References
Introduction
The evolution of technology and progress in engineering and instrument making industry are bound up with enlargement of new difficult – to – cut materials, such us using carbide – tipped products , ceramics, glass, ferrites, to creation of new for processing are used diamonds grinding wheels. Diamonds wheels, are weared during their using, that is why cutting ability and geometry of grinding wheels are chensed.
Dressing of diamonds grinding wheels owing with some difficulties. That's why diamonds grinding wheels are making with self – sharpening post characteristics.
1. Theme urgency
In modern mechanical engineering we know some ways of diamond grinding wheel dressing.
But dressing of wheels of those types could present certain difficulties.
The difficulty of this process is in diamond hardness, big hardness index and viscosity of bonding material.
Master's work in dedicated to research of effect of diamond disk's speed on the process of recovery of it's cutting ability when using loose abrasive.
We should use dressing of diamond wheel with loose abrasive as a foundation base.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The main goal of research is boost of performance and quality of dressing by choosing rational parameters of the process and leveraging of loose abrasive to acting face of wheels.
Main tasks of the research:
- Developing an construction for dressing with superimposition high–frequency vibrations to microsizing tool.
- Experimental efforts on how the relationship between speed of the wheel and abrading tool efforts on productivity of adhesive diamond wheel disposal.
- The analysis of loose abrasive's abrasive grains mutilation process during dressing.
- Determination of rational modes of diamond wheel's dressing.
Research object: diamond wheel.
Research subject: diamond wheel's dressing process using loose abrasive.
In master's work it is planned the obtaining of actual scienific results in these tasks:
- Determination of rational modes of diamond wheel's dressing using loose abrasive.
- Selection of loose abrasive's parameters for dressing.
- Development of methods and devices for diamond wheel's dressing using loose abrasive.
For experimental estimation of obtained theoretical results and formation latest research's fundament, as practical results it is planned to develop a new type device for diamond wheel's dressing:
- Design supply of this equipment and accessories .
- Diamond wheels of different types and purposes.
- Acting face of wheels conditions testing methods.
3. Main Part
Dressing is process of diamond grinding wheel's acting face leveraging with goal to deoxidate it's cutting ability and needed geometry of cutting faces.
Wheel's dressing is proceeded with working speed. Before lathe work it is needed to make the wheel 1 – 2 minutes of free rotation for heat penetration ofoperating mechanism), since the bounce of cold and hot bearing parts are different.
During the dressing a little layer is стачивается from the periphere of abrasive wheel.
The difficulty in process of diamond wheel's dressing, unlike abrasive ones, is in bigger hardness index of diamond, hardness and viscosity of bonding material.
The need of diamond wheel's dressing occurs in next cases: for disposal of new heel acting face's bounce after installing in on machine tool station; while correction of wheel's geometry in operation process; loss of cutting properties during operation.
The correct selection of diamond wheel capabilities, machining conditions and other technological factors while pass grinding of rectilinear faces must possibly exclude needs to dressing the wheel or minimize dressing operations count. But practically these needs appear in operational process.
Considering the hardness of diamond wheel's handling, it is used for their dressing such processing techniques as: disk grinding, electrochemical, electroerosion and electrocontact processing. The difficulty of processing is in large nomenclature of diamond wheels and in large diversity of bondings.
The alternative to electroerosion dressing are numerous mechanical dressing techniques. Mechanical dressing techniques are determined by variety of operations of mechanical impact on abrasive tools. All those techniques are directed to correct geometry of dressed tool and creation of necessary microprofile of wheel's working surface.
The performance of loose abrasive dressing is 2 – 3 раза higher, when abrasive disk dressing, but abrasive's need is 6 times less [3].
We at Mechatronic systems of mechanical – engineering equipment
cathedra of DonNTU developed new method of diamond grinding wheel dressing – loose abrasive dressing [4]. Main features of this dressing is purposeful impact of abrasive grains to grinding wheel's bonding and wheel's geometry correction.
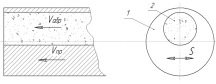
Picture 1 – View of abrading tool and abrasive stick:1 – abrading tool; 2 – abrasive stick.
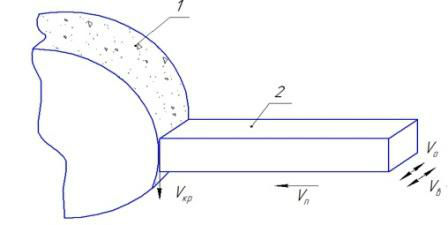
Picture 2 – Scheme of loose abrasive dressing of grinding wheel (1) using abrading tool 2 Vкр – linear speed of grinding wheel; Vо – speed of reciprocating motion of abrading tool along the moving line of grinding wheel; Vв – speed of abrading tool in high-frequency vibration
We at «Mechatronic systems of mechanical – engineering equipment» cathedra of DonNTU developed new method of dressing using loose abrasive (picture 2) [1]. In contrast to well – known dressing technique [2] of grinding wheel (1), which has linear speed Vкр, when abrading tool (2) uninterruptedly moved in direction of wheel's working surface with Vп speed and make reciprocating moves along the moving line of grinding wheel with Vо. speed. In new technique abrading tool additionally makes выполняет high – frequency vibrations with Vв speed, directed along moving line of grinding wheel, and vibration's frequency must be: