Abstract
Содержание
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Methodological basis of accounting for financial investments
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The main condition for the introduction of new forms of entrepreneurship based on private property, equity capital, is the development of an effective mechanism for financial investment. Investment activity of enterprises is one of the most difficult and risky types of business. Its results have a significant impact on the efficiency of entrepreneurship.
Among many reasons, the significant factors hindering the development of investment activity include incomplete and biased disclosure of information about investment processes in accounting and financial reporting, which does not allow to attract both external and internal investment resources in sufficient volume.
Improvement of investment attractiveness, expansion of volumes and forms of participation of foreign and domestic capital in the activities of business entities, access to international financial markets require the formation and improvement of adequate methodological support from accounting and its approximation to international financial reporting standards.
1. Theme urgency
Today, the issues of financial investments are studied by many scientists. Many scientific studies are devoted to the problems of determining the nature, classification, primary and subsequent evaluation, as well as the problems of accounting for financial investments. These works contain the analysis of primary, analytical, synthetic accounting of financial investments and problems associated with their accounting, and offer recommendations that could improve the situation. But, despite this, they have not been able to solve the problem to the end, because many contradictions have not only survived, but also escalated. Therefore, there is still a question of further improving the accounting of financial investments.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
Research object: organization of accounting and audit of financial investments in the conditions of activity of the enterprise.
Research subject: accounting and audit of financial investments.
Goal of research: development of recommendations for improving the accounting and audit of financial investments in the enterprise based on the analysis of the shortcomings of the existing accounting system, based on the materials of the enterprise.
In accordance with this purpose, the following tasks are solved:
- To consider the theoretical aspects of accounting for financial investments, as the object of accounting, to determine the classification criteria underlying the organization of accounting.
- To get acquainted with the organization of accounting of financial investments, in part: organization of primary, synthetic, analytical accounting.
- To consider the construction of the accounting process with respect to financial investments.
- To highlight the problems in the organization of accounting for financial investments.
- To analyze the organization of accounting and audit of financial investments of the enterprise, to provide recommendations for improving their accounting.
3. An approach to the unification of synthesis of Moore FSM on FPGA
Among the main documents regulating accounting at enterprises are the law of the DPR About accounting and financial reporting
[1], National regulation (standard) of accounting 1 General requirements for financial reporting
[2]. To account for financial investments provided Regulation (standard) of accounting 12 Financial investments
[3]. Investment activity in addition to the Regulation (standard) of accounting is regulated by many other laws, which define and explain the main aspects that you need to know when solving problems arising in the course of accounting for investment activities.
The purchased securities are divided into long-term and current financial investments. This distinction investment to date, essentially because they have different implications in accounting.
Long - term financial investments are investments for a period of more than one year, as well as all investments that cannot be freely realized at any time. These include long-term financial investments in debt securities, shares and other corporate rights.
Current financial investments have the following features: their maturity does not exceed one year or investments are made without the intention to receive income from them for more than one year. Current financial investments, in turn, are divided into cash equivalents and other current financial investments.
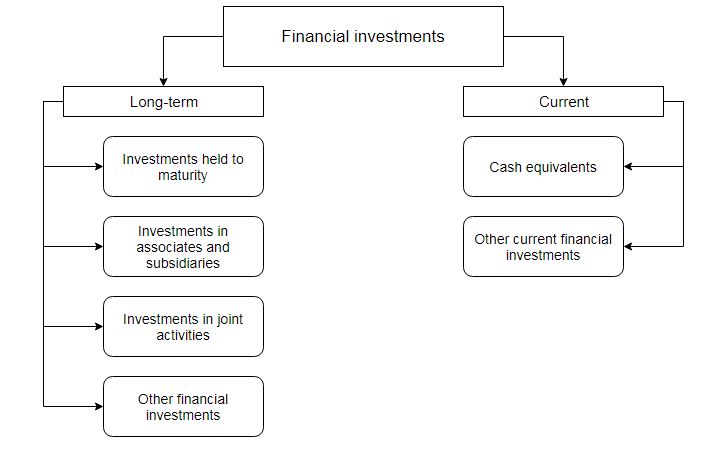
Figure 1 – Classification of financial investments
In the initial valuation, the principal is considered to be reflected in the accounting at their actual cost, which consists of fair value and expenses that are directly related to the acquisition. If the acquisition is made in exchange for equity securities, the cost of financial investments will be the fair value of the securities transferred. Similarly, when purchased in exchange for other assets, the cost is equal to the fair value of those assets.
Regarding further assessment it should be noted that financial investments (except those that are held until their maturity or are accounted for under the equity method in capital) are recorded at fair value. For the same financial investments, the fair value of which cannot be determined, it is noted that they are displayed at cost, taking into account the decrease in the utility of investments.
Financial investments accounted for using the equity method at the balance sheet date are carried at cost, which is determined based on changes in the total equity of the investee (other than those resulting from transactions between the investee and the investee).
This method is used if the investor acquires shares of another company, the share of which is from 20% to 50%. That is, the investor has an impact on the company in which he invested. The application of this method further indicates that the value of the investment should increase by the investor's share of net profit, capital gains and should decrease by the share of declared dividends. Upon receipt of losses by the invested company, the investor must reduce the value of the investment by a share in the losses.

Figure 2 – Cost of financial investments by equity method
(animation: 9 frames, 7 cycles of repeating, 123 kilobytes)
Financial investments held by the enterprise until maturity are recorded at the balance sheet date at the amortised cost of financial investments.
The financial investments held by the enterprise until maturity include the purchased bonds. To determine the amortized cost of bonds, the effective interest rate method is used.
International practice provides for two methods of depreciation – a straight-line method and the effective interest rate. In domestic practice, the advantage is given to the latter, since it is considered more accurate and methodologically correct.
Conclusion
A variety of approaches to the definition and classification of financial investments, the lack of clear regulation of this position in the regulatory field of investment activity has led to research in order to systematize existing options, and their analysis.
Due to the fact that today there are significant differences between national and international requirements for the assessment of financial investments, there is an objective need to bring the regulatory framework for accounting closer to international accounting legislation. All this will provide an opportunity for companies to increase the trust of foreign investors by improving the transparency and reliability of financial reporting.
Today, there are a number of unresolved problems and issues related to the clear legal regulation of accounting for financial and economic activities of enterprises, including financial investments. Solving these problems will improve the understanding of equity as an economic category, increase the efficiency of the enterprise and will help to maximize profits.
Recently, the legislative and regulatory framework has undergone significant changes to improve all systems. Enterprises need to carefully monitor all legislative and regulatory changes in accounting and financial reporting related to financial investments in order to prevent violations for non-compliance of accounting and reporting with legal requirements.
References
- Закон Донецкой Народной Республики
О бухгалтерском учете и финансовой отчетности
, принятый Постановлением Народного Совета от 27 февраля 2015 г. // [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://dnrsovet.su/... - Национальное положение (стандарт) бухгалтерского учета 1
Общие требования к финансовой отчетности
// [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: https://buhgalter911.com/... - Положення (стандарт) бухгалтерського обліку 12
Фінансові інвестиції
, затв. наказом Міністерства фінансів України №91 від 26.04.00 р. з ізм. від 27.06.13 р. // [Електронний ресурс] – Режим доступу: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/...
