 |
 |

 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||






 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
ABSTRACT
TOPIC: A study of ill-management of the case process manufacturing powder wire.
GOAL: To show the methods of mathematical modelling to use electrical power in the management process of metal pressure (ODM), sister profilegibki process in the production of powder wire.
Analysis of the functional integration schemes with different anchors drives
Mathematical model description
Virtual model SAU drive motor (peral. and after. Chart.)
References
Background and place.
Technological line reduction powder wire (PW) is going to direct current cable, the main elements of which are : roads and driving drums, are stretching redutsiruemoy wire across roads.
Production of PW provides basic technological requirements : speed wire should be permanent and set from 0 to the nominal value of a continuous manner; Because of a lack of exhaust devices profilegibochnom linear speed wire in the same cages; Ensuring the minimum tension wire cages between drivers (not zero); actuating cable device itself must issue a wire on reels, and the latter with a minimum of force namatyvat tension wire at the coil. Ramjet cable station is, therefore, hinges and creases wire absent, causing some difficulties.
Technical conditions under which it is necessary to ensure adequate control on the above requirements, the following :
- - mechanical part does not contain the pressure in the trails because of the distance operator mezhosevogo in your line. Consequently, the force of resistance completion PW missing;
- - no sensor tension between PW Trailing drums, the small size and the undesirability mezhkletevogo bending wire;
- - Sensor tension wire on reels also absent because of axial asymmetry wire (a ring);
- - the only sensor, which involves working the body is a line speed sensor wire;
- - mnogodvigatelny drive consists of DC motors with shaft angular velocity sensors and electromagnetic torque (current sensor).
Adequacy of continuous process is possible only when there is sufficient information on the condition of the body and an active force for it. Based on the above technical information on the conditions of the very minimum for objective reasons. [2]
Office applications may realize several ways. The challenge is how to choose the best way to manage with a minimum of input, and that it was the most adequate facility management.
The most common ways of managing multi-driven : the way of speed with speed manual correction, which requires strict discipline to ensure accuracy in protochke working machinery and the same angular velocity drums; The management of speed and torque, which requires top-level management with automatic correction of angular velocity, in the corner speeds are adjusted so as to ensure a given difference electromagnetic motors points (difference of points set by hand); the management of speed and torque, which regulates basic transmission speed, and other drives managed by permanent assignment of points (a pocket of the points have not been adjusted automatically and manually selected).
All of the above methods require technological discipline to save workings of machinery to further manual adjustment of the set points at the top level of government that leads to problems of governance, and these techniques do not provide the required reliability, predictability, as well as a PW.
The only option of individual drives can be only energy form changing of the body, whether it be required ventilation or flexible. This power does not depend on how modified internal diameter with lines stretching across his body of work, but a function of his physical condition, that is, temperature, the yield strength, viscosity, elasticity coefficient, etc. [2]
The essence means is that the angular speed synchronization engine drums exercise by regulating the size of each drive job drums, including Wall device. To maintain a required level of a linear velocity of the rocket total electrical power devices profilegibochnogo regulate for a given line speed.
Top
Analysis of the functional integration schemes with different anchors drives
For comparison means of electrical machines (for example, manufacturing welding wire powder and powder for steel wire melts) analyze existing SAU drive sluice cable operation of the mill and profilegibochnogo regulated electrical power to the anchor chain. [1]
Differences between the technology of production welding wire and steel powder that welding wire produced at the mill and neprivodnom redutsiruyut to begin driving cable and wire for the molten steel is driving profilegibochnom mill. The sluice cable operation with protivonatyazheniem is that the wire had been through the first haulage, is the first roll directly with him too, do not form loops, is the second dragging with it the second roll, etc. Each drum has its own unique drive with a DC motor independent institution. [1] The principle of the cable operation based on the performance of equality :
![]()
where ![]() - velocity of the metal,
- velocity of the metal, ![]() - square cross section.
- square cross section.
In the process of rolling this equality is violated by the wear of machinery. To restore equality (1) to automatically regulate speed intermediate drum during the cycle dragging. There are two ways to restore equality, which is by serial and parallel connections anchors all motors (functional scheme presented in the figure, 2).
The consistent pattern included (Fig. 1) as a result of the growing resistance to the motor shaft (external forces), the speed of the fall. It falls EDS engine, and begins to grow current anchors, the total for all engines. As a result, all the engines age electromagnetic moments (reduced speed) and will be restored equality (1). Similarly, an increase in engine speed to reduce the burden on local one.
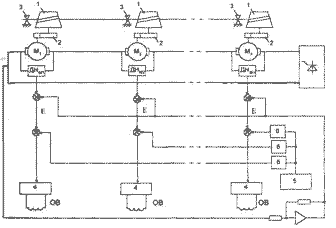
Figure 1-A functional diagram SUA with a serial connection anchors (1-pulling drums 2-reduktory, 3-voloki, 4-blok current regulation winding excitement 5-obschy source voltage setting 6-zadayuschie EDS)
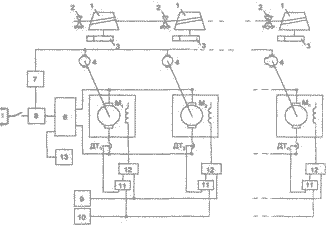
Figure 2-A functional diagram SUA connected in parallel anchors (1-pulling drums 2-voloki, 3-reduktory, 4-datchiki, 5-zadatchik speed, 6-reguliruemy source voltage 7-blok allocation max. Signal 8-ogranichitel, 9-zadatchik min. Current institute, 10-zadatchik boot 11-korrektory, 12-regulyatory currents CQ 13-zadatchik filling speed)
Consider the functional design of parallel connections anchors engine drivers involved in the process (Fig.2). Regulars dragging speed welding wire is by changing the value of the total voltage at all anchors engines. In this scheme for specifying the impact of the regulation voltage winding excitation (CQ) is directly proportional to currents associated with anchors engines, in addition, is a small elementary RDS.
Top
Mathematical model description.
The essence means is that the angular speed synchronization engine cylinder by means of power each drive working class including reels. To maintain a required level of a linear velocity of the rocket total electrical power devices profilegibochnogo regulate for a given line speed. [2]
The mathematical model describing the transmission of the next differential equations on the elements of power :
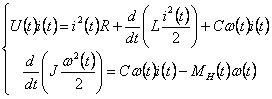
Here :
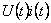 - electric power flowing to anchor motor;
- electric power flowing to anchor motor;
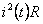 - Thermal-power Consumption in the anchor engine;
- Thermal-power Consumption in the anchor engine;
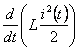 - power, Manhattan (output) inductor anchor;
- power, Manhattan (output) inductor anchor;
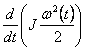 - power related to the kinetic energy electromechanical systems (electric-mechanical device);
- power related to the kinetic energy electromechanical systems (electric-mechanical device);
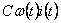 - E engine (performance);
- E engine (performance);
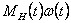 - mechanical power of the resistance impeding traffic system.
- mechanical power of the resistance impeding traffic system.
In an information useful option selected electromagnetic power ![]() (the same system (2) to the left side of the equation interesting) :
(the same system (2) to the left side of the equation interesting) :
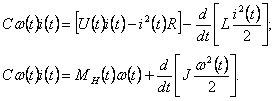
Consider the behavior of the rocket in the middle of strain between the two hoses drums. Let us take the example of two drum, shown schematically in Figure 3.
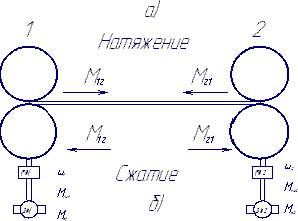
Figure 3. Interaction of body distorting instrument.
Moment of elastic in mezhbarabannom interval (MBP) is defined as the integral of the difference speed drives, with a ratio of elastic between drives.
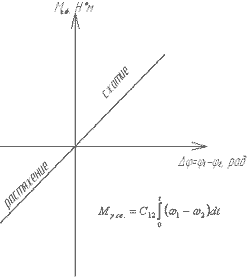
Combining mathematical model of drive drums and model of the body, we get depending on the speed and current anchor channel management and outrage. Applying to poluchenoy of the Laplace transform, we get gear as through management and outrage. Now, using Matlab Simulink application package may be obtained transitions, as well as the deformation of the body in the IPO.
Top
Virtual model SAU drive motor (peral. and after. Chart.)
Build one for the dvuhsvyaznoy electromechanical systems (EMS) with a serial connection anchors described engines (Decrease)
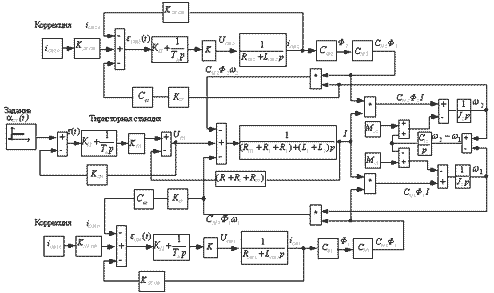
Figure 4-Structure mathematical model dvuhsvyaznoy EMS with a serial connection anchors engines.
Comparative analysis of the transition processes in the system are under the same nominal parameters engine own moments and loads parameters PI-regulyatorov.
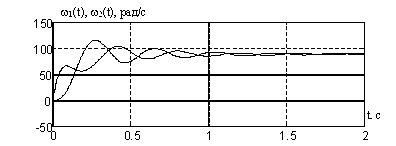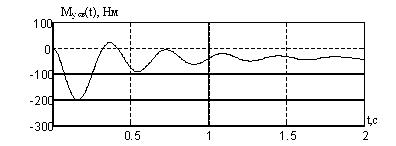
Figure 5 - Transition processes dvuhsvyaznoy EMS with a serial connection anchors engines.
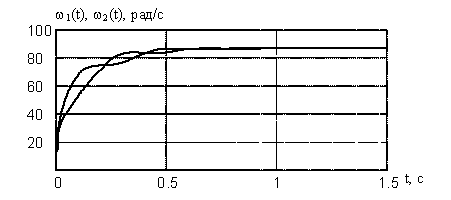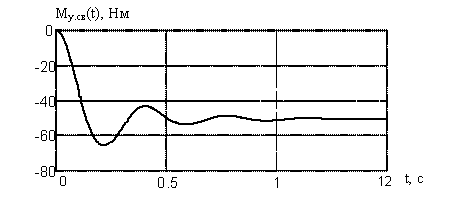
Figure 6 - Transition processes dvuhsvyaznoy EMS, managed to power.
The graphs show that the system is regulated by electrical power, has the best quality : less volatility and time setting. This is because continuous electro time EMS on power is far less than the same time constants consistent EMS. [3]
Then consider scheme parallel connections anchors drive motors. The model presented in Figure 7. As a pocket send voltage corresponding to a certain nominal capacity. Initiation of a step function change of the load on the shaft, the customary condition with a nominal value.
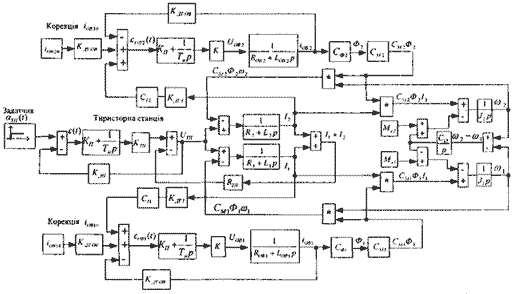
Figure 7-Structure mathematical model dvuhsvyaznoy EMS. connected in parallel anchors engines.
Simulation structural scheme (Fig.2) followed by a package of applications-Matlab Simulink 5.2, the transitions are presented in Fig 3. With the objective comparative analysis article summarizes the transitions (Decrease) engine speed and the time of elastic between transmissions received from modelling dvuhsvyaznoy EMS to power.
Comparative analysis of the transition processes in the system are under the same nominal parameters engine own moments and loads parameters PI-regulyatorov.
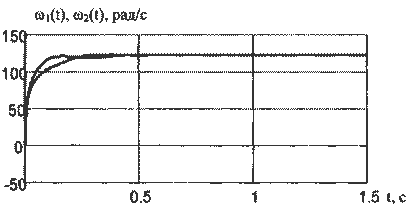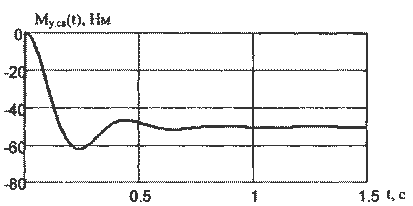
Figure 8 - Transition processes dvuhsvyaznoy EMS connected in parallel anchors engines.
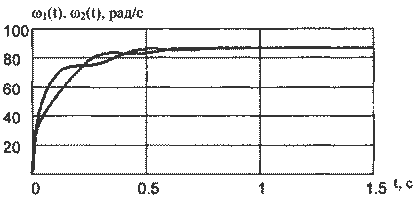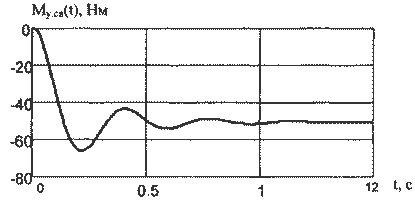
Figure 9 - Transition processes dvuhsvyaznoy EMS, managed to power.
The resulting model transitions of elastic and speed engines confirm theoretical dokazatelst-vo that controlling Trailing mills production welding PW management of power.
As a result of the Master's work anticipated polee detailed analysis of process parameters using various schemes including drives drums. A comparative analysis distress performance with that grown in the study for the production of PP in profilegibochnom molten steel mill. The result will be concluded that these processes are really a sister, and governance (using as a fundamental electromechanical power) is applicable in the production of powder welding wire.
Also expected to calculate the economic viability of the project after the introduction of the new system. Technical realization of the SU, base on the use of the latest technologies in the field of automation, have been outside the scope of the Master's work, but accepted as appropriate all of the task [5].
- Деклараційний патент на винахід № 36424А, Н 02 Р 7/68. Спосіб управління электроприводами неперервної технологічної лінії обробки металу тиском: Деклараційний патент на винахід № 36424А, Н 02 Р 7/68 /Титиевский В.М., Литвинов В.И., Горовой А.Б., Жукова Н.В., Рыпало Д.А., Подгорный И.В.; ВАТ «Завод «Універсальне обладнання». — № 99126860; Заявл. 16.12.99; Опубл. 16.04.01, Бюл. №3. — 5 с.
- Борисов А.А., Жукова Н.В. Наукові праці Донецького державного технічного університету. Серія: Обчислювальна техніка та автоматизація, випуск 12: - Донецьк: ДонДТУ, ТОВ "Лебідь", 1999.-327с.
- Н.В. Жукова, В.В. Червинский Матеріали ХІІІ міжнародної конференції з автоматичного управління (Автоматика-2006), м.Вінниця, 25-28 вересня 2006 року. - Вінниця: УНІВЕРСУМ-Вінниця, 2007.-600с.
- Жукова Н.В., Литвинов В.И., Червинский В.В. Наукові праці Донецького національного технічного університету. Серія: "Обчислювальна техніка та автоматика". Випуск 106/Редкол.: Башков Є.О. (голова) та ін. - Донецьк: ДонНТУ, 2006.-220с.
- А.Ю. Нихотин, Н.В. Жукова, В.В. Червинский Практика и перспективы развития партнерства в сфере высшей школы: Материалы восьмого научно-практического семинара. г. Донецк, 17-20 апреля 2007г. В 3-х томах. Том 3-Донецк, ДонНТУ, 2007 - 374с.

альтернативный e-mail
