Abstract
Attention! While working on the essay the master`s dissertation is still being written. Expectable date of completing the dissertation is July, 2019. The complete text of the dissertation and materials on the research topic can be received from the author or his scientific adviser after the specified date.
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Contents of the concept
corporate culture
, its functions and key features - 2. Sources, factors and directions, determining the change and formation of corporate culture in the organization
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The modern dynamically developing economy leads to the fact that firms and organizations are forced to constantly evolve in order not to remain outside the board of progress and business. The saturation of absolutely all markets with goods to such an extent that companies have to literally fight for buyers leads to a complete rethinking of the principles and objectives of the functioning of various structures within an enterprise.
This potential of the organization’s activities is largely ensured by the corporate culture. It is a system of generally accepted in the organization of ideas and approaches to the formulation of the case, to the forms of relations and to the achievement of the results of activity that distinguish this organization from all others.
The main goal of a corporate culture, as a phenomenon, is to help people more productively fulfill their responsibilities in organizations and get more satisfaction from it. And this in turn will lead to an improvement in the economic performance of the organization as a whole. After all, a cohesive, driven by a single goal, working as a streamlined clock mechanism, a team, will bring much more benefit.
Business efficiency for an organization is the most important indicator, without any doubt, therefore it is obvious that the influence of an organization’s corporate culture on it is enormous, which means that its study is an actual research task.
Relevance of the topic:
Modern goals of human development need to provide the necessary conditions for this, among which conditions for the use of labor resources, which are generally embodied in the category of quality of working life
, occupy an important place. It is the quality of working life that provides a combination of interests that are often incompatible: the tasks of social and economic development, the needs of the parties to social and labor relations, etc.
The object of the research is the formation of a corporate image in the DPR and the role of social standards in the quality of working life as a complex multi-level socio-economic system.
The subject of the research is the theoretical and methodological foundations for ensuring corporate image in the State Enterprise DonetskStandardizationMetrology
, aimed at improving its competitiveness.
Research methods:
Theoretical and methodological basis of the study are the fundamental principles of economic theory, scientific works of domestic and foreign scientists.
The practical significance of the results is to develop recommendations for improving the corporate image of the enterprise.
1. Contents of the concept corporate culture
, its functions and key features
At all times, the study of culture was given a lot of scientific work and its great importance was always noted in the development of a civilized society, the rallying of people and the creation of material and spiritual values. Currently, culture has penetrated almost all spheres of society and now the organization’s culture and corporate culture are defined and understood as a pledge of effective activity, and a lot of time is devoted to it.
After all, a team of a few dozen or hundreds of people cannot rally, or stand on the basis of mutual sympathy and love of all members. To do this, they are too different in nature, and feelings of sympathy are unstable and changeable. To solder people, we need clearer and stronger bases, such as ideas, rules, regulations, taboos. All this constitutes corporate culture. The purpose of building a culture is to ensure the commitment of people to the company and promote the manifestation of their potential.
Corporate culture — this is not only the company's image, but also an effective tool for strategic business development. Its formation is always associated with innovations aimed at achieving business — goals and, therefore, increase competitiveness.
Bearers of corporate culture are people. However, in organizations with a well-established culture, it is as if separated from people and becomes an attribute of the organization, its part, which has an active influence on workers, modifies their behavior in accordance with the norms and values that form its basis. Management uses this culture to attract certain types of workers and to stimulate certain types of behavior. Culture, the image of the company are supported or weakened by the reputation of the company.
At nowadays, it has become traditional to single out three levels of corporate culture (Fig. 1).
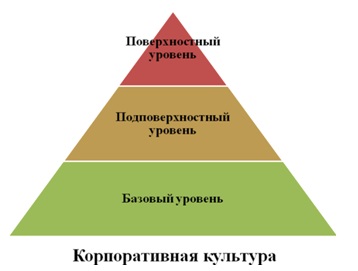
Figure 1 — Levels of corporate culture of the organization
- Superficial (symbolic) level — this is all that a person can see and touch: corporate symbols, logo, company calendars, company flag, company anthem, the special architecture of the building and Also, myths, legends and stories related to the founding of a company, the activities of its managers and prominent employees are also referred to the symbolic level. Such legends and stories are usually transmitted orally;
- Subsurface level — combines the values and norms, consciously recorded in the documents of the organization and designed to be guiding the daily activities of the members of the organization. At this level, the values and beliefs shared by the members of the organization are examined in accordance with the extent to which these values are reflected in symbols and language. The perception of values and beliefs is conscious and depends on the will of the people. Researchers often confine themselves to this level, since at the next level almost insurmountable difficulties arise.
- Basic (deep) level — basic assumptions arising from the members of the organization on the basis of personal patterns, supported by or changing successful experiences of joint actions and in most cases unconscious, some
air
of corporate culture, which is odorless and odorless, but not normally noticed. These basic assumptions are difficult to comprehend even to members of the organization themselves without special focus on this issue. These hidden and faithful assumptions guide people's behavior, helping them to perceive the attributes that characterize corporate culture.
The structure of a corporate culture includes the following elements: the mission of the organization, its philosophy, leadership style, values of the organization, the system of motivation, incentives, rewards and punishments of employees, which are shown in Fig.2.
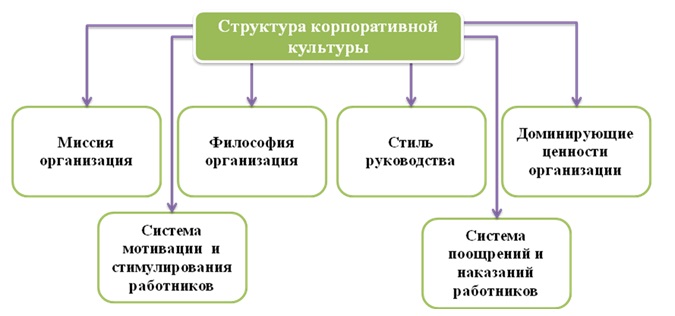
Figure 2 — Structure of corporate culture
Defining the essence of corporate culture, you must highlight it main functions, presented in Fig.3.
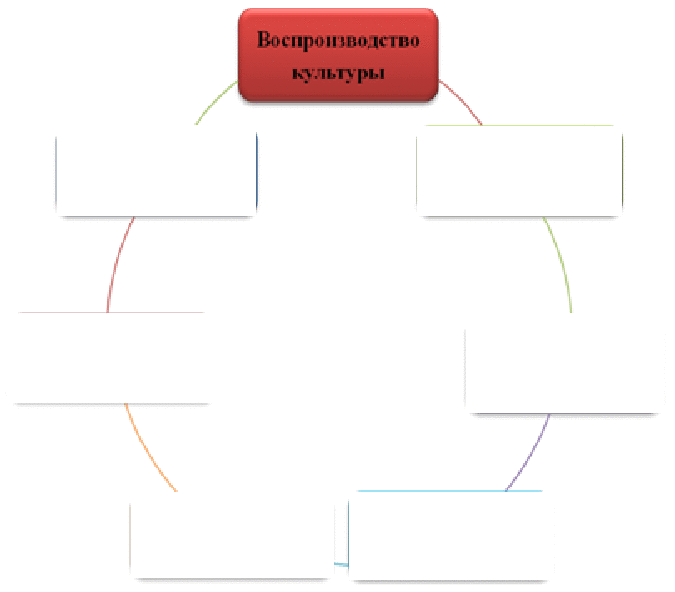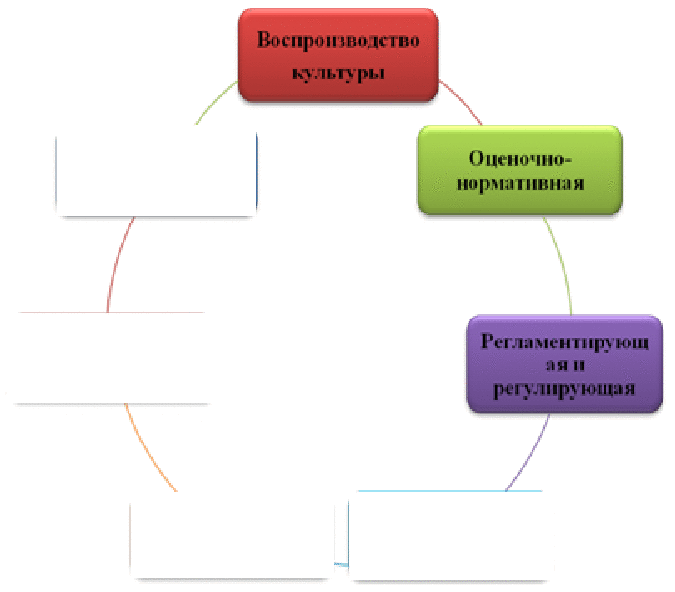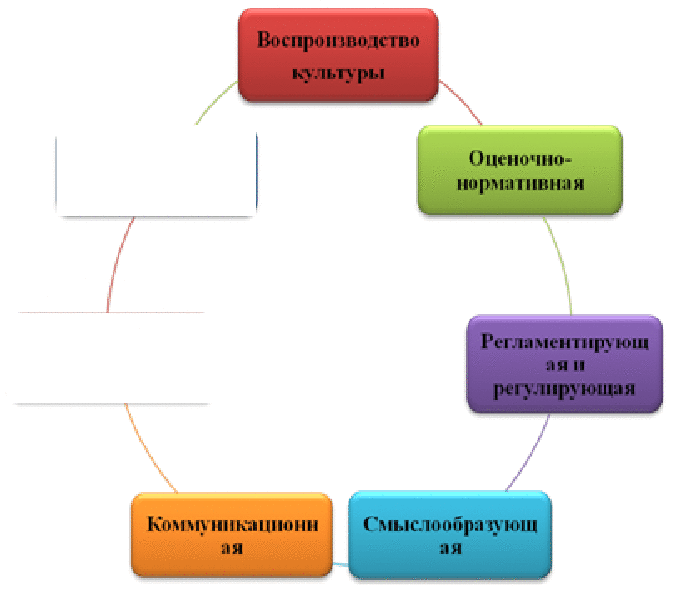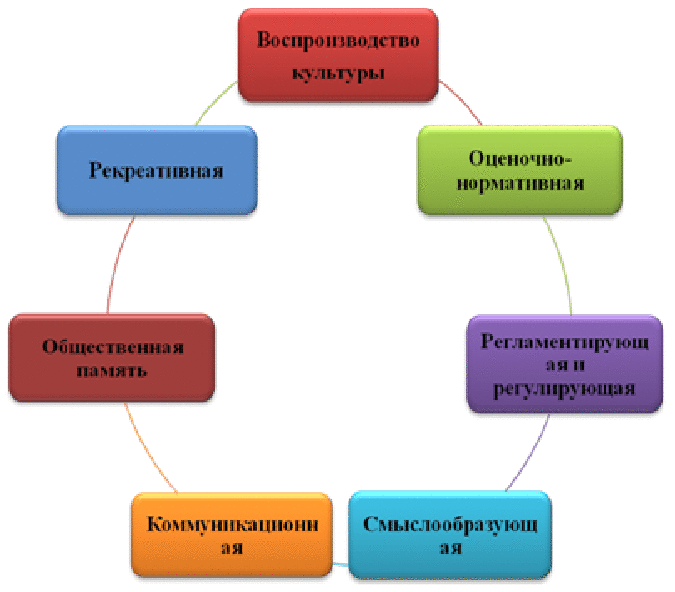
Figure 3 — Functions of corporate culture
(The animation consists of 7 slides: Corporate — Recreative — Public memory — Reproduction of culture — Estimated - normative — Regulatory and regulating — Meaning , size 26 KB)
- The reproduction of the best elements of the accumulated culture, the production of new values and their accumulation;
- Evaluation and normative function (based on a comparison of the real behavior of a person, group, corporation with our norms of cultural behavior, with ideals, we are talking about positive and negative actions, humane and inhuman, elegant and rude, progressive and conservative);
- The regulating and regulating function of culture, that is, the use of culture as an indicator and regulator of behavior;
- Cognitive function (for example, cognition and assimilation of corporate culture, carried out at the stage of adaptation of the employee, contributes to its inclusion in the life of the collective, in collective activity, determines its success);
- Semantic function: corporate culture influences a person’s worldview, often corporate values turn into values of an individual and a collective or conflict with them;
- Communication function — through the values adopted in the corporation, the norms of behavior and other elements of culture are ensured mutual understanding of workers and their interaction;
- The function of public memory, the preservation and accumulation of corporate experience;
- Recreational function — the restoration of spiritual forces in the process of perceiving elements of a corporation’s cultural activities is possible only in the case of a high moral potential of a corporate culture and employee involvement in it and the sharing of its values.
Thus, we can conclude that the value of corporate culture in the activities of the organization is very high. Effective management of an organization’s corporate culture can contribute to its successful operation and further development. From its level will depend on the level of competitiveness of the organization, and its reputation in the market of goods and services.
2. Sources, factors and directions, determining the change and formation of corporate culture in the organization
Changing corporate culture includes the formation of a new mission, the goals of the organization and its ideology, a model of effective leadership, the use of previous experience, ingrained traditions and procedures, an assessment of the effectiveness of the organization, its formal structure, design of premises and buildings, etc.
The possibility of changing a culture is influenced by the following factors: an organizational crisis, a change in leadership, a stage in an organization’s life cycle, its age, size, level of culture, the presence of subcultures.
Changing a culture requires a specific strategy for managing culture in an organization. She suggests:
- culture analysis, which includes auditing a culture to assess its current state, comparison with the intended (desired) culture and an intermediate assessment of its elements that need to be changed;
- development of special offers and measures.
The formation of a certain culture in an organization is connected with the specifics of the industry, in which it operates, with the speed of technological and other changes, with the characteristics of the market, consumers and etc. It is known that companies in the high technology
industries have a culture that contains innovative
values and a belief in change
. However, this feature may be manifested differently in companies of the same industry, depending on the national culture in which the organization operates.
Factors affecting the formation of corporate culture:
- individual autonomy — the degree of responsibility, independence and opportunities for the expression of initiative in an organization;
- structure — the interaction of bodies and persons, the current rules, direct leadership and control;
- direction — the degree of formation of the goals and prospects of the organization;
- integration — the extent to which parts (subjects) within an organization enjoy support in the interests of coordinated activities;
- managerial support — the degree to which managers provide clear communication links, assistance and support to their subordinates;
- support — the level of assistance provided by managers to their subordinates;
- stimulation — the degree of dependence of remuneration on the results of labor;
- identification — the degree of identification of workers with the organization as a whole;
- conflict management — the degree of decidability conflicts;
- risk management is the degree to which employees are encouraged to innovate and take on risk.
Sources of corporate formation culture:
- views, values, ideas of the founders of the organization;
- collective experience gained in the creation and development of the organization;
- new attitudes, values and ideas introduced by new members of the organization and leaders.
For the effective impact of corporate culture on the development of the enterprise, appropriate measures should be developed.
Their development should be carried out as follows directions:
- image formation enterprises and its components, such as the philosophy, mission and main goals of the enterprise;
- development of a non-traditional motivation system, including moral incentives, rituals, engaging employees to participate in management;
- development of a program for comparing the expectations and values of the candidate for the vacancy and the organization itself;
- integration of newly hired employees into the organization’s staff.
All these areas are interrelated. Only in unity they create the necessary synergistic effect of the corporate culture on the development of the enterprise, Fig.4.
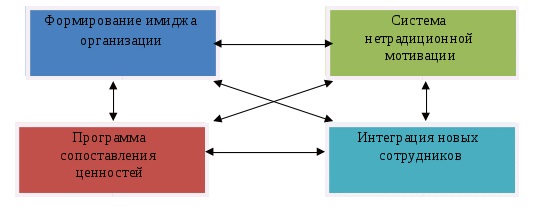
Figure 4 — Directions of the formation and development of corporate culture
The image of an enterprise is the positive image that develops with the customers of this enterprise: buyers and users of goods and services, suppliers, customers, partners, shareholders.
The image is made up of the mission of the enterprise, which reveals the reason and purpose of its existence, the difference of this enterprise from others.
The next step to create the prerequisites for a positive impact of corporate culture on the development of an enterprise is the formation of a system of non-traditional motivation, which includes moral incentives, participation in the processes taking place in the organization, and rituals of the enterprise.
In general, the process of changing and forming a corporate culture occurs through external adaptation and internal integration of the company. The process of external adaptation is associated with the search and organization of its niche in the market and its adaptation to the constantly changing external environment. The process of internal integration is associated with the establishment and maintenance of effective relationships in the work between team members.
Thus, the change and the formation of corporate culture is an integral part of the corporate management of the organization, which must be given a lot of strength and resources.
Conclusion
The problem of increasing the efficiency of management and organizations constantly arises before the leadership of any company. These problems are especially relevant for Russian corporations. And undoubtedly, the company's corporate culture is a decisive factor in increasing efficiency.
Effective corporate culture is the most effective way to unload the leader. It is better, with the participation of the team, sets the long-term goal of the organization, creates corporate standards that must be followed to effectively achieve this goal, convinces the correctness of these goals and standards of the organization’s employees, and finally introduces a mechanism for transmitting (broadcasting) these corporate values to the neophytes.
Summing up, it is necessary to note once again that corporate culture is a tool in the hands of a manager (manager), with which you can lead a company to success, prosperity and stability, but with inept or inappropriate use, directly opposite results are possible.
Therefore, the corporate culture must be studied, followed by its formation, improve and regulate its changes. It should become an integral part of the entire company, be adequate to modern requirements dictated by economic and technological development, the specifics of Russian legislation and mentality, as well as the specifics of a particular organization and help achieve the goals set, and, consequently, increase the efficiency of the company as a whole.
References
- Баринов В. А., Макаров Л. В. Корпоративная культура организации в России // Менеджмент в России и за рубежом. — 2002. — № 2.
- Колношенко О.В. Концепция менеджмента. Конспект лекций в схемах: Учебное пособие для вузов. — М.: Издательство
Экзамен
, 2007. – 286с. - Резник С.Д. Организационное поведение: Учебник. — 2-е изд., перераб. И доп. — М.: ИНФРА-М, 2009. — 430 с.
- IC CSR-08260008000
Social responsibility. Requirement
. - ГОСТ Р ИСО 26000-2012
Руководство по социальной ответственности
. - SA 8000 (Social Accountability)
Социальная ответственность
. - Ивановская Л.В. Управление персоналом: теория и практика. Кадровая политика и стратегия управления персоналом: Учебно-практическое пособие / Л.В. Ивановская. — М.: Проспект, 2013. — 64c..
- Егоршин, А. П. Управление персоналом: Учебник для вузов / А. П. Егоршин. — 3-е изд. — Н. Новгород: НИМБ, 2001. — 720 с.
