Abstract on the theme of master's work
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. Purpose and goals of the research
- 3. Theoretical aspects of formation of the strategy of anti-crisis development of socio-economic systems
- 3.1 The essence of anti-crisis management of socio-economic systems
- 3.2 The factors of the effectiveness of the actions of the manager of the anti-crisis development of socio-economic systems
- Conclusion
- List of used sources
Introduction
The unstable state of the economy over the past few years has adversely affected the work of most enterprises. The global economic crisis, the instability of the economic and political environment, the imperfection of legal and tax legislation have led to an increase in the number of insolvent enterprises that are on the verge of bankruptcy and in most cases are subsequently liquidated [11].
Anti-crisis management is not a new concept for the region's economy, caused by the existing conditions in which enterprises operate, but now, given all factors, this type of management is very relevant for our region. The emergence of anti-crisis management of the enterprise is aimed at their sustainable development and growth of the economy as a whole. It should also be noted that the theoretical approaches to determining its essence, features, practical significance are not yet fully formed and insufficient methodological elaboration is still at the stage of formation.
1. Relevance of the topic
The relevance of the chosen topic is that it is the anti-crisis management that can help minimize the negative consequences of the crisis, improve the financial system of the enterprise, develop and implement new activities related to the further development of the company. Therefore, an important place in the enterprise management system should be occupied by the anti-crisis management [12].
2. Purpose and goals of the research
The purpose of the work is a strategic direction of anti-crisis development on the basis of theoretical studies and analysis of the development potential of the construction industry in DPR.
The main goals of the research:
- To reveal the essence of anti-crisis management of socio-economic systems.
- To learn the factors of the anti-crisis development of socio-economic systems.
- To analyze the principles for the formation of a strategy for the anti-crisis development of the socio-economic system.
- To conduct diagnostics of the state and problems of development of the building industry in DPR.
- To analyze the factors and potential development of the building industry in DPR.
- To learn the principles of forming a strategy for the anti-crisis development of the building industry in DPR.
- To form directions for the anti-crisis development of the building industry in DPR.
An object of the research: the building industry in DPR.
A subject of the research: strategy for the anti-crisis development of the building industry in DPR.
The theoretical basis of this work were the works of domestic and foreign economists, whose works are mainly devoted to the problems of crisis management and crisis prediction, among which it is necessary to note such authors as V.V. Zhilchenkova, M.M. Musin, O.N. Sharnopolskaya, M. Meskon and others [7,13].
3. Theoretical aspects of formation of the strategy of anti-crisis development of socio-economic systems
The concept of «crisis» is a main while considering issues of anti-crisis management. From what content is put into it, the content of the crisis management depends directly.
3.1 The essence of anti-crisis management of socio-economic systems
The crisis belongs to the category of complex phenomena, without studying its nature and essence it is impossible to bring the controllability of systems to a qualitatively new level. The main purpose of crisis management is to regulate crisis and risk situations, to prevent them and to overcome negative social and economic consequences in the event of their occurrence. Therefore, one of the most important problems in the theory of crisis management - a detailed study of the nature of crises, the definition of their types and the development of a specific crisis management strategy [10].
In the history of mankind the crisis has always been connected either with a catastrophe or with a cataclysm. Natural or human forces caused trouble or an invasion, sharply worsening life. In recent years, in the modern literature, speaking of the crisis, they mean the spontaneous process of avalanche destruction of the system, and the regularities of this process are exactly the same for a variety of systems, be it the human body, family, organization or country. The main function of the crisis is the elimination of those elements that are not viable and least resistant. In the economy, crises contribute to the liquidation of weak enterprises with outdated methods of production and forms of organization of enterprises. Most enterprises do not react to their crisis. The crisis of the enterprise is caused by the discrepancy of its financial and economic parameters with the parameters of the environment. So, the crisis of a larger number of enterprises extends on all economy. Therefore, an important place in the enterprise management system should be occupied by anti-crisis management. Despite such an obvious need to study the issue of anti-crisis management of an enterprise and its application in practice, the definition of the very term «anti-crisis management» is ambiguous and can be treated in different ways [1,3].

Figure 1 – Interpretation of anti-crisis management
(animation: 5 shots, 169 Kb)
After learning the different approaches of scientists to the definition of this concept, it can be concluded that the crisis management of the enterprise is a clearly defined plan of systematic measures that take into account the specifics of the enterprise and industry that are able to adapt flexibly to changing market conditions and aimed at identifying, preventing and preventing the negative impact of crisis phenomena, as well as minimization of their consequences. The anti-crisis management of the enterprise is aimed at preventing or eliminating adverse business phenomena through the use of the full potential of modern management, the development and implementation of a special program at the enterprise that has a strategic nature that allows to remove temporary difficulties, preserve and increase market positions under any circumstances, own resources [2,5].
Therefore, the purpose of crisis management is the development and implementation of measures aimed at neutralizing the most dangerous trends leading to a crisis. This set of measures is designed to ensure a firm position of the enterprise in the market and its stable and stable financial activity under any economic, political and social changes in the state. The main task of crisis management is to prevent a crisis, which implies a comprehensive, systematic and strategic approach to analyzing and solving emerging problems. Also, the important task of anti-crisis management is to overcome the crisis that has arisen, that is, prevention of bankruptcy of the enterprise and restoration of its solvency. This is a management in the conditions of a specific crisis situation and is aimed at getting the enterprise out of this anti-crisis situation and restoring its competitiveness.
Crises are different, and their management can be different. This variety, among other things, manifests itself in the system and management processes (algorithms for developing managerial decisions) and especially in the management mechanism. Thus, assessing your own crisis and your inability to settle obligations, you can provide a set of measures to restore solvency based on an analysis of the financial stability of the organization and the reasons that led to the loss of its solvency to exclude or significantly reduce their impact on the financial condition of the enterprise. And the reasons can be identified only on the basis of professional analysis. In understanding the crisis, not only its causes, but also various consequences are of great importance: it is possible to renew the organization or its destruction, recovery or the emergence of a new crisis. The way out of the crisis is not always connected with positive consequences. It is impossible to exclude the transition to a state of a new crisis, perhaps even deeper and more prolonged. Crises can arise as a chain reaction. There is also the possibility of the preservation of crisis situations for a fairly long time. This may be due to certain political reasons. In general, the consequences of the crisis are closely related to two factors: its causes and the ability to manage the processes of crisis development.
The consequences of the crisis can lead to abrupt changes or a mild continuous and consistent exit. And post-crisis changes in the development of the organization are long-term and short-term, qualitative and quantitative, reversible and irreversible. Different consequences of the crisis are determined not only by its nature, but also by crisis management. Domestic and foreign practice shows that an effective crisis management strategy should unite all functional areas of management and lead to the mobilization of internal reserves to increase profitability and economic development of the enterprise. Most often, the effectiveness of crisis management is assessed by the degree of achievement of the set goals. The most important in the formation of the system of crisis management is to ensure conditions when financial difficulties can not be permanent. At each enterprise, a management mechanism should be established to address the problems that arise until they become irreversible. Managed process of preventing or overcoming the crisis, meeting the organization's goals and corresponding to the objective trends of its development, is an anti-crisis development of the enterprise [4,9].
3.2 The factors of the effectiveness of the actions of the manager of the anti-crisis development of socio-economic systems
The effectiveness of the withdrawal of the enterprise from the crisis, first of all, depends on the actions of the crisis management manager, his preparedness in the field of crisis management - the depth of knowledge of the fundamentals and ownership of the methods of anti-crisis development, the ability to apply them in practice in accordance with the situation, the ability to analyze and generalize the experience of crisis management for further its development. Anti-crisis development should be accompanied by an increase in its effectiveness. In turn, the increase in the efficiency of crisis management is determined by the growth of its potential, i.å. the possibility of positive changes, the availability of the necessary resources and conditions for their use.
In the tendencies of changing the potential and effectiveness of management, the dangers of the crisis are also hidden. Anti-crisis development, like any other, can be ineffective or more effective. The effectiveness of anti-crisis development is characterized by the degree of achievement of goals of mitigation, localization or positive use of the crisis in comparison with the resources spent on it. It is difficult to assess this efficiency in accurate estimates, but it can be seen in the analysis and overall assessment of management by the crisis management, its success or miscalculations [6].
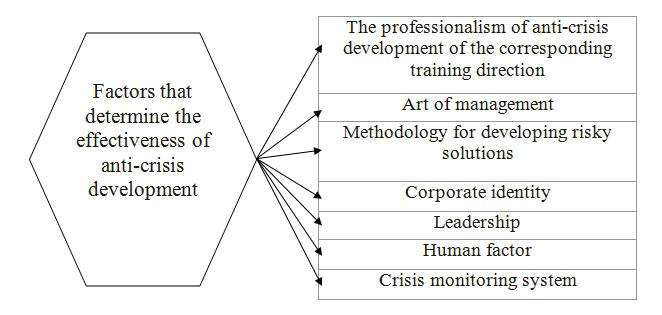
Figure 2 – Factors of the afectiveness of anti-crisis management
We can identify the main factors that determine the effectiveness of the actions of the crisis management. Their understanding and differentiation help them analyze and subsequently successfully apply in practice. Let's single out the main ones [8,10]:
- Professionalism of anti-crisis development and special training. In this case, we mean not only the overall professionalism of management, which, of course, is necessary, but also those professional knowledge and skills that reflect the features of crisis management. Such professionalism is born in the processes of special education, the purposeful accumulation of experience and the development of the art of management in critical situations. In recent years, more attention has been paid to specialized training of crisis managers who are able to take the enterprise out of the crisis with the least losses, their professional training is focused on crisis situations.
- The art of management, given by nature and acquired in the process of special training, should be highlighted specifically in the list of factors of the effectiveness of anti-crisis development. In many crisis situations, the individual art of management is the decisive factor in overcoming or mitigating the crisis. Therefore, for crisis management it is especially important to conduct psychological testing of managers, select those individuals who are able to respond sensitively to the approaching crisis and manage in extreme situations.
- Methodology for developing risky solutions. Such a methodology should be created and mastered, because it largely determines the qualities of management decisions, such as timeliness, completeness of reflection of the problem, concreteness, organizational significance. These properties are of particular importance in anti-crisis development. Scientific analysis of the situation, forecasting trends. These factors can not but affect the effectiveness of anti-crisis development. The vision of the future and not subjective, but based on an accurate, scientifically sound analysis, allows you to constantly keep in sight all the manifestations of the approaching crisis or pass.
- An important factor in the effectiveness of anti-crisis development is also corporatism, which can manifest itself in an organization or firm to varying degrees. Corporatism is the understanding and acceptance by all employees of the organization's goals, the readiness to work selflessly to achieve them, this is a special kind of integration of all business, social, psychological and organizational relations, this is internal patriotism. Corporateism is a reliable pillar of anti-crisis development. But it does not arise by itself, but is the result of management and an element of its purpose, as well as a means in the development mechanism.
- Leadership is also included in the aggregate of factors of effective anti-crisis development. But not every leadership. There are many of its shades and modifications. Leadership is determined not only by the personality of the manager, but also by the established style of work, the structure of the management personnel, strengthened by the trust in the manager, the authority of the authorities. The reliance on leadership can play a decisive role in overcoming the crisis or mitigating it. But this requires the search and design of leadership. This sounds unusual, but it will be understandable if you bear in mind that leadership is not only a manager's personality, but also a characteristic of the entire development system, a characteristic of the development organization. Efficiency and flexibility of management play a special role in the effectiveness of anti-crisis development. In crisis situations, there is often a need for quick and decisive action, operational activities, changing management of situations, and adapting to the crisis. Inertia can play a negative role in this case.
- A separate point is the human factor. To a certain extent, it reflects the factors of corporatism and leadership, the art of management. But for anti-crisis development, one must keep in mind that there is a concept of an anti-crisis team - the closest assistants to an anti-crisis manager who can enjoy his special trust and are able to implement a program of anti-crisis development in a coordinated and purposeful manner. There is a good expression «With him I can go to scouting». Intelligence is a collection of unforeseen extreme situations, which can be overcome only by people who are true to the common idea and design and those who unconditionally trust each other. The human factor also works in the anti-crisis development.
- A significant factor in the effectiveness of anti-crisis development is a system for monitoring crisis situations. It is a specially organized action to determine the probability and reality of a crisis and is necessary for its timely detection. An important circumstance for management is knowledge about the crisis, its nature, possible manifestations in the life of the system, which is the basis for developing measures to prevent or mitigate the negative and enhance the positive effects. With the increasing complexity of production management in its development must outpace development. Only then can it be effective. Therefore, the more we know about the processes of anti-crisis development, its technology, the more efficient this process will take place, the more stable our domestic socio-economic systems will work.
Conclusion
The anti-crisis management is a whole complex of interrelated measures from early diagnosis of the crisis to measures to overcome it, i.e. the essence of crisis management is the complex of measures for forecasting, identifying, preventing and eliminating crisis phenomena at the enterprise. Crisis management is based on the principles that distinguish crisis management from the usual. In anti-crisis management, the following functions are distinguished: pre-crisis management, management in crisis conditions, management of crisis recovery processes, stabilization of unstable situations, minimization of losses and missed opportunities, timely decision-making. In the practice of crisis management, a rich methodological basis has been developed, which is divided into two large groups of methods: diagnostic methods and methods aimed at overcoming the crisis, which, in turn, are divided into a number of specific methods [9].
Prospects for the economy of the DPR today lie far beyond the post-war reconstruction alone. It is clear that at the moment the only vital task is to stop the fighting, de-escalate the conflict and revive the lost industrial potential. However, today it is worthwhile to think about the fact that the world economy has already moved to the 6th and tomorrow will step into the 7th technological structure, and in them the regions where there are only metallurgical plants, mines and chemical plants will be on the roadside of civilization. Therefore, it is necessary to start developing a strategy for the long-term development of the NDP, which will include not only steps for post-war reconstruction, but also for the transfer of the Republic's economy to a new innovative development path.
While writing this abstract, the master's work has not been completed yet. Final completion: June 2019. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his supervisor after the specified date.
List of used sources
- Ageeva, E.N. Perfection of the methods of anti-crisis financial management of the company / E.N. Ageeva // Anti-crisis development. – 2014. – ¹4. – Ñ. 15-17.
- Antipov, D.V. Features of organizational development of enterprise management / D.V. Antipov // Vector of science. – 2013. – ¹ 3. – Ñ. 139-144.
- Varlamova, A.S. Analysis of financial stability and solvency of the enterprise / A.S. Varlamova // Problems of Economics and Management. – 2015. – ¹ 9 (49). – Ñ. 4-11.
- Vasilyeva, E.S. Economic mechanism of crisis management: an evaluation of efficiency / E.S. Vasilyeva / / Handbook of the economist. – 2014. – ¹ 3. – Ñ. 67-74.
- Glukhova, D.V. Perfection of the mechanism of anti-crisis financial management in organizations / D.V. Glukhova // Anti-crisis management from scratch. – 2016. - ¹ 4. – Ñ. 179-182.
- Egorova, L.I. Methods of financial recovery of an economic entity / L.I. Egorova // Financial Management. – 2013. ¹ 4. Ñ. 25-39.
- Zhilchenkova, V.V. Technology of Anti-Crisis Management // HSE "Donetsk National Technical University" // electron. journal. [Electronic resource] - Journal access mode.: http://ea.donntu.ru/handle/123456789/29445.
- Zaitseva, S.S. Managerial global diagnostics of a financial condition of the enterprise / S.S. Zajtseva // Business in the law. – 2013. – ¹ 2. – Ñ. 326-329.
- Kovan, S.E. The theory of anti-crisis management of the enterprise. - M .: KONKURS, 2009. – 157 ñ.
- Knaus, R.R. Diagnosis of the crisis of the enterprise / R.R. Knaus // The New Word in Science: Prospects for Development. – 2016. – ¹ 4 (10). – Ñ. 108-111.
- Kuznetsov, S.Y. Formation of anti-crisis financial strategy / S. Y. Kuznetsov // Economics. – 2013. – ¹ 4 – Ñ. 136-141.
- Minaeva, E.V. Anti-crisis management / E.V. Minaeva // A primer for the economist. – 2015. – ¹ 7 – Ñ. 37.
- Sharnopolskaya, O.N., Modern crisis management of organizational development of an enterprise / Materials of the II International Scientific and Practical Conference April 20, 2016 Donetsk, - Donetsk National Technical University, 2016. – Ñ. 32-39.
