Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. A multivariate optimization of the parameters of the trading system invariant to changes in the market environment
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
In the world financial system foreign exchange markets play significant role. They serve as basis for exchange rates, which, in turn, affect the internal and external economic policy of countries. Stock jobbing is a process that requires human knowledge of many sciences: probability theory, mathematical statistics, game theory, economics, etc. The market takes into account everything. The graph shows processes that span the globe.
It is multidimensional, chaotic, not a stationary process. The key point of decision-making in operations in the foreign exchange market is the filtration of market situation and its formalisation, based on these data the decision will be taken about buying and selling of currencies.
1. Theme urgency
One of the solutions of this problem would be the usage of the intellectual automated trading systems or decision support systems, which, like any machine, are not subjects to fatigue and stress. With the development of hardware and the adaptation of mathematical methods in the near future one should expect attraction of large-scale economic and mathematical methods in trading on the foreign exchange and stock markets [7].
Peculiarity of this work is a stress on creation of a clear rules of action for the current value in order to develop a decision support system, and creating, based on these rules, a mechanical trading system for the foreign exchange market. The paper considers the theory of filtration techniques such as wavelet transform, as well as methods of creation of decision support systems, which are devoid of subjective factors when trading at the financial markets, and can act as decision support systems [8].
2. Goal and tasks of the research
Objective: Analysis of methods of filtration dynamics of exchange rates, creation of mechanical trading systems based on indicated methods.
The main research tasks of the study:
- Investigate methods of filtration of currency rates.
- Assessment of ways of reducing hardware costs by Moore state machine coding.
- To analyze the process of making decisions in the foreign exchange market.
- Create a system of decision-making based on selected methods.
- Make a set of criteria for evaluation of mechanical trading systems.
- Develop recommendations for the use of the market system and the optimal characteristics of a given system.
Research object: graph of currency pair EUR/USD in 2011.
Research subject: methods of filtration dynamics of market rates, as well as the possibility of their integration into decision support system for improving the efficiency, adequacy and accuracy of decision making when trading at the currency markets.
The practical significance of the results of the study is that the method of predicting foreign exchange markets is proposed and the set of models and methods of decision-making is developed, which can improve efficiency and reduce costs for decision-making in any industrial and economic system, the financial results of which is associated with changes of the interbank exchange rates. The theoretical and methodological basis of the study were the works of local and foreign scientists concerning the development and application of digital filters in the currency markets, also rules for constructing automated trading robots have been analysed and selected. Solution of the problems set have been carried out using a systematic approach in the study of relationships, methods of structural-logical, economic and statistical analysis. The implementation of the tasks carried out has been performed in the MATLAB 7.12 environment.
3. A multivariate optimization of the parameters of the trading system invariat to changes in the market environment
Algorithm for formation of control trading signals based on the constructed indicator is as follows:
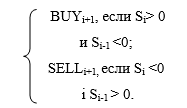
Graphic visualisation of the given indicator is the line, let us denote it – S. Its actual value – filtered value increment between successive levels of the time series.
If the indicator line crosses the zero point upward ("pure" value increment is positive), the operation of the currency purchase is made during the next price period. If the indicator line crosses the zero point down, the deal to sell currency is performed during the next price period.

Figure 1. The scheme of decision making when trading in the foreign exchange market
This is a turnover system and it implies a constant mechanical making of deals. Trading rules are programmed into mechanical trading system, and allow to analyse the current market situation 24/7 by dozens of currency pairs and avoid the "human factor" [3]. The human factor refers to fatigue during prolonged market analysis, consideration of the subjective factors that affect the quality of the analysis and the results of the trading system.
After analysing the data business decisions to buy or sell currencies are generated, after that this system stops functioning, and the produced signal is the result of a decision support system work [6]. If there is an analysis of test samples, the signal is compared to the standard, based on this comparison and potential profitability of transactions, conclusions on the effectiveness of the system as a whole are made.
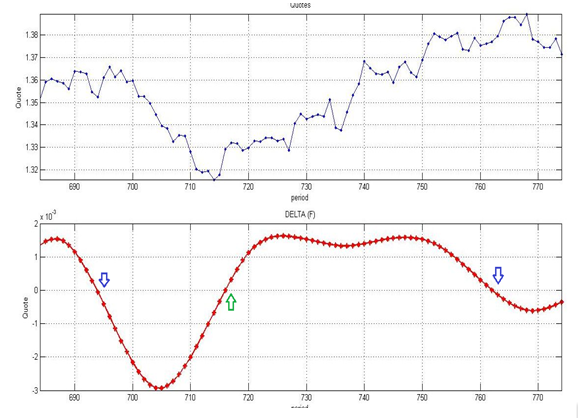
Figure 2. Graphical representation of wavelet-filter price increase.
After analysing the input data the decision support system produces one of the two signals (Table 1).
Table 1
The signals produced by the designed system
|
№ |
Signal |
The value of the signal |
|
1 |
-1 |
Open positions down (Sell currencies) |
|
2 |
1 |
Opening up position (buy currency) |
Table 2
Performance of trading system based on the moving of the average crossing
|
Index |
ТS-МА |
|
k1 |
1,17 |
|
k2 |
0,5 |
|
PF |
0,585 |
|
Profit |
1600 |
|
Loss |
1336 |
|
Кpr |
8 |
|
Кlos |
8 |
|
Кsum |
16 |
|
Кsh |
0,3 |
Analysing these results we can conclude that building of a mechanical trading system with these options is very risky and hardly will profit, and perhaps by changing market conditions, even brings losses.
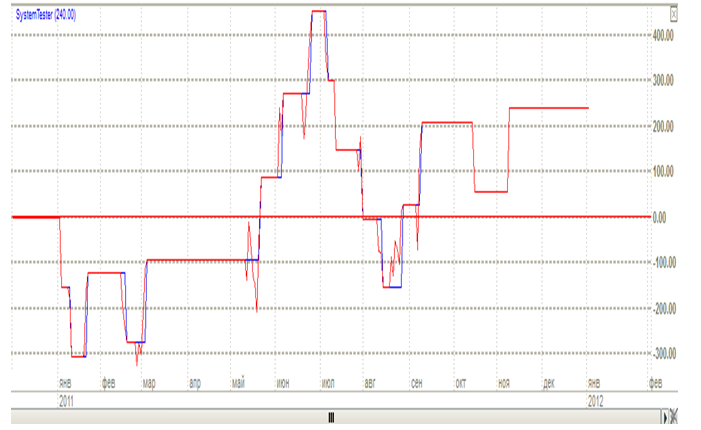
Figure 3. Changing the status of a deposit using the trading system moving average.
It should be noted that excessive optimisation of the parameters of moving averages during a trading period of time is a negative factor for its further use and a change in market conditions increase the risk of market trade and will not meet the test of general parameters of a mechanical trading system.
Sharpe ratio was 0.3 – a very low value; analysing the figure we can say that in the built system for 1 dollar venture CAR falls 0.3 dollar reward for risk. Use of this system is not recommended because it can cause damage to the investor.
Table 3
Performance of trading systems based on wavelet filtering
|
Index |
ТS-1 |
|
k1 |
3,5114 |
|
k2 |
94,6% |
|
PF |
3,3216 |
|
Profit |
12290 |
|
Loss |
200 |
|
Кpr |
35 |
|
Кl |
2 |
|
Кsum |
37 |
|
Rsh |
5,91 |
Analysing these results we can conclude that the built mechanical trading systems have acceptable quality for use in real trading. Total income earned while working on TS-1 was 12 290 dollars
The ratio of the number of profitable trades to their total for the base period was 94.6%. Only 2 of the 37 contracts were unprofitable. Profit factor for the resulting system was 3.3216 when working on the system with a constant fixed at $ 100 per lot. Risk calculated as RMS gains for these systems was 2.18% according to two strategies.
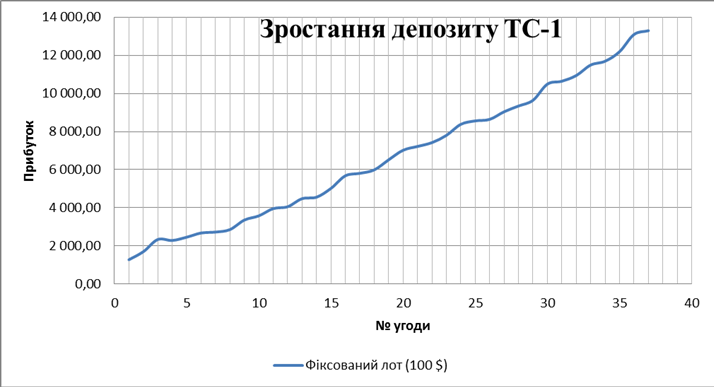
Figure. 4 Changing of the deposit using a conservative method of management.
Sharpe ratio was 5.91 – a high value; analysing the figure we can say that in the systems used $ 1 CAR falls risk 5.91 dollar reward for risk.
Thus, we can conclude that wavelet algorithms are well suited to reduce the noisiness of data and highlight the main trends. Management of data compression is made by changing only one parameter, which also can have a real counterpart. The main difficulty lies in the choice of the value of the level of decomposition and selection of wavelet functions, but experience shows that it should start with l, so that to change the standard deviation of the original data.
Determination of the maximum yield of the system allows obtaining benchmark market more suitable for the formal evaluation. Effectiveness of decision support systems is usually expressed as a percentage per annum obtained by testing on real rates of several markets.
Conclusions
The key point of decision-making in operations in the foreign exchange market is the filtration of market situation and its formalisation; on the basis of these data the decision will be taken about buying and selling of currencies. Analysis of existing literature sources and created trading system demonstrated that the method of wavelet decomposition is a highly effective means for filtering financial time series. In contrast to the filtration method of pricing which is based on moving averages, a method based on wavelet filtering time series has no lag on price chart and is characterised by minimal variation, bigger sensitivity, generates a greater number of control signals.
During this final work the following results have been achieved:
- Using a systematic approach decision-making process in the foreign exchange market was analyzed, an example of a decision support system for trading the currency markets is provided.
- Digital filtering techniques of market data methods wavelet decomposition were analysed. Based on oscillatory models of decision making recommendations on the application of this method in the construction of a mechanical trading system were made.
- The criteria of evaluation of the performance of automated trading systems were reviewed. The features of evaluating the effectiveness of decision-making in the interbank foreign exchange market were studied, which led to the conclusion that there is always a system that shows the best financial result for the test run results and is the most effective.
- Mechanical trading system for dealing of bank-based OLAP-processing for fast acquisition, analysis, data processing and decision to buy or sell currencies in real time was established. In particular, the analysis of financial time series based on wavelet transformation was made.
Testing the model on the example of data exchange on FOREX market led to the conclusion that its performance grew over the existing brokerage houses. Thus, the simulation results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method. The calculated performance of constructed systems were as follows: maximum profit with minimal risk showed trading system based on the method of deposit reinvestment capital. The system showed the yield at 1229% per annum at a conservative method of management. These figures are far bigger than the current offer in the largest banks in the country which attract foreign currency household deposits, plus to all this, the trader is free to manage their own funds daily, which will further increase the profitability of this activity.
Analysis of decision making in a system of inter-bank foreign exchange markets led to the conclusion that the reserve increase efficiency of decision making in the interbank foreign exchange transactions is to improve the quality of prediction of foreign exchange markets.
The possibility of reducing the noise component and fluctuations in the ranks, extracting the most relevant features for prediction. Based on this study it can be concluded about the effectiveness of wavelet analysis as a mathematical apparatus for processing financial data. Wavelet analysis allows information to prepare a prediction based on neural networks. Of course, the possibility of using wavelets are not limited to tasks. Statistical analysis, suppression of redundant information, cryptography and steganography, multimedia information processing – all are only a brief summary of the areas where the wavelets are the most active application.
When writing this master thesis have not been completed yet. Final completion: December 2013. Full text of the materials can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after that date.
References
- Петерс Э. Фрактальный анализ финансовых рынков: применение теории хаоса в инвестициях и экономике /Э. Петерс: Пер. с англ. – М.: Интернет-трейдинг, 2004. – 304 с.
- Матвійчук А. В. Економічні ризики в інвестиційній діяльності /А.В. Матвійчук. – Вінниця: УНІВЕРСУМ-Вінниця, 2005. – 205 с.
- Поляков П. И., Архипова С. В. Прогнозирование цен финансовых инструментов в условиях неопределенности / П.И. Поляков // Бизнес Информ. – 1999. – №13-14. – С. 51-53.
- Філіпенко А. С. Прогнозування валютних курсів / А.С. Філіпенко// Фінанси України.– 1996. – № 5. – С. 48-50.
- Игнаточкин В. Спектральный анализ валютных курсов или еще раз о фрак талах/В.Игнаточкин // Валютный спекулянт. – 2000. - №8. – С. 65-69.
- Колмогоров А.Н. Интерполяция и экстраполяция стационарных случайных последовательностей /А.Н. Колмогоров// Изв. АН СССР. Сер. мат. наук. – 1941. – №5. – С. 23-27.
- Приставка А.Ф. Статистична обробка даних/ А.Ф. Приставка.– К.: Нова, 2003. – 456 с.
- Блаттер К. Вейвлет-анализ. Основые теории / К. Блаттер. — М.: Техно-сфера, 2006. — 272 с.
- Добеши И. Десять лекций по вейвлетам: Пер. с англ. / И. Добеши. —Ижевск: НИЦ Регулярная и хаотическая динамика, 2001. — 464 с.
- Смоленцев Н. К. Основы теории вейвлетов. Вейвлеты в MATLAB /Н. К. Смоленцев. — М.: ДМК пресс, 2008. — 448 с.
- Матвійчук А. В. Економічні ризики в інвестиційній діяльності/А.В. Матвійчук. – Вінниця: УНІВЕРСУМ-Вінниця, 2005. – 205 с.
- Філіпенко А. С. Прогнозування валютних курсів/А.С. Філіпенко// Фінанси України.– 1996. – № 5. – С. 48-50.
- Шарапов О. Д., Дербенцев В. Д., Семьонов Д. Є. Економічна кібернетика / О.Д. Шарапов, В.Д. Дербенцев, Д.Є. Семьонов: Навч. посібник. – К.: КНЕУ, 2005. – 231 с.
- Смирнов А. В., Гизатулин А. М. Повышение эффективности управления рисками инвестиционных биржевых проектов/А.В. Смирнов,А.М. Гизатулин // Менеджер: Вісник Донецької державної академії управління. Науковий журнал. Випуск 3. – Донецьк: Дон ДАУ, 2003. – С. 140-143.
- Кан Н. Технический анализ/Н.Кан – Спб.: Питер, 2005. – 282 с.
- Мэрфи Д.Д. Визуальный инвестор. Как определить тренды/Д.Д. Мєрфи – М.: Диаграмма, 2004. – 326 с.
- Вайн С. Инвестиции и трейдинг: формирование индивидуального подхода к принятию инвестиционных решений/С.Вайн – М.: Альпина Бизнес Бук, 2006. – 534 с.
- Ковальчук К. Ф. Интеллектуальная поддержка принятия экономических решений/К.Ф. Ковальчук – Донецк: ИЭП НАН Украины, 1996. – 224 с.
- Фабоцци Ф. Управление инвестициями/Ф. Фабоцци: Пер. с англ. – М.: ИНФРА-М, 2000. – 932 с.
- Ситнік В. Ф. Системи підтримки прийняття рішень/ В. Ф. Ситнік. – К.: Техніка, 1995. – 162 с.
- Пересада А. А., Майорова Т. В. Управління банківськими інвестиціями/ А. А. Пересада,Т. В. Майорова.– К.: КНЕУ, 2005. – 387 с.
- Аль-Гулі Абед Саиф. Математичні моделі прогнозування динамічних рядів у дилінгових інформаційних системах: Автореф. Дис... канд. техн. наук: 05.13.06 / Харківський нац. ун-т радіоелектроніки. – Х., 2005. – 20 с.
- Найман Э. Л. Малая энциклопедия трейдера/ Э. Л. Найман. – М.: Альпина Бизнес Бук, 2005. – 403 с.
- Сафин В.И. Торговая система трейдера: фактор успеха/ В.И. Сафин. – Спб.: Питер, 2005. – 240 с.
- Абрамов А.В. Новое в финансовой индустрии: информатизация банковских технологий/ А.В. Абрамов. — СПБ: Питер, 1997 г.
- Гайкович Ю.В, Першин А.С. Безопасность электронных банковских систем/ Ю.В Гайкович, А.С Першин. — М: Единая Европа, 1994 г.
- Демин В.С. Автоматизированные банковские системы/ В.С.Демин. — М: Менатеп-Информ, 1997 г.
- Крысин В.А. Безопасность предпринимательской деятельности/ В.А. Крысин. — М:Финансы и статистика, 1996 г.
- Линьков И.И. Информационные подразделения в коммерческих структурах/ И.И. Линьков: как выжить и преуспеть. — М: НИТ, 2002 г.
- Титоренко Г.А. и др. Компьютеризация банковской деятельности/ Г.А. Титоренко. — М: Финстатинформ,2002 г.
- Міньков В. І. Деякі особливості розвитку фондового ринку України/ В. І. Міньков // Фінанси України. – 2005. – №12. – С. 104-114.
- Хьержик Д. Модель, цена и время/ Д. Хьержик. – М.: ИК «Аналитика», 2000. – 320 с.
- Андерсон Т. Статистический анализ временных рядов/ Т Андерсон. – М.: Мир, 1976. – 756 с.
- Сорос Дж. Алхимия финансов/ Дж Сорос. – М.: ИНФРА-М, 1998. – 436 с.
- Якимкин В. Н. Финансовый дилинг/ В. Н. Якимкин. Технический анализ. – М.: Омега-Л, 2006. – 480 с.
