Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Actuality of theme
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study, expected results
- 3. Analysis of the existing technological schemes of production of stamped-rolled railway wheels
- 4. Technique of modeling
- Conclusions
- List of sources
Introduction
In Ukraine, the production of railway stamped-rolled wheels organized by JSC "Interpipe NTZ" in Russia - JSC "Vyksa Steel Works" (VSW) and JSC "Nizhny Tagil Iron and Steel Works (NTMK)." These enterprises mastered a wide assortment of solid wheels, which differ both in form and size. The diameters of the rolling circle made of wheels in the range of 700-1270 mm. [3]
The most widely used in Ukraine, Russia and other CIS countries received a railway wheel with flat-conical disc has a diameter rolling circle ∅957 mm. The design and dimensions of solid wheels ∅957 mm determined in accordance with GOST 9036-88. [3]
1. Actuality of theme
Progress in Ukraine the level of technology stamping and rolling roughing wheels inferior to foreign analogues. This is due to wear and tear of the equipment and the backwardness of the technologies used and the lack of availability of modern means of the process of designing multijunction Forging deformation processes on line, which would allow, on the one hand, quickly, and with another - with sufficient accuracy to perform theoretical analysis of new technological modes of deformation of the metal presses in the Wheel-mill.
2. Цель и задачи исследования, планируемые результаты
Purpose - to develop and offer new technological schemes pressing blanks in order to reduce the technological allowances for machining. Investigation of temperature, deformation and strength deformation parameters of the proposed technology by finite element modeling of processes in a complex DEFORM-3D, taking into account differences in weight, shape defects initial blanks and billets decentering relative dies.
Results - will be developed technological scheme, the application of which will improve the accuracy and dimensional stability stamped wheel blanks.
Scope - ferrous metallurgy, production of stamped-rolled railway wheels.
3. Analysis of the existing technological schemes of production of stamped-rolled railway wheels
3.1 Forging line of "Interpipe - NTZ".
Used earlier of "VMZ" and is still used at JSC "Interpipe - NTZ" old way (Fig. 1) is characterized by low bandwidth press 50 MN, where such operations are carried out [3]: the final draft of the workpiece in the process ring centering ring floating on the axis of the press, filing under the top plate of the punch and clinch the second press stroke - distillation of the central part of the workpiece. Furthermore, the method distillation punch [3] in some cases it leads to asymmetry workpieces because it is difficult to provide an environment in which the axis of the punch, which is fed into a press rotary device, coincides with the axis of the ring technology.
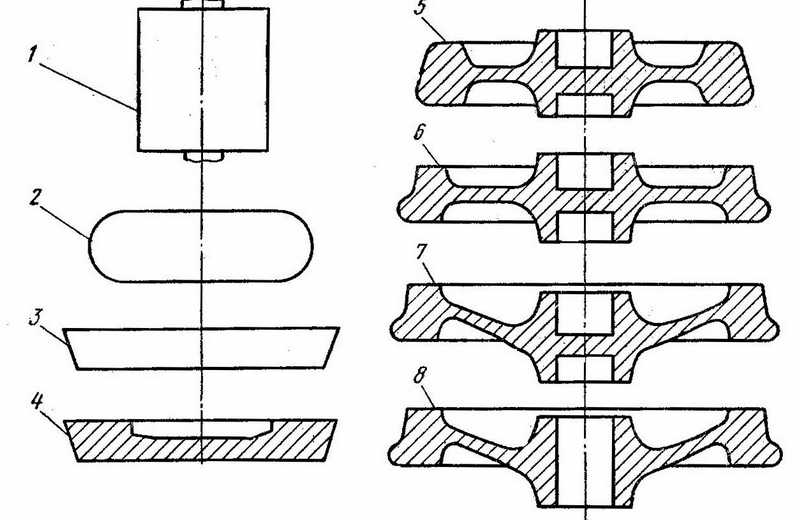
Figure 1 - Diagram of wheel deformation Forging blanks on the line of Interpipe - NTZ
1 - original billet;
2 - After harvesting rainfall smooth plates (20 MN press);
3 - After harvesting rainfall technological ring (50 MN press);
4 - workpiece after distillation punch (press 50 MN);
5 - wheel preform after forming in dies (press 100 MN);
6 - Rough wheel rolled on CPS;
7 - draft-wheel drive after bending and calibration (Press 35 MN);
8 - Rough wheel after flashing holes in the hub (35 MN press).
Laid on the lower die workpiece is centered on the press axis through the centering pevmaticheskogo trehrychazhnaya that coincidence does not always provide a vertical axis of symmetry with a vertical workpiece axis of symmetry of stamps (decentering workpiece axis axially stamps in industrial environments wheels may reach 5 mm or more [5]). As a result, even when applied to the molding preform axisymmetric obtain dimensionally stable preform wheel rim can not be guaranteed.
3.2 Forging line of "VMZ".
The most effective can be considered a relatively new method of production of wheel blanks [6], including the provisional draft of the workpiece smooth plates on the press 20 MN, the final draft of the workpiece in the lower ring technology, combined with distillation of the central portion of the preform (draft-distillation) on the press 50 MN, and stamping billet wheel with the rim disc and the hub on the press 100 MN. In step precipitation, a stable pre-diameter outer circumference of the preform by providing a uniform height precipitated preforms with a minimum of weights (15 kg). Then, before performing the final precipitation, the workpiece is centered on its side surface in the lower floating ring technology. Then, the final draft of the blank-distillation with top plate ploskokonichnoy per stroke of the press.
This method is now used at JSC "VMZ" (Figure 2). Its effectiveness is primarily in a substantial increase in productivity of the process.
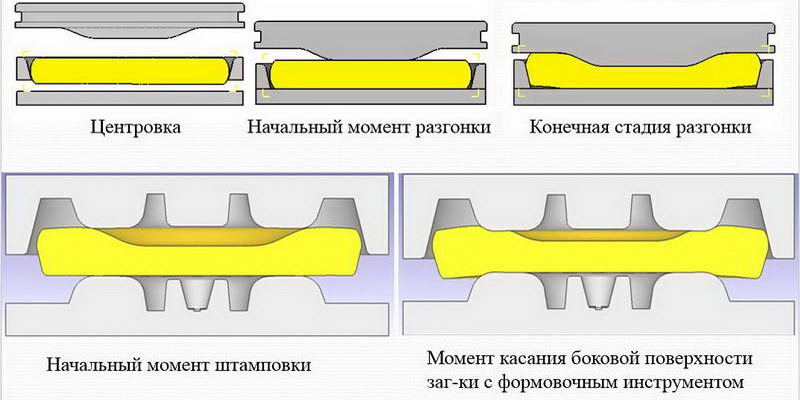
Figure 2 - deformation of wheel blanks on Forging line of "VMZ"
4. Technique of modeling
In the present work we performed formulation of the problem of modeling the deformation process multijunction wheel blanks followed by its implementation in the DEFORM 3D. Simulation performed for transient thermal mode preform, ie taking into account the heat exchange processes of metal machined to the environment as during the deformation, and during pauses mezhdeformatsionnyh, as well as the thermal effect of plastic deformation.[11]
Adopted by the constant temperature of the environment and gain value. This paper considers the technology of manufacturing blanks roughing wheels ∅ 957 mm. These wheels are made of steel wheel 2 (GOST 10791-2004). Used in modeling thermal properties of wheel steel were taken from the database DEFORM 3D for high-carbon steel. In the simulation for the procurement of used plastic material model. To simulate pressing tool has been selected the rigid material model. The behavior of the workpiece material in the solution described by the diagram "true stress - strain." The computer program stresses and strains used in the diagram "stress-strain" - is the equivalent voltage or von Mises.
In the simulation, we use the concept of flow stress, according to which a material deforms plastically, and the amount of stress is determined from the incremental amount of deformation of the flow curve. As a model adopted by the contact friction shear friction model.
The values of the friction factor chosen for the conditions of contact interaction with the workpiece in the presence of die tooling technology lubricants (0.3). When modeling was used automatic generation of finite element mesh[8]. It is sufficient to properly take into account the condition of impermeability of the metal workpiece through the walls of the tool. We used the finite element mesh with chetyrehuzlovymi tetrahedra, which allowed quite correctly describe a complex workpiece geometry (Figure 3).
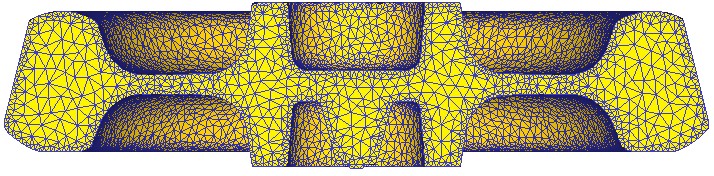
Figure 3 - The finite element model of the workpiece railway wheel (blank after molding press force of 100 MN).
In the simulation it was also a mode of compensation as the volume change during regeneration harvesting nets, and in the process of calculation. The target was chosen as the initial volume of the workpiece defined by the program file with geometry[11].
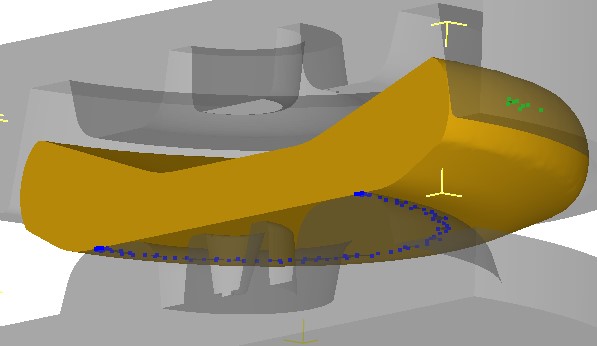
Figure 4 - The formation of the initial contact with the workpiece dies forming press 100MN.
Based on the above it was made mathematical modeling of precipitation, distillation and molding in. The initial data for the simulation were set on the basis of the actual experimental data on strain, force and velocity parameters of the above mentioned stamping blanks roughing wheels ∅ 957 mm, resulting in conditions of industrial production Forging line of "VMZ". The temperature of the press tools and rolls is assumed constant and equal to 300°C temperature issue billets from the furnace - 1260°C.
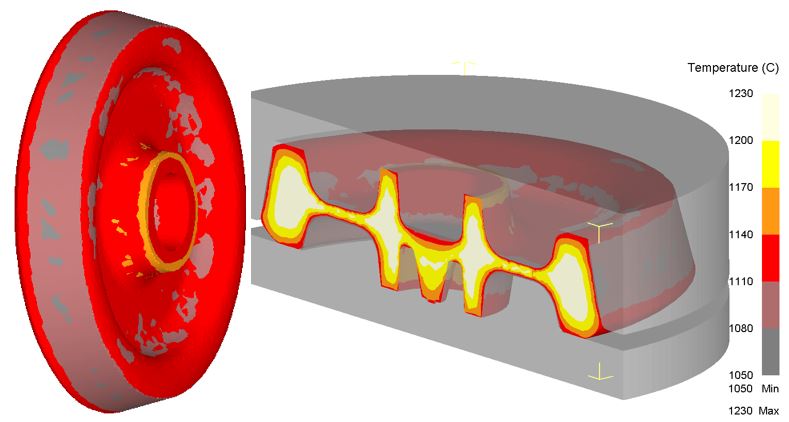
Figure 5 - Temperature gradient workpiece after forming.
Conclusions.
Wheel workpiece rim disc and the hub received on rail wheels rolling usually prepared starting from cylindrical blanks by implementing operations precipitation, distillation and successively forming on hydraulic presses of various installed power capacity.
Efficiency technologies for the production of stamped-rolled wheels are largely determined by the accuracy and dimensional stability of wheel blanks [2].
Also, there is a misallocation of magnitude deformation of the workpiece between the sedimentary and billet presses. Thus, the loading of the first, the sedimentary media (under, for example, JSC "Vyksa Steel Works" (VMZ) force of 20 MN) is close to the allowable, and the next, procurement press (50MN force), which is performed as a rule, only the distillation operation - underutilized.
In addition, in practice, centering deposition and accelerated blanks on the lower die molding press, the centering performed mechanically, does not guarantee sovpadannya axis with the axis of the workpiece and the dies results in asymmetric wheel blanks.
This work is aimed at determining the mechanisms and the development of technological schemes, to improve the accuracy and reduce the asymmetry of forged wheel blanks, as well as rational use loading presses.
List of sources
- Виробництво залізничних коліс / [Г.А. Бібік, А.М. Іоффе, А.В. Свят і др.]. - М.: Металургія, 1982. - 232 с.
- Шифрін М.Ю. Резерви продуктивності і виходу придатного при прокатці коліс / Михайло Юлійович Шифрін. - М.: Металургія, 1989. - 144 с.
- Яковченко А.В. Проектування профілів і калібрувань залізничних коліс А.В. Яковченко, Н.І. Івлєва, Р.А. Голишко. - Донецьк: Донецький національний технічний університет, 2008. - 491с.
- Шляхи зниження витрати металу при виробництві суцільнокатаних коліс / А.В. Яковченко, Б.А. Перков, Д.В. Корж [и др.] / / Металургійна і гірничорудна промисловість. - 2002. - № 4. - С. 42-44.
- Данченко В.М. Вибір технологічної схеми багатоперехідних штампування заготовок залізничних коліс / В.М. Данченко, Х. Дия, А.В. Шрамко / / Металургійна і гірничорудна промисловість. - 2010. - № 1. - С. 58-61.
- Сучасне обладнання та способи порізки злитків на окремі заготовки залізничних коліс і бандажів / Є.І. Шифрін, А.В. Шрамко, В.Л. Мережко, Л.В. Голубєва / / Металургійна і гірничорудна промисловість. - 2004. - № 1. - С. 48-52.
- Снітко С.О. Аналіз силових і швидкісних параметрів прокатки коліс / С.А. Снітко / / Наукові праці ДонНТУ. Металургія: Зб. наук. пр. - Донецьк, 2008. - Вип. 10 (141). - С. 163 - 172.
- Снітко С.О., Кравченко А.В. Новий спосіб деформування заготовок залізничних коліс на пресах і його технологічні можливості / / Металургійна і гірничорудна промисловість. - 2011. - № 7. - С. 222 - 226.
- Яковченко А.В. Удосконалення технології штампування колісних заготовок / А.В. Яковченко, А.А. Пугач, С.А. Снітко, Н.І. Івлєва / / Вісник Приазовський державний технічного університету. Серія: Технічні науки / Маріуполь: ПДТУ, 2012. - № 1 (24). - С. 94 - 99.
- Снітко С. А. Механізм виправлення асиметрії при штампуванні колісних заготовок / С.А. Снітко, А.В. Яковченко / / Обробка матеріалів тиском: зб. науч. тр., Краматорськ: ДДМА, 2012. - Вип.4 (33). - с.95-99.
- Снітко С. А. Технологічні схеми і механізми, що забезпечують підвищення точності і стабільності розмірів штампованих колісних заготовок / С.А. Снітко / / Сталь. - 2013. - № 10. - С. 72 - 80.
