Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Actuality of the theme
- 2. Objectives and tasks of the research
- 3. Construction of working curricula
- 4. Description of the current method of load distribution
- 5. Description of alternative methods of load distribution
- 5.1 Description of the first method of load balancing
- 5.2 Description of the second method of load balancing
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
In recent years, the process of automation touched not only the industrial, technical and technological areas of human activity, but also the information space, in particular libraries, museums, information centers. Automation is most affected by the information sector, because information needs a quick search, selection and storage, and also to provide access to it.
The main resource of any university – scientific-pedagogical workers (SPW). They directly support the implementation of the educational process, do most of daunting job. Level of training, reputation and competitiveness of higher education institutions, in turn, depend on the composition, condition and size of scientific and pedagogical workers, the effectiveness of their work [1].
1. Actuality of the theme
Nowadays, there are many practical and theoretical issues related to the topic of load distribution. The first question – to determine the correct number of researchers and scientific and pedagogical workers. Insufficient number leads to additional burden on teachers, which makes it difficult to perform basic work and reduces the quality of training of specialists, and the excess number of teachers leads to additional costs of universities, with limited financing of state budget results in a reduction spending on other items. Based on this it can be argued that the management of number scientific-pedagogical workers is one of the important problems of any university [1].
Thus, the introduction of alternative methods of calculating staffing will almost completely free from routine procedures related to the distribution of the load on faculties. This, in turn, significantly increases the effectiveness of training and methodological department of the university, improving the time and quality performance of the employees of the department. Also, it is possible the creation of other developers of new versions of this program.
2. Objectives and tasks of the research
The objective of research – make analyze the methods of distribution the staffing table between the departments of the University.
The main objectives of the research:
- Analysis of the construction of working curricula;
- Identifying weaknesses in the current system of distribution;
- The study of alternative methods of load distribution;
- Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of alternative methods.
3. Construction of working curricula
Working curriculum – is the main regulatory document direction (specialty) for the next academic year. Working curriculum is made on the basis of the curriculum for courses and includes a schedule of the learning process, the plan of the educational process by semester, which determines the list, the scope and sequence of disciplines, forms of training sessions and their volumes, the form of the current and total control, state certification, types of tasks for independent work of students [6].
4. Description of the current method of load distribution
The existing distribution system states of the faculty based on the calculation of workload departments and calculate the average load of a teacher of the University and ignores the fact that states institution planned by the Ministry of Education and Science and depend primarily on the total number of students, not the amount of workload.
Workload of the department for the academic year is determined by its assigned academic disciplines, practitioners, the types of tests and the final state certification of other types of training activities according to the operational curriculum of the speciality directions of preparation and higher education [9].
5. Description of alternative methods of load distribution
5.1 Description of the first method of load balancing
The aim of this method is to examine the process of automating the distribution of the load on faculties of the University by formalizing the approach to the creation and use of programmable automation equipment.
The basis of the method of distribution of states has the following characteristics:
- State of SPW (funding remuneration);
- The number of students on training courses and professions;
- The curriculum, the amount of academic disciplines, training, undergraduate and industrial practices, state exams.
Distribution of the state SPW of University (Ш) is carried out in four stages.
Stage 1. State University is divided into parts for the educational process (Шу) and the entrance examinations, the management graduate students, doctoral students, trainees (Ша) (pict. 1).
(рис. 1).Шу determined according to the document "Standards of time for calculation and accounting of educational work of teachers of high schools" (Order of Ministry of Education of Ukraine № 450) and distributed to the departments centrally.
Stage 2. Distribution of State (Шу) between the directions of preparation.
State of the i-th direction of preparation (Шу) is made in proportion to the total given contingent Nci students of this direction (pict. 1).
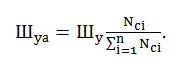
Picture 1 – Formula of calculation the state of direction of preparation
Nді, Nзі – accordingly contingents full-time students and part-time forms of education in each direction.
Stage 3. Distribution of staff across disciplines and types of sessions on of specific directions the curriculum.
Part of teachers, leading learning in a particular direction, provide training for the j-th discipline (or type of employment) in the k-th semester is defined by the relation (pict. 2).
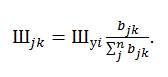
Picture 2 – Formula of calculation the state of the discipline
Stage 4. Distribution of state SPW between the departments of the university.
State staff of the department to ensure that the learning process is formed as the sum of the parts, disciplines and kinds of session, which are assigned to the department in all directions of training (pict. 3).
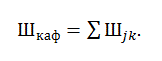
Picture 3 – Formula of calculation the state between departments
After considering this method of distribution state PPP can be concluded that the introduction of this method of load distribution will get rid of the factors that promote the emergence of the deficiencies identified [1].
5.2 Description of the second method of load balancing
The method is based on the number of hours calculated for each subject in the curriculum. According to the specifications for each direction there is a norm of the number of students per teacher. Also, for each stream of students each semester there is a norm of teaching hours. In combination with a known amount of hours for each discipline, it allows to develop a method of load distribution [10].
Conclusion
Were examined existing methods allocation staffing table between departments of the university.
Based on the decision of the shortcomings have been proposed methods of load distribution, based primarily on the total number of students rather than on the amount of work load. After analysis of these methods revealed the following benefits:
- methods stimulates the teaching of many credit courses in the same semester because this, without affecting the value of PVS, reduces the workload;
- allocation algorithm, which is based calculation was dependent on the ratio of hours of classroom and self-study student;
- unprofitable artificial formation of small streams and academic formation of incomplete groups [9].
After analyzing we can conclude that the introduction of methods of calculating staffing, training part will have most efficiency by reducing the time spent on routine operations calculating staffing table.
References
- Ломоносов О.В. Методические положения управления численностью научно-педагогических сотрудников высших учебных заведений / О.В. Ломоносов // Научно-методический журнал. - Вып. 7. Экономические науки. – Николаев: изд-во им. Петра Могилы, 2010. – 56-60 с.
- Васильева Т. Оптимальное распределение нагрузки на преподавателя [Электронный ресурс] / Т. Васильева. – Режим доступа: http://www.rusnauka.com/30_NIEK_2011...
- Васильев В. Механизм распределения штатов между кафедрами университета [Электронный ресурс] / В. Васильев. – Режим доступа: http://www.ict.edu.ru/vconf...
- Ломоносов О.В. Зависимость между основными трудовыми показателями высших учебных заведений III-IV уровней аккредитации / О.В. Ломоносов // Научно-методический журнал. – Вып. 86. Экономические науки. – Николаев: Изд-во им. Петра Могилы, 2008. – 117-124 с.
- Василенко А.Ю. Разработка веб-сервиса мониторинга успеваемости студентов [Электронный ресурс] / А.Ю. Василенко. – Режим доступа: http://www.masters.donntu.ru/2009...
- Структура учебных рабочих планов [Электронный ресурс] / Московский автомобильно-дорожный технический университет. – Режим доступа: http://www.madi.ru/study...
- Андреев В.В. Рейтинговая система учета успешности студентов/ В.В. Андреев, Н.В. Герова, М.И. Ведерникова и др. – М.: Бином, 2009. – 89 с.
- Сластенин В. Педагогика теории формирования содержания образования [Электронный ресурс] / В. Сластенин. – Режим доступа: http://www.university.kherson.ua/Information...
- Концепция распределения штатов профессорско-преподавательского состава // Научно-методический журнал. – Л.: Национальный университет «Львовская политехника». – 124-127 с.
- Евдокимов А.В. Система распределения учебной нагрузки университета / А.В. Евдокимов // Современная информационная Украина: информатика, экономика, философия: материалы докладов конференции, 26 апреля 2012 года, Донецк, 2012. – 316 с.
Important note
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2013. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
