Abstract
Contents
Introduction
The ability to assess events and calculate their probability – the amazing ability of the human mind. Even without a vision of the complete picture of an event, we can with some confidence to describe the result, or vice versa – to evaluate its premise. This ability is key in creating chips artificial intelligence. The solution to this problem will lead to a revolution in absolutely all fields of human activity.
Currently the circuitry used in commuter use Boolean logic in which an analog signal is clearly interpreted as 0 or 1, depending on the voltage across the transistor. Not difficult to guess that the construction of artificial intelligence systems need colossal number of processors. In turn, this leads to huge cost of funds, and a similar system will be similar to the size of the first host computer, invented in the 60‑ies.
Hence the need to create systems that are compact in structure, and allows us to solve the above problem.
In the 60s it began the rapid development of the field of mathematics, which began to consider the process of inference in conjunction with the theory of probability. This logic is beginning to be called probability.
The main difference between the probability of a Boolean logic –
statements are attributed not only the values of truth and falsehood in two‑valued logic, but continuous scale of truth‑values between 0 and 1, so that zero corresponds to an impossible event, a unit – is almost certainly. The values of truth in probability logic is the probability of the truth of statements degree of plausibility or confirmation
[1].
1 Actuality of theme
Replace Boolean logic circuitry will be a new revolution in all fields of human activities, because it allows several times to reduce the duration of the process of obtaining various tasks such as pattern recognition, decision‑making system, system diagnostics and other diseases.
In the master's work is carried out research of technologies to implement logic‑probability calculus in the field of applied sciences and research problems that can occur in the interaction of logical and probabilistic logic paradigms.
2 The purpose and objectives of the study, deliverables
The aim is to evaluate the possibilities of synthetic direction which connects:
The main objectives of the study:
- Famous destinations build reliable systems from unreliable elements [2].
- Expansion of Boolean logic, such as probabilistic logic (ul) and inductive logic.
Result of the work is to be a software system generation systems with probabilistic logic.
The development of this subject can reasonably talk about the relevance of the theme of the work.
The main issues to be resolved:
- Create and software implementation of a mathematical model of a system generating systems with probabilistic logic.
- Software development system and its basic operations.
- Possible scientific and practical results that are expected during the work, originality, significance.
Scientific novelty work lies in the selection and assessment method for transforming people are adaptive software system for the hardware model generation busting.
Practical significance the work is to create a software system for the hardware model generation busting.
3 Basic concepts of probability logic
Before you disassemble the probabilistic and probabilistic inference operation, you must first analyze the basic operations of Boolean logic.
The main operations include Boolean logic operation AND, OR, NOT . And some of them then you can get a equivalence, implication, Sheffer stroke, arrow Pierce, modulo 2 .
In the circuitry of these operations are reflected in the implementation of the so‑called logic gates – switching circuits that mimic the function of semiconductor chips. Logic circuits that implement the basic binary logic operations are called conjunctors, disjunctors and inverter .
For a better understanding of the circuitry of each logic circuit can be represented as an electrical circuit with pussycat. Below are diagrams inverter (fig. 1), conjunctor (fig. 4) and disjunctor (fig. 5) respectively.
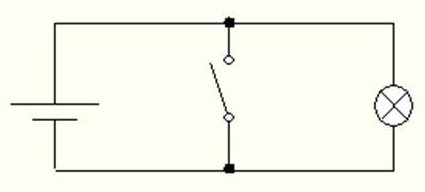
Figure 1 – The electrical circuit of the inverter
Below is a diagram of a circuit for different values of x switch (fig. 2, 3).
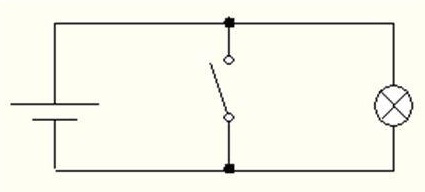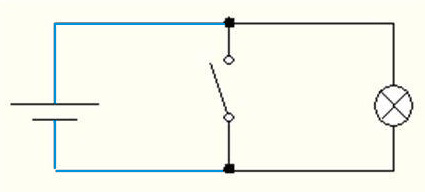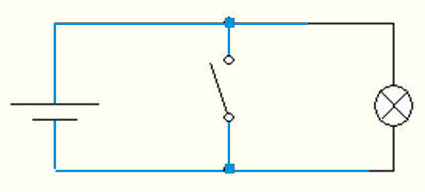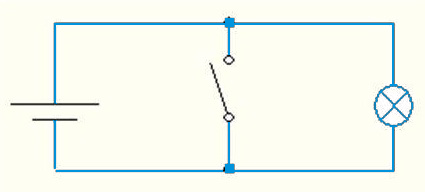
Figure 2 – Driving denial at x = 0. The lamp lights up
(animation: 10 frames, 7 cycles of repeating, 18.1 kilobytes)
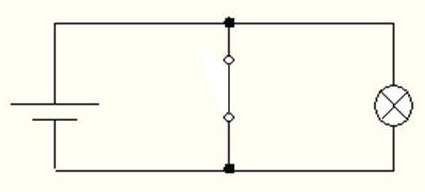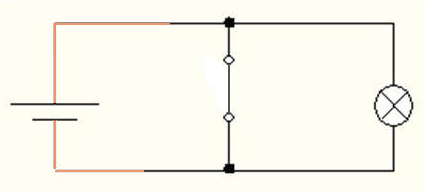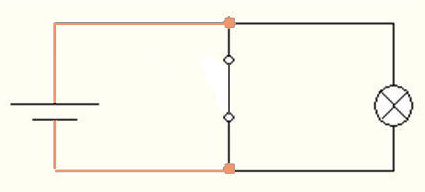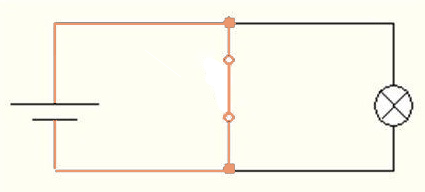
Figure 3 – Driving denial at x = 1. The lamp does not light
(animation: 9 frames, 7 cycles of repeating, 16.9 kilobytes)
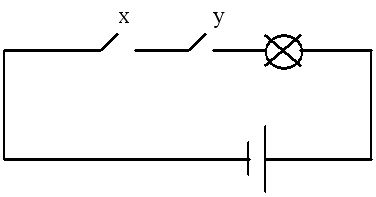
Figure 4 – Electrical circuit conjunctor
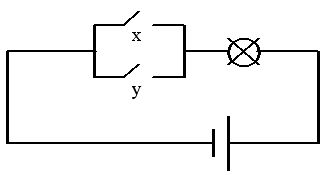
Figure 5 – Electrical circuit disjunctor
Having an idea of the standard logic gates, you can proceed to the probability of operations.
At the heart of probabilistic methods is Bayes' theorem , which allows you to rearrange the cause and effect – we can determine whether or not this was caused by the consequence of this cause [3].
Bayes' theorem:
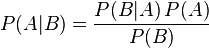
where A and B are events
P (A) and P (B) are the probabilities of A and B without regard to each other
P (A | B), a conditional probability, is the probability of A given that B is true
P (B | A), is the probability of B given that A is true.
Bayesian probability formula has long been used in programmirvoanii, for example, a spam filter based on the use of naive Bayesian classifier. Though probabilistic approach and distributed programming, the production of processors and not sdivinulos forward. It turns out this discrepancy: probabilistic methods work based on Boolean logic. Sophisticated probabilistic methods are working with hundreds and thousands of different parameters that must be handled with an acceptable speed. In the processing of a single parameter is about 10–15 standard logic gates. Thus the increase in the number of parameters leads to a colossal increase in the number of transistors. To solve this problem, scientists are trying to create a processor that could determine the most plausible answer to the challenge, t. E. To determine the probability of the event.
As one of the solutions to this problem was proposed by a special analog chip that can perform calculations in the analog domain using the pbits – analogue of probability bits, and then translates the results into digital form.
The basis for such a chip will act as a logic gate NAND (bar \ item Schaeffer) , the result of which would be calculated based on Bayes' theorem. Thus, if in the traditional NAND‑gate , the result is true if the two input signals do not match, the Bayesian NAND‑gate output value would be probability of coincidence of the two input signals . Thus, if a pbit = 1 – that means 100% probability of coincidence of the two input signals. Pbit is encoded using 8 binary bits, which makes it possible to get a result in the range of {0–256}.
The first chip based on probability was presented to the company in 2009. It uses Bayesian NAND‑gate, as well as special transistors, resistors. The first experimental design with a chip was LEC‑chip (LEC ‑ Lyric Error Corrector) – it allows you to fix errors in flash memory with 6‑times with superiority in speed over conventional chip‑corrector. Additionally, LEC wins energy consumed – with decreasing transistor count and reduced energy consumption.
Conclusions
The probabilistic logic – very promising profile multi‑valued logic. If you are using all of its potential, humanity as close approach to the creation of artificial intelligence.
Now you can watch how organizations and companies are showing interest in PCMOS‑schemes (Probabilistic Complementary Metal‑Oxide Semiconductor, a probabilistic complementary metal‑oxide semiconductor) chips and a probabilistic logic gates. The performance of the processor with the chip should be three orders of magnitude greater than the classical digital devices with the architecture of x86. A thousand times the power and decrease the cost of facilities necessary to perform statistical and probabilistic calculations ie one chip will replace the classic thousand
stones
.
It is worth mentioning that in the Soviet Union there has been a development of the so‑called analog computers . These machines are radically different from those of modern computers, instead of 0 and 1, they worked directly with the signals. Thus the work was not in the mode of switch
, and in the mode of rheostat
.
Source list
- Вероятностная логика [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии : Версия 53436483, сохранённая в 22:29 UTC 13 марта 2013 / Авторы Википедии // Википедия, свободная энциклопедия. — Электрон. дан. — Сан‑Франциско: Фонд Викимедиа, 2013. — Режим доступа: http://ru.wikipedia.org/?oldid=53436483.
- Нейман Дж.Вероятностная логика и синтез надежных организмов из ненадежных компонент // Шеннон К. Э. , Маккарти Дж. Автоматы Сборник статей. — Пер. с англ. — М.: Издательство иностранной литературы, 1956. — 403 с.
- Теорема Байеса [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии : Версия 71022965, сохранённая в 22:00 UTC 25 мая 2015 / Авторы Википедии // Википедия, свободная энциклопедия. — Электрон. дан. — Сан‑Франциско: Фонд Викимедиа, 2015. — Режим доступа: http://ru.wikipedia.org/?oldid=71022965.
