Abstract
Сontents
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of operation
- 2. The modern methods of cleaning of gases from a dust
- 3. Main directions of upgrade of the dust removal equipment
- 4. Theoretical bases of adhesion
- 5. Adhesion use for intensification of process of trapping
- Conclusion
- References
INTRODUCTION
In the Donetsk region concentrates the major part of the industrial infrastructure of the country [1]. A large concentration of industrial capacity is a major factor in environmental degradation. The most significant contribution to air pollution brought by enterprises coal, metallurgical and coking industries, as the manufacturing process involves grinding, transportation and processing of large amounts of dry dusting much material.
In the manufacture of various products as a result of mechanical, thermal and chemical processes the waste gases are formed, which dust is contained.
1. THE RELEVANCE
The complexity of the environmental situation in the areas where coking plants is largely determined by significant dust emissions. Emission estimates by expert commissions, the results of calculations of dispersion of pollutants, as well as analysis of the actual pollution at coke plants, show that in the surface layer of air of residential areas are exceeding the permissible concentration of coke dust and other suspended in air substances [2].
Coke dust emissions during dry coke quenching, ie. Aspiration and fugitive emissions installation coke dry quenching, wet quenching equipment, transportation facilities, screening and shipment of coke, as well as unloading (Extradition) of coke ovens are particularly problematic in the area of protection of the atmosphere at coke plants.
The problem of dust emissions at coke plants is the choice of dust collectors and ensuring their reliability and efficiency. For coke dust, this problem is caused by lack of knowledge about its physical and chemical properties (Dispersion, wettability, abrasiveness, etc.), which makes the selection dust control equipment. To address this urgent problem, special studies, both in the properties of coke dust and dust collecting in the area and aspiration
2. MODERN METHODS OF PURIFICATION OF GASES FROM DUST
Industrial enterprises in various sectors are commonly used dust collectors that provide dust collection of technological and ventilation gases. Industrial dust emissions by the process of education and physical and chemical characteristics can be divided into two basic groups: mechanical dust and fog [3].
Mechanical dust particles have a relatively large size from a few microns to several tens of microns. Sources of such particles can be batch, solid reaction products (salts, oxides, etc. etc.), slag, etc. comminute
Unlike solids, particles superfine mist. The size of such particles are tenths and hundredths of a micron. Dust, which is dominated by fumes, chemical and phase composition may differ significantly from the starting materials.
Capture particles from the gas stream is carried out in two ways:
- direct selection of the particle flux (e.g., loss of dust particles in the cyclone chamber);
- deposition on various surfaces, and solids (fibers in the fabric filter, the electrodes in an electrostatic precipitator in the form of droplets in wet scrubbers and the like).
Basic physical principles of separation (separation) of dust particles from the dust–laden gas stream:
- Bold under the action of gravity.
- Bold under the action of centrifugal force caused by rotation of the gas stream and is many times greater than gravity (cyclones, cyclones).
- Clash of dust particles precipitating from the body by the force of inertia (slow blow). This type of deposition is observed in the fabric filter (collision of dust particles to the fibers), scrubbers (collision of dust particles with drops), etc.
- Direct deposition, when a dust particle deposition takes place along the body at a distance less than the radius of the particle (assuming spherical particles), and thus collides with it. This type of deposition plays a crucial role in the fabric filter.
- Deposition of particles on the surface under the influence of diffusion in the gas stream passing along these bodies: Brownian (thermal motion of particles) and turbulent (with turbulence flow).
- Selection Electrostatic dust from the dust–laden gas stream is carried out under the influence of an electric field negatively charged dust particles. The electric field created using the discharge electrodes to which an electric current is fed negative polarity and high potential. On the electrostatic separation of dust particles (mist) of gas based action electrical filters.
- Isolation of the passage of a particle near a hot body. The particles are deposited on the colder surfaces surrounding the heated body.
Thus, the dust particles may be released under the action of forces caused by various physical phenomena, and the optimal choice of the purification process essentially depends on the properties of the deposited material.
3. MAIN AREAS OF DUST EQUIPMENT MODERNIZATION
To ensure effective cleaning of the exhaust air and gases is necessary in each case produce a preconditioned gas to be treated so as to conform to their technological parameters optimal characteristics gas purifying apparatuses. Preparation of exhaust gas to the purification of particulate matter normally carried out in the following directions:
- Enlargement of particle size using a variety of mechanisms of coagulation;
- Reduction of the concentration of suspended particles by pre–treatment of simple gases in non–energy devices;
- Cooling dusty gases;
- Hydration of dusty gases.
The integrated dust can efficiently capture cyclones. Enlargement of dust can be produced by turbulence, ionization or acoustic treatment of dust and gas flow [4].
A typical example of an effective combination with the turbulence in the moistening treatment is dust Venturi tube.
Air conditioning (training) gas before cleaning is done either to intensify the processes in the main scrubbing devices, or to ensure their normal operation.
There are four ways to change the properties of the gas:
- Cooling gases.
- Heated gas is used to avoid condensation of water vapor and acid.
- Moisturize dry gases.
- Introducing special additives gas stream (ammonia, sulfur dioxide, etc.), intensifying electrostatic process.
Gas cooling can be done by sucking outside air into the greatest possible distance from the machine that needs to be cooled gas, or, if not possible, then immediately after the point of suction should be placed mixing device, such as a zakruchivatelya flow turbulator or cyclone. [5].
Gas heating can be made by burning fuel in a separate combustion chamber with subsequent injection of combustion products into the stream of conditioned gas.
Coagulation is the process of adhesion of particles constituting the dispersed phase of the system, when colliding with each other. As a result, there is an integration of coagulation (aggregation) of the particles.
Coagulation may occur due to Brownian motion (thermal coagulation), as well as under the action of hydrodynamic, gravitational, acoustic, electric and other forces.
Thermal coagulation is divided into fast and slow. Under rapid coagulation understand sticking under the influence of Brownian motion. A slow coagulation coalescence occurs only as a result of accurate collisions.
АAcoustic coagulation. As a result of the action of ultrasonic vibrations at their smallest aerosol particles come to oscillate, collide with each other, stick together and form larger particles.
The effectiveness of coagulation depends on the concentration and particle size of the aerosol and the intensity and frequency of the sound field and the duration of exposure fields on aerosol.
Acoustic coagulation of suspended particles may in some cases be used in combination with electrostatic precipitators.
At different stages of production are used as single devices, and systems of several fundamentally different devices for dust collection. The most common type of equipment for dust in most enterprises are centrifugal dust collectors. They occur have high efficiency, relative cheapness and ease of construction, but their effectiveness is substantially dependent on the density and flow rate of purified air. Thus, at low air velocities greatly reduces the effectiveness of the inertial dust removal means, and higher speeds lead to re–entrainment of dust.
Precipitators for use of a new design in the chemical industry research is needed into the adhesive properties of trapped particles and the search for materials and coatings that will reduce the adhesive interaction of fine dust coke enterprises with the inner surfaces of the equipment. This will allow more efficient use of equipment.
Improving the efficiency of dust collection is possible in the following ways:
- Changing the geometry of the main structural elements of equipment to increase turbulence in the flow.
- Use of several stages in various dust collecting devices [6].
But the creation of a universal method for purification of gas from dust impossible as effectively working on some enterprises dedusting devices are often not effective for others. Reduced efficacy due not only to the various parameters of aerodynamic characteristics and concentration of dust abatement dusty gas, but also the processes of changing the geometry of internal cavities centrifugal dust collector and dusty gas transportation systems due to "sticking" of the particles transported material on the inner surfaces.
One of the promising areas of process control "sticking" of the material on the inner surfaces of equipment dedusting systems is the use of special coatings change parameters of particle deposition. But this method will be effective after the study of the mechanism of interaction of particles in the gas stream between themselves and their interaction with surfaces in the deposition.
The most common and effective equipment for centrifugal gas cleaning dust emissions from vehicles are cyclone.
Cyclones (Fig. 1) are the most common type of dust collectors, due to their ease of construction and relatively high efficiency. They provide an effective scrubbing dust particles size of 10 microns or more. In a smaller cyclones are used for pre–cleaning gases, as the first degree of purification and devices installed in front of a fine filter (eg filters or electrostatic precipitators).
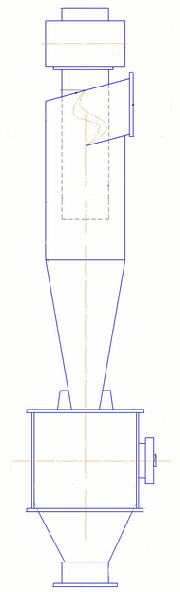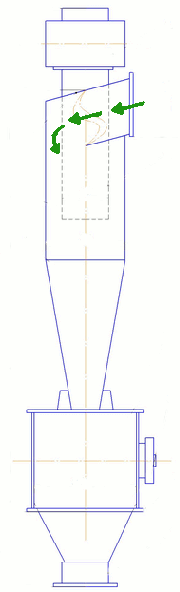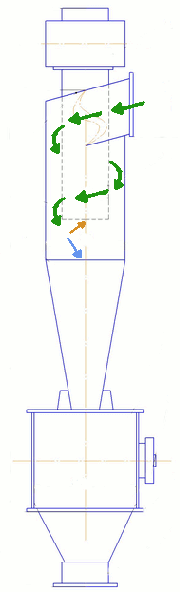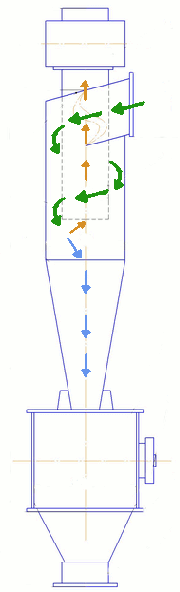
The main elements are the cyclone body comprises a cylindrical part 2 and the conical one, the exhaust pipe 6 and the hopper 7. Gas enters into the upper part of the housing through the inlet pipe 5, welded to the body tangentially. Dust is collected by the centrifugal force generated by the movement of gas between the enclosure and the exhaust pipe. Collected dust is poured into the hopper, and cleaned gas is discharged through the exhaust pipe.
Cleaning efficiency is determined by the composition and density of the particulate matter is collected dust and gas viscosity, which depends on its temperature. By decreasing the diameter of the cyclone and the increase up to a certain limit of the gas velocity in the cyclone cleaning efficiency increases.
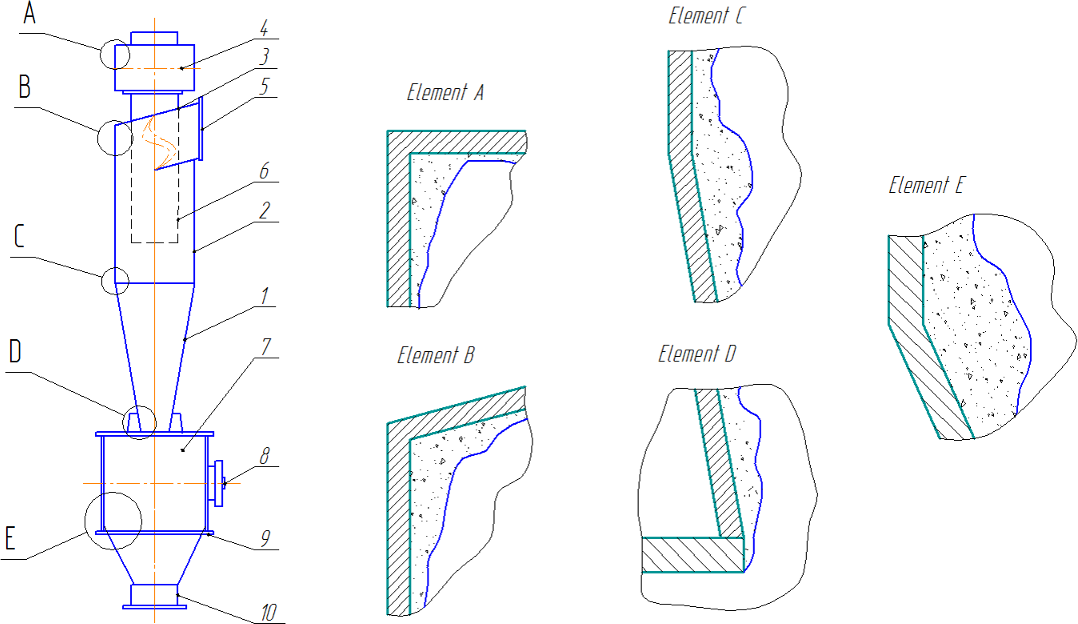
Figure 2 — Diagram indicating the cyclone zone sediments
There are several ways deposits (Figure 2):
- Sticky;
- Hang;
- Sticking;
- Arching.
To assess the degree of influence of internal deposits on the efficiency of dust collection equipment was carried out theoretical calculations of one of the most common dust collection devices. Considered working conditions with clean internal walls and the walls in the presence of sediments.
We have considered the influence of deposits on the inner walls of the inlet on the collection efficiency η. To carry out this calculation using the following formulas.
Velocity of the gas at the inlet pipe:
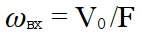
F — sectional area of the channel tube, m2;
V0 – volume of gas to be cleaned, m 3/h.
Calculations were performed on the influence of the degree of pollution cleaning efficiency by which we can draw conclusions.
With the increase in the adhesion layer Δ (Fig. 3)in the inlet pipe of the cyclone, reduces the amount of transmitted gas V0, which would entail a reduction in speed at the inlet of the cyclone thus lower efficiency.
The actual degree of cleaning is determined by the formula:
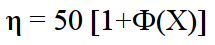
Ф(Х) – full gas purification factor.
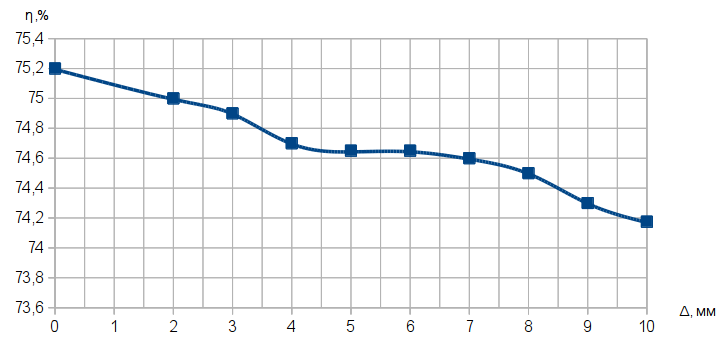
Figure 3 — Graph influence sediment layer on the cleaning efficiency
A similar decrease in efficiency due to the adhesion layer on the inner surfaces of the particles occurs with other types of dust control equipment.
At this point in the literature is insufficient data on the growth in the sediment layer of dust collection systems for coke plants, so to improve the efficiency of dust collecting devices and systems needs a deeper theoretical and experimental research and adhesive properties autohesion and dust particles.
4. THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF ADHESION
Adhesion is a process of interaction of the particles with a solid surface, and the interaction between the particles autohesion. Adhesion occurs when the contact bodies and is the result of molecular interaction, which is manifested by direct contact between the particles and the surface. The adhesive strength is dependent on the contact area with a flat surface, since the molecular interaction is proportional to the contact area. Autohesion force determined by the shape and condition of the surface of the particles [7].
In baghouses adhesion phenomena observed in the initial stage of dust when the particles deposited on the clean surface. Later, after the formation of a layer of particles, hold back the incoming dust caused by autohesion. The strength of adhesion of fine particles to the steel surface is several times larger autohesive particle interaction forces. Particle layer inside the apparatus modifies the geometry and thus reduces the efficiency of particle capture workspace.
The smaller the particle size of dust, the more easily they adhere to the surface of the device. Dusts, which 60–70% of the particles have a diameter less than 10 microns, behave as sticking together, although the same size of dust particles larger than 10 microns have good flowability [8].
In the case of a powder may be strongly off sleep difficulties in translation as a powder in aerated condition, and during its movement. For example, when transferring the powder particles in suspension using an air jet air pressure used to overcome the external and internal forces, which include adhesion between powder particles.
Good adhesion may promote the occurrence of aggregates, lumps of material build–up of deposits on the pipeline walls. This can lead to partial or complete clogging of the apparatus the dust clogging.
5. USE OF ADHESION FOR INTENSIFICATION OF CATCHING
The process comprises the steps of dedusting the movement of the particles to the surface of the precipitation, deposition of particles on the surface of fixing the subsequent removal of the dust cake. Adhesion this has an impact on all stages except the first, and when attaching and removing particles is a major factor. The magnitude depends on the thickness of the adhesive forces strong, hard destructible dust deposits on the inner surfaces of devices and flues. Increase of such deposits results in a partial or complete blockage apparatus dust clogging flues.
All these facts indicate the need to consider the adhesion when designing and operating dust control equipment to ensure the efficiency and reliability of its work. Depending on the magnitude of adhesion force should decide the question of admissibility of certain devices and separate units, some choose the optimal parameters of devices, the particle velocity in the machine.
One of the major characteristics of adhesion — the adhesive strength, which characterizes the specific destruction of adhesive contact force depends on the binding energy defined surface roughness, wettability, and other phenomena.
The greatest influence on the adhesion of dry powders have a molecular van der Waals forces that contribute to the interaction of molecules particles pulverized product and the wall of the cyclone. Thus the molecular adhesion forces depend on the surface of the cyclone as well as the area of contact with the surface of the particles of the cyclone [9].
The capillary adhesion forces occur when contacting the pulverized product with a moist surface of the cyclone. In this case, between the solid particle and the liquid surface of the sleeve is formed, leading to the appearance of surface tension forces. By friction between the particles, or on the inside of the equipment dust particles acquire electric charges. This facilitates the appearance of the electrical forces of adhesion, which leads to deposits of dried product, which is available on all types of equipment and can reach a considerable value [10].
Separation from the adhering surface layer of fine material the airflow is as follows. First upper detach the larger particles, and then fine particles come off, i.e. overcome the force of adhesion of the layer. Removing the upper particle is possible with Fад &%#62 Fаут. Autohesive particle separation process is called erosion. When Fад < Fаут out layer separation occurs at the interface surface–layer. In this case, the adhesion force are overcome. This process is called denuditsiey.
Neglecting electrical and capillary forces, the actual particle shape and other factors the force of adhesion can be expressed dependence:
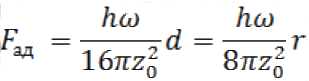
где hω– Lifshitz–Planck constant, J;
zo — gap between the particle and the plane in which the adhesion is maximized;
r – radius of the particle, m.
Adhesion strength decreases in proportion to the square of the size of the gap. Therefore, the fine particles (less than about 50 microns) have a greater contact area with respect to the large particle size, and their size, and their adhesion force value higher than with larger particles. For this reason, the separation of larger particles from the surface is required a smaller force than the lifting of small particles less than 50 microns.
Hence, large particles are detached from 50mk a first surface, at lower air flow rates.
CONCLUSION
Relevance of the work is to study the process of collecting dust and finding new ways to improve dust control equipment.
The analysis of various well–known methods and techniques to capture. The methods of calculation and design of the most common type dust collectors.
Provides information on the improvement of filter systems. Proposed options to improve dust separation process. studied various measures to reduce sediment layer of dust collection systems. The most versatile and effective way to deal with a layer of dust is a coating on the surface of aggregates.
Upgraded appliances and fixtures designed to determine the characteristics of small shear layers of fine features.
Experimental studies of the strength of the structural characteristics of the material. Identified influence of the nature of the friction pair materials on adhesion characteristics, friction coefficients for different pairs of materials.
Defined layer of growth hardened deposits of dust collection systems for coke plants.
Results is allowed to develop measures of modernization of equipment for dust.
References
- Горная єнциклопедия — Охрана окружающей среды — [Электронный ресурс] — Режим доступа http://www.mining-enc.ru
- Укррудпром — Восемь экологических проблем Украины. — [Электронный ресурс] — Режим доступа http://www.ukrrudprom.ua
- Справочник по пыле– и золоулавливанию / М.И. Биргер, А.Ю. Вальдберг, Б.И. Мягков и др.; Под общ. ред. А.А. Русанова.—2–е изд., перераб. и доп.—М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1983.—312 с., ил.
- Коузов П.А., Скрябина Л.Я. Методы определения физико–химических свойств промышленных пылей.—Л.: Химия, 1983. 143 с, ил.
- Ветошкин А.Г. Процессы и аппараты пылеочистки. Учебное пособие.—Пенза: Изд–во Пенз. гос. ун–та, 2005.—с.: ил. библиогр.
- Митина М.С., Кутняшенко И.В. Разработка оборудования для эффективного пылеулавливания/ XXIII Всеукраинская научная конференция конференция аспирантов и студентов
Охрана окружающей среды и рациональное использование природных ресурсов
., 16–18 апреля 2013 г., стр. 146–147 - Зимон А.Д. Адгезия пыли и порошков/ А.Д. Зимон.– М., Химия, 1967. – 363 с.
- Рудыка Е.А., Бредихин П.С., Матюшенко И.Н. Исследования адгезионных свойств пылевидных продуктов/ доцент Е.А. Рудыка, аспирант П.С. Бредихин, доцент И.Н. Матющенко// Вестник ВГУИТ. – 2012. – №2. – C.141–143.
- Письменный Е.Н., Туз В.Е., Лебедь Н.Л. Смачиваемость и адгезия пленки жидкости на стенки канала с сеточным покрытием/д–р техн. наук, проф. Е.Н. Письменный, канд. техн. наук, ст. науч. сотр. В.Е. Туз, канд. техн. наук Н.Л. Лебедь// Сб. науч. тр./ Нац. техн. ун–т Украины
КПИ
— Киев: Изд–во КПИ, 2009. – С.64–68. - Соболев А.А., Мельников П.А., Тютюнник А.О. Движение частиц в воздушном потоке/ канд. техн. наук, доц. А.А. Соболев, канд. техн. наук, доц. П.А. Мельников, соиск. А.О. Тютюнник// Вектор науки ТГУ. — 2011. – №3(17). – С.82–86.
