Abstract
Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. Construction of mine fans
- 1.1. Axial fans
- 1.2. Centrifugal fans
- 2. Regulation Fan operation
- 3. Methods of adjustment modes Fan
- References
Introduction
Modern mining enterprise is impossible without forced ventilation. Termination ventilation entails stop of a technological complex mine or mine, to get people to the surface, the cessation of all machinery. From a reliable, trouble-free operation of the system of ventilation depends entirely on security, and often the lives of people working in the mine.
Due to the availability of reliable conditions in the mine, the necessary power and controlled source of air movement of forces, as the main source of these forces used the fan.
The fans are widely used in all industries. Their drive consumes a huge amount of power generated in the country. In particular, in the mining industry to drive fans, serving mine, it takes up to 8? 10% of the electricity consumed by the entire shaft [1]. In this regard, the creation of highly efficient fans and their proper use is of great economic importance.
1. Construction of mine fans
1.1. Axial fans
Axial fan (Fig. 1) [1] consists of the impeller (RC) 1, which are fixed to the hub profile (in the form of an aircraft wing) 2 blade; the impeller rotates in the barrel or, as it is often called, the housing 3. In the impeller located straightener (CA) with fixed blades 4. Turn the impeller blades using a drive transfers the energy to move air. Rotor blades are made of steel or plastic (for fans of small size).
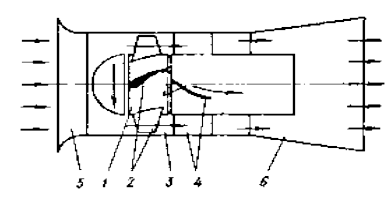
Figure 1 – Scheme axial fan: 1 – impeller; 2– blades impeller; 3 – housing; 4 – straightener; 5 – collector; 6 – diffuser
The axial fan air flow direction coincides with the rotational axis of the impeller. Air is drawn into the collector 5, extends between the blades of the rotating impeller, and then enters the straightener, thence to a diffuser 6 and is discharged into the atmosphere (when the fan on the suction).
Axial fans may be single-stage (one impeller) and two-stage. In the latter case, the fan casing are two stages operating in series and each having its impeller.Between the impeller is intermediate guide vanes (ON). Structurally, the guiding device consists of a fixed profile blades or profiled blades with an adjustable angle setting. Destination guide apparatus – air supply to the impeller set by him in some more effective direction and convert a large part of the kinetic energy of the flow (dynamic pressure) into potential (static pressure). Straightener is set for a second impeller along the jet. Both stages can be located on the same shaft or on separate shafts (fan WATER-16). The presence of two stages allows the fan to develop higher pressure.
1.2. Centrifugal fans
The basis of the fan (Fig.2) [4] of the impeller 1, between the front and rear wheels which are fixed wing blade profile such that their front edge located on a circle of smaller radius than the output of the tail portion. The impeller can be with forward curved blades in the course of the wheels, and radial backward curved impeller purpose - to transmit the drive power of the fan to move air. The impeller is rotated within a volute 2, made of sheet steel. A helical casing for the air supply in a certain direction and partial conversion of the dynamic pressure in the air flow into static pressure. Air is drawn into the fan through the inlet manifold 3, wherein the set does not rotate, but only rotate each blade about its axis 4 of the guide apparatus. The guide unit is designed to supply air to the impeller with a certain speed and a certain angle, it can adjust the operating modes of the fan.
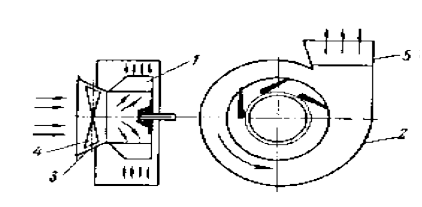
Figure 2 – Scheme centrifugal fan: 1 – impeller; 2 – volute; 3 – inlet manifold; 4 – guide vanes; 5 – Diffuser
2. Regulation Fan operation
Current adjustment modes include the need to control the fan in connection with certain processes (blasting, haul trucks with internal combustion engine failures in the scheme of ventilation shafts, etc.). The best option of the current regulation is the full automation of the ventilation system of the mining enterprise.
The ability to control fan operation usually it provided when selected. Already at this stage the possibilities of the fan to operate in modes higher and lower parameters [3].
This regulation is meant changing the angle of the vanes of the impeller in the axial fans and axial guide vanes in axial and centrifugal fans. Nor should we forget the speed control, of course, if the fan drive allows this type of regulation.
3. Methods of adjustment modes Fan
In the mountain aeromechanics are three possible options for adjusting the fan mode:
• regulation of the performance at constant depression
• regulation of depression at a constant performance;
• regulation while varying the performance and depression.
The practice is used mainly operational control [2] carried out with a change in both productivity and depression. Given the fact that the main parameter for which adjustment is made, is the amount of air entering the mine, depression becomes of secondary importance, its change is perceived as inevitable.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2015. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Гейер В. Г., Тимошенко Г. М. Шахтные вентиляторные и водоотливные установки: Учебник для вузов. – М.: Недра, 1987. – 270 с.
- Проблемы эксплуатации оборудования шахтных стационарных установок: Сборник научных трудов. – Донецк: НДИГМ им. М. М. Федорова, 2006. – 250 с.
- Демочко С. И., Кузнецов А. В., Паршинцев В. П. Неисправности шахтных вентиляторных установок главного проветривания. Справочное пособие. – М., 1990. – 188 с.
- Дулин В. С. Конструкции, технические и аэродинамические характеристики шахтных вентиляторов. Шахтные вентиляторные установки главного проветривания и их оборудование. – В кн: Горное дело: Энциклопедический справочник, т. 8. – М.: Госгортесхиздат, 1960. – C. 240–287.
