Abstract
Content
- Foreword
- 1. Topic relevance
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study
- 3. Existing models and methods review
- 4. The mathematical formulation of the problem
- 5. The study models based on Markov chains
- Findings
- List of sources
Foreword
In a market economy, the company is planning its own activities and determine the prospects of development. Independently planned measure, among others, was the profit.
Profit - is the final financial result and the main purpose of business and industrial activity, characterized by the efficiency of the businesses that are in the process of functioning tend to get the most profit through the production and sale of demand in the market of goods and services. [1]
Making a profit, and its capacity is the economic condition of the successful functioning of enterprises, industries and the economy as a whole. Amount of profits derived by an enterprise, due to the volume of sales of the product, its quality and competitiveness in domestic and international markets, the range, the level of costs and inflationary pressures which inevitably accompanied by the formation of market relations.
One of the main objectives of profit maximizing is the mastery of modern techniques of effective profit management, including its planning, creation and distribution of the company in the process, which involves the construction of an enterprise of the systems that support management, knowledge of the basic mechanisms of formation of profit, the use of effective methods of analysis, planning and distribution. [1]
Profit as a final financial results of the Company represents the difference between total revenue and the cost of production and sales, taking into account losses from various business transactions.
1. Topic relevance
Currently, trade is one of the largest sectors of the national economies of most developed countries. The activities of trading companies, especially large ones, is vulnerable to a number of factors and covers a wide range of issues of financial and economic, organizational, technological, and social issues.
The financial management of the enterprise is regarded as one of the important functions of the overall management system of enterprises.
For the enterprise question of formation and regulation of the pricing policy plays a huge role. On how the pricing is carried out in the enterprise, it depends for its profits. In addition, the existing conditions of a market economy now the price has become a significant factor in the competition.
In recent years, various aspects of financial management, taking into account the characteristics of the transformation period of the Russian economy were reflected in the fundamental works of scholars and specialists, as M.I. Bakanov, I.T. Balabanov, I.A. Blank, S. Bolshakov, A. Grachev, A.G. Karatuev, V.V. Kovalev, M.N. Kreinina, L.N. Pavlova, V.N. Female, N.F. Samsonov, E.S. Stoyanova, G. Hotinskaya, A.D. Sheremet and others. It should be noted as a number of works in this area of ??foreign scientists and specialists, in particular Kolassa Berner, J. and L. Brigham Gapenski, J. Van Horn, A. Marengo, M. Scott, D.P. Khan, etc.
Problems of financial management are devoted in works of M. Abryutina, L.V. Dontsovoj and N.A. Stanchev, O. Diagel, A.N. Kovalev and V.P. Privalov, E.A. Markoryana and G.P. Gerasimenko, G. Sawicki, G. Sokolova, etc. [2]
2. The purpose and objectives of the study
The aim is to increase the efficiency of financial activity through the use of modern methods and models for optimization and control.
To address this goal the following objectives:
- Analysis of the methods of optimization and regulation of financial activity;
- Study optimization models and regulation of financial activity;
- Selection and justification of the method optimization and regulation of financial activity;
- Developing a model of optimization and control of financial activity;
- Check the adequacy of the model;
- Planning and conducting experimental studies to determine the effective parameters of the model;
- Development of recommendations on the basis of experimental studies.
The object of study: improving the efficiency of the optimized criteria.
3. Existing models and methods review
Before the administration of the enterprise task - to choose such methods of accounting, which allows the most appropriate to calculate financial results and legally, through regulation of earnings to the extent permitted by the legislation.
It can identify the following specific methods of varying the financial results: [3]
- Varying the abroad the norm attributing of an asset to the basic means.
- In accordance with the decisions of the government carried out a periodic revaluation of fixed assets.
- Enterprises have the right to apply accelerated depreciation of the active part of fixed production assets.
- Regulations on Accounting and Reporting allows the use of different assessment methods of inventory (FIFO, LIFO, average prices).
and others.
It is necessary to distinguish between two kinds of prediction: the expert and formalized. [4]
Expert forecast future values ??implies the formation of an expert, that is, person who possesses a deep knowledge in a particular area.
Expert forecast is used when the object of forecasting either too simple, or, on the contrary, are so complex that it is analytically consider the impact of external factors is impossible.
These methods include the following methods:
- The method of expert assessments
- Method of historical analogies
- Method of foresight on the model
- Fuzzy logic
- Scenario modeling "what - if"
A formal prediction - this prediction on the basis of a mathematical model, which is the process of catching patterns, at its output is the future values ??of the process.
The goal of regression analysis is to determine the relationship between the original variable and many external factors (covariates). When using linear regression models predicting the result can be obtained more quickly than with other models. The disadvantage of non-linear regression models is the difficulty in determining the kind of functional dependence, as well as the complexity of the definition of the model parameters.
Autoregressive model is based on an assumption that the process value is linearly dependent on a number of previous values ??of the same process. Important advantages of this class of models is their simplicity and transparency of the simulation. The disadvantages are: a large number of model parameters, the identification of which is ambiguous and resource-intensive.
Currently, the most popular among structural models is based on neural networks, composed of neurons. With the help of neural networks is possible to model the nonlinear dependence of the future values ??of the time series and its actual values ??and the values ??of the external factors. The main advantage of neural network models is the non-linearity, ie ability to establish nonlinear relationships between the future and the actual processes. At the same drawbacks are the lack of transparency of the modeling complexity of the architecture of choice.
Exponential smoothing model is used to model the financial and economic processes. Advantages: Simplicity and consistency of their analysis and design. The disadvantage is the lack of flexibility.
Forecasting models based on Markov chains suggest that the future state of the process depends only on its current state and is independent of the previous ones. The simplicity and uniformity of the analysis and design models are based on the merits of Markov chains. The disadvantage is the lack of process modeling with long memory.
Classification and regression trees are another popular structural model for time series prediction. Structural models CART developed to simulate the processes, which are influenced by external factors as continuous and categorical. Advantages: scalability, which is possible due to fast processing of very large volumes of data, the speed and the uniqueness of the learning process of the tree. Disadvantages include the ambiguity of the algorithm for constructing the tree structure, the complexity of the question of when to stop further branching.
Addition to the above classes of forecasting models, there are less common models and forecasting techniques. Their main drawback is the lack of methodological basis, ie not provide details of how models and to measure their parameters.
Main advantages and disadvantages of the models and methods are listed below.
| The model and method | Accomplishments | Limitations |
| Regression models and methods | plainness
plasticity transparency of modeling uniformity of the analysis and design | the difficulty of determining the functional dependence
depending on the complexity of finding the coefficients lack of modeling of nonlinear processes (for non-linear regression) |
| Autoregressive models and methods | plainness
transparency of modeling uniformity of the analysis and design many count of examples | labor and resource intensive model identification
the impossibility of modeling nonlinearities low adaptability |
| Models and methods of exponential smoothing | modeling plainness
uniformity of the analysis and design | insufficient plasticity
narrow the applicability of the models |
| Neural network models and methods | nonlinear models
scalability, high adaptability uniformity analysis and design many examples of | lack of transparency
complexity of choice architecture stringent requirements for the training set the difficulty of choosing a learning algorithm resource intensity of the learning process |
| Models and methods based on Markov chains | ease of modeling
uniformity analysis and design | impossibility of modeling processes with long memory
narrow the applicability of the models |
| Models and methods on the basis of classification and regression trees | scalability
speed and ease of learning opportunity to take into account the categorical variables | ambiguity algorithm for constructing a tree
complexity of the issue stop |
4. The mathematical formulation of the problem
The mathematical formulation of the problem of forecasting the financial activities of the enterprise can be formulated as follows:
Cost of goods S is the sum of the cost of raw materials Ss, the cost of manufacture of goods Si, overheads Sr.
Profit (P) is the product of the price (P) on sales (Q) minus costs (Z):
Thus, the objective function is as follows:
П=F(P, Q, Z)
where P, Q, Z - criterias.
Our goal - to increase profits, respectively:
П → max
We define the limits for the criteria:
P>0, P → max
Q>0, Q → max
Z>0, Z → min
As sales (Q) and the costs (Z), we can not vary, it is necessary to determine the price components (P).
Price (P) is defined as the sum of the cost of the goods (S) and profit per unit П0:
P = S + П0
Since the problem of predicting financial activity is relevant and up to the end of the unexplored, it is proposed to use a forecasting model based on Markov chains.
5. The study models based on Markov chains
Such models suggest that the future state of the process depends only on the current state and is independent of the previous. In connection with this process, the simulated Markov chains must relate to processes with short memory. [5]
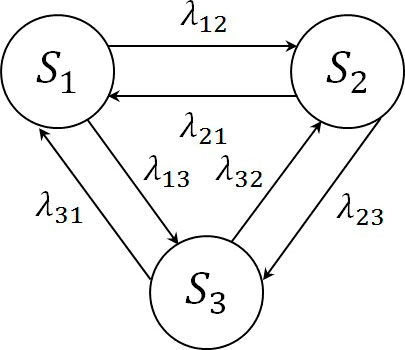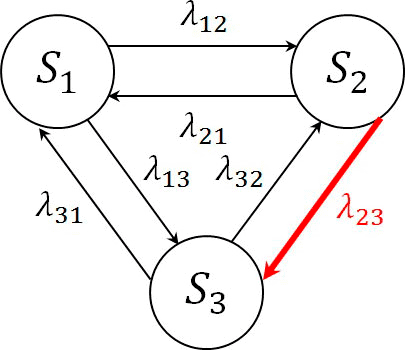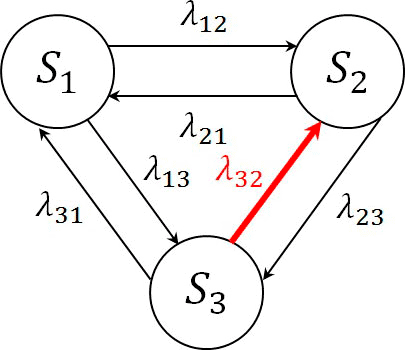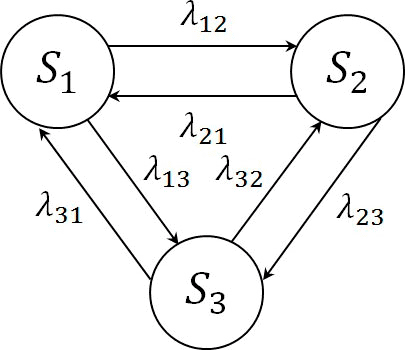
Example of a Markov chain for the process which has three states (animation, 8 frames, 134 KB, 6 cycles)
At figure S1, S2, S3, - the state of the process; λ12 - the probability of transition from state S1 in the state S2, λ23 - the probability of transition from state S2 in the state S3, etc. In the construction of a Markov chain is defined by a set of states and transition probabilities. If the current state of the Si, then as the future state of the process is chosen such a state Si, the probability of transition in which (λij) maximum.
The sequence of states S0, S1, S2, ..., Sk can be regarded as a sequence of random events. The initial state of S0 can be given in advance or randomly.
The probabilities of the states of the Markov chain is the probability of λj(k) that after the k-th step (and before the (k +1)-th), the system S will be able to Si (i=1, 2, ..., n).
The initial probability distribution of the Markov chain is called the probability distribution of the states at the beginning of the process:
λ1(0), λ2(0), ..., λi(0), ..., λn(0)
Since the system can be in one of n states, then for each time t must be set n2 of the transition probabilities Pij, which is conveniently represented by the following matrix (called transition or transition matrix):
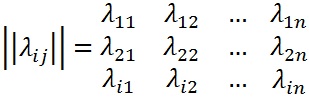
where λij - the probability of transition in one step from the state Si in the state Sj, λii - possibility of a delay system in the state Si.
The transition probabilities of a homogeneous Markov chain λij form a square matrix of size n*n. Note some of its features:
- Each row in the selected state characterizes the system and its elements represent the probabilities of all possible transitions by one step from the selected state, including a transition to itself.
- Elements columns show the probabilities of all possible transitions of the system in one step to a given state (in other words, the line refers to the probability of transition from the state, the column - in the state).
- Sum of the probabilities of each row is equal to one, as the transitions form a complete group of mutually exclusive events:
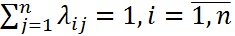
- Along the main diagonal of the matrix of transition probabilities are probabilities λii that the system will come from the state Si, and remain in it.
Thus, the structure of the Markov chain and the transition probabilities of states determine the relationship between the future value of the process and its current value.
Advantage of the model based on Markov chains are simplicity and uniformity of analysis and design. The disadvantage of these models is the lack of process modeling with long memory.
Findings
Predicting financial activity with the use of Markov chains is an important task for the modern market system. The proposed method is effective. Completed statement of the problem, which will decide the most goals. The developed model will improve the effectiveness of forecasting financial activity.
In writing this essay master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: winter in 2013-2014. Full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after that date.
List of sources
- Бухгалтерский учёт финансовых результатов [электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.buhucheta.net
- Методы и модели оптимизации ценовой и ассортиментной политики торгового предприятия [электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.dissercat.com
- Басовский Л.Е. Прогнозирование и планирование в условиях рынка: Учебное пособие. – М.: ИНФРА-М, 2001 г.
- Свободная энциклопедия «Википедия» – Прогнозирование [электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: ru.wikipedia.org/
- Свободная энциклопедия «Википедия» – Цепь Маркова [электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: ru.wikipedia.org/
- Алексеева М.М. Планирование деятельности фирмы: Учебн. - метод. Пособие. - М.: Финансы и статистика, 2000. - 248 с.
- Сидельников Ю.В. «Системный анализ технологии прогнозирования». – М.: Изд-во МАИ, 2007.
- Кун Т. Структура научных революций. – М.: ООО «Издательство АСТ», 2003.
- Сидельников Ю.В., Салтыков С.А. Процедура установления соответствия между задачей и методом. // Экономические стратегии, № 7, 2008. – с. 102–109. (в электронном виде - faqproject.ru)
