|
| |
| Dissertation | |
| Theme: Methods and facilities of spatial object's orientation indication device |
| Actuality |
Modern building is characterized high rates and large volumes of the erected buildings, and also by active introduction of new decisions on all of the stages of building. The basic distinctive signs of modern стройиндустрии can be formulated as follows:
- perfection of methods of calculation of build constructions, both due to development of calculable methods and due to the wideuse of numeral models;
- non-standard designer decisions, which at times can be described as bold, innovative, unique;
- application of innovative technologies and materials.
The transferred tendencies are, sure, by a positive fact, however exactly modern building is characterized also and by growth of number of failures. The point is that development of difficult mathematical models together with the high quality computing engineering generated the illusion of possibility to expect any сколь pleasingly non-standard construction with absolute, infallible exactness. Reality is such, that the very debatable problems of concrete embodiment cost after the slenderness of numeral model, in particular, statistical variation of descriptions of material of a build construction, in particular case soils of foundation. Presently control of spatial orientation of objects is conducted in many areas of scitech: in an engineer and instrument-making - for control of spatial parameters of wares and their spatial position, for the exact keeping of workings organs of measuring apparatus and machine-tools; in building - application of devices of orientation allows with high exactness to fix inclination of building or area of protective wall and control the angular moving of objects or their parts, displacements of soils in foundation of buildings
If information about these processes is got in good time, they can be taken into account, and possible negative consequences are taken to the minimum. In fact for the beginning of rescue operation it is extremely important to define a moment, when mechanical deformations will exceed a threshold value. In spite of the fact that the process of mechanical destruction of structure can occupy of short duration time (from a few seconds to hours) relatively, his «symptoms» can show up long before it. Maximally rapid reliable authentication of danger and instantaneous serve of signal allow to conduct evacuation and prevent negative consequences, related to the outgassing, fires, problems with an electrical equipment, including – with elevators.
The modern hardwares of the geotechnical monitoring become the necessary attribute of building of difficult buildings and buildings. They allow to carry out operative control of the state of the created or on-the-road build building, taking into account the got information correct project and technological decisions if necessary, to promote reliability and operating safety of the erected objects.
It is impossible beforehand to provide for, model and take into account all of variants of change of external factors (geological, technogenic, natural, anthropogenic) of affecting a build object in the process of his exploitation. However, and it is extremely important to realize it at planning, it is possible to develop and set the device of control of orientation after the state and stability of basic elements of determining operating safety of building is foundation, walls, ceilings, supporting columns, roof, bearings and power elements of construction.
Thus, the issue of the day to date is development of various devices and systems of monitoring of constructions of buildings and buildings, and introduction them in practice of building. |
|
| Review of methods and existent devices, choice of prototype |
The state-of-the-art review of existent methods of control was made for this purpose:
- the use of satellite methods of measurings;
- laser scan-out of buildings;
- method of the geometrical leveling;
- fiber-optics measurings systems;
- magnetic sensors of spatial orientation;
- the use of accelerometer.
Considered methods and devices of determination of spatial orientation of objects in points among all of failings, have one very substantial – they are too dear, for the use as stationary measurings devices at monitoring of buildings and buildings. Presently control of displacements, vibrations and rejections of objects conducted city services at certain intervals of time (one time in 5 years), but not which constructions, as often is in our time, and remain regardless quite. This question acquires the special actuality in connection with the collecting presently high rates of building, especially in unfavorable in geological relations districts to which our behaves and city. The devices of control, for the receipt of mass distribution, must possess a low cost and in also time to provide sufficient exactness. Because of these reasonings, it is suggested as prototypes to utillize the next sensors of spatial orientation. Akselerometry well befit for the use as sensors of control of perimeter of buildings and building, as allow with sufficient exactness to determine the vibrations (displacements) of objects. For the use as a sensor of inclination, accelerometers does not fit, as in the case of gradual the accumulation of tensions, deformation of object, can take a place gradually with speed which they are not sensible to. In this connection for basis of sensors of control of vertical line of buildings and buildings it is suggested to utillize the magnetic sensors (inclinometers) of spatial orientation of objects.
In master's degree work, with the use of package for engineerings developments of NI LABVIEW, to your attention the model of work of the simplest integral g-meter will be offered. Promodelirovany of reaction of g-meter on external influences, the graphs of acceleration are built, скокрости and displacements of objects, with the use of methods of double integration. The methods of determination of the wind and seismic loadings are considered in соответсвии with normative documents. The choice of primary measurings transformers is grounded. As sensors of control of perimeter of buildings the integral are chosen accelerometers type of ADXL 203, for control of vertical building line are magnetic sensors of angle of slope of PMP-S5TX. |
|
| Controlled loadings and influences |
The objects of control of the designed device are the followings types of the temporal loadings and their combination:
1) wind loadings;
2) seismic influences;
3) influences, grounds conditioned deformations;
4) snow loadings;
5) influences, conditioned a change humidity, усадкой and creep of materials;
6) loadings from people, animals, equipment;
7) oscillation or dynamic influences from a авто- and railway transport, lines of underground passage, equipment, set in buildings
and industrial options, located near-by existent buildings;
8) temperature climatic influences;
9) ice loadings;
10) explosive influences.
Most widespread and influential on build constructions, there are the wind loadings and seismic influences. Limitations of vibrations of constructions were set, they must not exceed 0,08 ì/ñ². The maximum horizontal moving of top of height buildings is accepted no more than 1/500 from their height. For the elements of constructions of buildings and buildings the maximum moving of which is not stipulated normative documents, the vertical and horizontal moving from quiescent, protracted and brief loads must not exceed 1/150 flight or 1/75 flight of cantilever.
The methods of determination of horizontal extreme relocation of framework buildings are set, coming from structural requirements (providing of integrity of filling of framework walls, partitions, window and door elements). It is necessary to determine the horizontal moving of framework buildings, as a rule, taking into account the heel (turn) of foundations. Thus loading from weight of equipment, furniture, people, warehoused materials and wares it is necessary to take into account only at the continuous even load of all of ceilings of multistory buildings these loadings (taking into account their decline depending on the number of floors), except for cases at which on normal external environments other load is foreseen.
It is thus necessary to accept temperature influences without the account of daily allowance vibrations of temperatures of outward air and overfall of temperatures from a sun radiation.
It is thus necessary to accept temperature influences without the account of daily allowance vibrations of temperatures of outward air and overfall of temperatures from a sun radiation.
|
|
 |
|
Picture 1 – Calculation dynamic model of building
Animation: GIF Animator, 4 picture frame, change picture frame - 1,5sec |
|
| At the calculation of buildings it is necessary to accept the most dangerous orientation of influence, realizing a maximum of dynamic reaction. |
|
| Raising of control task |
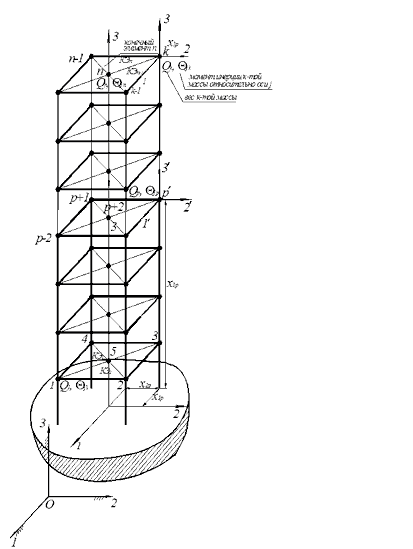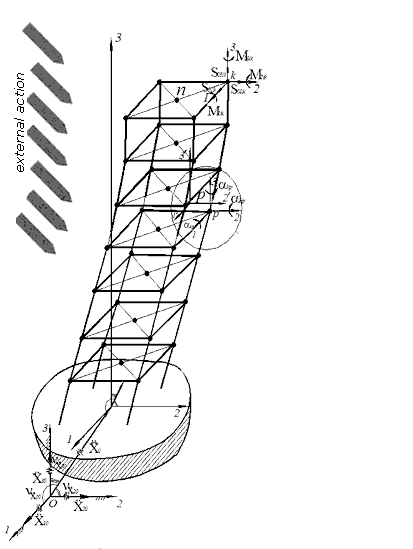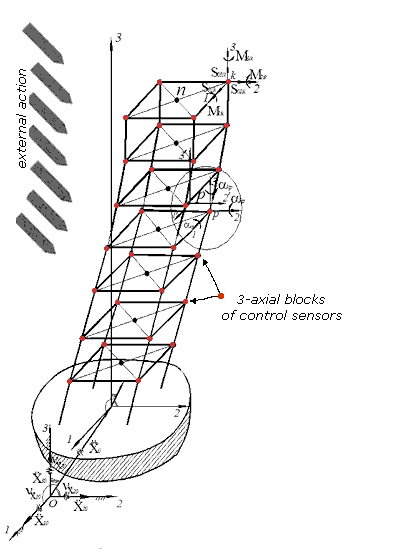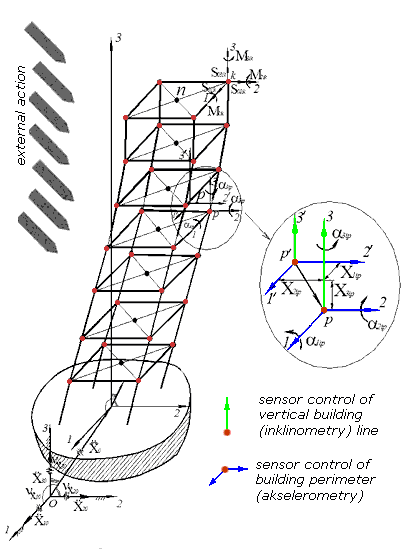
The device of determination of spatial orientation of objects is intended for the objective high-fidelity measuring of moving (inclination, vibrations) of the controlled objects (buildings, buildings) and elements of constructions from initial position, communication of data for a subsequent reflection, treatment, storage, and notification in the case of emergency situations. The designed device is intended for measuring of displacement, vibration and inclination of object. As a prototype the magnetic sensors of vertical control and integral accelerometers are chosen. Thus, basic data for planning it is been:
- sensors of control of perimeter of buildings, as which the biaxial integral are utillized accelerometers ADXL203, allowing to measure a linear acceleration on two mutually to the perpendicular axes;
- range of registration of processes - 0,1 ÷ 300 Hertzs;
- middle quadratic error of sensor - 0.25%;
- sensors of control of vertical line buildings, based on registration of moving of «freely hanging or floating» permanent magnet in relation to the receiving surface of magnetsensitive element;
- angular permission of DUN – 0,005°;
- range of measuring of inclination - to 10.
Requirements and limitations, laid on for development, followings:
- receipt of result of measuring at any moment of time;
- receipt of measuring result in a human-friendly form;
- as possible less vehicle expenses.
At planning of control device the special requirements are not pulled out to his mass.
As the recommended conceptual decision it is possible to offer following. Application of integral accelerometer and magnetic sensors will allow to transform moving (vibrations) and rejections of object from a vertical line in electric signals.
To the initial co-ordinates of object the testimonies of sensors set at first after setting. Possible deviations from initial data settle accounts on the basis of the proper build norms and rules. It is recommended to apply the developed device as a stationary setting at control of large and difficult objects, and also buildings higher 40 meters.
In the process of measurings it is possible to make both a few read-outs of the controlled information at stated intervals and to conduct continuous in time control of object. |
|
| Theoretical analysis and ground of functions of device |
Developed device of determination of spatial orientation, provides diagnostics of the state of on-the-road buildings and buildings, – vibration, deformation and rejection of constructions of buildings and buildings from project position. He is a new generation of apparatus for the dynamic analysis of stability of buildings and buildings.
Basic operations on determination of bodily condition of buildings and buildings, in particular – height, at influence of loadings, followings:
1) Registration (oscillography) of vibrations is in the different points of building in the places of possible amplitudes of the first three forms of eigentones. Duration of process of registration is set automatically, assuming its breaking up on separate representative records for forming of band of realization of casual process.
2) Treatment of the registered vibrations and functions of time of speed pressure: delete of трендов, smoothing out, balancing of stationary part of process, transition from a temporary realm in frequency the method of rapid transformation of Fur'e (FFT), I.e. receipt of peak frequency spectrums of vibrations of building and determination of inclination.
3) There is a construction of transmission function and fixing of its extremums von the got spectrums, as experimental frequencies of eigentones of construction, logarithmic decremeters of eigentones, distributing of amplitudes of transversal and longitudinal vibrations on the height of building.
4) Calculation determination of frequencies of eigentones of building from basic project data with the use of programmatic facilities, control of possible inclination of building.
5) Determination of durability, stability, wear and remaining resource of building by programmatic facilities. For buildings in seismically dangerous districts is calculation determination of remaining resource on seismic resistance.
As is generally known, in build constructions appearance of defects is caused by diminishing of areas of workings sections and moments of inertia from project parameters. Mechanical descriptions of materials (module of resiliency, coefficient of Puassona, normative resistance of construction materials) also can differ from project values both because of natural heterogeneity and on technological reasons. In the process of exploitation of constructions and in connection with the effects of senescence there is a further decline of the indicated parameters and, consequently, – to bearing strength. Characteristically, that here does not take a place noticeable decline of resource-demanding of constructions.
Procedure of estimation of bodily condition of building on the whole is set the cycle of analysis on basic bearings structural elements. In supposition, that at the estimation of durability and stability of buildings it is possible to ignore the change of mass descriptions, bearing ability it is possible to describe flexural inflexibility of weak sections of bearings structural elements of B = EJ, I.e. by work of the module of resiliency of E in the moment of inertia of normal section of J. The indicated pre-conditions enable to estimate bearing strength of building on the spectrum of frequencies of eigentones of Ti on n to the own forms (I = 1, 2, 3. n), related to middle inflexibility of B correlation: |
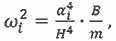 |
здесь m = const – const is linear mass; H – H is flight of structural element (for height buildings is a building height); αi – is a frequency coefficient, depending on resilient properties of supporting section.
We will enter time of t with beginning of counting out of t = 0, combined with the moment of input of building in exploitation. Vkrkhnyaya a formula determines the calculation frequency spectrum of constructions both new (i.e. at t = 0), and being in exploitation (at t > 0) at the input of the proper value of inflexibility of B.
Relies further, that the initial state of construction corresponds some basic (by a project) data. If building is projected on bearing strength from the concrete loading, the percent of diminishing of inflexibility will correspond the decline of this (by a project) bearing strength. If building is intended for service in a seismically active district, i.e. on a project is сейсмостойким on G of marks, the percent of diminishing of inflexibility will correspond the decline of the indicated (G) resource of seismic resistance.
Estimation of decline of bearing strength of building on the arbitrary temporal interval of t … t + Δt given on the difference of inflexibilities on the scopes of this interval, for which t = 0 (beginning of exploitation, project information) is the special case. In general case the relative wear of structural element is estimated on a formula: |
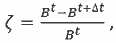 |
| and, for example, passing to fundamental frequency, in supposition, that a border condition was saved (i = 1, αi = const): |
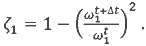 |
If the prognosis of wear is needed to on to information, to based on the theoretical considering about the accumulation of damages in course of time, an estimation suffices on a formula on this formula, as in this case both values of fundamental frequency are determined exactly a calculation.
the estimation of wear of on-the-road buildings there are current values of frequencies of ωt + Δt determine experimentally the spectrology of vibrorecord, and the percent of wear is determined a mean value on the n forms of eigentones of object: |
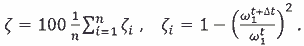 |
For holdings of frequencies gravimetric coefficients can be entered them relevance.
Root-mean-square rejection of frequency of Dω at the mean value of ωcp: |
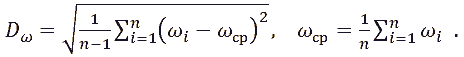 |
In this method the calculation values of frequencies are determined programmatic facilities taking into account the gradient parameters of building on co-ordinates, stratified and heterogeneity of crossrunners, and also to resilient pliability of foundation foundation. Exactness and authenticity of expressmethod is arrived at due to taking into account at the calculation of such factors, as an unevenness of distributing of inertia (mass) and rigid descriptions on co-ordinates, pliability of supporting section of construction and composite structure of sections.
Will define the remaining resource of building P as addition to unit (or in percents – to 100%) of size of wear ζ: |
| P = 1 - ζ |
For the extensive objects of type of smoke and vent pipes, as a rule, the records of vibrations, caused the wind loadings are utillized. Practically there is excitation of all of forms of eigentones of building in the indicated terms.
During measurings registration of акселерограмм is made, I.e. changes in course of time of accelerations of different points of object, and also (at possibility) synchronously-speed pressure of wind.
Results of control and estimation of the technical state are basis for a decision-making about possibility of further exploitation of technical devices, buildings and buildings, and allow to expose reasons of damages of separate parts and constructions, forecast speed of their wear and define a remaining resource.
Functioning of complex is based on the automatic computer operation of analysis of changes of spectral descriptions of the diagnosed building comparison (by a relation) of the experimentally measured and calculation (project) inflexibilities of weak sections of constructions.
Designed device is a highly sensitive multichannel apparatus. Highly sensitive сейсмовибрационные sensors (accelerometers, sensors of inclination) with the range of the undistorted registration of processes from 0,1 Hertzs to 30 Hertzs allow to probe both extensive height objects, having large periods of eigentones and buildings with a hard structural chart. Connection of sensors with a computer is carried out by means of flow line.
In a device it is possible to select eventual knots and central knot. He contains 4th instrumentation module, each of which contains 3-ех co-ordinate sensor with the channel of treatment of information and ACP. The base module is contained by the microcontroller block of treatment and indication. The central personal computer is equipped the package of the specialized software for a management, visualization, treatment and analysis of data, all of functions of device with the use of different algorithms of digital treatment of signals in temporary and frequency realms. Access to master data about stability of building, through the central personal COMPUTER, ordinary citizens can get, if they are of interest for them. |
|
| Conclusion |
| Research of device of spatial orientation of objects is made in the abstract of thesis (buildings and buildings). The state-of-the-art review of existent methods was made for this purpose, devices and systems, the choice of primary measurings transformers is grounded. As sensors of control of perimeter of buildings the integral are chosen accelerometers type of ADXL 203, for control of vertical building line are magnetic sensors of angle of slope of PMP-S5TX. The total constituents of errors of integral accelerometer are certain and the methods of the методи diminishing of errors are investigational. The electric of principle charts of connecting of sensors are developed. The analysis of loadings and influences, operating on buildings and buildings is conducted. Made рял models, in-use sensors in a package for engineerings developments of NI LABVIEW. The functional and structural diagrams of the designed device are also developed. For the mathematical providing of the probed objects, the analysis of dynamics of buildings is conducted, as an example, made calculation of reaction of building in the direction of wind. |
|
| Literature: |
1. Савицкий Г.А. Ветровая нагрузка на сооружения // М., 1972г., 111с.
2. Бараночников М.Л. Микромагнитоэлектроника. Т. 1. – М: ДМК Пресс, 2001. – 544 с.
3. Гудинаф Ф. Интегральные акселерометры // Электроника. 1993. № 7–8.
4. McCoy. Method and apparatus for measuring pumping rod position and other aspects of a pumping system by use of an accelerometer Pat. USA № 5406482, pr. 11.04.95
5. Глобальна система визначення місцеположення (GPS). Теорія і практика / Гофманн -Велленгоф Б., Ліхтенеггер Г., Коллінз Д. / Пер. з англ. під ред. Яцківа Я.С. - Київ: Наук. Думка, 1995.
6. СНиП 2.01.07-85*. Нагрузки и воздействия.
|
|
|
|
|
