendations for optimizing the capital management system in order to increase the competitiveness and long-term sustainability of the enterprise.
List of literature
-
1. Abramov S.I. Investment Management and Fixed Capital. Moscow: Exam, 2002. - 544 p.
2. Azizova K. M. Construction of a monitoring system for the functioning of enterprise capital // Municipal economy of cities: scientific and technical collection. Series: Economic Sciences. Ц Moscow: "Tekhnika" Publishing House, 2010. Ц No. 92. Ц P. 211Ц222.
3. Analysis and control in the enterprise capital management system: monograph / E.V. Mnich, A.D. Butko, O.Yu. Bolshakova, etc. Ц Kyiv: KNTU, 2005. Ц 232 p.
4. Afanasyev M.V. Enterprise Economics: a study guide for independent study of the discipline / M.V. Afanasyev, A.B. Goncharov. Ц Kharkiv: ID "INZHEK", 2003. Ц 409 p.
5. Blank I. Capital Management: Scholarly Course. Moscow: Nika-center, 2004. Ц 573 p.
6. Blank I.A. Financial Management [Educational course]. Moscow: "Nika-Center", Elga Ц 2001. Ц 528 p.
7. Bogacheva G.N. On the diverse interpretation of the category "capital" / G.N. Bogacheva, B.A. Denisov // Management in Russia and abroad. Ц 2000. Ц No. 1. Ц P. 13 Ц 24 .
8. Varicheva R.V. The concept of own capital / R.V. Varycheva // Bulletin of ZHDTU. 2010. Ц No. 2 (52). Ц P. 81-85.
9. Utchenko, O.B. Working capital management of the enterprise / O.B. Vatchenko, I.B. Takhmazova // Economic Space. Ц 2011. Ц No. 50. Ц P. 193Ц200.
10. Vorobiev Yu.N. Monetary capital of companies. Theory, practice, management: monograph / Yuri Nikolaevich Vorobiev, Kyiv National University named after Shevchenko. Ц Simferopol: Tavria, 2008. Ц 363 p.
11. Goncharenko A.M. Economic content and stages of capital management in mechanical engineering and services // Economics and management of enterprises in the machine-building industry: problems of theory and practice. Ц 2008. - No.2. Ц p.102.
12. Grachev A. Characteristics of the financial and economic condition of the enterprise: a rational mechanism for combining own capital, financial leverage, and solvency of the enterprise at the end of the reporting period / A. Grachev // General director . Ц 2004. Ц No. 11. Ц P.39-46
13. Grachev A.V. Growth of own capital, financial leverage, and solvency of the enterprise / A.V. Grachev // Financial Management 2002. - No.2.- P.21-34
14. Hreshchak M. Cost management / M.H. Hreshchak, A.S. Kotsiuba. Ц Kyiv: KNEU, 2002. Ц 131 p.
15. Grigorova Z.V. Formation and efficiency of using the basic capital of enterprises: author's abstract. econ. Sciences: 08.06.01.; European University / Zoya Valentinovna Grigorova. Ц Moscow, 2005. Ц 18 p.
