Abstract
Ñontents
- Introduction
- 1. Actuality of theme
- 2. Purpose and research tasks, planned results
- 3. Review of research-and-developments
- 4. Exposition of basic material
- 4.1 Concepts "efficiency" and "effectiveness"
- 4.2 Review of local sources
- Conclusions
- List of sources
Introduction
Actuality of research theme is determined the necessity of increase of efficiency of activity of enterprise on the basis of introduction of processnogo approach, at which basic attention is concentrated on processes, creating a value for an user and directly providing profitability of economic activity. In the conditions of modern market creation and introduction of the system of management of quality is expedient in organization on the basis of standards of series of ISO 9000, which will help to perfect allocation of resources, improve quality of activity, arrive at greater satisfaction of user.
1. Actuality of theme
For any type of organization the most actual task there is a construction of the effective system of management, which will provide implementation of tasks of organization and achievement of success in an external environment. One of important aspects of modern management is a selection of processes in control system by organization. Building any control system is possible only on the basis of synonymous certain objects which the system will consist of. The same behaves to the system of processnogo management organization.
2. Purpose and research tasks, planned results
For any type of organization the most actual task there is a construction of the effective system of management, which will provide implementation of tasks of organization and achievement of success in an external environment. One of important aspects of modern management is a selection of processes in control system by organization. Building any control system is possible only on the basis of synonymous certain objects which the system will consist of. The same behaves to the system of processnogo management organization. A process is the difficult enough object of management. Control system by the processes of organization includes: operating under transformation of entrances to the outputs, system of collection of information about the indexes of process, system of analysis of this information and acceptance of administrative decision a person, accountable for efficiency of process, system of continuous improvement of indexes of process and correctings operating under the removal of reasons of rejections during a process. The indexes of processes must be computer-integrated in the general system of administrative account of organization, and system of planning of activity of processes – in the system of the strategic planning of organization. Such method of creation of the system of processnogo management is based on principles of the system of management of quality, certain in the international standards of ISO 9000:2008) it is especially actual. Combination of principles of management and methods of management of quality organization allows organizations of any level of complication to build the system of effective every process control, tie up separate processes in the single system and build the mechanism of continuous improvement of activity of organization in this control system. The object of research of master's degree work is research of possibility of introduction of processnogo approach on the enterprises of different spheres of activity. A task consists in the decision of questions, related to optimization of biznes-processa, improvement of quality and diminishing of expenses. The purpose of master's degree work consists in the leadthrough of optimization of activity of enterprise from point of processnogo approach. Determination of efficiency of the conducted optimization.
Facilities of achievement of this purpose:
- determination for this process of entrances and outputs.
- determination of financial and informative resources.
- construction of chainlets of creation of value of process.
- drafting of the Gantt charts.
- to development of technical regulation, which will determine motion, results of process and order of process control.
3. Review of research-and-developments
Researches of theoretical, methodological and practical questions of economic analysis of the systems of management of quality were conducted many Russian and foreign scientists on different directions. At development of problems of quality management and systems of management of quality a large role was played by labours of V. Deminga, D. Dzhurana, to To. Isikavy, F. Krosbi, Taguti, And. Feygenbauma, Dzh. Kharringtona, At. Shukharta.
A large contribution to research of economic aspects of the system of management of quality was brought in by labours of such scientists: G.G. Azgal'dov, R.Ya. Belobragin, A.A. Bogdanov, B.I. Gerasimov, A.V. Glichev, D.S. Demidenko, N.D. Il'enkova, Dzh. Kampanella, Yu.a. Kulikov, V.A. Lapidus, D.S. Lvov, V.V. Okrepilov, S.V. Ponomarev, A.E. Khachaturov, V.E. Shvec, Dzh.?. Shottmiller.
Scientific labours of the transferred authors have an important theoretical and practical value. Going however examined in them near an economic analysis only partly allow to estimate efficiency of functioning of the systems of management of quality.[1], [2], [3]
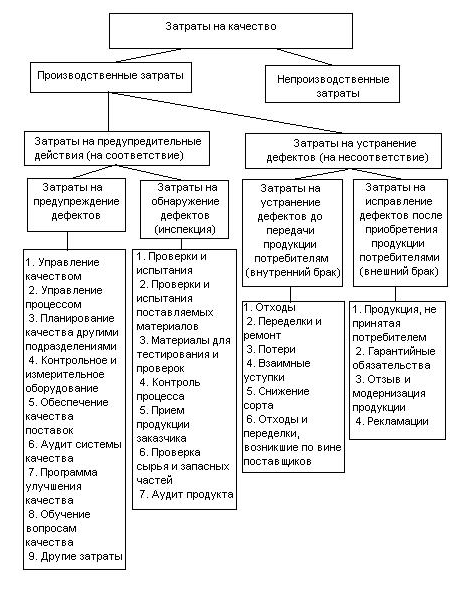
Pic. 1 – Structure of expenses on quality
4. Exposition of basic material
4.1 Concepts "efficiency" and "effectiveness"
Many specialists suppose that it is necessary to determine efficiency of the systems of quality, foremost, as economic efficiency by establishing a connection (functional or cross-correlation) between introduction of the systems of management of quality and financial performance of companies indicators. Interestingly to mark that different specialists quite variously understand this problem and accordingly choose the methods of its decision.Traditional economists search possibility of determination of economic efficiency of the system of management of quality within the framework of logic of traditional approaches. In obedience to this logic, economic efficiency is determined two methods.
An economic effect is determined as a difference of expenses before and after introduction of kakogo–libo measure. As economic results the followings cost indexes are examined: production volume; gross receipt (or turn); income; net profit. As set about expenses and results in time, at determination both it is suggested to take into account their raznovremennost' by procedure of discounting.[4]
In the «Large economic dictionary economic efficiency is determined as: result of economic activity, economic programs and measures, characterized the relation of the got economic effect, to the expenses of factors, resources, stipulating the receipt of this result, achievement of most production with the use of resources of certain cost volume».
In an electronic economic dictionary: "Economic efficiency is effectiveness of the economic system, expressed in regard to useful end-point of its functioning to the expended resources".
Also in an electronic source we meet such concept as: "Economic efficiency is an index, determined correlation of economic effect (result) and expenses, begetters this effect (result)".[6]
We see thus, that all these determinations are alike between itself and by semantic value practically coincide with determination which is given in the standard of ISO 9000:2008, where efficiency is determined as "connection between the attained result and used resources" In other words, economic efficiency is determined on the basis of betweenness by benefits and expenses on their receipt.Coming from determinations of economic efficiency, to set the index of efficiency without determination of expenses on quality is not possible.[7]
A. Feygenbaum on quality subdivided expenses into the followings groups:
- prophylactic, including planning of quality, I.e. expenses, related to some activity which reduces or fully prevents possibility of appearance of defects or losses;
- expenses on verifications, including on an inspection, I.e. expenses on determination and confirmation of the attained level of quality;
- internal losses, including expenses on a waster-waster and alterations, I.e. expenses, organizations borne inwardly, when the stipulated level of quality is not attained, I.e. till a product was sold;
- external losses, including expenses on maintenance of claims, and guarantees et cetera, when the stipulated level of quality is not attained, I.e. since a product was sold.[8]
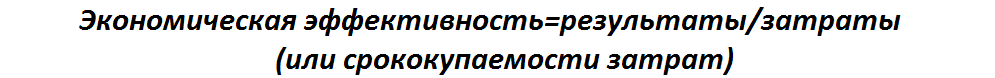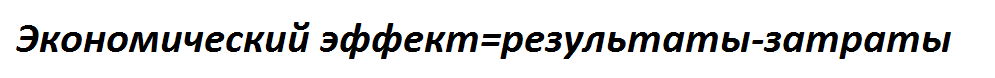
Åconomic Åfficiency
Structure of forming of expenses on quality of products and their kinds presented on a picture 1. However necessary it is to take into account that distributing of expenses on these groups very de bene esse. And the methods of count can be used in different organizations. But it is not substantial, as classification and break-down of expenses on quality is internal activity of every enterprise. Sufficiently, what would be complete concordance into an enterprise on the chosen kinds and categories of expenses. Categories of expenses must be permanent, not to duplicate each other.[9]
All basic data on expenses it is possible to get managing information in quality, which implies the conduct of the proper records within the framework of the operating system of quality. An analysis and estimation of expenses on quality enables an enterprise to manage expenses and to estimate influence of functioning of the system of quality on the results of activity.[10]
Expenses on quality are inevitable in activity of any enterprise, as it is impossible to eliminate useful expenses on quality, related to providing and maintenance of the attained level of quality. At the same time there is part of expenses which an enterprise can be delivered from, if will decrease the amount of disparities in the work and producible products (rendered services). Logic of free quality will start acting then, when the stake of expenses on warnings measures (useful expenses) will begin to grow. The amount of disparities will diminish due to the increase of preventive measures, that will provide companies high quality of products and services, will allow to decrease expenses on control and will be instrumental in an increase arrived. [11]
It is impossible to manage that can not be changed. Learning to measure and estimate efficiency of the inculcated system of management of quality, an enterprise is got by possibility to manage efficiency of the system of quality and to promote it. Classification of expenses on quality — only the first step in the direction of management expenses on quality and to the estimation of efficiency of the system of quality. For the valuable estimation of efficiency of the system of quality it is necessary to develop and inculcate the system of account and break-down of expenses on quality. Thus the followings tasks cost before an enterprise:[12]
–to classify expenses on quality;
–to expose the sources of data about expenses on quality;
–to choose a base for measurings;
–to define responsibility for collection and analysis of information;
– to manage expenses on quality within the framework of all company, subdivisions, separate processes.
After successful realization of the tasks described higher an enterprise can fasten the attained results and link aims in area of quality with financial performance of company indicators.Building of mechanisms of account and break-down of expenses on quality in everyday work of employees will be instrumental in more close integration of the system of quality with the system of financial management of company, due to what an utility, operative availability and evidentness of economic indicators of functioning of the system of quality, will rise for guidance.
Thus, a management efficiency of the system of quality is part of control system by the expenses of company. Those enterprises which carry out effective administrative strategy of optimization of expenses understand that a management expenses on quality is an instrument of decline of total expenses of company, increases of its profitability and strengthening of competition positions at the market.
4.2 Review of local sources
For the estimation of expenses on quality two basic models of estimation are presently formed: cost model of process, described in the Britannic standard of BS 6143:1992 "Guidance on the economy of quality. Part 1". Model of expenses on a process, and warning model, estimation and refuses (PAF), described in the Britannic standard of BS 6143:1990 "Guidance on the economy of quality. Part 2. Model of warning, estimation and refuses".
The first part is the "Cost model of process". On this conception all expenses are taken into account on implementation of process, which has the entrances and outputs, both desirable and undesirable.
The cost model of process supposes that all expenses on products can part on two categories: expenses, related to achievement of accordance in quality, and expenses, related to disparity in quality. Both these categories of expenses are examined as potential sources of economy. Thus in expenses on disparity in quality those expenses which are caused retreat from a designer, technological, normative, organizational document enter only, and charges do not enter on warning of retreats from a document (in-plant training personnel, reliability tests et cetera). Basic attention in the cost model of process is spared reduction of expenses on realization of processes.
At first we examine possible expenses on quality in the process of production or favour. It is further necessary to define the cost of all exposed expenses. It can be got from financial statements or by drafting of report on the cost of process. The groupment of the transferred indexes in a report does not decide problems, but allows them to expose.Even if the found decision of problem will be acknowledged useless from costliness or other reasons, a task must not be neglected — possibility to apply the found decision can appear later.
The basic task of such presentation of information is that after opening and determination of expenses on a process a his checking and continuous improvement feature appears on all categories. This system is applicable for all processes of different enterprises.
The second part is Model PAF (warning, estimation, refuse). In the model of PAF expenses, related to providing of quality, are broken up on two basic categories: expenses, related to disparity in quality (irretrievable) and expenses, related to achievement of accordance (prophylactic) in quality.
Expenses, related to accordance, are divided by expenses on an estimation and warning, and expenses, related to disparity, — on internal refuses and external refuses. In accordance with this standard will consider the nomenclature of expenses of all kinds.[13]
Expenses on warning:[14]
- planning of quality, development and constructing of measuring and proof-of-concept equipment;
- analysis of quality and verification of construction;
- verification and technical maintenance of equipment for measuring and tests;
- verification and technical maintenance of production equipment, in-use for the estimation of quality;
- guarantees of suppliers;
- training of personnels in area of quality;
- analysis of quality and program on perfection of quality.
Expenses on an estimation:[15]
- pre-production verification;
- leadthrough of alpha receiving tests;
- choice of control method;
- control and test;
- control and proof-of-concept equipment;
- materials, expended during the leadthrough of control and tests;
- analysis and lecture about the results of tests and control;
- field tests on a capacity, assertion and approval, estimation of ware-house supplies;
- taking of inventory of warehousing.
Expenses on an estimation will be justified on condition that it will be found out disparity till products will get to the user. Such actions can be:[16]
- tests of products or verification of document till it will be passed to the user;
- verification of documents and correction of errors till they will be shipped;
- renewal of the damaged surfaces;
- verification of geared-up accounts before sending to their users for payment.
The exposure of disparities on this stage eliminates serious expenses on refuses and failures in the future, and also helps to develop more effective methods of control. Expenses on accordance often name prophylactic or preventive expenses on upgrading. Such expenses are advantageous investments in the improvement of quality.
Expenses, related to the internal refuses: marriage; replacement, alteration and repair; search and debugging or analysis of defects and refuses; retests and control; permission on modification and concessions; lowering of class of quality; outages.
Expenses, related to the external refuses: complaints; guarantee return; rejected and returned products; losses of sales; charges on the review of products; responsibility for products.[17]
Expenses, related to the refuses or irretrievable expenses on quality average 4-5% from the volume of sales.
In order that to consider all losses, besides traditional expenses, it is needed to take into account the hidden expenses on disparity: table of contents of additional service service; delay with implementation of plans; delay with registration of documents; additional transportations; errors in registration of accounts on payment; incomplete implementation of the accepted orders; revision of construction of incongruous products; losses of time on contacts with the dissatisfied user; untapped production capacities and other.[18]
These charges not reflected in book-keeping documents make no less than 15-20% from the general volume of sales.
Efforts on the correction of disparities, exposed out of company, usually directed on renewal of trust of users, otherwise it threatens the loss of market.
Consequently, the not so much orgware of quality, how many disparity, treat expensive, resulting in alterations, repair and utilization of defective products.[19]
The considered model of PAF is easily used at the break-down of expenses on quality of products in industry, but in less degree applicable at the break-down of expenses on processes and services. The model of PAF is based on the calculation of concrete charges, related to the amount of concrete product.
Thus, presently for the estimation of expenses on quality the followings models of estimation are used: cost model of process and model of warning of estimation and refuses (PAF). However at the estimation of economic efficiency of the system of quality a model which an estimation will be conducted on must get out coming from the specific of enterprise.[20]
Conclusions
The mortgage of success of activity of any enterprise is covered in the permanent increase of efficiency and effectiveness of production, systematic analysis of production activity, development and introduction of measures aimed on the increase of efficiency and effectiveness of production.
Concepts "efficiency", "effectiveness", "process", "processnyy approach", were considered in this work, one of methods of estimation of efficiency of production processes is considered.
Effectively to function, organizations must determine and manage numerous associate and interactive processes. Often the output of one process forms the entrance of the following directly. Systematic authentication and management of the processes applied organization and before all providing of their co-operation can be considered "processnym approach". On the basis of processnogo approach organization must define the processes of planning, production and supplying to the products or favour.
By a management processes satisfaction of necessities of customers is arrived at. In the total a management the results of process passes to process control.Efficiency of activity of organization can be promoted due to creation and management the system of associate processes. It means that organization must aspire to the association of processes of creation of products or services with processes, allowing to watch accordance products or services the necessities of customer.
At writing of this abstract master's degree work is not yet completed. Final completion: December, 2015. Complete text of work and materials on the topic can be got for an author or his leader after the indicated date.
List of sources
- Universal quality management: Studies. for the institutes of higher./Aeoaeei O.P., Gurov A.I., Zorin Yu.v. and dr./iia red. O.P. Gludkina. – M.: of Radio and connection, 1999. – 600 p.
- Gissin V.I. quality of products Management: Uchebn. manual. it is Rostov of n/D: Phoenix, 2000. –256 p.
- George S. Vseobschee is a quality management: strategies and technologies: Studies. - M.: Victoria plus, 2002.
- Lapidus V.A. Universal quality (TQM) in Russian kompaniyakh/ Gos. un-t managements; nac. fund of training of personnels. M.: of OAO «Printing-house of «New», 2000. - 432.
- Adler Yu.p., Shper v.l. Indexes of producibility of processes are a brief review of the modern state. it is Announcer of engineer, 1994, No 7, P. 39-45.
- Keyn V.E. Producibility of process. it is Course on quality, 1992,No2,n.87-114.
- Gorlenko O.A., Miroshnikov v.v. : Creation of the management systems is in organization: Monograph. –M.: Engineer-1, 2002.-126n. Eliferov V.G., Repin of V.A.: Biznes-procesy: Regulation and management: Textbook. it is M. : Infra-mcode, 2005.-319n.
- Svitkin M.Z. Processnyy approach at introduction of the system of management of quality in organization // Standards and quality. - 2002. - ;¹3.
- Vishnyakov, O. Processno-orientirovannyy approach in a management organization / O. of Vishnyakov, I. Dyatlova [Electronic resource]. it is access Mode: http://www.oracle.com/global/ru//
- Sergey Turko. 10 laws of processnoy logic // Standards and quality. – 2006. - ?5. – P. 46 - 48.
- Sergey Turko. 10 laws of processnoy logic // Standards and quality. – 2006. - ?6. – P. 58 - 61.
- Repin V.V., Eliferov V.G. the Processnyy going near a management. Design of biznes-processov. – M.: RIA «Standarty and quality». - 2004. – 408s.
- ISO 9001:2000 (2008) Systems of management of quality. Requirements. 4th publ. – 12-15.-Eca.ISO-2000
- RD IDEF 0 – 2000 «Methodology of functional design of Idef0». – Vved. 2000. – M.: IPK publishing House of standards. – 75c.
- Guidance on conception and use of processnogo approach for the systems of management. Document of Iso/tc 176/sc 2/n 544R3, on October, 15, 2008.
- Kharrington James, Esseling K.S., Nirvegen Kharm Van. Optimization of biznes-processov. Documenting, analysis, management, optimization.- Publishing house: BMikro, 2002 .-320 p.
- Khammer of M., Champi Dzh. Reinzheniring of corporations: The manifest of revolution is in business. Trudged. with angl. – SPb: Publishing house With.- university, 1997. Page 21.
- Roter M., Shuk D. Uchites' to see biznes-processy: Practice of construction of maps of streams of creation of value – Al'pina Business of Axle-bearings, Moscow. 2008. – 144s.
- Momot A.I. Management of quality and elements of the system of quality: Textbook. it is a 2th publ., dop. and rassh. it is Donetsk: Nord–Press, 2005. – 320s.
- Glukhov a.I. Estimation of competitiveness of commodity and methods of its providing: The train aid of M.: Marketing, 2004. — 458 p. .
