Valentina Levitasova
Faculty of economics and management
Department of economic cybernetics
Speciality Economic cybernetics
Stochastic model of optimal investment management
Scientific adviser: Ph.D., Olga Dmitrieva
Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Overview of research and development
- 4. Formal description of an existing optimal investment management stochastic model with random return and transaction costs
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The research of investment portfolio management processes in financial assets is important, first of all, from the standpoint of solving the general investment problem. Matter how effectively adjusted the portfolio investment mechanism, because it largely determines the functioning of the whole economic system.
Master's work is dedicated to the problem of choosing effective options for portfolio management, that allow to determine the best strategies for investing in securities to generate income.
In the scientific literature, these problems are addressed in the framework of portfolio theory, the basic concepts that were developed in the second half of the XX century.To address the issues related to the portfolio securities management in the modern economic literature has been accumulated a large methodological potential. This problem involved such foreign and domestic authors: W. Sharp, G. Alexander, L. Dzh. Gitman, R. Vince, H. Markowitz, M. Miller, V. Faltsman, V. Kitov, V. Dementieva, S. Horosheva, B. Alehin, M.E. Kolomina, A. Pervozvansky, M. Alekseev, Ya. Mirkin, A. Fadeev etc.
1. Theme urgency
In modern conditions with nonstationarity, stochasticity, and crisis phenomena of different nature traditional portfolio theory and the classical methods of financial mathematics, aimed at optimizing investment portfolio, are inadequate. So the question of diagramming investment management, with all features of modern environment and limitations of existing models, is still relevant.
The urgency of this work is due to a strong interest to the topic of investment management in modern science, on the one hand, and its insufficient development, on the other hand. Consideration of issues related to this subject is both theoretical and practical significance.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The purpose of the master's work is development and analysis of stochastic models of optimal investment management, which is built on the portfolio theory principles, but also consider availability of return risky assets stochastic variations and transaction costs associated with the buying and selling operations.
To achieve this goal it is necessary to solve the following problems:
- to explore contemporary approaches to optimal investment management by analyzing general portfolio theory and the main existent investment management models;
- to consider and explore the existent stochastic models of optimal investment management, which are adequate in current variable market conditions;
- to realize programmatically investment management model through evolutionary modeling techniques;
- to analyze the proposed model of optimal investment management.
Research object: portfolio management process.
Research subject: stochastic methods and models of optimal portfolio management.
3. Overview of research and development
Сurrent approaches to optimal investment management were examined. Effective forming of portfolio management strategy is one of the major problem in modern investment theory.
There are various portfolio theories. Some scientists determine the investment portfolio as an aggregate of funds invested in securities [4, 8] . Others divide all investment projects into real investment portfolio and securities portfolio [12, 15] . In this case, the securities portfolio is mainly formed after the determination of the company investment policy and after construction of real investment portfolio.
Portfolio management involves planning, analysis and management structure in order to achieve the investment goal. Сreating a portfolio investor is guided by certain principles [11] .

Figure 1 – Types of portfolio diversification (animation: 3 frames, 5 cycles of repeating, 29,6 kilobytes)
Portfolio diversification process as one of the most effective investment portfolio balancing methods was considered. There are different ways of diversification, which depend on portfolio management strategy (Fig. 1) [13, 14, 18] .
Markowitz model [9, 19] is a two-criteria optimization problem ( return minimization and risk minimization), which shows that an investor can reduce portfolio risk by choosing uncorrelated stocks. This approach involves utilization of a large number of statistical forecasts, and accompanied by a number of errors.
The basis of the CAPM model [5, 6, 9, 20] is necessary risk premium indicator, and market portfolio rate of return is the only factor of the securities market, which is considered in this model. The model is not adapted to the actual market conditions, it does no take into account the possibility of bankruptcy, transaction costs and taxes, it is considered that changes in asset prices do not depend on past price levels.
Dynamic capital management methods, in particular investment management analysis based on optimal f
[7, 16, 17], which allows to determine the optimal amount of investment capital, which should be used in the current account in order to maximize return growth. Shortcomings of this method were identified .
Today, scientists develop models that can remove above shortcomings, therefore, optimal investment management question remains relevant.
4. Formal description of an existing optimal investment management stochastic model with random return and transaction costs
The problem of financial assets optimal allocation was considered. It is assumed that investor can either hold cash or invest in some risky asset with random return, and risky asset value is distributed according to a geometric Brownian motion defined by:
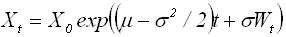
where Xt – risky asset value;
X0 – risky asset initial value;
μ, σ – activity options;
t – time variable;
Wt – standard Brownian motion.
Time benefits are taken to be prescribed by exponential dependence e– βt , where β characterizes present advantages compared with future.
Cash utility is equal to their quantity and risky asset utility with value X is given by the function R(Х) , which reflects the investor unavailability to risk. Concerning the R(Х) function concavity will be provided subject to X> 0.
There are the following expenses during the cash transfers into shares and the other way round:
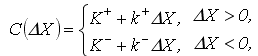
where K+,K− – fixed costs;
k+,k− – proportional costs.
If money is valued only during their use, these variables can be defined as:
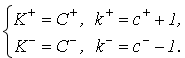
where C+,C− and c+,c− – value of fixed and proportional costs at the market.
Investor's control is a pure impulse control. This is pair set (τi+,ΔXi+) and (τi−,ΔXi−), which determine time moments and additional investment amount in shares, or their sales size. The problem is solved in admissible controls class А(х), because it makes no sense to increase infinitely investments amount Х if the marginal investment utility is reduced and the marginal utility of cash remains constant.
The benefit of an individual investor's strategy is defined as:
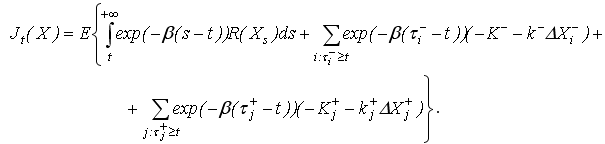
Investor's expected utility function is defined as utility, matching the best of all possible strategies:
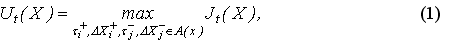
where Ut(X) – expected utility;
Jt(X) – utility from an individual investor's strategy.
Model focuses on the effective construction of optimal control. It is believed that investor can borrow any amount of money, so considered management problem can be generalized to the multiple assets case X1,X2,...,Xn with utility functions R1,R2,...,Rn and different fixed and proportional costs. Therefore, it is necessary to solve independently maximization problem (1) for each of the assets to find the optimal investment strategy.
Necessary conditions on the solutions will be obtained for two sites, both passive and active. It is assumed that the utility function is twice continuously differentiated everywhere except terminal number of points[10].
Conclusion
Modern portfolio theory involves the assumption that investors have the opportunity to distribute wealth among different available investment areas, that is, to form an investment portfolio. There are two parameters, which are criteria for investment decisions evaluation – expected return and standard deviation of return.
Market provide opportunities of selecting the desired combination of expected return and investment risk are limited. Rational investors are always trying to form effective portfolio. Effective portfolio type, that investor choose depends on his individual attitude toward the benefits between risk and expected return.
In considered models the process of creating an optimal portfolio includes following assumptions: the market is efficient, assets are liquid and divisible, there are no taxes, transaction costs and bankruptcy, all investors have the same expectations, can take a loan and provide funds at an interest rate without risk, investors are rational, they try to maximize their utility, return is only a function of risk, changes in asset prices do not depend on past price levels.
Considered optimal investment management model takes into account following shortcomings of modern portfolio theory: stochastic changes of risky assets retutn, transaction costs represented by fixed and proportional contribution.
In future is planned to expand and improve considered stochastic investment management model. This optimization problem has large dimension and relates to the NP-hard class. Therefore to implement it proposed evolutionary modeling methods, in particular genetic algorithm.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2014. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Cadenillas A. Optimal central bank intervention in the foreign exchange market / Abel Cadenillas, Fernando Zapatero // Journal of Economic Theory. – 1999. – № 87. – Р. 218–242.
- Gabriela M. Optimal stochastic intervention control with application to the exchange rate / Mundaca Gabriela, Bernt Oksendal // Journal of Mathematical Economics. – 1998. – № 29. – Р.225– 243.
- Lions P.L. Optimal control of diffusion processes and Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equations / P.L. Lions // Partial Differential Equations. – 1983. – №8. – Р.1101 – 1174.
- Грідасов В.М. Інвестування: Навчальний посібник./В.М. Грідасов, С.В. Кривченко, О.Є. Ісаєва. – К.: Центр навчальної літератури, 2004. – 164 с.
- Боди З. Принципы инвестиций / З. Боди, А. Кейн, А. Маркус. – [4-е изд.]. – Вільямс, 2002. – 984 с. раздел2.4
- Буренин А.Н. Управление портфелем ценных бумаг / А.Н. Буренин – М.: НТО им. акад.. С.И. Вавилова, 2008. – 440 с.
- Винс Р. Математика управления капиталом. Методы анализа риска для трейдеров и портфельных менеджеров; [Пер. с англ.] / Р. Винс – М.: Альпина Паблишер. – 2001. – 400 с.
- Гитман Л. Дж. Основы инвестирования; [пер. с англ.] / Л. Дж. Гитман – М.: Дело. – 1999. –1008 с.
- Довбенко М.В. Современные экономические теории в трудах нобелиантов: Учебное пособие / М.В.Довбенко, Ю.И. Осик – М.: Академія Естествознания, 2011. – 350с.
- Китов В.В. Оптимальное управление инвестициями в актив со случайной доходностью при транзакционных издержках / В.В. Китов // Математическое моделирование. – 2007. – том 19, №5. С. 45 – 58.
- Кох И. А. Элементы современной портфельной теории / И. А. Кох // Экономические науки. – 2009. – №8. С. 267–272.
- Крейнина М.Н. Финансовый менеджмент; [учеб. пособие] / М.Н. Крейнина – М.: «Дело и Сервис». – 2001. – 400 с.
- Липсиц И.В. Экономический анализ реальных инвестиций; [учеб. пособие] / И.В. Липсиц – М.: Экономистъ. – 2004. – 347 с.
- Мойсеєнко І.П. Інвестування: Навчальний посібник / І.П. Мойсеєнко – К.:Знання,2006. –490 с.
- Павлова Ю.Н. Финансовый менеджмент [учебник] / Ю.Н. Павлова – М.: ЮНИТИ-ДАНА, – 2001, – 269 с.
- Смирнов А.В. Новое в динамическом управлении капиталом / А.В. Смирнов, Т.В. Гурьянова // Научные труды Донецкого национального технического университета, серия «Информатика, кибернетика и вычислительная техника». – 2008. – Вып. 10 (153). – С 230–233.
- Смирнов А.В. Об «оптимальном f» Ральфа Винса / А.В. Смирнов, Т.В. Гурьянова // Научные труды Донецкого национального технического университета, серия «Информатика, кибернетика и вычислительная техника». – 2008. – Вып. 9 (132). – С 216–220.
- Фабоцци Ф. Управление инвестициями; [пер. с англ] / Ф. Фабоцци – М.: ИНФРА-М, 2000. – 932 с.
- Шапкин А.С. Экономические и финансовые риски. Оценка, управление, портфель инвестиций / А.С. Шапкин – М.: Дашков и К, 2003. – 544 с.
- Шарп У. Инвестиции; [пер. с англ.] / У. Шарп – М.: ИНФРА-М. – 1998. – 1028 с.
