RESEARCH OF BROADBAND PASSIVE OPTICAL ACCESS NETWORKS (LR-PON)
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Review of research and development
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
PON technology is considered one of the most promising technologies for broadband access over a fiber optic channel. It is a rapidly developing one, one of the most effective technologies for building multi-service access networks in the "last mile" section. Such networks, due to their longevity, low attenuation of the optical signal and huge bandwidth, make it possible to fully discover the economic potential of the family of FTTx architectures (English fiber to the x optical fiber to point X).
Based on PON technology, completely passive optical communication networks of the tree topology with the central node OLT (optical line terminal) and subscriber nodes ONU (optical network unit) are built. The central node OLT provides connection to the backbone network and subscriber nodes ONU, receiving and transmitting data. On the branches of the tree are installed passive components - splitters (splitters), completely independent of power and maintenance. The central node of the OLT may comprise several transceiver modules providing information to ONU subscriber units, each of which can provide high-speed Internet access to hundreds of subscribers.
The newest LR-PONs can have downstream and upstream speeds of 10 Gbps and 2.5 Gbps, respectively. Scalability of the network reaches 100 km. Up to 17 power dividers can be used here. Each of the dividers works with different pairs of ascending and descending streams, separated by the wavelength and serving up to 256 ONUs. In total, up to 4352 ONUs can be connected to the OLT. LR-PON networks have the topology of a multistage tree with many branches and allow the integration of optical access networks and zonal networks. Extended functionality LR-PON offers significant cost savings by reducing the number of required optical-electrical-optical conversions. Thus, the trend of PON development leads to a change in the structure of urban networks in the direction of reducing the number of hubs. [ 1 ]
1. Theme urgency
One of the most important requirements for modern telecommunications systems is secrecy and confidentiality of communication. In fiber-optic communication lines a reliable, protected infrastructure should be formed using all available means and methods of information protection.
Information security of communication lines includes:
- protection against accidental actions of the intruder;
- protection against the intentional actions of the offender;
- protection against security threats.
Now a new generation of PON networks has appeared, which is expected to be used more widely than previous ones, and therefore the danger from information threats has become higher.
It is assumed that LR-PON networks will have comprehensive security systems. To ensure the protection of information in LR-PON, it is necessary to develop and implement an information protection subsystem.
The main objectives of information protection, which should include:
- prevention of leakage of information through technical channels (including through the possibility of secretly receiving information in the form of technical devices);
- prevention of unauthorized destruction, distortion, copying, blocking of information;
In particular, a subsystem of protection against unauthorized exposure is needed, its main task is to counter theft, damage and distortion of data, including the protection of system resources.
Unauthorized access to the FOCL, despite the complexity and high cost, is still possible. Methods of removal, which can be used to intercept information from a fiber optic link, can be divided into three groups:
- by the method of connection: unbroken, discontinuous, local, extended.
- by the recording method and the amplifier;
The interception of information by any of the above methods is possible only if the integrity of the outer cable protective sheath is broken and direct access to optical fibers. The confidentiality of the information transmitted over the fiber-optic communication can be ensured by using special methods and means of protecting the linear tracers from unauthorized use.
There are many meteos that can be used, it is necessary to choose their combination in the best way, so that they work as quality, and they do not increase the cost of the system.
Thus, the task of developing a subsystem for detecting unauthorized intrusions of an integrated information security system in LR-PON networks is acoustical.[2]- [3]
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The goal of the research is to increase the level of information security of the new generation of LR-PON passive optical networks by improving the complex information security system based on modern methods of detecting unauthorized exposure.
The main objectives of the study:
1. Analyze existing methods of an integrated information security system in passive optical infocommunication networks;
2. Identify the range of tasks to ensure information security of the new generation of LR-PON passive optical networks;
3. Develop a subsystem for detecting unauthorized intrusions of a complex system of information security in LR-PON networks based on committed methods of detecting unauthorized exposure;
4. Develop a model of a subsystem for detecting unauthorized intrusions of an integrated information security system in LR-PON networks;
5. To model the developed model, to assess the qualitative indicators of its functioning and the expected effects from its implementation;
6. To evaluate the economic effectiveness of the proposed solutions;
7. Allocate occupational safety measures.
3. Review of research and development
Recently, fiber-optic communication lines (FOCL) are one of the most promising and developing directions of building a communication network in the world. In the field of information transmission systems with a large information capacity and high reliability of operation, FOCLs have no competitors. This is explained by the fact that they significantly exceed the wired ones by such parameters as throughput, length of the regeneration section, and also noise immunity.
It is believed that the fiber optic link, due to the peculiarities of the propagation of electromagnetic energy in the optical fiber (OB), has increased secrecy. This is explained by the fact that the optical radiation, which is the carrier of information, propagates to the OB according to the law of total internal reflection, and for electromagnetic radiation, the electromagnetic radiation decreases exponentially. Areas where electromagnetic leakage and unauthorized information removal (NSI) are possible are relatively small, "classical" radio engineering methods (transceiving equipment, regeneration points) are studied and localized. For this reason, these areas can be relatively easily put under control.
There is always the possibility of removing information from the optical fiber cable. Unauthorized access to fiber-optic lines, despite the complexity, is still possible. Methods of removal, for intercepting information from a fiber-optic link, can be conditionally divided into several groups:
1. By the method of connection:
1.1 is seamless;
1.2 Discontinuous;
1.3 local;
1.4 extended.
2. By the method of registration and amplification:
2.1 passive - registration of radiation from the side surface of the OB;
2.2 active - registration of radiation output through the side surface of the OB with the help of special means that change the signal parameters in the VOLT;
2.3. Compensation - registration of radiation output through the side surface of the OB with the help of special means, followed by the formation and insertion into the radiation of radiation compensating for the loss of power in the emission of radiation;
All unauthorized actions of the attacker can be represented by six areas, each of which has the following objectives:
- analysis of traffic;
- eavesdropping;
- Deliberate delay of information;
- denial of service;
- changing QoS service quality characteristics;
- spoofing, that is, the transfer of information by an attacker to the network on behalf of another person.
The number of possible unauthorized impacts in the LR-PON network has been reduced to two: eavesdropping (traffic analysis) and "service disruption."
The list of unauthorized impacts can be expanded, but they will relate to network protocols, control systems, whereas we are interested in unauthorized impacts associated with the LR-PON network infrastructure.[4]-[5]
There are several methods for implementing unauthorized actions from the attacker: removing a portion of the optical signal power; Influence on information signals by means of signals of the malefactor entering into their spectrum, and also not entering into a spectrum of information signals.
For the analysis, these protection methods are chosen, because they can be implemented quite easily and cause other consequences when comparing them with other types of unauthorized influences on other types of networks. These types of impacts are easily realized due to the technologies already available on the market, which threatens the security of LR-PON networks.
Each of the components that make up the LR-PON network can be the source of unauthorized exposure through it.
The methods of quantum cryptography potentially provide a high degree of protection against interception of information on the communication line due to the transmission of data in the form of individual photons, since the non-destructive measurement of their quantum states in the communication channel by the interceptor is impossible, and the fact of interception of photons from the channel can be detected by changing the probabilistic characteristics of the photon sequence .
The topology of PON's passive optical network(image 1) plays an important role in the security and security of the network as a whole. Obviously, the most secure network will be a network with a star topology, in which a separate optical cable will go directly from the service provider's building to the user. The use of such a topology is unlikely because of the large capital costs of building a network. But unauthorized exposure at one point will not affect all other users of the network in any way, and it will be easier to detect unauthorized exposure.
Building a network with a topology of the "tree" type is economically advantageous, as optical splitters appear in the network, solving the problem of laying an optical cable to each subscriber or to a group of subscribers. But in the event that unauthorized exposure will be made just before the optical splitter, the result will be a deterioration in the quality of the service or its termination at once for many users.
The situation will be different if the attacker produces "eavesdropping". This type of exposure is more secretive and is not aimed at disrupting the service, but on receiving information signals for further work with them. Considering the eavesdropping effect in the 1st case, the amount of compromised information will be much less than in the case of the topology "tree" or the topology "network". In more complex topologies, when multiple splitters are used, unauthorized eavesdropping is difficult to detect.
On the backbone optical networks, expensive information protection solutions can be used to ensure reliable and secure data transmission. But using the same solutions on PON networks would negate all the advantages of this technology, which are to provide a wide range of consumers with broadband services.[6]-[8]
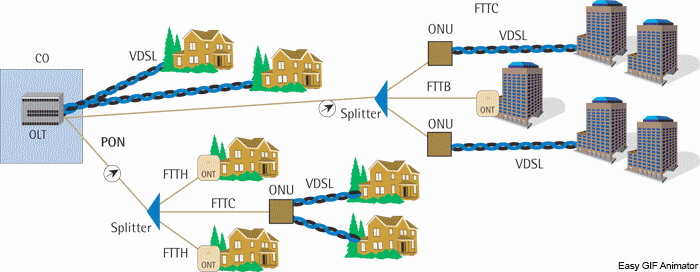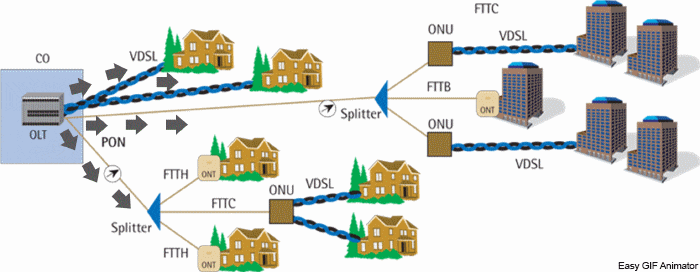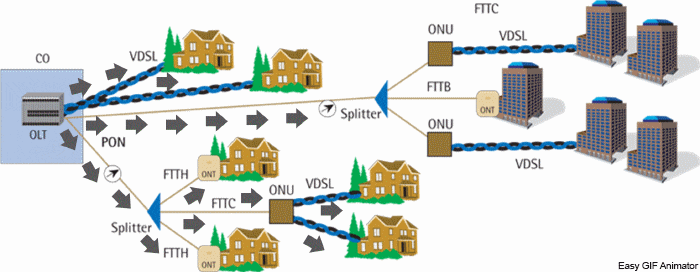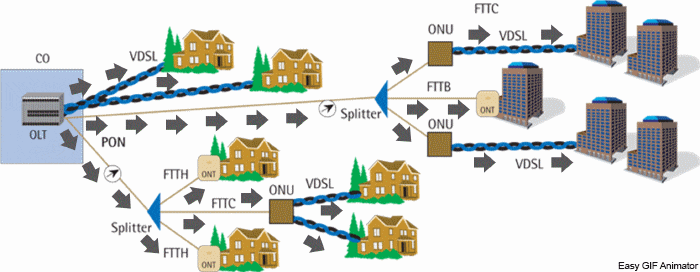
Figure 1 - LR-PON network architecture (animation: 12 frames, infinite repetition of cycles, 83 kilobytes)
At present, work is underway to develop new methods for detecting unauthorized exposures. They are based on comparison of the received signal with the value obtained as a result of mathematical modeling of the communication channel. The use of similar techniques in the LR-PON network, taking into account the dynamic nature of user changes, and therefore the network architecture, is difficult. Thus, for PON networks new methods of detection of unauthorized impacts are required, which should combine a high degree of protection and high technical and economic indicators.
In fact, the possibilities of these methods will be somewhat different due to such reasons as the speed of detection of unauthorized exposure, the location of detection of unauthorized exposure (one or another segment of the network), etc.[7],[9]
Conclusion
There are various options for constructing specific systems, differing in the degree of protection and control of NDs for information transmitted over the fiber optic link. This makes it necessary to conduct special studies to assess the implemented scientific and technical solutions and their compliance with the requirements for ensuring the protection of information.
It should also be noted that all of the above protection methods and their combinations can ensure the security of information only within the framework of known ND models. At the same time, the effectiveness of protection systems is determined both by the discovery of new ones and by the improvement of NSI technologies using already known physical phenomena. Over time, the enemy can learn new methods of interception, it will be necessary to supplement the protection, which is not characteristic of cryptographic methods of protection, which are calculated for a sufficiently long period.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the need to research and search for effective protection of fiber optic links in LR-PON networks is the task of today's task.
When writing this essay, the master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: June 2018. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after the specified date.
References
1. Анализ живучести мультисервисных сетей связи, построенных по технологии PON [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа:https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/analiz-zhivuchesti-multiservisnyh-setey-svyazi-postroennyh-po-tehnologii-pon – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
2. Коваль І.Б. Защита информации в волоконно-оптических линиях связи [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа:http://intkonf.org/koval-ib-zaschita-informatsii-v-volokonno-opticheskih-liniyah-svyazi/ – дата доступа: декабрь 2017.
3. В.А. Михеев Основы постороения подсистемы защиты информации многофункциональной информационной системы [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа:https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/osnovy-postroeniya-podsistemy-zaschity-informatsii-mnogofunktsionalnoy-informatsionnoy-sitemy – дата доступа: декабрь 2017.
4. Защита информации на волоконно-оптических линиях связи от несанкционированного доступа [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа:http://pnzzi.kpi.ua/2/02_p249.pdf – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
5. Проблемы защиты информации, передаваемой по волоконно-оптическим линиям связи, от несанкционированного доступа [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа:http://emag.iis.ru/arc/infosoc/emag.nsf/0/c0a700122533e000c32575be003cb751?OpenDocument – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
6. Изучение способов съема информации с волоконно-оптических линий [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа:https://bibliofond.ru/view.aspx?id=607283 – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
7. Вопросы информационной безопасности сетей PON [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа: http://www.tssonline.ru/articles2/in-ch-sec/vopr_inf_bezopasn_setey_pon – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
8. Каналы и методы несанкционированного доступа к информации [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа: https://studfiles.net/preview/5828099/page:16/ – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
9. Технические средства защиты информации [Электронный ресурс] – режим доступа: https://doklady.bsuir.by/m/12_104571_1_62726.pdf – дата доступа: ноябрь 2017.
