Abstract
IntroductionThe Coal industry is branch with the heaviest, harmful and dangerous working conditions. One of such factors is the coal dust. The maintenance of a dust in a suspension during coal dredging in clearing and preparatory developments exceeds maximum–permissible norms in tens and hundreds times. The dust gets to a human body, being dissolved in a saliva or besieged on mucous membranes of respiratory tracts, turning thus into liquid poison. As a result of impact of a dust on a human body there can be eye and skin diseases, diseases of the top respiratory ways and lungs. The disease which is accompanied dust fibrozy, is called as a pneumoconiosis. Pnevmokanioz – the occupational disease developing at long inhalation of a dust. 1. TimelinesAnnually on the majority of mines reveal to ten and more cases of diseases of a dust etiology. Not the exception is made by mine of Dzerzhinsky. Only in 2012 11 cases of diseases are revealed. It means that in mines paramount value has to be given to fight against a dust. The main reason for incidence of workers a pneumoconiosis is excess of admissible norms of a dust content of air on workplaces in excavations. The existing complex of removing dust actions based on application of water, provides at the best decrease in a dust content of air at 10–15 times. 2. Purposes and problems of the student workThe aim of the work is the choice of measures to reduce dust in the mine named after Dzerzhinsky, Dzerzhinskugol. To achieve the goal in the work necessary to solve the following problems
3. Brief characteristics of the area, field and layersOn administrative division the territory of mine of a name Dzerzhinsky is a part of the city of Dzerzhinsk of Donetsk region of Ukraine. In the mining relation the mine is separate division of the state enterprise Dzerzhinskugol of Ministry of Fuel and Energy of Ukraine. The industrial platform of mine is located directly in the city. The mine is connected by branch lines to TsOF "Dzerzhinsky" and railway stations the Curve End face and Magdalinovka. Coals are presented in the form of layers by capacity from 0.4 м to 2.0 м The mine of Dzerzhinsky was founded in 1860. The last reconstruction of mine is executed in 1987 which included reconstruction of the main skipovy trunk of Pugachyovk with simultaneous implementation of the new horizon of 1146 m. The mine of Dzerzhinsky is opened by four is central the located trunks: "Pugachyovka", "No.4", "Central", and "New". The mine fulfills cool layers with a hade 56°–60°. The mine of Dzerzhinsky is carried to dangerous on sudden emissions of coal and gas the Way of airing of mine the soaking up. The fulfilled air from mine is given the fan of the main airing by VTsD–47U established on a surface near a ventilating trunk of Pugachyovk. The second VTsD–47U fan – reserve. Airing of all extraction sites – vozvratotochny. On all sites, except layers Thick and Derezovka, is applied pneumatic energy. The compressed air in mine moves from the compressor station located on a mine industrial platform 3.1 Characteriatics coal layerCapacity: Geological: 0.86–1.10 M; Useful: 0.82–0.98 M; Taken out: 1.02–1.44 M layer 62° Hade. Coal l7В layer – Pugachevka throughout an extraction field is sustained on the power and a structure, consists of 1 pack of coal. On contact with a roof slate carbonaceous and clay, scaly, loose, weak, capacity 0.04–0.12 M lies. Availability of carbonaceous and clay slate in a roof considerably reduces coupling of layer with lateral breeds and there can be a spontaneous collapse of coal from the hanging massif. Gipsometriya of layer the quiet. l7В layer dangerous on sudden emissions of coal and the gas, dangerous on the coal collapse, dangerous on an explosibility of a coal dust. Tectonic violations of explosive character aren't predicted. 4. Analiz employed at the mine complex de–dusting activitiesDesign of a complex of removing dust actions has to be carried out at a development stage of construction projects and reconstruction of mine, opening and preparation of extraction sites of the horizons, blocks and panels. According to requirements of Safety rules, the section on fight against a dust has to contain:
In the mine construction project of Dzerzhinsky such section is, but in a limited size. Antidust actions are given in the passport of an extraction site 65–1146 M of l7В layer presented for the analysis, however without their corresponding choice by calculation for specific dust suppression and the demanded scheme of dust suppression. When developing actions and recommendations proposals of specialists of mine on improvement of a complex obespylivaniye have to be considered. 5. Characteristics of the de–dusting activities5.1 Pre–wetting coal arrayFormation on the horizon is fulfilled potolkoustupami 1146 m, a height of 10–12m each notched hammers. The passport provided fight against a dust by water forcing in layer through the short wells drilled from a lava perpendicular to the plane of a face. (fig. 1) 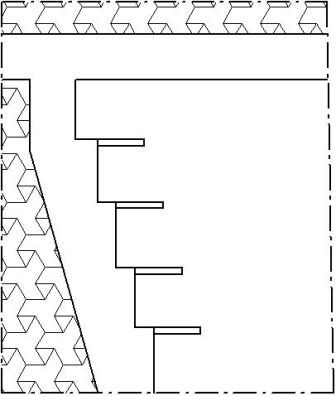
Fig. 1. The technological scheme of application of preliminary moistening of the coal massif at molotkovy dredging of coal on cool layers. Parameters of wells:
Sealing of wells is carried out by the flexible hose hydrolocks maintaining pressure to 300 kg/cm2. The consumption of water on one well makes 3,5–4 M3, time of forcing of one well till 12 o'clock at average rate of forcing of 5–6 l/min. Rate of forcing depends on the fortress of coal and can hesitate from 2 to 10 l/min. At the same time two pumps UGN per day it is possible to process 2 ledges. 5 days are spent for all lava. Ledges are processed serially. Thus, taking into account a glade hydroprocessing provides a week podviganiye of a lava on 8–10 meters. Considering the aforesaid it is possible to note that on working off of the massif of two ledges, taking into account a layer vybrosoopasnost, 2 changes plus one change repair and one for performance of protivovybrosny actions are involved. 2 ledges are every day excluded from the general production cycle of coal mining, that is losses of production make 35–40 t. The same situation and on other three layers, except m3 which is fulfilled by means of the panel board unit and where fight against a dust, is generally conducted by means of an irrigation. The applied scheme of short wells has essential shortcomings since process of forcing joins in the general production cycle of coal mining, and, at least, two ledges per day part in coal mining don't take since delivery processes are involved in them. Other schemes of forcing which were at different times applied and applied on have the same shortcomings, as forcing through short wells, and long wells demand the bulky equipment and complicate works on carrying out штрека. Other technological schemes practically aren't present. Analyzing references it should be noted that efficiency of dust suppression at various schemes of forcing of water in coal layers is almost equivalent and makes 70–80%. Developed earlier technological scheme of forcing driving through wells of limited length with a "dot" source of forcing (fig. 2) excludes all negative sides which are noted when forcing through short wells from a breast of a clearing face and long wells drilled of preparatory developments. At identical efficiency of dust suppression drilling and forcing to the hanging massif from a glade excludes hindrances for works in clearing and preparatory faces. 
Fig. 2.(animation - 22 frames, 73,9 kilobytes) The technological scheme of forcing of water through the rising wells of the limited length drilled from a glade, with a "dot" source of forcing. Applying this scheme on layers only at the expense of it it is possible to increase load of each clearing face on 35–40 t that considerably will affect mine production as a whole. The scheme of wells of limited length with a "dot" source of forcing provides drilling of wells up to 20 meters long to the hanging massif from a glade. Wells are drilled diameter 43 мм and pressurized in a well end face by a hydrolock 5 long. The distance between wells makes 10 м. The hydrolock in an end face of a well is sent in addition by pieces of the pipes with a diameter of 16 mm connected among themselves carving соединенияеми. It is known that water when forcing on cool layers moves mainly up. It is explained by action of the main three reasons: increase in pressure of breeds and gas with depth; unloading of the overlying massif and related, directed up, gas migration; capillary raising of water. Proceeding from the above it is possible to note that the way of forcing through the wells drilled from a glade in the hanging massif technologically has advantages before other schemes since exempts from the works connected with forcing a clearing face and preparatory development. The residual dust content remains quite high in this connection additional measures for fight against a dust are required. This irrigation on loading point and at the exit from a lava, an irrigation of the beaten–off mountain weight in preparatory development and an obmyvka of the settled dust on development walls before conducting explosive works. And even at this package of measures on fight against a dust in productions of cool layers it isn't possible to reach sanitary standards of a dust content therefore workers and the supervision, taken on a clearing and preparatory work, are equipped with antidust respirators of various modifications. Water supply in a cutting zone, i.e. drilling with washing of a boring trifle has to be an indispensable condition when drilling shots and wells, both on coal, and on breed. In this case, in a complex, the effect of dust suppression will make to 99 %. 5.2 Dust suppression foam dustApplication for fight against a dust is based on the following preconditions. Foam has considerably the bigger volume, than liquid of which it is formed. It allows to increase a surface of interaction of liquid with a dust, to fill space about cutting bodies of the extraction car, to limit a source of foaming and to prevent transition of a dust to a suspension. Foam moistens a dust as solution of frother has in comparison with water lower superficial tension better, and duration of interaction of a layer of foam with a dusty surface always is more than time of contact of a drop of solution with the motes weighed in air. When putting foam on a dusty surface its cleaning at the expense of retraction of motes in a foam layer is observed. It is caused by the processes proceeding in a fine at its destruction: liquid absorption from flat thin sites of a film in reinforced, a rupture of films, etc. It is established also that to vials of foam always it is more than force of adhesion of particles of a dust, than to a surface of the corresponding solution. Experiments show growth of efficiency of catching of thin fractions of a dust by vials of PEAHENS solutions by 3–4 times in comparison with drops. Large volume of researches on application of foam was carried out in faces with a cool bedding of layers, when drilling wells, when conducting explosive works, etc. In all cases dust suppression by foam was more effective, than traditional ways – preliminary moistening and an irrigation. This way will be applied after development in Ukraine foams meeting sanitary standards. Gidroobespylivaniye (an irrigation, dust suppression by foam) provides decrease in a dust content of air to level close to maximum permissible concentration on layers which belong to the IV category of a pylnost below. When dredging layers over IV categories need to be supplemented a gidroobespylivaniye with means of catching of a dust. The estimated scheme of application of foam is given in fig. 3 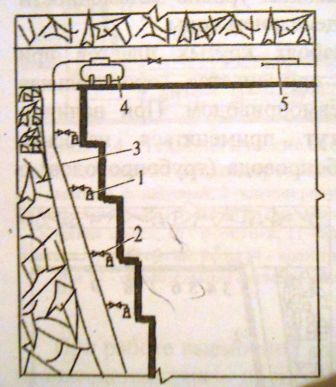
Fig. 3. The technological scheme of application of foam at molotkovy dredging of coal on cool layers.1 – the foamer; 2 – gate; 3 – zaboyny water supply system; 4 – batcher of a smachivatel; 5 – shtrekovy pipeline. 5.3 Water unitsThe Residual dust content of air on a network of excavations, as a rule, is at rather high level and the air streams proceeding from clearing and preparatory developments, and also passing on a network of developments, need an additional obespylivaniye. To an obespylivaniye of air streams we apply water air (tumanoobrazuyushchy) veils. For creation of water veils of the VZ–1 type use ploskostruyny nozzles. 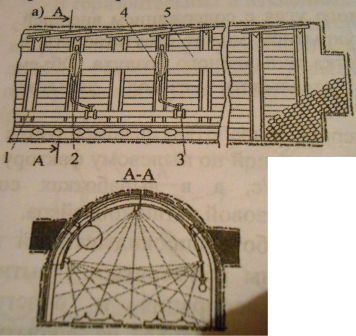
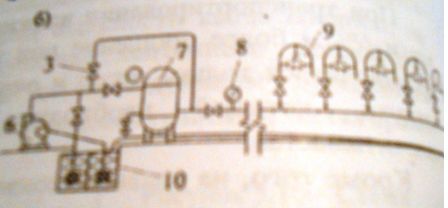
Fig. 4. Technological schemes of cleaning of a dust of ventilating streams in preparatory developments by water veils of the VZ–1 type. More effective are the tumanoobrazuyushchy veils created by tumanoobrazovatel of the OP–1 or TZ–1V type. For formation of a water fog in tumanoobrazovatel water and the compressed air are brought. 5.4 Dust suppression by an irrigationEssence of dust suppression by an irrigation is that at interaction of a drop of liquid to a particle of a dust there is its wetting, capture by a drop and sedimentation of the turned–out unit – a dust particle – water. In irrigation systems as sprinklers use the nozzles giving a compact stream and universal nozzles, a torch of a various form: conical (KF) – in the form of a continuous cone, umbrella (ZF) – in the form of a hollow cone, ploskostruyny (PF) – in the form of a flat fan. Designation of nozzles specifies a torch form, coefficient of a consumption of water and a corner of solution of a torch. For example, the nozzle of KF 1.6–75 is a conical nozzle with coefficient of a consumption of water 1,6 and a corner of solution of a torch 75 °. At all systems of an irrigation use for water purification of shtrekovy FSh–1M, FSh–200 filters, FC or FKV is obligatory. The pneumohydroirrigation can be applied to creation of water air veils and for the purpose of increase of efficiency of an irrigation or need of reduction of humidity of coal and a consumption of water in two and more times – a mix of the compressed air with water. The supply of a water air mix to nozzles is made by water supply and the compressed air in the mixer. At a pneumohydroirrigation thin dispergating of water, and, therefore, is reached and sedimentation is thin the dispersed dust. In order that the fog didn't dissipate in development, and went to a dust source, nozzles in which the double torch of the dispersed water is formed are applied: the external – grubodispersny and internal – fine, and also nozzles with variable dispersion of tonkodispergirovanny water which are protected with nozzles with uniform distribution of grubodispergirovanny water. ConclusionsIn this work were carried out objectives, namely: information on mine, the mining–and–geological characteristic, the layer characteristic is provided, the l7В layer dust content is calculated, actions for decrease in a dust content on an extraction site of l7В layer of mine "of F.E.Dzerzhinskogo" as GO "Dzerzhinskugol" гор. 1146 м were chosen. Список источников
|
