Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. A review of existing control systems this class of objects. Classification of control systems.
- 4. Simulation of the control system automatic recognition of the real user and a computer program.
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Introduction
A botnet is an army of infected computers under the control of a remote attacker.
Widespread broadband access technologies has led to significantly improve the ability of
botnets to launch attacks such as denial of service
, infecting millions of computers with
spyware and other malicious code, theft of confidential data, large-scale spamming, wrap
clicks, blackmail and extortion. To date, botnets are a major threat to Internet security.
Attack using a botnet easy to order, and hackers are at an unprecedented rate and exploit new
vulnerabilities. Typically, a single botnet consists of tens of thousands of computers.
Botnets are difficult to detect because of their topology is dynamic in nature, which allows
you to bypass the most common remedy. Units of information security measures must be taken to
prevent contamination of corporate computers and protect corporate resources from attacks using
botnets.
Botnet – a computer network consisting of a number of hosts from running bots – standalone software. Most often, the bot in the botnet is a program that secretly installed on a victim's computer and allow an attacker to perform certain actions using the resources of the infected computer. Typically used to send spam, brute force on the remote system attacks denial of service [6].
Botnet is one of the finest choices of cyber weapons with high computing power, and is a wonderful way to make money anonymously [3]. The organizer of the network can control the infected computers on the network from anywhere, with virtually no risk of being detected. The owners of its computers are often unaware that they are infected and are used by hackers, are controlled by third parties. These zombie machines are included in the multi-million botnet. The simplest structure of the botnet is presented in figure 1.
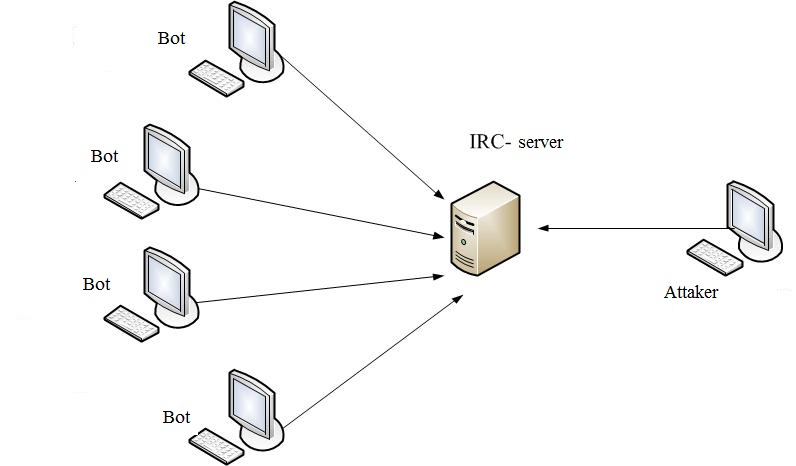
Figure 1 – The simple structure of the botnet
A botnet can be used for various purposes [2] from the usual spamming to attacks on government networks. Briefly review the options for using botnets:
- Spamming. Experts estimate that about 80% of spam is sent just using botnets. The average spammer earns about 50-100 thousand dollars a year on such networks. Botnets designed to send spam can also collect email addresses from infected machines.
- Cyber-blackmail. One of the most widely used methods of use of a botnet – conducting
large-scale DDoS-attacks (distributed denial of service attack,
denial of service
). In the course of this attack with zombie computers to the server is sent a large flow of false requests as long as the server is overloaded and will not available to users, after which the botnet owners are demanding a ransom for stopping the attack on the server. Since the successful conduct of business today is not possible without the work on the internet, site owners will agree to pay a ransom faster than turn to law enforcement. - Anonymous access to the Web. This use botnets allows hackers on behalf of infected computers to carry out hacking, theft of money from bank accounts, etc.
- Sale and rental of botnets. Using this option the owners of botnets also can make money illegally.
- Phishing (an online scam, the purpose of which is to gain access to confidential data of users – login and password). Botnet allows phishers to quickly change the address of a phishing page using the infected machine as a proxy server, and thus hide the real address of the page.
- Theft of confidential data. This kind of use of a botnet can steal all kinds of user data, which are then resold or used for mass infection of web pages in order to expand the botnet.
The current classification of botnets is very simple. As such, it is based on only two important parameters – the architecture of botnets and the protocols used to manage them. As its most important parameter is the architecture, we consider this aspect in more detail.
Architecture botnets are usually divided into two main types – with a centralized and a decentralized topology. Sometimes add one more, a mixed type, combining the features of the first two, but nothing new in it [4].
Regarding the protocol distinguish IRC-oriented, IM-oriented, Web-based, and many others.
Classification of botnets based on the architecture of botnets and the protocols used to control the bots [1]:
- The centralized topology (single point of control, C&C – Command & Control Centre). All of zombie computers are strictly connected to one master node. Control Center monitors the status of connected bots, accumulates they collect data and issues commands, and constantly waiting for the connection of new bots, registering them in its database. To manage the network owner needs access to the C & C, from where you can see all the connected computers-bots. This type of zombie networks is currently the most common because they are easier to build and easier to manage them. The structure of centralized botnet considered in figure 2. Elimination of node C&C is just a block botnet, and for stealing enough to take control of the center.
- Distributed topology (P2P-botnets). Here bots do not connect with a single point of
management, and with a few neighbors, and infected machines on the famous principle of
peer-to-peer, that is, the
point-to-point
. The structure of decentralized botnet considered in figure 3. Eliminate or steal such a network is much more difficult, because the owner to manage the entire botnet enough to have access to at least one of the machines zombie network. On the other hand, to control P2P-botnet is not as convenient as a network with C&C.
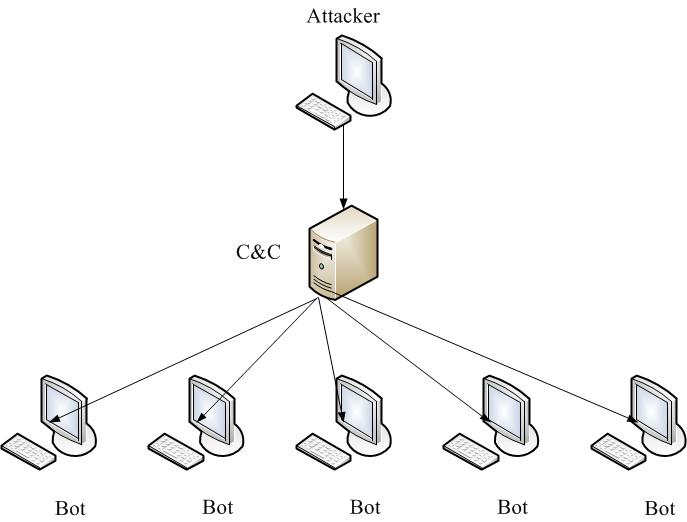
Figure 2 – A centralized topology botnet
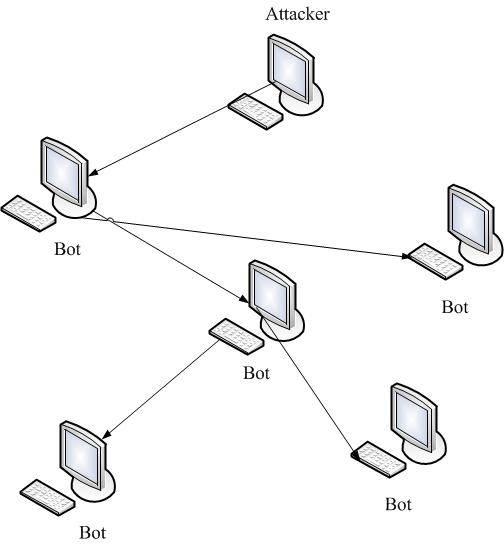
Figure 3 – The decentralized topology botnet
Classification of botnets respect of network protocols [7]:
- IRC-oriented. This is one of the first types of botnets, where control bot was based on IRC (Internet Relay Chat). Each infected computer connects to the body of the program specified in the IRC-bot server, came to a specific channel and waited for instructions from his master.
- IM-oriented. Used for data transmission channels of IM-services (Instant Messaging), such as AOL, MSN, ICQ, etc. Problems arise when creating a separate account IM-services for each bot, so the low popularity of such botnets. The fact is that bots have to go to the Web and always be present online. Since the majority of IM-services are not permitted in from different computers using the same account, each robot must be your number IM-service. In this case, the owners of IM-services strongly impede any automatic registration of accounts. As a result, owners of IM-oriented botnets severely limited in the number of available registered accounts, and thus in the number of bots simultaneously present in the network. Of course, the bots can use the same account, go online once a certain period of time, to send data to the host and the room for a short time to wait for an answer, but it is very problematic: such a network responds to commands very slowly.
- Web-based. Bot joins with a particular Web server, receives commands from and transmits the response data. Such botnets are popular because of the relative ease of development, a large number of web servers on the Internet and ease of management through a web interface.
- Others. In addition to the above, there are other types of botnets, which are connected through their own protocol, based only on the protocol stack TCP/IP: use a common protocols TCP, ICMP, UDP.
1. Theme urgency
Relevance of the topic caused important problem that has arisen about fifteen years ago – a botnet (zombie networks), and its still very much underestimated as long as there is no leakage of valuable information from the firm, did not disappear with the money and bank cards other troubles.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of the study is to develop a control system of automatic recognition of the real user and a computer program simulation of a botnet and then applying algorithms and methods to intercept and destroy bots.
The main objectives of the study:
- Analysis of the characteristics of the object of control:
- consider the structure of the control object;
- examine the functioning of the control object;
- review the existing level of organization management.
- A review of existing control systems that class of objects:
- classification of management systems;
- assessment of the characteristics of the control object.
- Statement of the problem.
- Synthesis algorithm of the system.
- Simulation of a botnet.
- Analysis of the results obtained.
The study is planned to get the algorithm of the control system automatic recognition of the actual user and the computer program, the model of the system and evaluate the simulated performance.
3. A review of existing control systems this class of objects. Classification of control systems.
The control system of automatic recognition of the actual user and the computer program is designed to prevent theft, loss of data, loss of finances and image of the company, as well as many other unpleasant factors. The structure of this system is shown in figure 4.
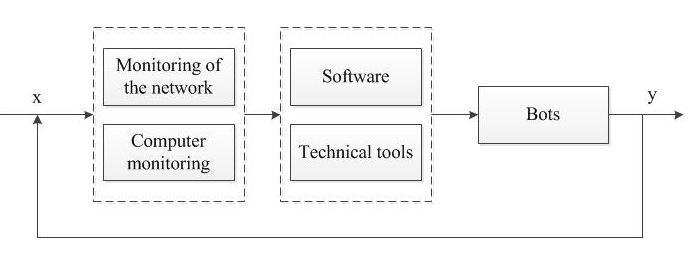
Figure 4 – The control system of automatic recognition of the actual user and the computer program
In figure 4, we consider another attack of zombies. When the signal input to the control system's happening simultaneous monitoring of the Internet and your computer using the software, and technical controls that analyze the input signal. Detection of a botnet attack these systems entail signaling software and hardware, blocking boats, and then search for and lock the center of a botnet.
A striking example of a botnet is a visual representation of DDoS-attacks on the server (see figure 5).
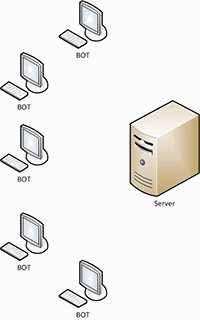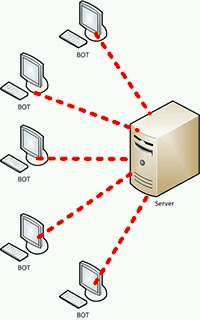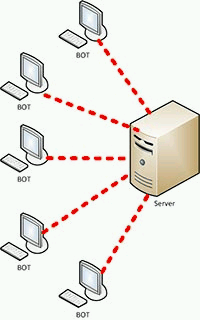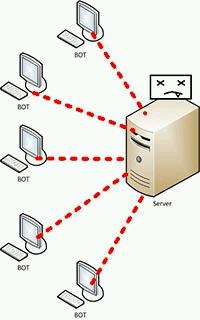
Figure 5 – DDoS-attack on the server, (animation: 4 frames, 4-cycle repetitions, 72 kilobytes).
With DDoS-attack on the server bots on infected computers awaiting the command from the host. Upon receipt of the necessary command of the attack a specific server, each computer will send a huge number of small packets. When you overload the server a large number of packets the server ceases to function for a long time [5].
Can identify two main types of management of this class of objects:
- Security software.
- Technical means of protection.
To software protection include:
- Norton AntiBot. Protection against bots, active behavioral analysis.
- Check Point. Collecting data from a unique global network of threat detection sensors and dissemination of this information by security gateways worldwide.
Technical means of protection against botnets:
- detection devices and the suppression of DDoS-attacks Cisco Guard and the Cisco Anomaly Detector. The devices are the most functional and powerful of the existing solutions for the suppression of the most dangerous by far the threats from botnets, namely DDoS-attacks.
- Solution Cisco Service Control Engine (Cisco SCE) has the ability to control the traffic broadband subscribers in the network.
- device IronPort S-series has the ability to monitor traffic on the 4th level with speed of 1Gbit/s, detecting and blocking malicious connection attempts resources the Internet.
- Cisco Security Agent protects servers, personal computers and POS-terminals of the most common attacks using botnets: installing software bots, spyware programs, software for remote control, as well as targeted and completely new attacks.
- Cisco IPS sensors use anomaly detection algorithms to detect and blocking attacks using botnets.
- Cisco NetFlow – this is the best of the industry represented by the implementation of Flow-protocols telemetry function, allowing to obtain data on the operation of routers running Cisco IOS ®. Thanks to its scalability and ability to provide traffic reports in networks of all sizes Cisco NetFlow technology has become the standard method for obtaining useful information for traffic management and security in networks of both operators and carriers.
- Cisco Global Site Selector – this device is the global load balancing, which can also be used as a DNS-server that provides a scalable service name and address for business networking and telecom operators.
Control system automatic recognition of the actual user and computer program provides a two-level protection on the one hand on the software and technical level, and the other – the Internet home and working machines in order to further detect and partial or complete elimination of the botnet.
Figure 6 shows the algorithm of the proposed system.
Consider in more detail the algorithm, since the algorithm for monitoring the working machine (box 2 in Figure 6) in two cases:
- Emergence of a new or modified file (figure 7).
- Starting a new process (a process that was not included in the system administrator approved list) (figure 8).
In existing components for this system include algorithms auxiliary subsystems that will not only work as much as possible to protect the Organization (website), but also to discover the source of the negative impact, namely:
- Algorithm for software that will interact with the hardware means for collecting and analyzing statistics of input traffic.
- Algorithm for the detection system command center of a botnet.
Detection of botnets is primarily based on the analysis of network traffic. The aggregate Information on abnormal changes in the volume of incoming and outgoing traffic gives a clear picture about attempts to disrupt, to carry out information theft and other effects on the system. Therefore, the algorithm for the collection and analysis of statistics is an important input traffic component of the entire system.
Neutralization of the source of negative impact on the work of the organization is also a important task, because of the failure to comply may be repeated, and the fight against the influence of a botnet requires a lot of resources and time. Detection algorithm the command center of a botnet is shown in figure 8.
This method is based on the discovery that a host can be in one of three states – or legitimate IRC-client or bot, which is in the idle state team or bot able to attack. Each of these states correspond to specific values average packet length and packet forwarding frequency.
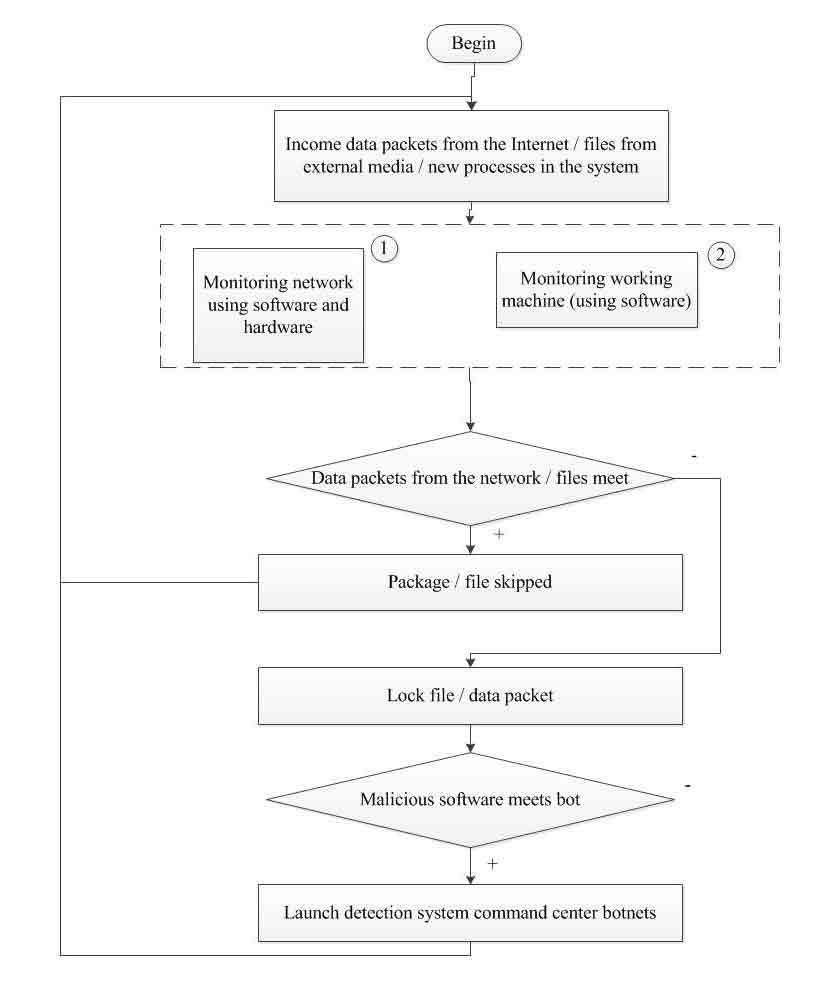
Figure 6 – The algorithm of the automatic control system recognition of the actual user and the computer program
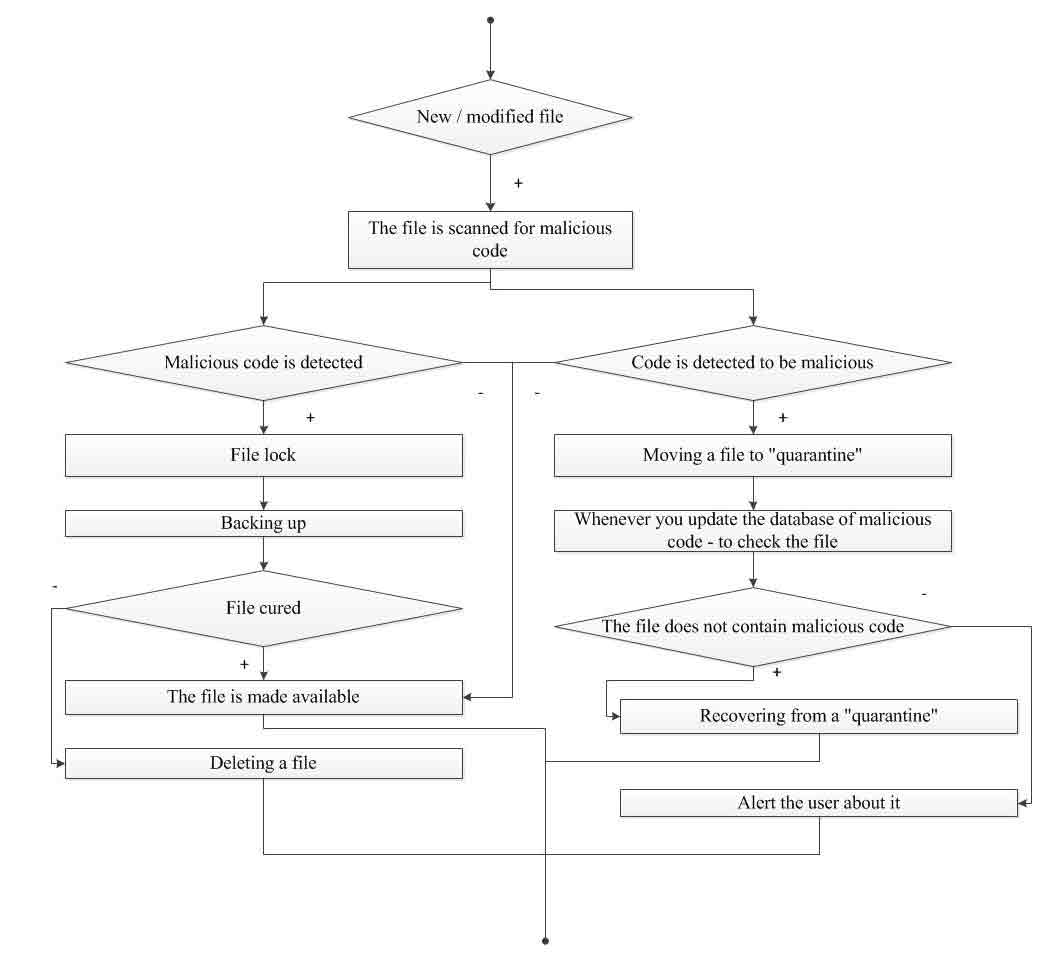
Figure 7 – Algorithm monitoring computer (in case of a new or modified file)
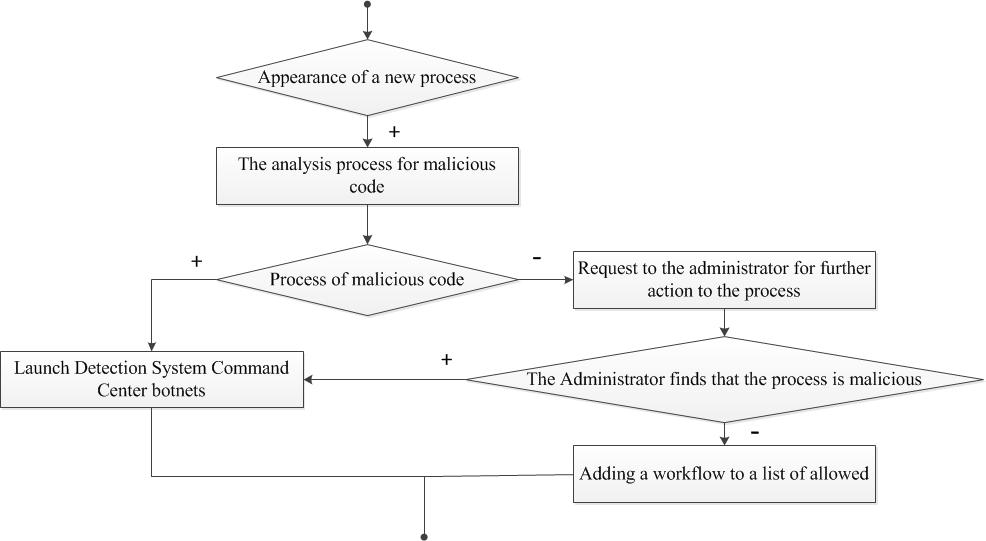
Figure 8 – The algorithm works in computer monitor (in the case of a new process)
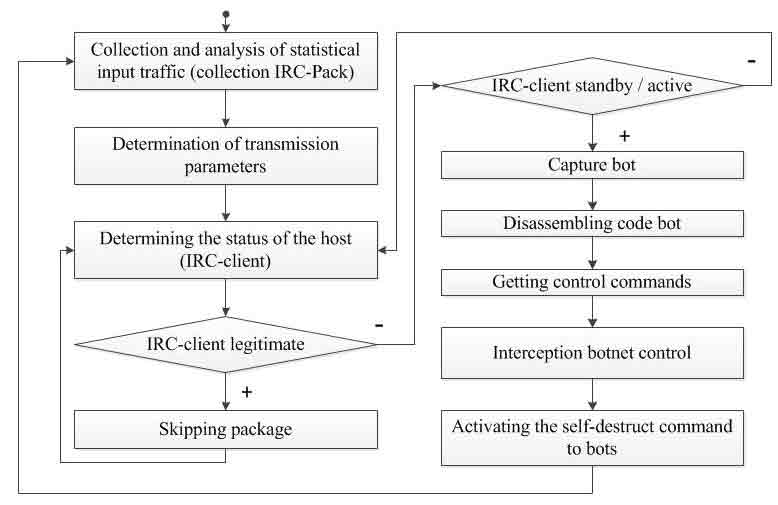
Figure 9 – The detection algorithm is the command center of a botnet
4. Simulation of the control system automatic recognition of the real user and a computer program.
In the simulation control system automatic recognition of real use and computer program is planned to develop a model of botnet based on the model small network of computers and a remote server that will be attack. Will be analyzed the work of botnet, and then applied the model of the system of protection and performed further analysis of the results.
Conclusion
Analyzing the current situation of development of cyber crime, you can come to the conclusion that botnets are one of the most profitable areas, as well as that attackers are unlikely to do refuse from this type of earnings and, in turn, is unlikely to disappear in the competition business, where the security of information and the stability of web sites is the key successful operation of enterprises and companies, as well as public networks. While the experts warned of the dangers posed by the development of botnets, most business owners, State refuse to take any measures to protect against them as long as faced with a similar problem, and the zombie network all continue and continue to develop.
As a result of this work was:
- The characteristics of the control object (consider the structure of the object management, reviewed the functioning, reviewed the existing level management organization).
- A review of existing control systems to the object class (held Classification of control systems).
- Algorithm control system automatic recognition of the real Users and computer programs.
- Modeled and analyzed the work of botnets and the automatic control system recognition of the real user and a computer program.
Note
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2013. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Официальный документ Cisco, Ботнет: новый характер угроз, Cisco Systems, Inc, 2008, 9 с. – URL: http://www.cisco.com/web/RU/downloads/Botnets.pdf.
- Богданова, И.Ф. Информационная безопасность: классификация компьютерных угроз / И.Ф. Богданова // Интернет и современное общество: Труды ХI Всероссийской объединенной конференции(28-30 октября 2008 г., Санкт-Петербург). - СПб.: Факультет филологии и искусств СПбГУ, 2008. - С. 27-29. - URL: http://conf.infosoc.ru/2008/pdf_HI/BogdanovaN.pdf
- К.Л. Берлизева, Ю.М. Монахов, «Подготовка экспериментов по проверке работоспособности метода обнаружения ботнетов на основе кластерного анализа и метода обнаружния ботнетов на основе скрытой марковской гибридной модели», url: http://izi.vlsu.ru/HTC/1.pdf.
- И.В. Котенко, А.М. Коновалов, А.В. Шоров, «Исследование бот-сетей и механизмов противодействия им на основе имитационного моделирования», url: http://simulation.su/uploads/files/default/2012-kotenko-shorov-1.pdf
- Pub. No.: US2011/0004936 A1. Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011. Botnet early detection using hybrid hidden Markov model algorithm, Hahn-Ming Lee, Ching-Hao Mao, Yu-Jie Chen, Yi-Hsun Wang, Jerome Yeh, Tsu-Han Chen (TW).
- В.Д. Погребенник, П.Т. Хромчак, Національний університет
Львівська політехніка
,кафедра захисту інформації, «Розроблення моделі системи виявлення центрів управління ботнетами»,url: http://archive.nbuv.gov.ua/portal/natural/Vnulp/Avtomatyka/2009_639/16.pdf - Wernhuar Tarng, Cheng-Kang Chou and Kuo-Liang Ou, A P2P botnet virus detection system based on data-mining algorithms, International Journal of Computer Science & Information Technology (IJCSIT) Vol 4, No 5, October 2012.
